CT and MRI are radiation diagnostic methods that open new horizons in the study of neurosurgical and neurological diseases of the brain. Computed tomography has been known for quite a long time, and is currently widely used to study bone tissue, most often when assessing their damage: injuries, fractures, etc.
MRI appeared relatively recently and has established itself as one of the most effective diagnostic methods due to its ability to identify pathological processes of various origins that occur in the brain and accurately determine their localization. The high spatial resolution and variety of contrast types inherent in the MRI method make it possible to clearly visualize the gray and white matter of the brain, monitor the processes of brain maturation, and assess the condition of the bone marrow and soft tissues.
Computed tomography (CT) is an X-ray diagnostic method that involves obtaining a series of layer-by-layer images of the area under study of a certain slice thickness, from which a volumetric projection is built. In most cases, CT is the most informative in assessing the condition of bone structures and lungs.
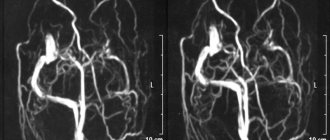
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an absolutely harmless and painless research method, during which tissues and organs are scanned in three projections. This allows the radiologist to fully assess the condition of the area being examined. In addition, the MRI method allows you to obtain images of the vessels of the brain and neck vessels without the introduction of a contrast agent.
What is the difference between CT and MRI of the brain and which examination method should I choose?
What are CT and MRI?
Both computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are two effective hardware-based research methods that allow, without instrumental intervention, to obtain a clear, detailed picture of the state of the brain and the vessels that supply it. The basic principle of both examination methods is to obtain anatomically accurate images, on the basis of which doctors of various specialties then determine the diagnosis and prescribe therapy. There are three basic tomographic protocols, the same for both MRI and CT:
- native brain tomography;
- brain tomography with contrast;
- angiography of cerebral vessels.
The main differences between CT and MRI are:
- in the method by which the images are obtained;
- in the list of contraindications;
- in possible complications;
- in the price of tomography.
How does a CT scan differ from an MRI of the brain?
| COMPUTER TOMOGRAPHER | MAGNETIC RESONANCE TOMOGRAPHER |
The principle of operation of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner
Diagnosis of brain diseases using MRI is one of the most harmless and harmless examination methods.
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the ability of high-frequency radio waves to cause vibrations in the hydrogen atoms present in the body's cells when they are exposed to a powerful magnetic field. The MRI machine records the received impulses, which are then processed by a computer. Due to the fact that different tissues of the body are characterized by signals of varying intensities, high-frequency images of the substance, meninges and vascular bed are formed with high spatial resolution. The increased power and ultra-sensitivity of modern tomograph models have made it possible for doctors to diagnose millimeter changes at an early stage of their occurrence. An MRI machine, depending on the type of model (open or closed), resembles a large installation with a narrow pipe in the center or a magnetic canopy. During the examination, the patient lies, as still as possible, on a mobile table that is placed inside the tomograph. An MRI scan lasts from 20 to 40 minutes, depending on the purpose and examination protocol. It is quite comfortable for the patient. Only loud noises from the machine can cause slight concern. This noise is safe for the patient. It occurs due to vibration of the metal coils in the device, which is caused by rapid pulses of electricity. The induction power of a tomograph (fullness) is one of the most important parameters of a tomographic installation. It is measured in Tesla. There are three types of devices that differ in magnetic field strength: low-field (0.3-0.5 Tesla), high-field (1-1.5 Tesla) and ultra-high-field (3 Tesla or more). The higher the induction level of the tomograph, the better the quality of the images it produces.
Initial appointment with a NEUROLOGIST
ONLY 1800 rubles!
(more about prices below)
The principle of operation of a computed tomograph
CT scans of the brain are performed using a device called a spiral CT scanner.
