Our clinic specializes in neurology and we perform electroneuromyography. We have competent specialists and modern equipment : an electroneuromyograph, a transcranial magnetic stimulator, equipment for studying evoked potentials, etc. We usually offer electromyography 7 days a week, including Saturday and Sunday. You will receive the ENMG results and a description of them by your doctor. A formal referral is not required.
Electroneuromyography (ENMG) is a study of indicators of electrical activity of nerves and muscles in response to their electrical or magnetic stimulation.
We carry out almost all the main electroneuromyography techniques (ENMG, needle EMG, TMS), incl. in diagnostically difficult and non-standard cases. We perform a range of electromyography techniques that assess the different functions of different motor and sensory nerves. A group of experienced neurologists is at your service, incl. neurologist-immunologist.
- Electromyography of the upper and lower extremities
- Electromyography of the median, radial and ulnar nerves, brachial plexus. ENMG for carpal (carpal tunnel) Guyon's canal syndrome. ENMG brushes
- Electromyography of the lumbosacral plexus, sciatic nerve, tibial and peroneal nerves. Electromyography of the foot
- Spinal cord studies using electroneuromyography
- Electroneuromyography (ENMG) of the facial and trigeminal nerve. Electromyography of the face, facial muscles and masticatory muscles. Electromyography in dentistry
- Decrement test for myasthenia gravis. EMG for myasthenia gravis. Study of neuromuscular transmission
- Stimulation electromyography. Diagnosis of tunnel syndromes, polyneuropathy, mononeuropathy
- Needle myography / Needle electromyography / Needle EMG / Needle ENMG
- Electromyography with transcranial magnetic stimulation
In fact, electroneuromyography (ENMG), electromyography and myography are synonymous names for the same group of diagnostic studies . These are studies of the electrical potentials of nerves and muscles using various methods of stimulation. We will choose the method of stimulation (weak electrical discharge, electromagnetic field, etc.) depending on what problem needs to be found or excluded. It is very important that we understand the essence of your problem and the purpose of the study, so be sure to take with you the results of all previously performed studies: MRI, CT, ENMG, tests, referrals and conclusions of specialists, etc., if they have been performed.
Just doing ENMG is not enough: the results of myography are calculated, interpreted and described by the doctor immediately after the study. You will receive a detailed study protocol with measurement results and a description from the doctor. All calculations and descriptions are already included in the price of ENMG.
Cost of electromyography. The price of myography depends on the research technique. The volume and, accordingly, the price of ENMG in many cases can be reduced by choosing the most suitable research technique, and we use quite a lot of techniques. Therefore , when going to our clinic for electromyography, please take with you the results of previously performed studies, tomograms, tests, consultations, if any. This will help us choose the electromyographic technique that best suits the diagnostic task, and in many cases reduce the cost of electromyography.
Electromyography of the upper and lower extremities
We offer electromyography of the upper and lower extremities, mainly for polyneuropathy of various origins, damage and compression of nerves. ENMG in these cases helps to determine the cause and location of damage, compression or inflammation of the nerves of the arms and legs. Depending on the task of electroneuromyography, we can offer you myography of only the upper or lower extremities or a joint study of the upper and lower girdles (i.e. myography of the upper and lower extremities in one study); the price for electromyography of each belt in this case will be lower.
Stimulation electromyography of the lower extremities
Why do electromyography of the lower extremities?
Electromyography of the lower extremities is carried out to identify changes, pathological processes, lesions that pose a threat and can even lead to paralysis.
If you make a timely diagnosis and understand the cause of damage to specific nerves, you can prevent dangerous conditions and maintain the functionality of the lower extremities for many years. Electromyography of the lower extremities reveals a wide range of diseases and pathologies. Among them:
- motor neuron disease;
- autoimmune myasthenia gravis;
- Lambert-Eaton syndrome;
- radiculopathy;
- tarsal tunnel syndrome;
- plexopathy, etc.
The study identifies nerve lesions (one or more), and also determines the stage, extent of this lesion, prevalence, mechanism of development, nature and level (systemic or local).
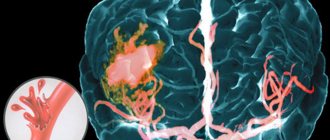
Spinal cord studies using electroneuromyography (ENMG, EMG)
The purpose of electromyography in diseases of the spinal cord is to clarify the diagnosis and cause of the disease, to distinguish diseases of the spinal cord from diseases of the peripheral nerves and muscles with similar symptoms (treatment varies). What other methods are often used when examining the spinal cord?
