Comparison of the effectiveness of Cortexin and Piracetam
The effectiveness of Cortexin is quite similar to Piracetam - this means that the ability of the drug substance to provide the maximum possible effect is similar.
For example, if the therapeutic effect of Cortexin is more pronounced, then using Piracetam even in large doses will not achieve this effect.
Also, the speed of therapy - an indicator of the speed of therapeutic action - is approximately the same for Cortexin and Piracetam. And bioavailability, that is, the amount of a drug reaching its site of action in the body, is similar. The higher the bioavailability, the less it will be lost during absorption and use by the body.
Comparison of the effectiveness of Cortexin and Nootropil
The effectiveness of Cortexin is quite similar to Nootropil - this means that the ability of the drug substance to provide the maximum possible effect is similar.
For example, if the therapeutic effect of Cortexin is more pronounced, then using Nootropil even in large doses will not achieve this effect.
Also, the speed of therapy - an indicator of the speed of therapeutic action - is approximately the same for Cortexin and Nootropil. And bioavailability, that is, the amount of a drug reaching its site of action in the body, is similar. The higher the bioavailability, the less it will be lost during absorption and use by the body.
Comparison of the safety of Cortexin and Piracetam
The safety of a drug includes many factors.
At the same time, with Cortexin it is quite similar to Piracetam. It is important where the drug is metabolized: drugs are excreted from the body either unchanged or in the form of products of their biochemical transformations. Metabolism occurs spontaneously, but most often involves major organs such as the liver, kidneys, lungs, skin, brain and others. When assessing the metabolism of Cortexin, as well as of Piracetam, we look at which organ is the metabolizing organ and how critical the effect on it is.
The risk-benefit ratio is when the prescription of a drug is undesirable, but justified under certain conditions and circumstances, with the obligatory observance of caution in use. At the same time, Cortexin does not have any risks when used, just like Piracetam.
Also, when calculating safety, it is taken into account whether only allergic reactions occur or possible dysfunction of the main organs. In other matters, as well as the reversibility of the consequences of using Cortexin and Piracetam.
Comparison of the safety of Cortexin and Nootropil
The safety of a drug includes many factors.
At the same time, with Cortexin it is quite similar to Nootropil. It is important where the drug is metabolized: drugs are excreted from the body either unchanged or in the form of products of their biochemical transformations. Metabolism occurs spontaneously, but most often involves major organs such as the liver, kidneys, lungs, skin, brain and others. When assessing the metabolism of Cortexin, as well as Nootropil, we look at which organ is the metabolizing organ and how critical the effect on it is.
The risk-benefit ratio is when the prescription of a drug is undesirable, but justified under certain conditions and circumstances, with the obligatory observance of caution in use. At the same time, Cortexin does not have any risks when used, just like Nootropil.
Also, when calculating safety, it is taken into account whether only allergic reactions occur or possible dysfunction of the main organs. In other matters, as well as the reversibility of the consequences of using Cortexin and Nootropil.
Comparison of addiction between Cortexin and Piracetam
Like safety, addiction also involves many factors that must be considered when evaluating a drug.
So, the totality of the values of such parameters as “o syndrome” for Cortexin is quite similar to the similar values for Piracetam. Withdrawal syndrome is a pathological condition that occurs after the cessation of intake of addictive or dependent substances into the body. And resistance is understood as initial immunity to a drug; in this it differs from addiction, when immunity to a drug develops over a certain period of time. The presence of resistance can only be stated if an attempt has been made to increase the dose of the drug to the maximum possible. At the same time, Cortexin has a fairly low “syndrome” value, just like Piracetam.
Comparison of addiction between Cortexin and Nootropil
Like safety, addiction also involves many factors that must be considered when evaluating a drug.
So, the totality of the values of such parameters as “o syndrome” in Cortexin is quite similar to the similar values in Nootropil. Withdrawal syndrome is a pathological condition that occurs after the cessation of intake of addictive or dependent substances into the body. And resistance is understood as initial immunity to a drug; in this it differs from addiction, when immunity to a drug develops over a certain period of time. The presence of resistance can only be stated if an attempt has been made to increase the dose of the drug to the maximum possible. At the same time, Cortexin has quite a small value of “syndrome”, however, the same as Nootropil.
Comparison of side effects of Cortexin and Piracetam
Side effects or adverse events are any adverse medical event that occurs in a subject after administration of a drug.
Cortexin's side effects are almost the same as Piracetam's. They both have few side effects. This implies that the frequency of their occurrence is low, that is, the indicator of how many cases of an undesirable effect of treatment are possible and registered is low. The undesirable effect on the body, the strength of influence and the toxic effect of Cortexin are similar to Piracetam: how quickly the body recovers after taking it and whether it recovers at all.
Comparison of side effects of Cortexin and Nootropil
Side effects or adverse events are any adverse medical event that occurs in a subject after administration of a drug.
Cortexin's side effects are almost the same as Nootropil's. They both have few side effects. This implies that the frequency of their occurrence is low, that is, the indicator of how many cases of an undesirable effect of treatment are possible and registered is low. The undesirable effect on the body, the strength of influence and the toxic effect of Cortexin are similar to Nootropil: how quickly the body recovers after taking it and whether it recovers at all.
