What is the essence of the EEG procedure?
An electroencephalogram records electrical signals from brain cells and allows us to identify epilepsy, trauma, neoplasms, inflammatory processes, and changes in blood vessels. Pathology is indicated by disturbances in the electrical activity of neurons, which are recorded using special sensors placed on the patient’s head.
Using an electroencephalogram, the doctor can:
- analyze the performance of the brain;
- identify foci of pathologies;
- assess the nature and extent of damage;
- confirm or clarify the diagnosis;
- monitor the effectiveness of the treatment.
What does a brain MRI show?
Having received 3D images of the brain in different projections, the doctor has the opportunity to examine each area in detail. This allows us to draw conclusions about:
- processes occurring in brain tissue;
- condition of blood vessels;
- the presence, location, shape and size of neoplasms, hematomas or blood clots;
- the presence, stage and localization of other brain pathologies.
Thanks to MRI, it is possible to visualize the brain in different projections, which significantly increases the information content of the examination
If the results are not accurate enough or additional visualization of a specific area is required, an MRI of the brain with contrast may be ordered. The introduction of a contrast agent makes it possible to obtain a more accurate idea of the structure of brain tissue or pathological formation and to clarify its boundaries.
In what cases is EEG prescribed?
After a conversation with the patient and studying the medical history, the specialist decides to prescribe encephalography. Typically, indications for an EEG are frequent headaches, sleep problems, fainting, fatigue and chronic fatigue.
Deterioration in well-being may be a sign of disorders in the functioning of the brain. The above ailments often arise due to:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- pathologies of blood vessels of the neck and head;
- inflammatory processes in meningitis and encephalitis;
- endocrine disorders;
- malignant or benign neoplasms.
For patients suffering from epilepsy who have undergone neurosurgical interventions and head injuries, EEG monitoring is mandatory.
Types of brain diseases
Any disease that affects the walls of blood vessels in the brain leads to disruption of the functioning of not only other organs, but also the entire body. Most men who have reached the age of forty experience so-called cluster pain. They manifest themselves in the form of attacks of very sharp pain, developing into a chronic disease. The causes of this problem may be hormonal imbalance, vascular aneurysm, or the presence of a pituitary tumor. If you have such pain, you should see a doctor in a timely manner for a thorough examination. Let's look at the most common diseases:
1. Alzheimer's disease
Atrophy of nerve cells occurs due to the production of pathological and harmful protein to the body. The initial stage of the disease has virtually no symptoms, but the Alzheimer's patient becomes more inattentive and distracted.
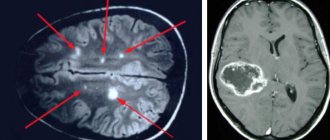
2. Malignant and benign brain tumors
The formation of proliferating cells, the nature of which is not characteristic of the human brain. New growths increase in size, and thereby the pressure inside the skull increases. The main symptom characterizing the presence of a tumor is a headache that occurs in the morning and is accompanied by vomiting. Over time, there is a noticeable deterioration in memory and thought process, and serious mental disorders occur.
3. Epileptic seizures
Disorder of brain functions of a recurrent nature. During the onset of epilepsy, the patient may lose consciousness and experience limb spasms. In a generalized seizure, both hemispheres are affected; in a local seizure, one of the two is affected.
4. Benign headaches
They are not related to serious damage to areas of the brain. Usually caused by weather conditions and uncomfortable hats. However, if you experience frequent and systematic pain, you should consult a doctor to schedule an examination to rule out the presence of serious pathological changes in the body, tissues and blood vessels of the brain.
5. Vegetative-vascular dystonia
A disease most common among young people. It is characterized by a disorder of the nervous system and is accompanied by severe headaches, attacks of irritability and psychosis, and decreased ability to work. Sometimes a headache is accompanied by vomiting, severe heart pain, and high blood pressure.
6. Vascular diseases
One of the most dangerous groups of brain diseases that cause serious harm to the human body, in most cases causing severe consequences and dangerous damage to tissues and organs. A vascular disease never goes away without leaving a trace, so the patient can suffer severe complications in the form of partial or complete paralysis, as well as remain disabled for life.
Let's take a closer look at the main causes of vascular diseases:
How to prepare for an electroencephalograph examination?
Monitoring the electrical activity of the brain does not require complex training. During the examination, it is important to simply follow the doctor's instructions and remain calm. Flashes of light and noise are part of the procedure.
Three days before the examination, it is recommended to stop taking tranquilizers, anticonvulsants and sedatives. 24 hours before the examination, do not drink tea, coffee, energy drinks, or eat chocolate. The day before monitoring, wash your hair. Have a snack an hour before the examination. Before starting, loosen your hair and remove metal jewelry.
How to do an MRI of the brain
Only the patient’s head enters the tomograph chamber, so the feeling of enclosed space is minimized
There is no need to prepare specially for the study. The only requirement is not to wear metal or jewelry, hairpins, or watches when going for an examination (or be prepared to remove them or take them out of your pockets before placing them in the tomograph). Also, during the procedure you cannot have magnetic media (flash drives, bank cards, etc.) with you, since the information stored on them will be destroyed.
The diagnosis will take 30–40 minutes. You cannot move your head during the process, but this restriction does not apply to the facial muscles. You can even talk to your doctor while he takes sequential pictures. From time to time, the doctor himself will contact the patient to inquire about his well-being.
If you suffer from claustrophobia, but an MRI of the brain is necessary, you need to say this in advance. Then the doctor will suggest taking a sedative before starting the procedure.
