Anxiety disorders are a common mental illness. Pathologies of this type do not belong to the group of severe ones. They are not accompanied by psychotic manifestations and behavioral disorders, but when they reach serious proportions, fears not only worsen the quality of life, but can pose serious problems for a person.
What is an anxiety disorder
Anxiety is a person’s tendency to worry. Many people experience anxiety before any important events or activities, and such worries are quite natural. Medical attention is required in cases where anxiety and fear occur for no apparent reason. A human condition accompanied by uncontrollable fear and a persistent feeling of anxiety is called an anxiety disorder (AD). Under the influence of anxiety, a deterioration in concentration is often observed, and a person often falls into depression. In most cases, the disease is completely curable. If you do not seek help from a doctor, the risks of complications and the occurrence of depressive disorders and pathological addiction increase.
Clinical manifestations of anxiety neurosis
The disorder is manifested mainly by general anxiety. Patients are also diagnosed with various physiological manifestations caused by disturbances in the functional activity of the autonomic nervous system.
Mental symptoms:
- feeling of anxiety (often unmotivated);
- excited state, excitement (agitation);
- phobias (fears);
- general depression;
- sleep disorders (insomnia);
- hypochondria;
- obsessive thoughts.
Important: With this pathology, derealization is often observed, i.e., a violation of the perception of surrounding reality. It is also possible that there is a disorder of self-perception, i.e. depersonalization, which in severe cases causes thoughts of suicide.
Autonomic and somatic symptoms:
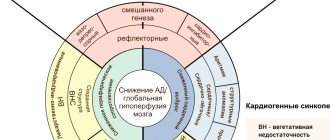
- recurrent headaches;
- dizziness;
- arterial hypertension;
- cardiopalmus;
- peripheral circulatory disorders;
- breathing disorders (psychogenic shortness of breath);
- nausea;
- bowel dysfunction (constipation or diarrhea).
With chronic anxiety neurosis, during the period of exacerbation, patients become whiny and irritable. A characteristic manifestation is also the so-called. panic attacks. Making a diagnosis is the task of a qualified psychiatrist. Symptoms characteristic of anxiety neurosis appear in a number of other mental disorders.
Causes of anxiety
Why does anxiety occur and where does it come from? The amygdala, an area of the brain, is responsible for human emotions. As a natural adaptive reaction, every person has anxiety, but not everyone has anxiety disorders. According to numerous studies, experts identify several main factors that provoke the development of an anxiety disorder:
- hereditary predisposition;
- characteristics of upbringing and the prevailing atmosphere in the family;
- frequent traumatic situations;
- somatic diseases;
- inability to overcome crisis situations;
- self-dissatisfaction, low self-esteem and other internal conflicts;
- disruption of thinking processes.
Excessive consumption of alcohol, strong coffee, lack of sleep, and frequent stress make the human autonomic system more sensitive and increase the risk of developing anxiety disorders.
Causes of fear neurosis
A serious life shock or a very responsible situation can lead to the appearance of an illness. However, this is not an exhaustive list of reasons, since they are divided into two types:
Mental:
- psychological trauma;
- dramatic life changes;
- constantly being surrounded by anxious people.
Physiological:
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- hormonal disbalance;
- hereditary predisposition.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
Depending on the symptoms caused by anxiety and fear and the level of severity of the pathology, experts distinguish several types of anxiety disorders.
Panic disorder
People suffering from this type of illness experience a sudden and repeated feeling of horror. They occur even in the absence of specific events or emotional upheavals. Intense sweating, increased heart rate, dry mouth, feeling of suffocation, dizziness and lack of understanding of current realities are the dominant signs of panic disorders.
Social disorder
This type of pathology is also called social phobia. The disease manifests itself through the fear of getting into an awkward situation, the fear of becoming humiliated or the object of criticism. Often such anxiety is caused by low self-esteem. Sudden attacks can occur almost any time and anywhere - during group activities, while in a shopping center, cinema and other public places, when talking with a well-known person in the presence of strangers and other situations. When an anxiety attack occurs, facial flushing, nausea, hand trembling, and uncontrollable urges to urinate occur. The patient himself understands that his reaction is causeless and excessive, but he cannot control himself.
Adaptive phobias
These are anxiety and fears that arise in a specific specific environment. An attack can occur when a person is near animals of a particular species (for example, snakes), while in a confined space, at a height, or in the dark. Fear of air travel and medical procedures also belong to the group of specific phobias. When a person encounters a frightening stimulus, he immediately triggers anxiety, which manifests itself with corresponding signs. If the disease is not cured in a timely manner, then soon the person will simply limit himself to a full life.
