These include:
- Myopia (nearsightedness).
- Hypermetropia (farsightedness).
- Astigmatism.
Ametropia may be due to the structure of the eye. In this case, this condition is permanent (often congenital), the eye requires correction (glasses/lenses).
However, there are acquired conditions that are reversible. But if there is no proper treatment or correction, this condition can turn from transient to permanent, or lead to an increase in already existing ametropia.
Myopia (nearsightedness)
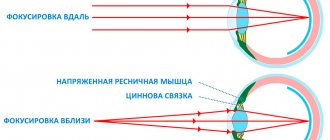
With myopia, the eye is enlarged in the anteroposterior segment (longer) and, as a stronger, “convex” lens, refracts the light entering the eye more strongly. This causes the focal length to be projected in front of the retina when looking into the distance.
Diverging (minus) lenses help to “pull” the focus back onto the retina and restore clear vision. Since myopia is a permanent condition (remember that this is a feature of the structure of the eye), glasses / soft contact lenses are constantly prescribed. At the age of up to 40 years, they are prescribed for constant wear (for near, distant). After 40 years, these glasses are only worn when looking into the distance, because presbyopia comes into force - an age-related decrease in distance vision, but more on that a little later.
Laser vision correction (LASIK technique) helps to achieve the effect of constantly wearing glasses/lenses, i.e. it allows you to see well without the use of optical correction.
Prices for diagnostic services and consultation with an ophthalmologist
| Type of medical service | Service price in rubles |
| Complete ophthalmological examination | 1000 |
| Complete ophthalmological examination of children | 1100 |
| Consultation with an ophthalmologist for eye disease in an adult | 500 |
| Consultation with an ophthalmologist for eye diseases in children over 3 years of age | 700 |
| Selection of simple glasses with a prescription | 500 |
| Selection of progressive, office glasses with prescription | 700 |
| Selection of contact lenses with training and prescription | 1000 |
| Selection of contact lenses without training | 600 |
| Training in the use of contact lenses | 400 |
Treatment methods
Hardware treatment of eyes in children
Treatment with ophthalmological devices makes it possible to achieve a lasting therapeutic effect in young patients. In some cases, it is possible to completely get rid of pathologies such as amblyopia, impaired binocular vision, and false myopia.
Perifocal
The lenses have a corrective effect for myopia. Perifocal models are aimed at correcting central and peripheral vision, which provides excellent visibility and a pronounced therapeutic effect.
Ophthalmological device "Rucheek": accommodation training
The device is a system in which light emitters are located at different distances from the patient’s eyes. Training is carried out by adjusting the image position and the speed of changing “pictures”.
Ophthalmological device "Cascade"
Impact on the visual function of the eyes with light and color stimuli that dynamically move over a certain distance in a closed tube. Particularly effective for accommodation disorders and restoration of binocular vision.
Ophthalmological treatment device "Visotronic M3"
The ophthalmic myotrainer relaxer has a complex effect on the organ of vision and oculomotor muscles. Particularly effective for eye accommodation disorders, as well as during myopia, hypermetropia and computer syndrome.
This is interesting
Blue light and optical coatings that reduce its transmission
Do I need to correct my vision and why is it so important?
What diseases can be diagnosed based on the condition of the eyes?
Preserving vision and eye health with Crizal Eyezen lenses
Which spectacle lenses should I choose? Choose your glasses with Crizal Corner
Astigmatism
It is a structural feature of the cornea that leads to vision distortion and/or double vision. It can be present either isolated in the eye or accompany myopia or myopia. For the purpose of correction, glasses with a cylindrical component in the lens or soft contact lenses (SCL) are prescribed. Externally, these glasses are no different from ordinary ones. Performing LASIK can correct the structure of the cornea, and the patient will forget about astigmatism.
It is important to understand that properly selected glasses do not worsen your vision! It is a myth.
Over the past decade, devices designed to simplify our lives and communications have become firmly established in our everyday life. Wearable electronics come in a variety of shapes, sizes and purposes. People have been using a personal computer for even longer. And it’s hard to calculate how long a person has been using printed publications.
An increase in tasks that require long-term visual load, as well as the emergence of new professions where the main activity is performed at the computer, leads to an increase in disorders associated with increased visual load.
These conditions can be acute, subacute, become chronic, or lead to changes in the structure of the eye:
- Presbyopia.
- Spasm of accommodation.
