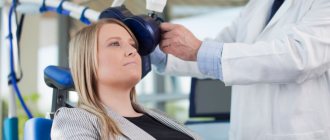
Transcranial Dopplerography is an ultrasound method for checking the functioning of the arteries and veins of the brain, blood flow speed and vascular capacity. The study allows you to evaluate the qualitative characteristics of blood inflow and outflow, as well as detect obstacles to blood flow and signs of high blood pressure. During the procedure, examination is carried out in the head and neck area.
To understand what we are talking about, let’s break down the definition into its components:
- Ultrasonic – performed using ultrasonic waves that pass through tissues of different densities at different speeds. The advantage of using them is their complete safety and the possibility of applying the method to all patients at any age and condition without contraindications.
- Dopplerography is a technique that allows you to estimate the speed of blood movement through a vessel: waves strike red blood cells and change frequency in proportion to their speed of movement. A visualized display of wavelengths is displayed on the screen and allows you to make assessments about the condition of the vessels, based on the research methodology.
When is an ultrasound scan performed?
The most common reasons for visiting a doctor are headaches of any kind, migraines, dizziness (especially when moving), noise in the head or ears. Headache may be accompanied by a feeling of flies flashing before the eyes, weakness (in particular, sudden attacks of weakness, which is accompanied by numbness of the limbs), problems with speech, and lack of air. Vascular pathology can be suspected due to motion sickness in transport, dependence on weather conditions, or reduced adaptation to other similar loads. The most serious manifestation in this group is syncope.
Vascular diseases inside the skull can result from problems with the musculoskeletal system - observed with osteochondrosis, vertebral hernias, and pathology in the cervical spine. Blood circulation is also impaired as a result of a head injury.
Vessels can suffer not only in the brain, but throughout the body - Doppler ultrasound is prescribed to people with:
- high risk of developing cardiovascular diseases;
- vertebrobasilar insufficiency (VBI);
- transient ischemic attack (TIA);
- cerebrovascular disease;
- strokes (prognosis of recovery, development of complications, relapses, etc.).
Transcranial Doppler ultrasound is also performed on infants in cases of suspected cerebral vascular anomaly.
If there are cases of atherosclerosis or arterial hypertension among relatives, or someone has experienced heart attacks and strokes, then after 55 years of age, regular research is recommended in order to detect and eliminate the disease in its infancy.
Indications for transcranial Doppler ultrasound
There are many reasons why you may need to undergo Doppler ultrasound. Transcranial Dopplerography of cerebral vessels
may show a large number of deviations from the norm.
Vascular malformation
It is a congenital disease that affects the development of the vascular system. Manifests itself in the form of plexuses of abnormal vessels of various sizes. It is dangerous because it can cause subarachnoid hemorrhage of a non-traumatic nature. Among other things, steal syndrome may develop, and malformations may begin to compress the brain tissue.
Cerebral circulatory disorders
TCD is used quite often to examine cerebral vessels. It may be necessary to identify the cause of problems with cerebral circulation. They may consist of the formation of blood clots, loops and kinks in blood vessels. Often the cause is: the formation of narrowings, aneurysms or embolism.
Atherosclerosis of the arteries of the neck and head
It consists of damage to areas of blood vessels by atherosclerotic plaques, which either significantly narrow the lumen of the vessel or clog it completely. In advanced cases, treatment is performed surgically. TCD is used to examine vessels because it allows one to determine not only the presence of plaques, but also their size and location.
Encephalopathy
Occurs in chronic cerebral vascular diseases that slowly progress. This disease combines cognitive impairment, disruptions in the emotional and motor spheres.
How the method works
Transcranial Dopplerography of vessels is performed in M-mode. This is the most modern and convenient mode, combining speed and information. It displays blood flows located at a depth of 30-90mm, while mechanically changing the depth to view certain structures is not required - scanning is performed automatically.
