After a person has at least once been in a state of severe alcoholic intoxication, due to the consumption of large quantities of alcoholic beverages, he begins to be interested in the question: will the organs and their functions be restored? It is especially important whether brain cells are able to recover after quitting alcohol. The same question is asked by a person undergoing rehabilitation after treatment for chronic alcohol addiction.
There are times, especially on holidays, when a person, without meaning to, drinks a very large dose of alcohol in a short time. It is clear that you should not expect pleasant sensations after this. People who suffer the most are those who are not used to drinking alcoholic beverages, or who do so rarely and in small portions. They will have headaches from drinking alcohol for a long time.
Research shows that only five percent of ethanol leaves the body naturally, that is, through sweating and urination.
The rest of it is broken down in the body, and it will take some time to remove all the breakdown products of ethanol from the body. It also depends on the physical condition of the person, what age he is, and his gender. And of course, what drinks did he drink and in what quantities.
Destructive effects of ethanol on brain cells
There is no doubt that ethanol destroys brain cells. This is evidenced by gait disturbances, inhibition of reactions, and memory disorders. As soon as ethanol stops entering the body, functions are gradually restored.
Everyone knows that alcohol is harmful to health. It all starts with a violation of consciousness, and can lead to the fact that a person becomes disabled forever. There are some factors that help determine how much damage is done to brain cells and what effect ethanol has on them.
These include:
- how often a person drinks alcohol and in what quantities;
- at what age did he start drinking alcohol, and when did he become dependent on alcohol?
- what gender is the person, how old is he, is he educated, is there a genetic predisposition to alcohol addiction, and have there been any cases of chronic alcoholism among relatives;
- what physical condition the person is in;
- whether fetal alcohol syndrome has been observed in humans.
Disorder of consciousness for a short time, which occurs after drinking alcohol, occurs much more often than doctors previously claimed. Such a result can be defined as a possible consequence of alcohol intoxication, which does not depend on whether the person has symptoms of chronic alcohol dependence or how old he is.
Scientists conducted an experiment trying to identify the negative effects of ethanol on brain cells associated with short-term consciousness disorders. More than seven hundred students participated in the experiment. They all answered the same question: has it ever happened to you when, waking up in the morning, after a night of alcoholic outpourings, you were unable to remember what you did in the evening and where you were?
More than half of the youth already had experience of drinking alcoholic beverages, and answered in the affirmative: yes, after drinking a large amount of alcohol they experienced memory disorders. Forty percent of them said this had happened in the past year, and nine percent of respondents had consumed alcoholic beverages in the past two weeks and experienced brain fog.
What are the consequences of abuse?
In those who abuse alcohol, the death of neurons occurs rapidly. Alcohol dependence develops and rapid degradation occurs. Here's what alcohol does to the body:
- Physiological changes. The thinking organ loses volume, its convolutions gradually smooth out, numerous hemorrhages and necrosis appear on the surface of the cortex, and voids appear in the tissues. Blood vessels are affected, endocrine functions are disrupted, circulatory disorders and toxic damage to the brain appear. Liver dysfunction also develops.
- Nervous disorders. Emotional instability and depressive states appear that can only be treated with medication.
- Specific neurotic disorders. A number of specific diseases are a consequence of alcoholism and appear more often after stopping drinking alcohol: alcoholic epilepsy, delirium tremens, hallucinosis, paranoia, etc.
- Dementia. Problems arise with the simplest mental operations, critical thinking decreases, moral degradation develops, dementia and diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, etc. appear.
Sometimes symptoms of the consequences of alcoholism can be seen even one or two decades after stopping the abuse. These are external manifestations such as:
- hypermia;
- exaggerated gestures;
- violation of muscle tone;
- parkinsonism.
See the infographic for more details:
A history of alcoholism can sometimes be determined by a number of signs, even after many years of a person’s sober life.
The effect of alcohol on the female brain?
Complications caused by drinking alcoholic beverages are more serious in the fairer sex than in men.
It has been experimentally proven that ethanol behaves much more aggressively towards the cells of a woman’s body than towards the cells of a man. Organs and their functions are more susceptible to the negative effects of alcohol. The destruction of the liver, damage to the heart muscle and cells of the nervous system occurs faster.
Having carried out a comparative analysis of the results of studies of the human brain using MCT, scientists have established the fact that the negative effects of ethanol manifest themselves in the fact that the brain decreases in size.
The degree of such a decrease is the main indicator that organic changes are present in the brain cells. And the longer the experience of drinking alcohol, the higher these indicators.