- PINA (habitual excess tension of accommodation).
- Paresis and paralysis of accommodation.
- Accommodative asthenopia.
Diagnostics
Signs of paralysis of accommodation have common symptoms with diseases such as optic neuritis, sarcoidosis, glioma, Lyme disease. It is important to conduct a thorough diagnosis in order to exclude the listed pathologies and confirm cycloplegia.
The study is carried out with cycloplegic drugs. They turn off the accommodative muscle, allowing you to examine a person's refraction. It is an invaluable diagnostic tool in the evaluation of patients with impaired vision and ocular deviation. The method is justified by the fact that patients have different levels of accommodation at different times of the day.
The study not only allows you to determine the refractive error, but also dilates the pupil, preparing the patient for an ophthalmoscopic examination. All children need a thorough ophthalmoscopic examination, which allows the doctor to find out the cause of cycloplegia.
Helps determine myopia in patients with accommodative esotropia, prevents over-correction in myopic patients. The study is also useful in prescribing correction in patients with limited cooperation with subjective refraction and amblyopic patients with chaotic accommodation.
Indications for cycloplegic refraction in adults are limited. This is due to a decrease in the amplitude of accommodation. This examination is most often recommended for children; adults are prescribed:
- perimetry;
- visometry;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- rheoophthalmography;
- MRI, , ultrasound.
In older and younger children, cycloplegic refraction can confirm the diagnosis of accommodative spasm, paresis, or paralysis. The study allows you to assess the true anomaly by relaxing accommodation.
Presbyopia
When the ciliary muscle is tense, the ligaments of Zinn, to which the lens capsule is attached, relax. As a result, the lens becomes more convex, slightly lowered, and the pupil narrows, providing clearer near vision. As the lens becomes more convex, it gains additional optical power, thereby bringing the focal length closer to the eye. However, after 40-45 years, the lens loses its elasticity and cannot fully take on a convex shape. The ciliary muscle also loses its strength with age, and presbyopia gradually increases.
This condition is not a pathology, but a physiological norm. It cannot be excluded, but it can be delayed for several years.
The onset of presbyopia is accelerated due to:
- long absence of rest,
- stressful situations,
- chronic lack of sleep,
- deficiency of vitamins A, B, C,
- abnormal visual loads.
When presbyopia has already set in, the most correct decision would be to select glasses for correction. These glasses are prescribed only for close work (reading, writing or working on a PC).
Everyone is susceptible to presbyopia: nearsighted, farsighted and emmetropic (lack of ametropia). But it manifests itself in different ways.
- Emmetropia
. In this case, presbyopia proceeds in the usual way with manifestation at 40-45 years and the prescription of weak positive glasses. - Farsightedness.
Since in this case the patient already needs plus glasses for distance, the optical power of the glasses for near is added to the power of the glasses for distance. The need for glasses for near vision may appear as early as 35 years of age. - Myopia.
Patients use minus distance glasses. But we remember that the correction for near is added to the necessary correction for distance. Therefore: either the patient needs weaker minus glasses, or (with weak myopia) presbyopic glasses will be needed much later than usual.
Spasm of accommodation
An acute condition in which distance vision is significantly reduced. In this condition, the ciliary muscle is sharply spasmed, the eye acquires a pronounced myopic refraction, but with maximum correction it is not possible to bring the eye to vision 1.0 (100%).
It most often occurs at the age of 12-18 years, appears abruptly, perhaps due to stress, the patient begins to see nearby objects (eyelashes, for example). There may also be pain in the area of the brow ridge.
Causes: stress, poisoning with organophosphorus compounds, use of cholinomimetics (pilocarpine hydrochloride).
In the treatment of accommodation spasm, drugs that relax the ciliary muscle are used. For persistent conditions, drugs are prescribed for a longer period. In some cases, treatment by a psychotherapist is necessary.
Habitually excessive tension of accommodation (PINA)
This is a chronic overstrain of the ciliary muscle, leading to the appearance of myopic refraction (false myopia - pseudomyopia).
The following features are noteworthy:
- school age, adolescence,
- complaints of decreased distance vision,
- develops gradually
- the appearance is associated with an increase / intensification of visual load.
Many clinical and experimental studies have proven the connection between accommodation disorders and childhood myopia, as well as the progression of myopia. PINA is inextricably linked with myopia, so it makes sense to remember what factors influence the appearance and progression of myopia.