Comparison of ease of use of Cortexin and Piracetam
This includes dose selection taking into account various conditions and frequency of doses. At the same time, it is important not to forget about the release form of the drug; it is also important to take it into account when making an assessment.
The ease of use of Cortexin is approximately the same as that of Piracetam. However, they are not convenient enough to use.
The drug ratings were compiled by experienced pharmacists who studied international research. The report is generated automatically.
Last update date: 2020-12-13 10:32:27
Comparison of ease of use of Cortexin and Nootropil
This includes dose selection taking into account various conditions and frequency of doses. At the same time, it is important not to forget about the release form of the drug; it is also important to take it into account when making an assessment.
The ease of use of Cortexin is approximately the same as Nootropil. However, they are not convenient enough to use.
The drug ratings were compiled by experienced pharmacists who studied international research. The report is generated automatically.
Last update date: 2020-12-13 10:32:27
Which is better: Piracetam or Cortexin?
Despite belonging to the same pharmacological group, some indications for use of the drugs differ.
Piracetam is more effective for:
- komah;
- dementia without behavioral disorders and aggression;
- cortical myoclonus;
- sickle cell anemia.
The use of Cortexin is advisable in the following cases:
- brain inflammation;
- epilepsy;
- acute period of stroke;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- brain diseases accompanied by overexcitation, hyperkinesis, seizures;
- delayed psychomotor and intellectual development in children.
Cortexin is considered a safer drug with better tolerability. It, unlike Piracetam, does not provide a stimulating effect and has a small number of contraindications and side effects. Cortexin is approved for use in children of the first year of life, while Piracetam in solution is prescribed only after a year, and tablets - after 3 years.
Piracetam is more convenient to use: it can be taken in tablets or capsules, or given as injections into a muscle or vein. Cortenxin is given only intramuscularly, and the drug does not have a tablet form at all.
Piracetam is much cheaper than Cortexin, but is used over a longer course.
Comparative analysis of the effectiveness of Piracetam and Cortexin
Piracetam
Piracetam is the first of the nootropics with a 50-year history of clinical use in pediatrics, therapy and gerontology. The drug is a derivative of pyrrolidone (a chemical relative of GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter of the central nervous system).
The main direction of influence of Piracetam:
- Activation of excitatory neurotransmitters - acetylcholine, dopamine and partially serotonin, which, subject to active mental activity, improve memory functions. This allows it to be used to restore and enhance concentration and memory, but mainly with minor deviations in the functioning of these processes.
- Piracetam also reduces blood viscosity and enhances the trophism of nerve cells, increasing the uptake of glucose and oxygen by neurons, activating carbohydrate and energy metabolism. This property is effectively used in the treatment of oxygen starvation and intoxication by external toxic agents and partially by endogenous substances during stress, neuroses and depression.
- Neuroprotection in diagnosed diseases is weak; Piracetam acts more like a preventive antioxidant.
However, the effectiveness of Piracetam is most clearly expressed only in the treatment of various perinatal encephalopathies (mainly birth injuries and hypoxia) in infants, improves interhemispheric interaction (speech, systematization of information, planning) and motor coordination, helps with learning and mental work of a child and an adult. Sometimes Piracetam helps relieve mild emotional disorders. Severe vascular and neuronal diseases of the brain, such as ischemia, stroke, Alzheimer's disease and other dementias, are only slightly relieved by Piracetam.
In 2007, the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences recognized the drug as outdated and ineffective. If we compare Piracetam with Cortexin, the latter has a more pronounced and widespread effect.
Cortexin
Cortexin is a hydrolyzate of neuropeptides from the brain of pigs and cattle, developed by domestic pharmacologists 30 years ago. All nootropics of animal origin have a multidirectional effect and are highly effective not only in eliminating mild and moderate mental disorders, but also in treating severe brain damage as a result of traumatic brain injury, ischemic stroke (if administered in the first 6 hours), age-related and acquired neurodegenerative diseases.
Action:
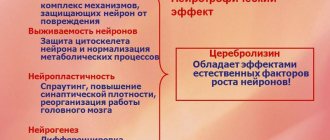
- Neuroprotective. Cortexin has been proven to reduce the lesion in ischemic stroke, provided that treatment began in the first 6 hours of the disease. Under the influence of the drug, programmed apoptosis of nerve cells is inhibited, and the death of neurons from intoxication by external and endogenous agents is reduced.
- Stimulation of neurogenesis. The peptide nature of the lysate makes it possible to induce the synthesis of neurotrophins - growth factors of new nerve cells. This property of Cortexin allows one to restore higher mental functions of the brain after extensive strokes.
- The anti-stress effect due to a decrease in cortisol levels and an increase in serotonin production is greater than that of glycine and other mild antipsychotics. Used in the treatment of severe neuroses, depression, chronic stress.
- Improving metabolism in nerve cells. Restoring the balance of inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters, optimizing the emotional sphere and mental activity.
- Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity.
There have been insufficient clinical studies that can clearly define the scope of Cortexin's capabilities, however, the drug appears to be a promising agent in a series of new generation neuropeptide nootropics.
The effect of Cortexin and Piracetam is cumulative, but the response rate to Cortexin is higher. Therefore, in some cases, Piracetam and Cortexin are used together at the beginning of the course.
Cortexin is a prescription drug and is available only in injection form. Piracetam is used both in the form of injections and in the form of tablets and capsules.