In addition, the results of the experiments showed that both women and men who suffer from alcohol addiction face certain problems when they have to learn something or remember any information. All this occurs due to frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Note that the male representatives who participated in such an experiment had twice as much experience of regular consumption of large amounts of alcohol than the fairer sex.
It turns out that the negative effects of ethanol on both the male and female brains manifest themselves in the same ways. But it is necessary to take into account that women took exactly half as much alcohol. From all this we conclude that ethanol has a stronger effect on the female brain.
In contrast, two articles were recently published in an American publication discussing the role of gender in the effects of ethyl alcohol on the body.
The authors came to the opposite conclusion, that is, according to them, ethanol has the same effect on everyone without exception. This means that experiments of this kind need to be continued in order to find out the specific effects of ethyl alcohol on a woman’s brain cells.
History of the study of effects on the brain
For a long time, people understood perfectly well that it is the head that rules our actions and thoughts. Anatomy evolved and the study of the brain developed through extensive laboratory experiments on mice, the results of which were then used in the study of human anatomy.
The story of the discovery of the reward center in the brain
In 1952, American researcher James Olds discovered a pleasure center in the brain of rats. The discovery was made by accident at McGill University in Canada. There was a laboratory there to study the effects of electrical impulses from implanted electrodes on different parts of the brain. Electrodes were implanted into the center of wakefulness and the hypothesis was considered that the rat avoided the place in the cage where it was exposed to current. The entire batch of rats confirmed this hypothesis except one. Only one kept trying to return to the place where the electrode implanted in her brain was subjected to electric shock.
Trying to understand the reason for this strange behavior, James Olds discovered that the electrode was implanted with an error, namely in the adjacent part of the brain. This is how the pleasure center in the brain was discovered, first in experimental rats, and then in people. By influencing this part of the brain, the rat could induce feelings of pleasure and happiness. It was noticed that in experiments in which pressing a lever sent an impulse to the brain in the “happy zone”, sometimes the experimental animals were so carried away by giving themselves pleasure that they were no longer interested in anything else, neither food nor the search for sexual partners, which was unusual for behavior animals.
Are there pleasure centers in the human brain?
After experiments on influencing certain areas of the brain responsible for feelings of pleasure and happiness were carried out on people, it became clear that there are areas in the brain responsible for the feeling of euphoria. Irritation of this area in large quantities can cause dangerous phenomena for humans or animals. In experiments on animals, they could bring themselves to death, interested only in stimulating the “pleasure zone” in the brain.
After studying these phenomena by leading scientific laboratories, the technology for a person to obtain a sense of pleasure and enjoyment became clear.
Dopamine is the “master” of pleasure.
Several areas in our brain are responsible for receiving pleasure and pleasure. And it receives irritation due to chemicals called neurotransmitters. For example, neurons of the already known “pleasure centers” release dopamine in cases where a person receives a psychological stimulus or the anticipation of receiving it. This can be sexual pleasure, food and many other stimuli. Even the memory of these stimuli and pleasures can cause a large flow of neurotransmitters responsible for pleasure.
But drinking alcohol also causes large releases of dopamine. Sometimes even much greater than with all other incentives.
Thiamine deficiency and Korsakoff-Wernicke disease
If a person systematically drinks alcohol, without control over the amount he drinks, and this lasts for quite a long time, then he has every chance of developing brain dysfunction or damage to his cells. Moreover, this can be caused by the consumption of large amounts of alcohol, or there may be serious disturbances in the liver due to chronic alcohol dependence.
For example, most people suffering from chronic alcohol addiction have a lack of thiamine in their bodies, or as it is also called vitamin B1. It may be lacking due to poor nutrition, metabolic disorders in the body and, of course, due to the abuse of alcoholic beverages. It plays an indispensable role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. It supports the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system, digestive tract, and nervous structures.
Most people suffering from chronic alcohol addiction are deficient in vitamin B1. And this can lead to such a serious illness as Korsakoff-Wernicke syndrome, or more precisely, Wernicke syndrome and Korsakoff syndrome.
Wernicke's disease is characterized by paralysis of the eye muscles, disturbance of consciousness and impaired coordination of movements. Sometimes a patient with a similar syndrome cannot independently find the door of the room to leave, he cannot move without someone else's help. If at least one of the signs of the disease appears, you need to urgently seek medical help.