Our many years of experience suggest that electroneuromyography is one of the most accurate methods in diagnosing diseases such as:
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Various myelopathies, i.e. spinal cord entrapment, spinal circulatory disorders
- Herniated discs with entrapment of the spinal cord or its root
- Paralysis and paresis of unknown origin
- Unexplained walking and sensory disturbances
- Spinocerebellar degenerations are a group of hereditary diseases of the spinal cord and the entire central nervous system
- Neuroinfections with damage to the spinal cord (myelitis, spinal arachnoiditis, encephalomyelitis, radiculitis, neuroradiculopathy) and their consequences
Needle myography in the study of the spinal cord. Needle EMG is perhaps the most informative electromyography technique for studying the spinal cord. Needle myography allows you to evaluate the work of spinal cord motor neurons (motoneurons are the cells that control muscles), the condition of the muscles themselves (differential diagnosis of spinal cord diseases with muscle diseases), peripheral nerves, and even evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. After performing a needle EMT, in many cases it is possible to accurately say about the condition of the pathways passing through the spinal cord to the muscles, whether the patient has amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, whether there is a prospect of restoring walking, how the peripheral nerves of the arms and legs feel. Read more about needle myography.
Diagnosis of the spinal cord using electroneuromyography (ENMG) using surface electrodes. The simplest method of ENMG - diagnosing diseases of the spinal cord - is the study of electrical potentials of muscles using the application of surface electrodes. Disturbance in the conduction of signals along the spinal cord is immediately reflected in the electrical activity of the muscles and can be recorded using electromyography. We rarely use superficial myography in the study of the spinal cord due to its poor information content. Needle myography and ENMG with transcranial magnetic stimulation help to create a more accurate picture of the condition of the spinal cord.
Electromyography of the spinal cord with transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) provides information about the spinal cord's ability to carry stimulation from the brain to the periphery, to the arms and legs. With TMS, the brain is stimulated by a short magnetic pulse, then transforms the magnetic pulse into an electrical pulse, and the electrical pulse, in turn, is recorded and measured by a diagnostic device and analyzed. Basically, the study of the spinal cord with TMS is used in the diagnosis of paralysis, paresis and walking disorders in doubtful and unclear cases. Read more about electromyography with TMS.
Diagnostics of the ascending tracts of the spinal cord (conductors of sensitivity). Somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs) are a study of the ascending nerve pathways that transmit signals from sensory receptors in the body through the spinal cord. Learn more about somatosensory evoked potential testing.
Stimulation electromyography during examination of the spinal cord. Stimulation electromyography is a method of examining peripheral nerves that allows one to examine the conductive function of nerves and determine the location of damage or destruction of nerve fibers. This method is excellent for identifying diseases of the peripheral nerves, which must be differentiated from damage to the spinal cord (symptoms may be similar, but treatment may be different). With stimulation ENMG, some parameters of spinal cord function are also indirectly assessed. Learn more about stimulation electromyography.
Diagnostic technique
There are needle and stimulation ENMG techniques.
Stimulation ENMG
Examines the conduction of an electrical impulse along a nerve, through the junction of muscle and nerve - the neuromuscular synapse.
To test the motor function of a nerve, disposable electrodes are glued to the skin in the projection of the muscles that are innervated by the nerve selected for study. The doctor records resting electrical potentials, then after stimulation with magnetic wave pulses. When the muscle gives the maximum response, stimulation is stopped. Bioelectric signals received from the patient’s muscle and nervous tissue are captured by receiving electrodes, amplified by an analog-to-digital converter, and calculated by a computer program.
Sensitivity testing is carried out according to the same scheme. The neuromyogram graph allows the doctor to understand which part of the nerve is involved in the pathological process, whether the axon or myelin is affected.
Needle ENMG
Records muscle changes. In case of nerve injury, it determines the prospects for restoring muscle function and the possibility of conducting a nerve impulse through damaged structures.
Very thin needles are used as electrodes, which are inserted directly into the muscle. The electrode reads information about the work of the muscle, the speed of the impulse, and evaluates the affected area. This is the most informative method for studying the neuromuscular system.
There should be no pain during the procedure. Patients with a low pain threshold may experience discomfort when inserting a needle electrode and a tingling sensation during stimulation.
Decrement test for myasthenia gravis. EMG for myasthenia gravis. Study of neuromuscular transmission
"Decrement test". The main problem with myasthenia gravis is the inhibition of the transmission of excitation from nerves to muscles. Hence the reversible myasthenic weakness of muscles of various groups. Accordingly, EMG - the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis is based on the study of the transmission of excitation from nerves to muscles. The decrement test is a convenient and fairly reliable option for studying neuromuscular transmission in cases of suspected myasthenia gravis. When conducting the decrement test, we are guided by generally accepted international standards, i.e. We usually study 5 muscles. Each muscle under study is subjected to rhythmic stimulation (i.e., it makes artificially induced contractions), and we record the electrical characteristics of the muscle’s responses to stimuli. Decrement is a gradual decrease in the intensity of muscle responses characteristic of myasthenia gravis in response to its rhythmic stimulation. The presence of a clinically significant decrement usually indicates a disorder of neuromuscular transmission: myasthenia gravis or myasthenic syndrome.
