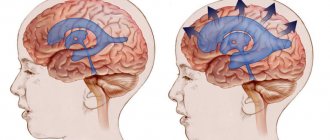
Echoencephalography: what is it?
Echoencephalography (Echo EG) is an ultrasound diagnosis of the brain. It allows you to examine the state of cerebral (brain) structures and indirectly assess the state of the blood vessels of the head.
The basis of the method can be described as follows: the tissues of the human body have different densities and structures, therefore sound waves, passing through different types of tissues of the brain, are reflected differently. The structures involved in signal reflection produce different waves. By the reflected wave, you can understand where the source of pathology is located. The type and extent of damage to nerve cells is also determined.
Echo EG is a non-invasive method, it takes place without intervention inside the head, without anesthesia. During the examination, the body is not irradiated. No contrast agent is used, there will be no allergies. It is not painful and you do not need to specially prepare for the test.
Indications and contraindications
A child’s brain echo is prescribed for the following conditions:
- Delayed mental and physical development.
- Sleep disorders.
- Muscle hypertonicity.
- Cramps.
- Urinary incontinence (enuresis).
- Logoneurosis (stuttering).
- Head injuries and bruises.
- Nervous tics.
- Hydrocephalus.
Echoencephalography is also performed for frequent intense headaches, dizziness, nausea regardless of food intake, fainting, a feeling of lack of air, decreased concentration and other neurological symptoms.
Echoencephalography of the brain in children is used to assess the effectiveness of treatment and to monitor the patient’s condition. In case of severe pathology, Echo EG data is taken to make a preliminary diagnosis.
The procedure has no contraindications, except for open wounds, infections, skin defects at the site of application of the sensors. If there are open wounds on the head, it is better to do a CT scan.
Procedure modes
Transmission
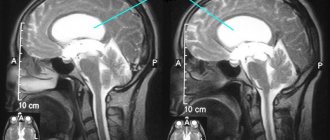
Two U3 sensors are installed on your head on the same axis so that they are on the same line. The first sensor scatters the signal, and the second sensor’s task is to catch the reflected impulses. In this way you can recognize the “midline of the head.” It is approximately located near the anatomical midline.
If you have damaged the soft tissues of your head, suffered bruises or other injuries, this may be an accumulation of blood under the periosteum or in the skull area, this will not be a problem.
Emission mode
This time, only one sensor is needed; it is placed on special places on the head, these places are easily penetrated for ultrasound. It happens that you have to move it a little, thereby you can adjust the sensor signal and produce the best image.
How to prepare
Echoencephalography can be done on patients of any age, women during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
The procedure does not require preparation. There is no need to follow a special diet, take a contrast agent or carry out additional manipulations. It is best to conduct the examination after sleep.
Contact gel is applied to the scalp where the sensors are attached. The doctor moves the sensor. After the procedure, the gel must be wiped off, so you should take a towel for the examination.
Where to get an echocardiogram
Standard echocardiography is carried out both in public medical institutions (clinics and hospitals) and in private medical centers. To register for an examination, you must provide a referral from your attending physician or cardiologist.
More specific types of echocardiography - transesophageal examination or stress echocardiography - can only be performed in specialized medical institutions, since they require special equipment and personnel who have undergone special training.
How is a head echo performed on a child and in what ways?
The doctor should tell you how to prepare your baby for an Echo EG of the brain and what are the features of the examination of the child.
There are two ways to conduct an Echo EG:
- Transmission. Two sensors are used. They are applied on both sides of the head at the level of the temporal bone above the ears. One sensor sends a signal, the other receives. It is necessary that the sensors converge in one axis.
- Emission. This method uses only one sensor.
For young children, neurosonography is performed instead of echoencephalography. This is a scan through the large fontanel. In infants, the fontanelles have not yet ossified, so the ultrasound wave easily passes through the tissue.
The manipulation is carried out without anesthesia. The only difficulty is that it is difficult for children to remain still during the examination. The parents' task is to hold the head and calm the baby.
The procedure takes 10-15 minutes. After this, decryption is done.
Echo EG is often used to monitor the patient's condition during treatment.
