Even a minor blow to the head area can lead to a concussion, but for a person it may go unnoticed. The fact is that the symptoms of a concussion can be “fuzzy”, appearing a few days after the incident, or even be asymptomatic, but at the same time have serious consequences several years later. This is the danger of this injury: undiagnosed symptoms of a concussion lead to such serious consequences as encephalopathy, migraines, constant headaches, vegetative-vascular dystonia and even tumors.
Possible symptoms of a concussion
- Brief confusion or loss of consciousness. With a strong blow, the moment of injury disappears from memory.
- Dizziness even at rest, and when turning, bending or other changes in body position, the symptom intensifies.
- Severe headache, nausea and vomiting.
- Double vision, inability to concentrate on one point.
- Increased sensitivity to light and sounds.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Reaction inhibition - the victim gives an answer to the question after some time.
- Pale skin, weakness, sweating.
Important! A concussion is not always accompanied by visible head injuries, so the absence of wounds does not exclude brain injury.
Manifestations of concussions
The main symptom of a concussion is loss of consciousness at the time of injury. The only exceptions may be children and the elderly. Immediately after a concussion, you may also experience:
- one-time vomiting;
- increased breathing rate;
- increased or slow heart rate;
- impaired memory for current or previous events.
These deviations bother you for a short time, the condition soon returns to normal. Blood pressure quickly returns to normal limits, but in some cases it can persistently increase - this is due not only to the injury itself, but also to the stress factors accompanying it. Body temperature during a concussion remains normal.
Upon restoration of consciousness, typical complaints are
- headache;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- noise in ears;
- flushes of blood to the face;
- sweating;
- sleep disturbance.
According to a study conducted in 2021 on the basis of the Research Center for Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Traumatology of the Moscow Department of Health, in adolescents in the acute period of a mild concussion, indicators for such parameters as
- performance
- fatigue
- restoration of performance
- pace of activity
- concentration of attention
There were also difficulties in solving intellectual problems in the form of difficulties in generalizing and diversity of judgments; a significant number of impulsive errors were noted when completing tasks.
With a concussion, the general condition of the victims usually improves quickly during the first, and less often, the second week. However, it should be taken into account that headaches and other subjective symptoms can last much longer for various reasons.
Summary table of common concussion symptoms
| Early symptoms (should go away within a few hours at most) | Late symptoms (last from several days to several weeks) |
|
|
Features of manifestations in children and the elderly
The pattern of concussion is largely determined by age factors.
In infants and young children, concussion often occurs without impairment of consciousness. At the time of injury - sharp pallor of the skin (primarily the face), rapid heartbeat, then lethargy, drowsiness. Regurgitation occurs during feeding, vomiting, anxiety, and sleep disorders are noted. All manifestations disappear within 2-3 days.
In children of younger (preschool) age, concussion can also occur without loss of consciousness. The general condition improves within 2-3 days.
In older people, primary loss of consciousness due to a concussion is observed much less frequently than in young and middle age. At the same time, pronounced disorientation in place and time often manifests itself. Headaches are often pulsating in nature, localized in the occipital region; they last from 3 to 7 days, differing in significant intensity in people suffering from hypertension. Attacks of dizziness are common.
First aid for concussion
- If one or more symptoms are present, immediately call an ambulance or take the victim to a doctor.
- Treat a wound on the head if it appears as a result of an impact.
- For an hour or until the doctor arrives, it is important not to fall asleep, but to remain at rest.
- If you lose consciousness, lay the person on his side, bend his knees, and put his hands under his head.
- If symptoms of a concussion do not immediately appear, it is recommended to rest and not begin vigorous activity.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing a concussion, it is especially important to take into account the circumstances of the injury and information from witnesses to the incident. Traces of trauma on the head and factors such as alcohol intoxication, the psychological state of the victim, etc. can play a dual role.
A concussion often has no objective diagnostic signs. In the first minutes and hours, the doctor and other witnesses may see a loss of consciousness (for several minutes), twitching of the eyeballs when looking away to the side, disturbances in balance and coordination of movements; victims complain of double vision.
There are no laboratory or instrumental signs for diagnosing a concussion:
- There are no fractures of the skull bones during the concussion.
- Pressure and composition of cerebrospinal fluid without deviations.
- Ultrasound examination (M-echoscopy) does not reveal displacement or expansion of the midline structures of the brain.
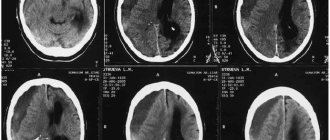
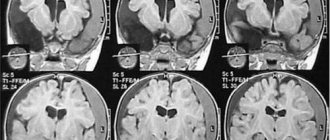
- Computed tomography in patients with concussion does not reveal traumatic abnormalities in the state of the brain substance.
- Magnetic resonance imaging data for concussion also do not reveal any damage.
A concussion often masks more severe traumatic brain injuries, so patients are subject to emergency hospitalization in a neurosurgical hospital (or another profile where neurotraumatological care is provided) mainly for examination and observation.
Thus, a concussion can be identified based on:
- data observed or reported by the patient about loss of consciousness at the time of injury.
- nausea, vomiting, complaints of dizziness and headache.
- absence of signs of more severe injury (loss of consciousness for more than 30 minutes, convulsive seizures, paralysis of limbs).
Recommendations for the treatment of concussions
If hospitalization is not required, with the permission of a doctor, a mild concussion can be treated at home:
- Bed rest and rest are required, no work. Long sleep is very important.
- You cannot read, watch TV, play computer games or use gadgets.
- Under no circumstances should you play sports.
- You are allowed to listen to music, but not through headphones.