Generalized disorder
It is expressed by sudden anxiety about any event, the likelihood of which is not justified and may not occur at all. With this type of illness, anxiety is not limited to any specific circumstances, so it is difficult for a person to determine the most dangerous situations for him. People suffering from generalized TR experience tachycardia, muscle tension, trembling, sweating, and dizziness. To make a diagnosis, such symptoms must continue for at least six months.
Agoraphobia
This is a group of TP, which simultaneously includes several phobias that combine the fear of crowded public places, as well as open spaces. For example, when visiting a store, being in a large crowd or in other crowded places, a person experiences anxiety. It manifests itself as palpitations, difficulty breathing, profuse sweating, and dizziness. Some people even have a panic attack.
Post-traumatic stress disorder
Occurs as a consequence after an extreme situation, for example, after rape, a natural disaster, an accident, abuse or bullying and other shocks. It manifests itself as sleep disturbance, increased heart rate, sweating, and suffocation.
Emotional disorders
This type of TR is typical in childhood. Panic may arise as a result of prolonged separation from parents, after severe emotional shock, or as a result of parental abuse of the child. It often happens that, not knowing how to eliminate an anxiety attack, a parent increases their anxiety even more.
Situational anxiety
A sudden change of events causes discomfort in a person. For example, dismissal from work, unplanned forced relocation, divorce and other life events. Everyone may have their own reasons, and one person may experience fear in a situation in which another does not react to it at all.
Progress and consequences of late treatment
The development of neurosis does not have a specific time frame. Progress depends on the root cause, current circumstances and the strength of character of the person himself. Experts distinguish three stages:
- Initial. A person reacts poorly to stressful situations. Feels irritated and angry for no reason. May complain to a specialist about sleep problems.
- Moderate (hypersthenic). Characteristic signs are associated with increased excitability. Overexcitation is observed, hysterics and attacks of anger are possible.
- Hyposthenic. Accompanied by loss of interest in life. The patient gets tired excessively and quickly, falls into apathy.
At the first manifestations of HP, it is urgent to conduct a full examination. Long-term non-intervention leads to difficulties in the family and at work, inadequate assessment of personality, and the development of concomitant chronic diseases (disorders of the heart rhythm and the muscle itself, gastrointestinal pathologies, vascular disorders). If a person does not treat neurosis for more than 6-24 months, he may encounter a neurotic personality change. In this case, the condition will be irreversible. Outbursts of anger will increase, self-control will decrease to a minimum, and obsessive-compulsive syndrome may appear.
Main symptoms of TR
All possible signs of TR are divided into physical and psychological. Physical symptoms include:
- rapid pulse;
- labored breathing;
- dizziness and headaches;
- feeling of tightness in the chest;
- shiver;
- heartache;
- numbness of the limbs;
- increased sweating;
- pain in the stomach, heart;
- nausea;
- hot flashes;
- violation of thermoregulation;
- insomnia;
- general weakness.
Psychological symptoms include a feeling of fear, insensitivity to reality, disorientation, and causeless panic.
How to get rid of neurosis and neurotic state?
Neurosis is characterized by a violation of the psychological state that occurs in a person in the process of prolonged moral pressure, internal contradictions, chronic fatigue, and a general violation of the daily routine, nutrition and sleep.
The treatment of neurosis should be based on an integrated approach. The ideal fight against neurosis would be to combine psychoanalytic therapy with a person’s recognition of his neurotic state, accompanied by a persistent desire to overcome it. At the same time, it is possible to include medications in the treatment of neuroses that are prescribed exclusively by a doctor.
Pharmacotherapy gives excellent results, but only with a short-term effect. As soon as the effect of the drug ends, the neurosis and neurotic state returns with the original pronounced effect.
Here is a list of medications that doctors usually prescribe for drug therapy for neurosis:
Antidepressants
An antidepressant is a drug that blocks an enzyme that destroys dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine, as a result of which the concentration of such hormones increases. The mood of the person suffering from neurosis improves accordingly. There is no habituation from the use of these drugs, the speed of reactions does not decrease, and there is no need to fear any side effects. However, the disadvantage of treatment with antidepressants is that this drug accumulates in the blood only over time and the corresponding reactions appear only after about a couple of weeks. The treatment course is usually two to three months.
Tranquilizers
Tranquilizers reduce reactions to various stimuli, inhibit the nervous system and have an anti-anxiety effect. The main danger of these drugs is getting used to them and losing concentration. After taking tranquilizers, you should not drive vehicles or do work that requires precise coordination of movements.