Echocardiography in children
As noted above, the undeniable advantages of EchoCG are the non-invasiveness, painlessness and complete safety of this method of cardiac research. The manipulation is not associated with radiation exposure and does not provoke any complications. Therefore, if there are appropriate indications, the study can be recommended not only for adults, but also for children.
Diagnostics will help to timely detect congenital pathology in young children, which, in turn, will make it possible to select the most effective treatment. As a result, the child will be able to lead an absolutely fulfilling life in the future.
Indications for echocardiography in a child are:
- Heart murmurs.
- The appearance of shortness of breath either during physical activity or at rest.
- Blueness of the lips, nasolabial triangle, fingertips.
- Decreased or complete lack of appetite, too slow weight gain.
- Complaints of constant weakness and fatigue, sudden fainting.
- Complaints of frequent headaches.
- Discomfort behind the sternum.
- Decrease or increase in blood pressure.
- The appearance of swelling in the extremities.
Taking into account the fact that the method is safe, echocardiography can be performed on children more than once in order to track the development of the disease or assess how effective the treatment is. If any pathological changes have been identified, a study is carried out at least once every twelve months.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Interpretation of results: norm and possible diseases
To make a correct diagnosis, the results of the Echo EG and the patient’s complaints are compared. The decoding is carried out either by a neurologist or a laboratory specialist. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. When interpreting data, the doctor’s experience and precise adjustment of the equipment are important.
To decipher Echo EG data, the doctor looks at three indicators of the echo signal:
- Initial complex. The signal is reflected from the bone, soft tissue, meninges and lateral ventricle on the side where the scanning occurs.
- Ultimate complex. This is the reflection of an ultrasonic wave from the bones of the skull and soft tissues of the head of the opposite hemisphere.
- Between them, a stable M-echo signal is recorded, which is reflected from the middle parts of the brain: epiphysis, pineal gland, septum pellucidum, and others. M-echo is essential for diagnosis.
Echoencephalography can be performed in two modes:
- M-method. One-dimensional scanning in which a graph is displayed on the screen
- Ultrasound scanning. 2D scanning. The brain is imaged in two planes.
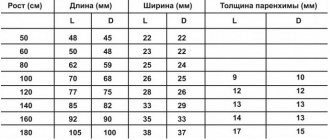
Normally, the M-echo distance should be the same on one side and the other of the head. If the deviation is more than 1-2 mm (in children up to 3 mm), then this may be a sign of conditions such as hematoma, cerebral edema, abscess (accumulation of pus), intracerebral tumors, bruises and neoplasms. An increase in the volume of the lateral ventricles and the 3rd ventricle indicates the presence of hydrocephalus.
In a state of wakefulness, sleep, anxiety, the EG echo shows its rhythm: alpha, beta, delta or theta rhythm. Normal frequency is alpha rhythm, 8-13 Hz, beta rhythm, 13-30 Hz, theta rhythm, 4-7 Hz, delta rhythm, 0.5-3 Hz.
In case of severe disorders, electroencephalography is used as a preliminary diagnostic method. Additional research methods, such as magnetic resonance imaging, may be needed.
Preparation rules
Despite the simplicity of the echo procedure, you should properly prepare for the study. Experts point out that to obtain information about the functioning of the brain, you will not need to change your diet or take medications.
However, the reliability of the result may be affected by:
- sleep disturbance – it is recommended to get a good night’s sleep the night before the examination;
- hunger – on the day of the diagnostic visit, a light breakfast is necessary;
- stress – the procedure is absolutely painless, so no need to worry;
- bad habits - doctors advise to refrain from abusing tobacco and alcohol products.
In addition, you should be prepared that for some time, while the specialist performs ultrasound diagnostics, you will need to keep your head and body still in order for the result to be accurate and informative. Therefore, echoencephaloscopy in young children is performed in the presence of parents who hold their heads in the desired position.
If there are damage to the scalp, even superficial to the skin, they can distort the ultrasonic waves. The study must be postponed until the wounds have healed or resort to other techniques that allow such tissue defects.
What pathologies can echoencephalography reveal?