During the examination, the patient's body is exposed to several beams of X-rays released by the emitter sensor at different angles. Unlike conventional radiography, which offers only a flat image from several positions, a CT scan of the brain produces a set of images in the form of small sections in different projections. To do this, the device's sensors move in a spiral around the patient's body, recording information received from different angles. On a computer, this information is combined into three-dimensional models (tomograms) of a specific area or lobe of the brain. The power of a CT scanner depends on the number of slices the scanner makes per revolution of the gantry ring. The higher the shearing ability of the unit, the more accurate the scanning results will be. In St. Petersburg clinics today you can undergo examination using 4-340 slice computed tomographs. A high-quality CT scan of the brain will require a device of 32 slices or higher.
To obtain CT images of the vessels of the head, the patient is injected intravenously with an iodine-containing contrast agent, which stains the vascular bed well. Without it, high-quality visualization of the vascular system of the head and neck is impossible. The CT scan procedure is absolutely silent and fast. The average scan duration is about 5-7 minutes.
Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI is a study that allows you to obtain layer-by-layer images using safe electromagnetic radiation. The duration of the procedure is from 20 minutes, while all high-field devices have a closed circuit, patients are in a “tube”, which in some cases causes discomfort.
Abnormalities in soft tissues are clearly visible on MRI.
There are open devices that allow even people with claustrophobia to undergo research. However, their power is usually not enough to accurately diagnose brain pathologies. The optimal field strength should be 1.5 Tesla.
Diagnostic advantages and disadvantages of brain MRI
The strength of MRI is the fact that the magnetic resonance imaging scanner is able to record even the most minor changes in soft tissue, so it has better sensitivity:
- to differentiate gray and white matter of the brain;
- for studying the cerebellum, posterior fossa and temporal lobes;
- to record the consequences of vascular lesions of the brain, such as thrombosis, embolism, even if they are small;
- differential diagnosis of tumor formations;
- detection of a cyst, hematoma or ischemic tissue damage;
- for pathological disorders caused by diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and senile dementia.
Magnetic resonance diagnostics is prescribed if it is necessary to find out the cause:
- frequent fainting and dizziness;
- frequently recurring severe headaches;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- progressive loss of vision and hearing;
- to conduct preoperative diagnostics and ensure high-quality monitoring of the effectiveness of treatment measures.
Pros of MRI
The advantages of MRI are:
- high information content and accuracy of results;
- absolute safety for health, since the doctor does not use X-rays;
- when using MRI of the brain with contrast, a hypoallergenic substance is used, which almost never causes a negative reaction in the patient;
- no complications;
- the opportunity to conduct a full examination even for pregnant women without fear of harming the fetus;
- the earliest possible diagnosis of diseases even at the stage of absence of symptoms characteristic of the pathology.
It should be noted that today there is an extremely limited list of brain pathologies that cannot be determined using magnetic resonance. MRI is the gold standard in medicine for a comprehensive examination of the brain.
Cons of MRI
The disadvantages of the study include the peculiarities of the interaction of the magnetic field with metal objects and electronic devices, which excludes access to MRI in patients:
- with artificial heart valves and stimulators;
- working insulin pumps;
- surgical staples, pins, prostheses;
- any metal objects that can move under the influence of a powerful magnetic field.
The accuracy of the resulting images may be compromised for those with tattoos made with metal-containing inks.
In most cases, dentures, braces and crowns will not cause interference (artifacts) on MRI images. The small closed space of the magnetic resonance imaging scanner, the duration of the diagnosis, the need to remain still and the presence of loud sounds can be an obstacle to the examination of patients suffering from claustrophobia and people with nervous and mental disorders. Sign up for diagnostics
If in doubt, sign up for a free consultation or consult by phone
+7
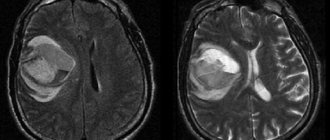
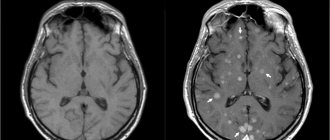
CT scan of a patient's brain
Maximum depth of detail is the primary criterion for the advantage of computed tomography. It clearly shows manifestations of vascular atherosclerosis, swelling of arterial walls, and changes in the tissues of the skull bones.
