The brain is the main organ of the central nervous system. It consists of more than 35 billion cells. There are 5 parts of the brain that interact with each other using neural connections:
- Oblong. Responsible for protective reflexes (sneezing, coughing, vomiting), food (sucking, salivation, swallowing) and cardiovascular (regulation of the heart and blood vessels, as well as breathing and hearing).
- Posterior section. His “conscience” includes facial expressions, chewing reflexes, balance and muscle function.
- The middle one is responsible for muscle tone and skin pigmentation.
- Intermediate regulates metabolism, cardiovascular activity and sleep.
- The final (large) is the highest center of mental activity. Responsible for smell, hearing, vision, movement.
call me back
Brain Facts
- The average brain weight is 1300-1400 grams. That is, having a mass of no more than 2% of the entire body, it consumes a quarter of all energy.
- The brain is 60% fat.
- Has no pain receptors. Therefore, when neurosurgeons perform operations, they inject painkillers only into the scalp
- From large doses of alcohol, the brain loses the ability to create memories. Therefore, when a person has a large dose of alcohol, he does not remember the events that occur.
- The brain often doesn’t care whether you actually do something or imagine it in pictures. If you imagine a dangerous and extreme situation in your mind, your heart rate will immediately increase. This feature of our psyche has long been known to athletes. Many of them do visualization before competitions: they imagine all sorts of situations that could happen to them during tournaments. Research has proven that this method improves the performance of athletes because it prepares their muscles and body.
- There is a phenomenon known as phantom pain. For example, when a person's leg is amputated, he still experiences pain in it. This happens because there are nerve endings in the brain that are responsible for sensing pain in that leg.
Classification
Brain tumors, depending on the nature of their origin, are divided into:
- primary, formed from cerebral tissues;
- secondary, arising through metastasis against the background of malignant neoplasms localized in other areas of the body.
Depending on the location of the tumor, it can be located inside the brain or in its soft, hard membranes, blood vessels, and bones of the skull. Also, all neoplasms are benign and malignant. The first type can, under the influence of negative factors, transform into a cancerous disease; also, in the case of rapid tumor growth, compression of sensitive nerve tissue occurs, which entails other irreversible processes.
Symptoms of brain diseases
The most common brain diseases include atherosclerosis, stroke, tumor, vascular aneurysm, and Alzheimer's disease. According to statistics, up to 85% of people are predisposed to developing diseases related to the blood supply to the brain. Such data are a consequence of the unhealthy lifestyle of modern man. The danger of brain diseases lies in their asymptomatic nature. That is, for a long time they do not make themselves felt.
Common symptoms of brain diseases include:
- Frequent headaches that do not go away even after taking medications.
- Memory impairment.
- Constant fatigue.
- Fainting.
- Cramps.
- Fever. Body temperature can reach up to 40 degrees.
- Weight loss to the point of exhaustion.
Specific symptoms of atherosclerosis:
- Noise in ears. It occurs when a cholesterol plaque has blocked 60% of the blood flow in an artery.
- Decreased erection. If a man under 50 years of age has decreased erection, then such a patient's risk of dying from a myocardial infarction is many times higher than that of the same person with normal erectile function.
- Coldness in the extremities. The vessels become stiffer and blood flows through them worse.
Specific symptoms of stroke:
- Numbness of the face and limbs.
- Double vision.
- Difficulty moving.
Every third death in Russia is associated with this pathology.
Stroke happens:
- Ischemic. Associated with blockage of arteries, cessation of blood flow to the brain and necrosis of its tissue. The cause of the appearance is blockage of blood vessels leading to the brain due to atherosclerotic plaque. The second reason is the occurrence of a blood clot in the heart when it is not working properly (for example, during an arrhythmia). As a result, the blood clot “runs” into the brain vessels, causing thrombosis.
- Neurological. Associated with hemorrhage and hematoma formation inside the skull. It occurs due to high blood pressure when, at its peak, a small vessel inside the brain ruptures and a hematoma appears.
There are signs of a stroke that, if recognized in time, can save a life. To make it easier to memorize, they can be combined into the word “IMPACT”:
- Smile. If a person cannot smile and one of the corners of his mouth is drooping.
- Movement. A person cannot move both arms or legs at once.
- Articulation. A person cannot say anything clearly, not even his name.
- Solution. To save a person, you should take him to the hospital and carry out the necessary examinations within 1-2 hours.
Specific symptoms of Alzheimer's disease:
- Avoiding contact with people.
- Lost in space.
- Decreased emotionality and interest in life.
- Hallucinations.
Alzheimer's disease is a form of dementia that occurs in older people. It is most often found in patients who have crossed the threshold of 65 years. At the moment it is incurable.
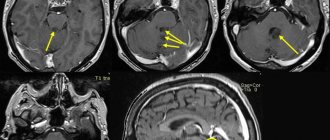
Specific symptoms of a brain tumor:
- The headache does not go away within two weeks to a month.
- Headache is accompanied by vomiting, hearing loss and coordination.
- Motor perseverations (inability to stop performing an action).