Transcranial Dopplerography of the vessels of the brain and neck is performed using a sensor that emits ultrasound waves that pass through the tissue and return. The intensity of the impulse changes over time, which is immediately reflected on the monitor (the indicator is affected by heart contractions). When there is a lot of blood in the vessel, the graphic image becomes thicker, when there is little blood, it becomes thinner. Several pulses are reflected on the monitor simultaneously. Back-and-forth wave flows are displayed in different colors (blue and red, respectively). As a result of the study, a graphic report with digital values is generated, on the basis of which the specialist makes conclusions.
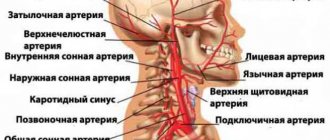
Transcranial Dopplerography of the vessels of the head has several features, the main one being the difficulty of penetration of the ultrasound signal through dense bone. To reduce the influence of this factor, the doctor uses “ultrasonic windows”, which are located in the places of thin natural openings in the skull. Through them, sound easily enters the skull, which makes it possible to study some of the vessels.
The most convenient accesses:
- in the area of the orbit of the eye (orbital) - demonstrates the condition of the orbital and internal carotid arteries;
- above the occipital protuberance (suboccipital) - through this access the segments of the vertebral arteries entering the skull and the basilar artery are studied;
- above the temporal bone (temporal) - helps to examine the ICA, ACA, MCA and PCA, the functions of the anterior and posterior communicating arteries);
- in the area of the craniovertebral joint.
To increase the information content of the method, compression tests are additionally used, during which the carotid artery above the mouth is compressed for 3-5 seconds. In general, the procedure takes from 15 to 40 minutes, depending on the presence of deviations and the need for their detailed study.
general characteristics
Transcranial Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive method for diagnosing vascular disorders, based on ultrasound waves. It is most often used to assess the condition of cerebral vessels. Such an examination allows you to diagnose serious pathologies at an early stage. In addition, it is possible to examine the vertebral artery, vessels and veins of the neck.
During the examination, ultrasound waves are passed through the head. They are reflected from red blood cells in the blood, and special sensors detect these waves. This allows you to assess the condition of all large vessels and arteries supplying blood to the brain. Using TCD, it is possible to detect disturbances in the intensity of blood flow and its speed.
Important: transcranial Doppler ultrasound helps to examine vessels that are inaccessible to other research methods. With its help, you can examine the walls of blood vessels from the inside.
This became possible after the discovery of laws by physicist Christian Doppler that made it possible to estimate the speed of blood flow using ultrasonic waves. This method helps to see the blood vessels of the brain at different depths. And modern devices can reflect the state of blood circulation in real time.
When a patient is prescribed this examination, many are afraid because they do not know what it is. The main feature of transcranial Doppler ultrasound is that it is a non-invasive diagnostic method, that is, it is performed without surgery, is painless and does not cause any discomfort. In addition, there is no harmful radiation exposure. Ultrasound waves are considered the safest for both diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, TCD is used at any age, for any health condition.
What does the study reveal?
Transcranial Dopplerography of cerebral vessels provides reliable data on the state of blood vessels and blood flow and allows for a correct diagnosis.
Ultrasound ultrasound helps to identify:
- vasospasms and increased intracranial pressure, which cause headaches;
- cervical artery stenosis;
- thrombus formation;
- pathological tortuosity of the vessel;
- deviations in the condition of the vertebral arteries;
- deviations in the venous blood flow of vessels in the head and neck, etc.
Transcranial Doppler ultrasound of an infant is performed to analyze the condition of blood vessels and prescribe timely treatment if the child was born prematurely and has low weight, developmental defects, cerebral hernia, brain pathologies detected during pregnancy, intrauterine infections, etc. Most often, instead, at an early age, when the bones of the skull are still quite thin and there is a fontanel, neurosonography is performed.
Older children are prescribed the procedure if they experience headaches and dizziness, moodiness, restlessness, fatigue, poor sleep, or the presence of diseases that directly affect the quality of cerebral circulation (diabetes mellitus, vasculitis, arterial hypertension.
What does transcranial Doppler sonography show?