Echo EG shows the brain parts and large blood vessels. This diagnostic method allows timely detection of diseases such as meningoencephalitis, hydrocephalus, neoplasms and strokes. The procedure is available for all categories of patients: children, adults, nursing mothers, and also during pregnancy.
Using echoencephalography, you can identify not only the localization of the pathological process, but also understand how large the lesion is.
Neoplasms, meningoencephalitis, dropsy, intracerebral hemorrhage
In patients with long-term illness, a large shift in the M-echo may indicate the appearance of a tumor. The size of the displacement depends on the exact location of the tumor in the hemisphere. If the tumor is located in the middle sections, the displacement may be 2 mm, or may not be observed at all.
Meningoencephalitis is an inflammation of the brain and meninges. The disease is caused by microorganisms. The carriers are ixodid ticks.
Hydrocephalus (water on the brain) is an excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity. EchoEG data should alert you if the index of the third ventricle is less than 22. Normally, 22-24.
During a stroke, if the M-echo is displaced by 5 mm or more in the first days, then this is a hemorrhagic type. If it moves by 2.5 mm, then the disease is ischemic.
Types of echocardiography
Today, there are several types of echocardiography. What specific type of study to conduct is decided in each specific case by a cardiologist.
One-dimensional
At the moment, this type of echocardiography is rarely used independently, because it is considered less informative than others. No image of the heart is generated during the procedure. The data is displayed on the screen in the form of a graph. Using M-echocardiography, the doctor can determine the volume of the heart cavities and evaluate their functional activity.
B-echocardiography (two-dimensional)
During B-echocardiography, data from all structures of the heart enters the computer and is displayed on the monitor in the form of a black and white image. The doctor is able to determine the size of the heart, find out the volume of each of its chambers, the thickness of the walls, assess the mobility of the valve leaflets and how the ventricles contract.
Doppler echocardiography
As a rule, this study is performed simultaneously with B-echocardiography. It allows you to track blood flow in large vessels and on the heart valves, identify reverse blood flow and its degree, which may indicate the formation of pathological processes.
Contrast echocardiography
This test makes it possible to more clearly visualize the internal structures of the heart. The patient is injected intravenously with a special contrast agent, after which the procedure is carried out as usual. This procedure allows you to examine the inner surface of the chambers of the heart. Contraindications for this study are individual intolerance to contrast and chronic renal failure.
Stress echocardiography
To diagnose hidden heart pathologies that manifest themselves exclusively during physical activity, a special type of study is used - stress echocardiography. It makes it possible to identify diseases in the early stages, which do not remind of themselves if the patient is at rest. Stress echocardiography is recommended to assess the condition of blood vessels and their patency, to find out how great the risk of complications is before performing surgical interventions on the heart and blood vessels. The procedure is also carried out in order to determine how effective the therapy for coronary heart disease is and to determine the further prognosis for this disease.
There are several contraindications to stress echocardiography. It should not be performed on patients suffering from severe respiratory, renal, hepatic or heart failure. It is also contraindicated in case of myocardial infarction, aortic aneurysm and a history of thromboembolism.
Transesophageal echocardiography
This is a special type of study, during which an ultrasound-generating sensor is lowered through the oropharynx through the esophagus to the required depth. Since the sensor has very small dimensions, it passes through the esophagus without problems. However, such a study is considered quite complex and is carried out exclusively in specialized medical centers. In addition, there are special indications for it. In particular, a transesophageal examination is performed in cases where a standard transthoracic examination does not allow assessing the condition of the heart and its structures. In particular, when doubts arise about the correct functioning of a previously prosthetic heart valve, if an aortic aneurysm and atrial septal defect are suspected, as well as if the patient has been diagnosed with infectious endocarditis and the doctor suspects an aortic root abscess.
At the same time, this type of study has contraindications from the upper digestive tract, namely, any tumor formations of the esophagus, bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract, the presence of a large diaphragmatic hernia or dilation of the esophageal veins. Transesophageal examination should not be performed in patients with severe osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, instability of the cervical vertebrae, or a history of esophageal perforation. Diagnosis may be complicated in patients with thyroid diseases.