- Inattentiveness and forgetfulness progresses.
Brain tumors are divided into benign, malignant and metastases. In the case of benign, the disease develops gradually, slowly and gently over several years.
Types of brain tumors:
- Intracerebral. The most common and aggressive form is glioblastoma. It is almost impossible to defeat her. The tumor grows through healthy tissue and cannot be localized.
- Extracerebral. They grow on the base or surface of the skull.
- Metastases are secondary brain tumors. The main cancer cells penetrate the bloodstream into the brain and cause the growth of metastases.
Sign up for a consultation
Reasons for the development of pathology
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of pathology. Among them:
- skull and brain injuries;
- immunodeficiency states;
- exposure to carcinogenic chemicals and toxic substances;
- deviation in the formation of brain tissue during intrauterine development;
- negative impact of ionizing radiation;
- genetic diseases: von Recklinghausen syndrome, Turco syndrome, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Gorlin disease.
The main causes and mechanisms that lead to the process of tumor formation are currently not fully determined.
New growths inside the skull are more common in people whose relatives have had cancer. Patients with weakened immune systems are also at risk. In children, brain tumors in 40-50% of cases occur against the background of a genetic disease (von Recklinghausen syndrome).
Risk factors
Brain diseases can be caused by various reasons related to lifestyle, as well as existing health problems.
- Smoking. Nicotine and other substances contained in tobacco smoke provoke atherosclerosis and vascular aneurysm at a high rate.
- Low physical activity. Physical education improves the plasticity of the brain - its ability to create new connections and transform itself. Accordingly, if a person does not perform even minimal exercise, his brain does not create new neural connections and quickly destroys old ones.
- Male gender. According to research, men are more likely to suffer from brain diseases because they lead an unhealthy lifestyle.
- High blood pressure. As a result of surges in blood pressure, protrusion of the vessel wall in a weak spot may occur.
- Poor nutrition and obesity. If a woman’s waist exceeds 88 cm, and a man’s waist exceeds 102, it is necessary to adjust your diet. With obesity, insulin insensitivity develops (cells lose sensitivity to the hormone, and the pancreas produces more of it than normal).
- Alcohol. The alcohol contained in alcoholic drinks is absorbed into the blood, enters the brain and destroys its cortex.
- High cholesterol. It affects blood vessels, forming cholesterol plaques on their walls, interfering with normal blood flow.
- Stress. Recent studies have shown that stress impairs brain function due to the production of cortisol (the stress hormone).
- Age. Many diseases begin to appear younger and appear at an earlier age than decades ago. For example, cholesterol plaques begin to form in the blood vessels of the brain by the age of 35, which can lead to atherosclerosis.
- Genetics. If your close relatives have developed brain diseases under 50 years of age, then you are at high risk.
- Infections and inflammations. They affect the brain matter, disrupting the functioning of the immune system and brain.
Symptoms of pathology
As a rule, in the presence of cerebral neoplasms, general cerebral disorders occur, and focal neurological signs are also observed. Common symptoms include:
- constant headaches of a bursting nature that do not go away after treatment;
- nausea and vomiting that occurs due to headache;
- dizziness, in some cases loss of consciousness.
Speech and hearing impairments, motor and sensory processes, epilepsy attacks, changes in visual fields, and psychoemotional disorders may also be observed.
Diagnostics
To diagnose a tumor in the brain, a comprehensive examination is performed. Conducted:
- assessment of general status, neurological symptoms;
- fundus examination;
- electroencephalography;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- various neuroimaging methods.
Echo-EG, EEG, vascular MRI, lumbar puncture, stereotactic biopsy can also be performed.
Treatment methods
Conservative therapy may include painkillers, antiemetics, sedatives and psychotropic drugs. To cope with brain swelling, glucocorticosteroids are used.
Conservative treatment does not help eliminate the main cause of the pathology, so surgery is necessary to remove the tumor. Depending on the type of neoplasm, its location and size, stereotactic radiosurgery or shunt surgery may be used. Additionally, radiation and chemotherapy may be prescribed.
Organic brain damage – relationship with functional disorders
Historically, earlier in psychiatry, all mental illnesses were divided into organic (in which the substrate can be identified - the site of the lesion, the cause of the process) and functional (which are caused exclusively by social and behavioral factors).
However, with the development of medicine, this division lost its relevance and showed that exclusively organic and exclusively functional disorders are rarely encountered.
For example, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) used to be considered purely functional, since its cause was the direct fact of suffering mental trauma. Now it has been proven that the emergence and development of PTSD is associated not only with the presence of mental trauma, but also with certain characterological characteristics of the individual, including those of an organic nature, the so-called. pathoplastic basis (organic lesions at the subclinical level, preceding the manifestation of PTSD, such as post-infectious processes, trauma during childbirth, etc.).
Modern instrumental studies have now proven that patients with panic disorder exhibit diencephalic insufficiency.
According to G.L. Voronkov, there are practically no organic mental disorders in their pure form; they are always a combination and interpenetration of organic and functional symptoms.