Most people suffering from alcohol dependence, along with Wernicke's syndrome, experience Korsakoff's syndrome, which is also called alcohol paralysis. With this disease, memory impairment is observed, when he forgets everything that happened to him before the disease, but can describe in great detail the events that took place several years before.
In addition, he remembers well everything that happens to him after his illness. The patient begins to invent non-existent events, or talk about those that really happened, but at the same time greatly distorts the facts. All this is accompanied by disorientation. The patient ceases to navigate the world around him and himself. Sometimes, even after seeing his reflection in the mirror, the patient does not realize that it is him.
Call us now:
+7 (812) 454-00-50
Prices for Ultramed clinic services
Questions and answers
Question from Igor, St. Petersburg.
So is it good that alcohol brings so much happiness?
Igor, such a feeling can only develop at the first fleeting glance at the problem. If we look deeper, we will see real problems from the effects of alcohol on the brain. Large amounts of dopamine released literally “out of nowhere” interrupt any other “ordinary” signals from joyful or happy events. Alcohol thus switches the attention of the nerve endings responsible for processing pleasure and joy to itself. It seems to immerse a person in a bath of artificial pleasure, like all other drugs. Alcohol is a drug, which was approved by the World Health Organization in 1975. And as soon as a person, figuratively speaking, gets out of this bath of joy, euphoria and pleasure (for example, the supply of alcohol has run out), he begins to be oppressed by the “boring” environment around him and the “boring” events that were previously cheerful and joyful, but now they there is not enough “power” to compare with the “super power” of alcohol’s effect on the body. Therefore, the person again climbs into the “alcohol bath” where everything is good, euphoric and pleasant for him.
But that's not so bad. When drinking alcohol for “taking such baths”, it oxidizes inside the body and produces very toxic substances during its processing, which leads to permanent poisoning of the body from drinking alcohol. Chronic diseases appear, sometimes organs and health “fail”. The total effect of alcohol on a person is an increase in body diseases, including chronic ones, personality degradation, loss of contact with the social world, problems in the family and at work. At an advanced stage of alcoholism, there is often a desire to constantly drink alcohol, failure of any organs due to health, the inability to enjoy events around, and complete degradation of a person.
Question from Alexey, Kirovsk, Leningrad region.
How to get rid of the harmful effects of alcohol on the brain?
Alexey, there is only one way to get rid of the influence of alcohol on the human body - stop drinking alcohol. This is very difficult to do, since alcohol has a narcotic effect on the human brain, but it is possible. Some people manage to do this on their own. Many people are unable to stop drinking on their own and need the help of a professional narcologist.
Alcohol addiction can be treated in our narcological clinic, where the best doctors in St. Petersburg can help you stop drinking alcohol.
Is it possible to restore brain cells?
It was believed that a person is born with a specific number of brain cells, and if they are somehow damaged, then they cannot be restored. Scientists believed that neurons under the influence of ethyl alcohol were destroyed and no longer function. in order to restore their activity it is necessary to strengthen the remaining nerve cells, since there is no possibility of adding new ones. But in the second half of the last century, scientists discovered that the formation of new neurons is possible. This process is called neurogenesis. After this discovery, scientists developed a new approach to the treatment of disorders of brain cells.
Recovery after long-term use
Is the functioning of the thinking organ restored after quitting alcohol and how long does it take? In recent decades, medical scientists have argued that brain cells and neurons are capable of recovery, since their gradual death is a natural process.
The only problem is that in alcoholics, the rate of destruction of neurons significantly exceeds the rate of their rebirth . And the process of their restoration after long-term use takes quite a long time: years, and sometimes decades, but still does not lead to the absolutely desired result.
To return the thinking organ to an adequate state, a number of conditions must be met:
- Stop drinking alcohol 100% for at least a year, or better yet, for good.
- Undergo detoxification with the help of medications, as well as follow a special diet that will help cleanse the blood vessels.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle that is beneficial for blood vessels: follow an appropriate diet, lead an active lifestyle.
- Engage in prevention and replenish losses: take vitamin-mineral complexes, antioxidants, etc.
But even if you follow these rules, you cannot accurately answer how long it will take for all mental functions to be restored.
Is there any benefit?
Where did the theory come from that alcohol can be good for the brain, if ethanol is so harmful to blood vessels and neurons?
The fact is that in limited quantities (50-150 ml for wines and 30-50 ml for strong drinks), as well as in the composition of medications, ethyl alcohol can be beneficial under certain conditions.
- It relieves vascular tone , reducing blood pressure, reducing tension, and improving blood circulation in the brain.