Proserine test or proserine test. Prozerin is a drug, one of the effects of which is a reversible improvement in neuromuscular transmission. In doubtful cases of diagnosing myasthenia gravis, we use prozerin to perform the test. The proserine test (proserine test) is as follows:
- First, we conduct an EMG - a standard Decrement test. Detection of neuromuscular transmission disorders during the decrement test may be an indication for conducting a proserine test.
- We introduce proserin. Prozerin is administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously using a syringe, then absorbed and improves neuromuscular transmission.
- We repeat the decrement test against the background of the action of proserin. If prozerin significantly improves the performance of the decrement test, then a violation of neuromuscular transmission is considered proven.
Symptoms of myasthenia gravis
Most often, myasthenia gravis begins with weakness of the eye muscles: drooping eyelids and/or double vision of objects occurs when trying to focus on them. Later, weakness in the limbs occurs, problems with performing everyday activities due to the inability to raise and hold arms in a certain position, climb stairs or lift objects. In severe cases, there is a worsening of the existing symptoms of myasthenia gravis, which are accompanied by problems with swallowing, pronouncing certain sounds, and the throwing of food into the nose during swallowing.
We recommend that you be examined for myasthenia gravis if such symptoms occur in order to prevent further development of the disease.
Differential diagnosis between myasthenia gravis, paraneoplastic myasthenic syndrome, myopathy, polyneuropathy
Myasthenia gravis is just one possible cause of muscle weakness. The task of establishing the true cause of muscle weakness arises quite often. The usual differential diagnostic series in such cases is:
- Myasthenia gravis, congenital myasthenia;
- Myasthenic syndromes associated with cancer (paraneoplastic myasthenic syndromes), for example, Lambert-Eaton syndrome;
- Myopathy and amyotrophy, i.e. hereditary or acquired (metabolic disorders, the effect of certain medications, etc.) muscle disease with gradual destruction and muscle weakness;
- Polyneuropathy, i.e. of various natures, a decrease in the conduction of excitation along the peripheral nerves themselves;
- Myelopathy, i.e. diseases of the spinal cord of various nature.
In this case, we conduct a series of electromyographic studies using various techniques. We select EMG methods based on the clinical picture of the disease: to identify polyneuropathy, myasthenia gravis, myopathy or myelopathy, respectively. In these cases, we also recommend that you consult a neurologist (neurologist-immunologist) in our clinic and conduct some laboratory tests. Data from tests, examination by a neurologist and EMG results complement and specify each other, helping to accurately determine the cause of muscle weakness and find the correct treatment path.
What laboratory tests can we perform for muscle weakness:
- Antibodies to the acetylcholine receptor (diagnosis of myasthenia gravis);
- Antibodies to skeletal muscles (diagnosis of polymyositis and polymyalgia, autoimmune myopathy);
- Myositis-specific antibodies (diagnosis of polymyositis and polymyalgia);
- Antineuronal antibodies (diagnosis of paraneoplastic neurological diseases);
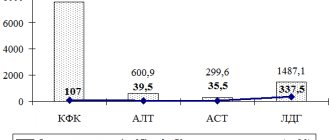
- Creatine kinase (CK) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) are muscle enzymes (markers of muscle tissue destruction in myopathy, polymyositis and other muscle diseases);
- Studies of immune status, autoimmunity, diagnosis of concomitant infections.
Stimulation electromyography. Diagnosis of tunnel syndromes, polyneuropathy, mononeuropathy
Using stimulation electromyography, we can reliably diagnose disturbances in the conduction of impulses along nerves in various diseases, when planning surgical operations on the nerves of the arms and legs.
Stimulation electromyography is a method for studying the peripheral nerves of the arms, legs or face. Stimulation ENMG examines the response of muscles to electrical stimulation of a nerve at different levels, starting from its exit from the spine and further along its course in the arm, leg or facial nerve system.
| Stimulation electromyography of the upper limbs, electroneuromyography (ENMG) of the upper limbs / EMG of the hands |
Thus, we can accurately diagnose damage and disease of nerve fibers and their condition after injury or unsuccessful surgery, when the nerve can become scarred or cut. This study is informative for carpal tunnel syndrome, in which we recommend additionally performing needle electromyography to see if there is a tendency for the nerve to recover, which is important when deciding whether to perform surgery. Thanks to the study, we will be able to see an increase in resistance to the passage of nerve impulses, which can develop as a result of neuroinfections, metabolic disorders due to diabetes mellitus or poisoning with toxic substances, including alcohol.