The chain is built as follows: heredity, trauma to the cervical spine, unfavorable environmental conditions, excessive visual load -> pseudomyopia, PINA -> true myopia, PINA -> progression of myopia -> complications of myopia.
PINA is most often caused by prolonged, abnormal visual load at the wrong distance.
Myopia appears (but this is false myopia), which completely corrects vision to 1.0 (100%)
The mistake in this case would be to immediately prescribe glasses. After a course of treatment with drugs that relax the ciliary muscle, and a visual load determined by the doctor, glasses may not be needed. There are cases when, after a course of treatment, false myopia turns into farsightedness.
The sooner a child starts using tablet computers and similar electronic devices, the sooner and more likely he will develop PINA, which turns into myopia.
Weakness of accommodation
A condition in which accommodation is difficult (near vision). This is a long-term condition that is often accompanied by PINA. If accommodation is weak, the ciliary muscle cannot remain in a tense state for a long time; it weakens.
Patients complain of fatigue and fatigue when reading and writing. The closest point of clear vision approaches the eye. In this case, the ciliary muscle must be stimulated. The drug of choice is Irifrin 2.5%. Weakness of accommodation can also lead to the appearance or intensification of existing myopia.
Treatment
Special exercises and physical therapy
Gymnastics for the eyes is carried out in combination with exercises and massage for other parts of the back, as well as the head and temples. It allows you to restore the muscle frame.
Gymnastics for the eyes strengthens the ciliary muscle, allowing the eye to adapt faster. Special exercises help adjust the level of curvature of the lens.
Physiotherapy is carried out after relief of the signs and causes of the disease. It allows drugs to better penetrate tissues.
Eye drops
Medicines relieve spasms. Prescribed:
- Cyclomed;
- Atropine.
Medicines dilate the pupil. Sometimes Irifrin is used, which relaxes the ciliary muscle as much as possible.
The course of treatment and dosage is determined by an ophthalmologist after a comprehensive examination of the patient’s eyes and determining the cause. Sometimes it is enough for a patient to use eye drops for 1 week to obtain a positive effect.
Treatment is carried out in combination with exercises and physiotherapy, since eye drops provide short-term results.
Surgical intervention
The operation is performed if the disease has led to myopia, which is difficult to correct with glasses or lenses and the patient constantly has to use vision correction devices.
Paralysis and paresis of accommodation
This is an acute or subacute condition in which the eye loses the ability to see an object located at close range.
There are disorders of the central
or
peripheral
origin.
Peripheral genesis is a consequence of the use of m-anticholinergics (Atropine).
Central - may be a consequence of an acute illness: intoxication, influenza, scarlet fever, diphtheria, poisoning with carbon disulfide, lead, injury or tumor of the central nervous system, severe stress. Well corrected with plus glasses.
In this case, it is possible to assign:
- temporary plus points,
- the drug pilocarpine,
- acupuncture, laser stimulation of the ciliary muscle.
Prognosis and prevention
Spasm of accommodation is a reversible functional disorder that responds well to treatment. Drug therapy quickly relieves spasm of the ciliary muscle through forced relaxation. But in order to achieve a good result, it is necessary to carry out a full program of therapeutic measures, eliminating the causes that led to the occurrence of the disease. Its early detection and treatment can prevent the development of myopia.
Prevention of accommodation spasm usually includes measures for the general health of the body, frequent walks, proper nutrition, a good night's rest, sports or physical exercise. An important point in this complex is compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards for visual work: proper illumination of the workplace, control of sitting and posture, maintaining the required distance when working with a monitor or printed text, taking mandatory breaks during work, etc. For farsightedness and astigmatism, you need selection of optical correction and regular completion of functional rehabilitation courses.
Accommodative asthenopia
This is a symptom complex that includes discomfort, fatigue during prolonged work, and decreased vision at distance and near. Patients report pain.
During the examination, there may be slight refractive errors (myopia, hypermetropia), which are either not corrected at all or incorrectly corrected.
It is necessary to use adequate optical correction, stimulate the ciliary muscle, and use adrenergic agonists.
If you feel that your vision has deteriorated - this is interfering with work, reading, etc., you should consult an ophthalmologist to determine the cause. The doctor can make the right decision based on the examination and examination: what measures to take, whether to prescribe treatment or choose glasses for temporary or permanent wear.