After you have learned what TCD is, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the data that will become known as a result of the procedure. The following will be taken into account:
- vein or artery wall thickness, diameter;
- minimum and maximum blood flow speed, its nature;
- resistive and ripple indices.
Each of these indicators may indicate the presence or absence of disease.
The speed of blood flow through the arteries
A TCD examination may show an abnormality, which is a deterioration in blood flow. The cause may be the presence of blood clots or plaques, as well as other problems that can be identified through duplex testing.
Venous drainage from the cranial cavity
There can be many reasons for this phenomenon; they may include severe traumatic brain injuries, the occurrence of tumors that compress blood vessels and/or brain tissue. Often, outflow occurs against the background of a stroke and its consequences, with a decrease or underdevelopment of the network of blood vessels.
Degrees of development of the collateral network of brain vessels
TCD examination can reveal underdevelopment of the blood vessel network. It often causes problems with blood supply to the brain. All detected violations are recorded in the conclusion.
How the research works
No special preparation is required before the study. Basic recommendations include avoiding vascular medications, smoking, and drinking alcohol before the procedure. The area of examination that the doctor deals with is the skull and neck.
Transcranial Dopplerography of cerebral vessels is performed in the supine position. The doctor places the patient on the couch, placing a small cushion under the head. For better conductivity of ultrasound waves, a conductive gel is applied to the areas where the examination will be carried out.
The doctor touches points on the head and neck through which information can be obtained with a special sensor and from time to time gives commands (breathe more often, turn your head, stop breathing for a while, etc.). Several times throughout the study, the doctor performs a compression test, which may cause slight discomfort, but lasts no more than 5 seconds. Examination of non-intracranial vessels occurs in the neck area.
The results of the study are displayed on the screen of the device, after which they are stored electronically in the clinic database for subsequent analysis by a specialist, or recorded on a disk and transferred to the patient if he is being examined by another doctor.
Preparing for Dopplerography
Carrying out this procedure does not require special preparation. The patient only needs to stop using all vascular medications, alcohol, and not smoke immediately before the procedure.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 5/5 — 2 votes
Share article on social networks
TCDG of cerebral vessels: interpretation of results
The results of vascular TCD are assessed in real time by a functional diagnostics physician. Due to the fact that the image appears on the screen, the specialist can immediately draw a conclusion about the condition of the arteries or veins. During triplex scanning, the vessels are colored red and blue. This allows us to judge the interaction of the venous and arterial systems. Thanks to TCD, it is possible to estimate the speed of blood flow through the vessels and its direction. Dopplerography also allows one to judge the condition of the valve apparatus, the inner wall of the arteries. Slow blood flow or its turbulence indicate the presence of a narrowing of the lumen of the vessel. In this case, consultation with a neurologist and a vascular surgeon is necessary.
Examination technique
Transcranial Doppler sonography is performed with the patient sitting on a chair. This access performs duplex or triplex scanning. The ultrasound sensor is placed relative to the auricle. The study begins from the front, then the device is moved upward (to the temporal and parietal region), and then back. This allows blood flow to be assessed in all areas of the brain one by one. At the end of the study, the sensor is placed in the back of the head. In this way, one can judge the state of the cerebellar zone, the veins of Galen and Rosenthal. Transcranial scanning also evaluates the condition of the vertebral artery.
How the research is carried out
The duration of transcranial Doppler ultrasound does not exceed 20 minutes. Since ultrasound waves pass only through soft tissues, the occipital, temporal, and orbital areas are examined.
A specialist uses an ultrasonic sensor to examine the origins and course of the arteries. Hemodynamic parameters (velocity, volume of blood flow, presence of turbulence) and intracranial pressure are also measured. The study provides information about the condition of the orbital, cerebral, basilar, and vertebral vessels.
Preparation for TCD of arteries and veins of the head and neck
Dopplerography of the arteries of the head and neck is not accompanied by harmful effects and is a painless method. Therefore, preparation for TKDG is not necessary. Particularly sensitive patients should be explained the purpose of the procedure. Sedatives are not indicated as preparation. Before the procedure, you need to remove jewelry and put away your mobile phone.