- Determines deformation of the facial bone and maxillary sinuses. He will see the presence of injuries to the cerebral cortex.
- Reveals the causes of the disease without resorting to contrast. Does not cause pain to the patient.
- On a CT scan, the doctor looks at the soft tissue structures of the brain, along with the vessels of the circulatory system and the cranial bones. The image of the area being examined is clearer than on an x-ray.
- A CT scan of the brain can be performed in emergency situations, in particular in cases of intracranial hemorrhage.
- If during the procedure the patient accidentally disturbs the immobility of the body, then there will be no interference in the image.
- Implants implanted into the body that contain metal will not be prohibited for diagnosis.
Today, CT, which does not cause any discomfort to a person, is an alternative to laparoscopic examination.
Diagnostic advantages and disadvantages of brain CT
The radiation produced by a CT scanner makes hard and soft tissue more visible, so CT is most sensitive for:
- detection of acute parenchymal or subarachnoid hemorrhages;
- intracranial trauma or damage to the skull bones;
- detection of hidden blood clots;
- aneurysm;
- calcifications of cerebral vessels.
Preference is given to computed tomography of the brain if there is a suspicion of basal skull fractures, bone disorders, aneurysms, hemorrhages, or hemorrhagic stroke. Given the short diagnostic time, CT is performed when it is urgently necessary to make an accurate diagnosis for vital indications, for example, after accidents, in order to determine the presence of traumatic brain injuries and find out what type of surgical intervention is required.
Pros of CT
Advantages of diagnostics:
- fast execution;
- accessibility - a computed tomograph is available in almost every hospital in St. Petersburg;
- high information content.
Cons of CT
As a rule, for those who choose between CT or MRI of the brain, the main disadvantage of multislice computed tomography is the presence of x-ray radiation. The average radiation dose is 3-5 mSv per scan. Therefore, the examination is not carried out on pregnant women, as well as children under 3 years of age. Another danger is the iodine-containing contrast agent, which under certain conditions can cause serious allergic reactions or complications and poor health after the procedure.
If you have a headache, you should definitely do an MRI of the brain.
Most often, patients who are bothered by headaches come for MRI of the brain. But in 80% of cases it is a tension headache associated with stress, fatigue, neck muscle tension, scalp tension, etc. None of this can be seen on an MRI. Such patients turn out to be healthy from an organic point of view: they have no changes in the substance of the brain. And their headaches should be treated by neurologists and cephalologists. Using MRI, you can exclude possible tumors, strokes, developmental features, anomalies, etc., but finding and treating the cause of the headache is the task of other specialists.
Cost difference
These types of scanning are comparable in price.
