Why does hemiplegia occur?
The cause of hemiplegia is either damage to the motor parts of the cerebral hemisphere opposite the paralyzed side of the body, or damage to the spinal cord on the same side where symptoms are observed. It would seem that there are few possible reasons, but, in fact, completely different processes can lead to the occurrence of these lesions. The most common of them, oddly enough, is strokes. In addition, injuries, infectious diseases and even tumors can lead to the appearance of symptoms of hemiplegia.
However, in this whole series of reasons, childhood hemiplegia stands apart, since it is usually congenital. Birth injuries can lead to it, but in about 3/4 of cases the cause is a violation of intrauterine development. In both cases, such hemiplegia in children is a form of cerebral palsy.
Diagnosis of cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy) in the early stages
Doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute argue that the possibility of correcting disorders in cerebral palsy depends on the timely diagnosis of the disease. At the first behavioral disturbances in a child, you should contact your pediatrician and find out whether his development is normal. At home, you can notice the first signs of cerebral palsy, which will then progress. These include:
- at the age of 1 month - lack of reaction to loud sounds, restless sleep;
- 4 months - children do not respond to sound by turning their heads, do not show interest in toys and other objects;
- 7 months - the child cannot sit independently, some patients have difficulty holding their head up;
- 12 months - the child does not begin to pronounce individual words, performs most actions with one hand;
- at any age - squint, convulsions, sudden movements, gait disturbances (lack of support on the full foot).
The most informative method for diagnosing cerebral palsy is MRI. The examination should be carried out when the first symptoms appear, as well as if there is a similar diagnosis in the anamnesis of relatives. The diagnosis must be differentiated from other pathologies that manifest similar symptoms. These include early hereditary ataxia, consequences of traumatic brain injury, phenylketonuria, galactosemia, schizophrenia and other disorders.
Types of hemiplegia
There are several ways to classify hemiplegia, each of which serves a specific purpose: classification by cause (organic and functional); by localization (cerebral hemiplegia and spinal hemiplegia); according to the relative location of the lesion and symptoms (contralateral hemiplegia or homolateral hemiplegia); on the side of the body on which paralysis is observed (right-sided hemiplegia and left-sided hemiplegia); according to symptoms (spastic hemiplegia and non-spastic hemiplegia). Let's look at each option in more detail.
Classification of hemiplegia by cause is the first thing you need to pay attention to. The fact is that in addition to organic hemiplegia - the one in which real damage to nerve cells leads to the development of muscle paralysis, there is also functional hemiplegia, which is also called alternating. And with it, symptoms can appear and disappear spontaneously, usually during times of increased nervous excitement. Depending on what type of hemiplegia was identified, treatment will differ radically.
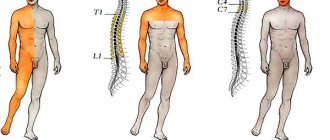
Classification by location is used to figure out where exactly the lesion is located. As we have already written, damage to the brain - cerebral hemiplegia - leads to the appearance of symptoms of hemiplegia on the opposite side of the body, and damage to the spinal cord - spinal hemiplegia - on the same side. This is “contralateral” and “homolateral” hemiplegia. It is important to clarify that when the spinal cord is affected, the term “central hemiplegia” is sometimes used. The concepts of “right-sided hemiplegia” and “left-sided hemiplegia” speak for themselves.
The diagnosis of “spastic hemiplegia” implies that in addition to the loss of the ability to make voluntary movements, there is also noticeable overstrain in the muscles. This is what childhood hemiplegia usually is - it is cerebral hemiplegia and in most cases it occurs in patients with cerebral palsy. The non-spastic form is very rare, and, as the name implies, muscle spasms are not observed with it.
Manifestations of hemiplegia
In any case, the main manifestation of hemiplegia is the complete loss of voluntary movements on one side of the body. This is what distinguishes hemiplegia from hemiparesis - with it, movements may be difficult or weakened, but the very ability to perform them remains. In addition, along with disturbances of voluntary movements and muscle spasms, other symptoms are present - an increase in healthy reflexes and the appearance of pathological ones, for example. You can often notice a change in the color and temperature of the skin on the paralyzed side, as well as swelling. Sometimes with hemiplegia there are also accompanying symptoms, such as epilepsy. All this data together helps doctors establish the most accurate diagnosis and select the optimal treatment regimen for hemiplegia.
Methods for treating hemiplegia
Treatment of hemiplegia always relies on three pillars: drug therapy, surgical treatment and rehabilitation. Each of them complements the other two and they all work together for a common result, so they should be approached with equal attention.
Medicines help reduce the level of spasm, which makes life and care for patients easier, and most importantly, gives scope for rehabilitation. In addition, there are attempts to use nootropic drugs to treat the cause of hemiplegia - brain damage, but it is important to note that these are methods without proven effectiveness.
Surgical interventions also serve the purpose of reducing the level of spasticity and provide more opportunities for subsequent rehabilitation - staged fibrotomy according to the V.B. method. Ulzibata, for example, will free chronically spasming muscles from contractures, which in such a situation inevitably arise and in themselves further limit movement. Without this, further rehabilitation for hemiplegia would be much less effective and probably much more painful. The latter in itself reduces the effectiveness of rehabilitation procedures.