- You can use herbal sedative drops or herbal infusions.
- In your diet, you should give preference to dairy and plant products, limit salt intake - to prevent increased pressure, including intracranial pressure.
If the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner and all recommendations are followed, recovery will occur quickly and without complications.
First aid
First steps if you suspect a concussion:
- Call an ambulance or go to the emergency room.
- The patient should be examined by a traumatologist or neurologist, and an X-ray of the skull will be taken; if necessary and if possible, CT or MRI of the brain (carrying out these examinations is a chance to avoid underestimating the severity of the injury, but such equipment is not always available). In the absence of CT or MRI, M-echoscopy is performed.
- When the diagnosis is confirmed, patients are hospitalized in a neurosurgical or trauma department for observation, so as not to miss a more severe injury and to avoid complications.
First aid for concussions
First aid for a victim with a concussion is to give him a comfortable horizontal position with his head slightly elevated.
If the person who has received a concussion continues to be unconscious, the so-called rescue position is preferable -
- on the right side;
- the head is thrown back, the face is turned to the ground;
- the left arm and leg are bent at right angles at the elbow and knee joints (fractures of the limbs and spine must first be excluded).
Photo: universal position of a patient with a concussion, provided there are no fractures
This position, ensuring the free passage of air into the lungs, the unhindered flow of liquid from the mouth to the outside, prevents breathing problems due to the retraction of the tongue, the flow of saliva, blood, and vomit into the respiratory tract. If there are bleeding wounds on the head, apply a bandage.
All victims with a concussion, even if it seems mild from the very beginning, must be transported to an emergency hospital, where the primary diagnosis is clarified. Patients are placed on bed rest for 1-3 days, which is then, taking into account the characteristics of the course of the disease, gradually changed to ward rest. The length of stay in the hospital is from 3 to 7 days, and then, in the absence of complications, discharge from the hospital for outpatient treatment (lasting up to 2 weeks) is possible.
Disability
According to forensic medical criteria, a concussion is considered to be a minor injury to health and the percentage of loss of ability to work is, as a rule, not determined.
A medical labor examination determines temporary incapacity for work from 7 to 14 days. Long-term and permanent disability usually does not occur.
However, in 3% of patients after a concussion, moderate disability may occur due to exacerbation and decompensation of existing chronic diseases, as well as with multiple repeated injuries. Patients who do not comply with the recommended treatment regimen and behavior are particularly at risk.
Sources:
- Gorina I.S. Disturbances of higher mental functions in adolescents after mild traumatic brain injury, - National Journal of Psychology, 2021.
- Keith A. Scoroza, MD. Current Concepts in Concussion: Initial Evaluation and Management, - American Family Physician, 2021.
- Association of Neurosurgeons of Russia. Clinical recommendations. Mild traumatic brain injury, 2021.
Treatment of concussions
In case of a concussion, treatment is prescribed by a neurologist.
Drug treatment for concussion is often not required and is symptomatic (the main treatment is rest and healthy sleep). Pharmacotherapy is mainly aimed at normalizing the functional state of the nervous system, eliminating headaches, dizziness, anxiety, insomnia and other complaints.
Typically, the range of medications prescribed upon admission includes painkillers, sedatives and sleeping pills, mainly in the form of tablets, and, if necessary, injections.
Among the painkillers, the most effective drug for a given patient is selected:
- analgin,
- pentalgin,
- dexalgin,
- sedalgin,
- maxigan, etc.
They do the same for dizziness, choosing one of the available medications:
- belloid,
- cinnarizine,
- platiphylline with papaverine,
- tanakan,
- microzer, etc.
Used as a sedative
- valerian, motherwort, corvalol, valocordin,
- tranquilizers grandaxin, sibazon, phenazepam, nozepam, rudotel, etc.
To eliminate insomnia, it is prescribed at night
- donarmil,
- relaxon.
Conducting a course of vascular and metabolic therapy for concussions contributes to a more rapid and complete recovery of brain dysfunction. A combination of vascular (Cavinton, Stugeron, etc.) and nootropic (Nootropil, Pantogam, Noopept, Mexidol, etc.) drugs is preferable.
Possible combinations could be as follows:
- "Cavinton" 1 tablet (5 mg) and "Nootropil" 2 capsules (0.8 mg) three times a day for 1-2 months
or
- “Stugeron” 1 tablet (25 mg) and “Noopepta” 1 tablet (0.1 mg) three times a day for 1-2 months.
A positive effect is brought by the inclusion in the course of therapy of drugs containing magnesium (Magne-B6, Magnelis, Panangin) and antioxidants Cytoflavin 2 tablets 2 times a day, Mildronate 250 mg 1 tablet 3 times a day.
To overcome frequent asthenic phenomena after a concussion, one of these drugs is prescribed:
- "Phenotropil" 0.1 1 time in the morning,
- "Cogitum" 20 ml once a day,
- “Vazobral” 2 ml 2 times a day,
- multivitamins and polyminerals such as Unicap-T, Vitrum, etc. 1 tab. 1 per day.
Tonic preparations include ginseng root, eleutherococcus extract, lemongrass fruit, Saparal, and Pantocrine.
In elderly and senile people who have suffered a concussion, anti-sclerotic therapy is intensified - statins are prescribed (atorvastatin, rosuvastatin). They also pay attention to the treatment of various concomitant diseases.
After suffering a concussion, the patient is placed under dispensary observation by a neurologist at his place of residence. He visits the doctor several times throughout the year, undergoes an examination, and, if necessary, examinations. If no pathological abnormalities are detected during this time, then the person is removed from the dispensary register.