Sedatives
These medications help treat mild types of neurotic disorders. Their action is approximately similar to that of tranquilizers, but their effectiveness is not as high. There is no addiction to sedatives, and there are generally no side effects. When treating neuroses, they often resort to harmless herbal sedatives, such as valerian tincture, hawthorn decoction, and so on. Although there are also medications, by the way, made on a plant basis, such as Fitorelax, Novo-Passit and others.
Let me remind you that neurosis responds well to pharmacological therapy, which gives only a short-term effect! The disease returns and intensifies with each new round, therefore, when the first signs of a neurotic state occur, psychoanalytic therapy is strongly recommended.
Psychoanalytic therapy, which in turn is included in the health insurance system in a number of European countries, can greatly help stabilize the psycho-emotional state, get to the bottom of internal conflict and phobias, and explore the nature of the emergence of a neurotic state and panic attacks.
TR treatment methods
A psychotherapist treats anxiety disorders in patients. Treatment options include medications, therapeutic modalities, and changes in the person's lifestyle.
Therapeutic treatment
TR treatment begins with a conversation between the doctor and the patient. During the conversation, the nature of anxiety is assessed, and factors that alleviate and aggravate the pathology are determined. For anxiety disorders, cognitive behavioral and psychotherapy provide good results. When conducting sessions, special psychological techniques are used to help the patient make changes in his behavior, thoughts and feelings that help get rid of fear and anxiety and aimed at recovery. It should be understood that the main cause of anxiety is often a psychological problem, therefore, without an individual course of psychotherapy, it is difficult to achieve recovery and the disease will return again and again. The psychotherapist will teach the patient to change negative emotions and thoughts to positive ones, to get rid of feelings that provoke anxiety attacks.
Drug treatment
Taking medications usually begins simultaneously with psychotherapeutic treatment. Pharmacological therapy includes:
- antidepressants. They normalize mood, relieve emotional stress, irritability, anxiety, apathy;
- anti-anxiety or anxiolytics. Suspends and prevents acute attacks of fear and panic;
- sedatives. They have a calming, relaxing effect and normalize sleep.
In each case, drugs are prescribed based on the patient’s personal characteristics (gender, age, concomitant diseases) and clinical picture.
Lifestyle change
If a person wants to get rid of anxiety disorders forever, then along with therapy and drug treatment, he needs to exercise daily, monitor the normalization of sleep, eat right, reduce caffeine consumption, and give up bad habits. A big plus for achieving a positive result will be quitting smoking.
Who is most susceptible to developing phobic neurosis and for what reasons?
This ailment can develop both as an independent disease against the background of existing specific character traits and temperamental characteristics, and as a complication of existing diseases - psychopathy, psychasthenia, alcoholism, drug addiction. Neurosis with fears can aggravate the course of diseases of internal organs (myocardial infarctions, strokes), oncological processes, endocrine pathologies. Both men and women are susceptible to phobic neurosis. The primary development of symptoms of the disease is characteristic of adolescence, as well as the transitional stage from maturity to old age. You can often observe phobias in women during menopause.
People's fears develop against the background of:
- chronic psychophysical fatigue and overstrain;
- received mental trauma;
- any long-term, debilitating disease;
- regular lack of sleep and poor nutrition;
Treatment of anxiety disorders in
Psychotherapists strongly recommend that everyone pay attention to their psychological state and, if even minor deviations from the norm are detected, seek professional help. Any increased anxiety that lasts for several hours or even several days is already a reason to consult a doctor. The psychotherapeutic center employs experienced psychotherapists who can help anyone in the treatment of anxiety disorders. When working with a patient, doctors use an integrated approach, combining pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy. This allows you to achieve positive results in the most difficult situations. Benefits of treatment in:
- accurate diagnosis in accordance with international standards;
- 100% effectiveness and safety of treatment;
- complete confidentiality;
- affordable price.
Doctors help patients get rid of anxiety disorders forever, even in the most hopeless situations. The prices for treatment are reasonable and justified by the quality of the services provided.
First aid for a panic attack
First of all you need to:
- “remove” the object of fear (take the person out of a crowded place or, conversely, out of a cramped room, etc.);
- provide a flow of fresh air;
- remove clothing that is constricting your neck and chest;
- Ask the nearest store or kiosk for a disposable paper bag (these are usually used to package take-out food), open it, have the person press it tightly to their face, cupping their nose, mouth and chin, and take several deep breaths. This way you can quickly cope with hyperventilation - one of the most severe symptoms of a panic attack.
Even a single such episode is an indication for contacting a specialist.
Why suffer from irrational fear, limiting yourself in many ways? We will help you get rid of anxiety and worry! You can find out more about the treatment of phobic neurosis from our operators by calling 8(969)060-93-93 .