- Removes fatty deposits in the arteries and blood clots in the veins, thereby cleansing the bloodstream. It is known that low doses of alcohol actually help cleanse the blood vessels in the brain.
- Thins the blood , preventing thrombosis and strokes.
- Promotes the absorption of medicinal substances from drinks and medicinal tinctures, helps their rapid and high-quality absorption by the body.
That is, alcohol may indeed not harm you in any way, but on the contrary, become an assistant in improving the health of the brain.
But at the same time:
- you cannot deviate from the prescribed dosage (and very few people can do this);
- It is necessary to use this remedy only from time to time and for therapeutic purposes. It is better to relax after a hard day using other methods, without alcohol;
- drink only really healthy drinks, the value of which is the presence of important vitamins, minerals, organic acids and antioxidants.
Effect on the central nervous system
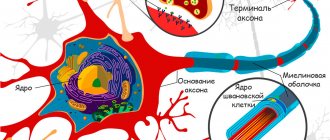
It is the central nervous system that is most sensitive to the effects of ethanol.
.
Alcohol, as well as substances formed during its breakdown, quickly penetrate the blood-brain barrier and are found in brain tissue even several days after sobering up and detoxification. As practice shows, by the end of the second stage of alcohol addiction, up to 70% of patients suffer from cognitive disorders
, and with strict abstinence from drinking, cognitive functions are only partially restored. Many patients, even after recovery, suffer from amnesia and dementia.
The harm of alcohol to the central nervous system is due to the direct damaging effect of ethanol on neurons
, withdrawal syndrome after abrupt withdrawal of alcohol,
hypoxia
, secondary
nutritional deficiency
.
Acute alcohol intoxication is accompanied by severe neurological disorders:
- speech and motor coordination disorders;
- changes in behavior that are not typical for a person (vulgarity, rudeness, swagger predominates, emotional elation can sharply give way to gloominess, irritability and malice, aggression);
- memory lapses.
With withdrawal syndrome (especially in the absence of professional drug treatment), more severe complications cannot be excluded:
- depression with suicidal tendencies;
- delusional ideas;
- auditory, visual and tactile hallucinations;
- delirium;
- severe insomnia;
- generalized seizures.
In the post-intoxication period, the harm of alcohol is manifested by secondary disorders against the background of insufficient intake of magnesium, thiamine, calcium, and other macro- and microelements. Developing:
- Alcoholic dementia
, which manifests itself as a deterioration in intelligence, memory, and the ability to evaluate and analyze what is happening around. Personality changes are typical: a person becomes selfish, withdrawn, suspicious, and often makes offensive statements about loved ones. - Wernicke's encephalopathy.
Signs of this syndrome are acute mental disorders (confusion, apathy, drowsiness), unsteady gait, dizziness. During an exacerbation, the patient is not able to adequately respond to what is happening, he is disturbed by random memories and visions, and is not attentive. - Korsakov psychosis.
Accompanied by problems with long-term and short-term memory, and gaps in memories are replaced by false, fictitious images. As the disease progresses, the patient becomes incapacitated and apathetic. - Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome.
The disease combines amnesia and mental disorders typical of encephalopathy. Recovery is possible, but after long-term complex therapy.
A complete bouquet of diseases in one glass
The complete list of diseases caused by excessive alcohol consumption includes hundreds of items. It also includes such serious psychological pathologies as schizophrenia and psychopathy. Alcoholism causes both physical and psychological dependence on ethanol. To successfully combat the disease, it is necessary to use complex treatment, being observed by several diverse specialists at the same time.
A chronic alcoholic loses his desire for life without having access to another portion of alcohol. His mood and well-being directly depend on alcohol. Along with it, he receives a charge of false cheerfulness. At the same time, due to the critical consumption of dopamine reserves in his body and the cessation of the production of neurotransmitters, a clinical picture of personality destruction is observed.
The absence of the next portion of alcohol that is so necessary for the patient can be compared with the withdrawal symptoms that occur in a similar situation among drug addicts. The main symptoms of this condition:
- • Unreasonable restless state.
- • Obsession with certain states.
- • The appearance of hallucinations.
Depending on the characteristics of the body, prolonged and continuous use of alcohol results in a state of confusion – the so-called “delirium tremens”. A person becomes dangerous both for himself and for others. He often develops Korsakoff's syndrome. Signs of such a disease are incessant hallucinations and partial memory loss with filling in the gaps with fictitious events.