After this, rehabilitation comes into play - there are many ways and techniques, and many of them can really make the lives of patients with hemiplegia much easier. These include physiotherapy, for example electrical muscle stimulation, which helps reduce spasticity, and various massage techniques, and physical therapy, including the use of special equipment.
One of the most important rehabilitation methods is to involve the patient in normal daily activities - this helps not only to reduce the symptoms of hemiplegia, but also teaches new skills and helps socialization.
Among the relatively new rehabilitation techniques is “mirror therapy,” which actually uses mirrors to help the patient concentrate on one side of the body. According to studies from 2018-2019, mirror therapy shows significantly better results than conventional rehabilitation, although the specific mechanisms of its action are not yet fully understood.
There is one more aspect that is not directly related to the treatment of hemiplegia, but is very important for maximizing the results of therapy. This is Wednesday. A barrier-free environment is important for both children and adult patients with hemiplegia, and inclusive education helps children socialize better and quickly learn new skills.
Treatment methods
Specialists at the Clinical Brain Institute offer individual treatment and adaptation programs for patients with various forms of cerebral palsy. The main goal of the work is maximum socialization of the child, teaching self-service skills, and developing intellectual abilities. Techniques are also used that significantly improve the condition of muscles with hyper- and hypotonicity and prevent significant deformation of skeletal development.
Basic methods of treating cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy)
Treatment methods for cerebral palsy are a set of measures aimed at improving the patient’s quality of life and his socialization. Despite the fact that the disease is chronic and does not end with complete recovery, it is necessary to constantly take measures to improve the child’s quality of life. Doctors may recommend the following treatment methods:
- therapeutic massage is one of the main methods of reducing muscle tone;
- therapeutic exercises (if possible) - special exercises to restore coordination of movements and symmetrical muscle development;
- electroreflexotherapy is a method of stimulating brain neurons, as a result of which the clinical picture of the disease is expected to be smoothed;
- classes with a speech therapist;
- work using animals, including hippotherapy;
- Loading suits - allow you to correct the position of the body and promote the correct development of the spine.
Classes with children must be carried out regularly. During the growth process, it is possible to prevent dangerous complications of cerebral palsy and promote the symmetrical development of skeletal bones and muscle mass. In advanced cases, surgical intervention may be indicated, during which muscle defects and contractures are eliminated, and tendon plasty is performed.
Using assistive devices
Therapy for cerebral palsy includes the use of additional devices. It is important to pay attention to the child’s motor activity and complicate tasks as he develops. During the exercises, it is important to perform them correctly using the right muscle groups. Classes take place with a specialist and at home, and can be carried out using additional equipment:
- walker is a device that is used not only for learning to walk, but also for correcting balance and balance;
- parapodium - a system of orthoses that allows you to move independently even in the absence of muscle tone in the lower extremities;
- verticalizer - a special fixator thanks to which the child can stand independently (this is important, among other things, for the proper development and functioning of internal organs);
- bicycles - models with three wheels, easy to operate, which allow you to move around with reduced function of the lower extremities;
- devices, splints, splints for correcting the position of the limbs.
For maximum socialization of a child, it is important to devote time to physical activity. Modern devices (wheelchairs, bicycles, walkers and parapodiums) allow you to move independently, even with decreased muscle tone. This development allows you to avoid the manifestation of muscle contractures and achieve maximum symmetrical development of muscles and bones. In addition, the room should be equipped with special devices for comfortable movement of the child, handrails, a bathing chair and other auxiliary devices.
Prognosis for hemiplegia
With functional hemiplegia, the prognosis is as favorable as possible - such conditions usually disappear completely and without a trace.
With organic hemiplegia, everything is somewhat more complicated. On the one hand, given that hemiplegia does not progress on its own unless caused by a tumor, worsening of symptoms over the course of life cannot be expected. On the other hand, it is important to remember that both cerebral hemiplegia and central hemiplegia lead to a decrease in muscle activity on one side of the body, and because of this, additional symptoms may develop - deterioration in joint mobility, the appearance of bedsores, or the formation of blood clots.
Unfortunately, at the current stage of development of medicine, one cannot expect a complete and complete disappearance of the symptoms of organic hemiplegia. But, despite this, with timely and comprehensive treatment in patients with hemiplegia in general and specifically in cases of cerebral palsy in the form of spastic hemiplegia, very noticeable improvements are possible, both in terms of symptoms and in terms of quality of life and socialization.
We hope that now for you the expressions “Central non-spastic right-sided hemiplegia” or “Cerebral spastic left-sided hemiplegia” will not sound like a Chinese letter or a sentence!
Return to list
Diagnosis of double hemiplegia
Despite the pronounced symptoms, it is necessary to carry out a multi-level diagnosis, because the cause of double hemiplegia can be a number of other neurological diseases of the central nervous system:
- thorough neurological examination using metameric technologies;
- MRI of the brain and cervical spine;
- CT;
- electromyography. It aims to determine the level of muscle activity;
- Ultrasound of head and neck vessels;
- Eye test and dryness