| Service | Price | Discounts | Phone number for appointment |
| CT scan of the brain | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of cerebral vessels | from 4400 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT tear ducts | from 2800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the larynx | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the nose | from 2600 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT ear | from 2100 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the thyroid gland | from 2800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the skull | from 2900 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of neck vessels | from 4400 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| Service | Price | Discounts | Phone number for appointment |
| CT scan of one part of the spine (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccyx) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT joint (knee, elbow, shoulder, hip, ankle, wrist) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the jaw joint | from 1300 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of ribs | from 4200 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the hand | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the foot | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the pelvis | from 2500 rub. | 372-65-26 | |
| CT scan of the bones of the hip, face, leg | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| Service | Price | Discounts | Phone number for appointment |
| CT scan of the throat and larynx | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the heart and coronary vessels | from 9900 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the lungs and mediastinal organs | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the retroperitoneum (kidneys and adrenal glands, urinary tract, soft tissues and lymph nodes) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the abdomen (liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the pelvis in men (prostate, bladder, ureters, rectum) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the pelvis in women (uterus, vagina and appendages, ovaries, bladder, ureters, rectum) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT colonoscopy | from 4000 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT virtual bronchoscopy | from 4500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the urinary system (kidneys, bladder, urinary tract) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT pancreas | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the pelvis and abdomen | from 4400 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT urography | from 4400 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the mammary glands | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT soft tissue (one area) | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT soft tissue of the neck | from 2500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| Service | Price | Discounts | Phone number for appointment |
| CT angiography of cerebral vessels | from 4500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of neck vessels | from 4500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of the thoracic aorta | from 5800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of the abdominal aorta | from 5800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of limb vessels | from 9800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT scan of the coronary vessels of the heart | from 9500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of the pulmonary arteries | from 4500 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of the renal arteries | from 5800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of the pelvic arteries | from 5800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| CT angiography of the iliac artery | from 5800 rub. | up to 20% discount at night | 372-65-26 |
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of the brain | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of cerebral vessels (arteries) | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland (without contrast) | 3500 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast | from 7500 rub. | from 6990 rub. | |
| MRI of the brain and pituitary gland | 6800 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of the brain and cerebral vessels | 6600 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of the paranasal sinuses | 2900 rub. | 2690 rub. 2100 rub. in the Armed Forces | 2990 rub. 2100 rub. in the Armed Forces |
| MRI of the central nervous system (MRI of the brain, MRI of the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral region) | 13200 rub. | 9590 rub. | 10790 rub. |
| Contrast administration (based on patient weight) | from 3000 to 5000 rub. | only during the daytime | from 3000 to 5000 rub. |
| Recording an MRI examination on film | 500 rub. | 450 rub. | 450 rub. |
| Duplicate photo | 800 rub. | 800 rub. | 800 rub. |
| Duplicate description of MRI study | 300 rub. | 300 rub. | 300 rub. |
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| Shoulder MRI | 4000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| MRI of the elbow joint | 4000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| MRI of the knee joint | 4000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| MRI of the ankle | 4000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| MRI of the hip joints | 5000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| Appointment with an orthopedist | 1800 rub. | free after MRI | free after MRI |
| First aid program for joints (8 studies + appointment with an orthopedist + MRI of the joint) | 13000 rub. | 7500 rub. | 7500 rub. |
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of the cervical spine or cervical vessels | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the thoracic spine | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the lumbosacral spine | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the craniovertebral junction | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the sacroiliac joints | 4000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| MRI of the coccyx | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of two parts of the spine | 6600 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of three parts of the spine | 9900 rub. | 6900 rub. | 7900 rub. |
| MRI of the central nervous system (MRI of the brain, MRI of the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral region) | 13200 rub. | 9590 rub. | 10890 rub. |
| Appointment with a neurologist | 1800 rub. | free after MRI | free after MRI |
| Comprehensive body diagnostics (MRI of the thoracic spine, MRI of the lumbar spine, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the kidneys, ultrasound of the bladder, consultation with a neurologist, consultation with a therapist) | 11700 rub. | 7000 rub. |
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of cerebral vessels (MR angiography) | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of neck vessels (MR angiography of the neck) | 3500 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the brain and cerebral vessels | 6800 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| Comprehensive examination of the vessels of the brain and neck | 6600 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MR arteriography | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
Which is better - CT or MRI of the brain?
In the case of complex anomalies of the brain and vascular system, CT and MRI perfectly complement each other and together provide the most complete and comprehensive information.
However, any diagnosis has its own nuances and subtleties that are understandable only to medical specialists. Therefore, it is best when the choice of diagnostic method is made by your attending physician, guided by the primary diagnosis, the purposes of the tomographic examination and your state of health. Medical centers are constantly improving examination protocols in order to increase diagnostic accuracy. Therefore, if you are concerned about your well-being, and you have no direct contraindications or restrictions, it is better not to put off going to the diagnostic center for too long. Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging will quickly and efficiently help you find out if everything is okay in your head. Author: Belik Ekaterina Mikhailovna
Radiologist with 19 years of experience