Do ENMG: How is ELECTRONEUROMYOGRAPHY performed?
Electroneuromyography (ENMG) - registration of the degree of conductivity of nerve fibers and the nature of muscle contractions using a special device - a myograph. The specific method of conducting an ENMG examination depends on its type.
Special sensors applied to certain areas of the body evaluate neuromuscular transmission: the condition of the sensory and motor nerves of the arms, legs and face, spinal root nerves and even the gray matter of the spinal cord.
There are three main types of electroneuromyographic examination:
Superficial ENMG is a study of the efficiency of the passage of nerve impulses along peripheral nerve fibers, this examination uses surface electrodes that are applied to certain areas of the skin to record muscle activity during voluntary contraction; Needle ENMG is a study of the functional activity of muscles, carried out using special needle electrodes inserted into the muscles; Stimulation ENMG is similar to superficial ENMG with simultaneous stimulation of nerve fibers away from the recording electrodes. The use of all three methods allows you to reliably assess the state of the neuromuscular system, as well as diagnose the level, degree, stage of the pathological process and reliably make a diagnosis.
Needle myography / Needle electromyography / Needle EMG / Needle ENMG
Needle electromyography (EMG) is one of the best methods for studying nerves and muscles today. Needle EMG is used to diagnose the condition of the muscles themselves, and those nerves that conduct signals from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles. To conduct the study, the doctor inserts a thin sterile needle into the muscle being examined - an electrode (we use disposable needles), with which the electrical muscle potential is measured. Muscle electrical potential deviates from the norm in diseases of the central nervous system and nerves of the upper and lower extremities.
By the bioelectrical activity of the muscle, we can diagnose the presence of muscle diseases (myopathies of various natures), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, polymyositis and other rheumatic muscle lesions, look at the tendency to restore damaged nerves, determine where the problem is located - at the level of the peripheral nerve or nerve cells of the spinal cord, assess its nature and even determine the presence/absence of an inflammatory process. Needle electromyography plays a very important role in deciding whether it is advisable to perform surgery to restore a peripheral nerve, because With the help of this study, we will understand whether there is reinnervation (restoration of nerve conduction) or whether this nerve is completely lost.
How is electromyography of the lower extremities performed?
Electromyography of the lower extremities is carried out using a special device - an electromyograph. It consists of the device itself and electrodes separated from it by wires. With needle electromyography, electrodes are inserted with a thin needle under the skin; with superficial electromyography, they are applied on top of the skin. After installing the electrodes, the device transmits impulses and records the response of the muscles and nerves. The activity and capabilities of muscles in a state of both rest and excitement are studied. The built-in program records and analyzes the received data, after which the doctor can draw up a conclusion.
Electromyography of the lower extremities lasts about 1 hour. It is well tolerated by patients and does not cause significant discomfort. The group’s doctors make sure that the time spent in the clinic is filled with pleasant emotions and make every effort to relieve possible emotional stress in the patient before diagnosis.
Electromyography with transcranial magnetic stimulation
Transcranial magnetic brain stimulation is a method of measuring the conductivity of the descending nerve pathways that carry impulses from the brain to the arms and legs.
How is electromyography with TMS performed? Using a special magnetic coil, the doctor delivers an impulse to the cerebral cortex (the coil is simply applied to the head). In the brain, the magnetic impulse is converted into an electrical one, which, in turn, travels from the cerebral cortex to the peripheral nerves in the limbs, where it is recorded by the device. Based on the speed of conduction of this impulse and various additional parameters, it is possible to accurately determine whether there is a conduction block at the level of the spinal cord or brain.
Main indications for ENMG with transcranial magnetic stimulation. TMS is mainly used to diagnose disorders of the upper and lower extremities, such as walking. Here it is very important to distinguish muscle paralysis (damage to the nerve innervating the muscle) from muscle disease (damage to the muscle cells themselves from toxic effects, trauma, etc.). We also recommend this research method to determine the cause of bladder dysfunction (urinary retention, loss of urge to urinate), since with the help of transcranial magnetic stimulation it is possible to understand whether the cause of bladder dysfunction is a disturbance in the conduction of impulses along the spinal cord or there is another reason.
Advantages of performing electromyography of the lower extremities at the Mother and Child clinic
The group is the undisputed authority and leader in the provision of medical services. We have created comfortable diagnostic conditions in which your health is given special attention.
Our advantages:
- electromyography of the lower extremities is carried out using modern electromyographs;
- the ability to choose a clinic and doctor;
- electromyography is carried out by specialists with extensive experience who understand the specifics of the study;
- reasonable cost of electromyography of the lower extremities;
- make an appointment at a time convenient for you;
- the opportunity to undergo a consultation immediately after electromyography.
It is very important to get diagnosed on time! Contact the group if you need a high-tech examination of the lower extremities!