How is an EEG performed?
The examination takes place in several stages.
Preparatory stage
- the patient enters the office, protected from light and sound;
- an encephalograph “cap” consisting of special sensors is put on it;
- The sensor wires are connected to a device that records the bioelectric impulses of the brain.
Diagnostic stage
- the encephalograph transmits data to the monitor in the form of a graph;
- the power of electric fields and its distribution in different parts of the brain are recorded;
- Functional tests are carried out: the patient is asked to blink, look at flashes of light, breathe less often or deeper, listen to a sharp sound.
Final stage
- the electrodes are removed from the patient;
- print out the results.
Express diagnosis of the causes of headaches
Posted at 02:20h in Services by doctor
When a person has a headache, diagnosis is a mandatory element to determine the real cause of the negative symptom and to completely eliminate it. The range of possible causes of headaches is so wide that even the most experienced doctor with extensive practical experience cannot do without multidirectional diagnosis of headaches.
During a preliminary verbal interview and examination, several criteria for the main assumptions are identified, some are excluded when studying the anamnesis, others require verification or confirmation.
How long does the electroencephalogram procedure take?
A regular encephalogram (routine EEG or diagnosis of a paroxysmal state) takes from 20 to 30 minutes.
During the examination, a number of tests are carried out:
- rhythmic photostimulation;
- hyperventilation;
- load in the form of slow blinking.
If it is necessary to evaluate certain brain functions, the specialist adds additional tests, which he informs the patient about in advance. Such tests include:
- clenching your fingers into a fist;
- being in the dark;
- sleep deprivation for a certain period;
- night sleep monitoring.
Diagnostic methods for headaches
There is a special questionnaire that allows the patient to verbally describe his or her feelings. Migraine and cranialgia present similar symptoms; lesions in the skull, neck or spine may be accompanied by characteristic symptoms in other parts of the body.
Brain pathologies are often diagnosed only through hardware studies. Therefore, not only complex, but also differential diagnostics are carried out using laboratory and instrumental research methods. They are prescribed after an examination and anamnesis based on the data reported by the patient and available in his medical history.
When the study is considered sufficiently complete, the data obtained is analyzed. If a clinical picture emerges that indicates the possibility of developing several diseases, without any special arguments that outweigh the opinion in one direction or another, differential diagnosis is carried out.
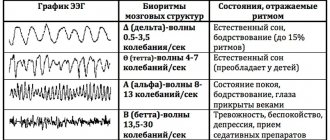
Encephalogram
A study based on the study of brain function. Electrical potentials are emitted from the scalp, which are recorded on the encephalogram. By recording bioelectrical activity, the electroencephalograph, using special sensors attached to the skin according to the international scheme, produces an indirect result in the form of a recording on a paper tape or a converted file on a computer. Sometimes several types of studies are done - regular (routine), long-term or overnight EEG.
An electroencephalogram may be required to confirm information about negative processes in the brain, tumors and injuries, determine the exact location of the damage, and determine the state of the central nervous system.
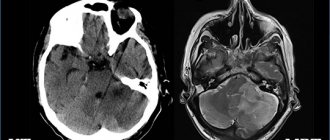
CT scan
Headache is only one of the symptoms for which a CT scan is recommended. Computed tomography is a non-invasive way to obtain information if the disease is accompanied by weakness and lethargy, hearing and vision impairment, and lack of coordination of movements that accompany frequent headaches.
The main purpose of a CT scan is to detect damage to brain cells and structures and transfer the obtained data to a storage medium accessible for study.
Magnetic resonance imaging is used as a research method for chronic headaches, if there are accompanying symptoms - dizziness, loss of consciousness, abnormal blood pressure and tests confirming the presence of tumors. Until recently, it was considered an auxiliary diagnostic method, helping to confirm an existing assumption.
Now this method of layer-by-layer scanning is capable of identifying diseases of the central nervous system, lesions of the pituitary gland, tumors of the brain, hemorrhages, and showing some diseases of the organs of vision and hearing.
Angiography
Allows you to examine the condition of blood vessels in the head area. This is done in three ways:
- using an X-ray machine and an injected contrast agent;
- using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner and drugs with gadolinium;
- using a CT scanner and a substance containing iodine to produce a contrast image.
The procedure is carried out by an angiography technician, who also gives a preliminary assessment of the resulting picture, and then a neurosurgeon or vascular specialist studies the results.
Spinal tap
A procedure that rarely brings pleasant sensations, but is safe if the sample is taken by an experienced doctor. It is carried out in case of suspected presence of an abscess or tumor; it helps to determine the composition of the CSF. After taking the puncture, the contents are subjected to detailed examination.
Interpretation of survey results
Even a qualified specialist is not always able to accurately name the cause of the patient’s poor health and immediately make a diagnosis. The doctor may be alerted to focal changes on the EEG. In this case, magnetic resonance imaging will be required to exclude a tumor or cyst.
When you contact a medical doctor, you will be able to undergo all examinations as quickly as possible, without delaying your visit to specialists.
If you need to do an EEG of the brain and you want to do it using modern expert-class equipment and in the shortest possible time, call the phone number listed on the website or leave a request in the feedback form.
Medical staff will answer your questions and conduct all necessary examinations within one business day. Let's take care of your health together!
What is the difference between CT and MRI of the brain?
Computed tomography is the only method that can compete with MRI. The principles of their operation differ, first of all, in the nature of the radiation: magnetic for MRI and x-ray for CT. For this reason, the first can be performed repeatedly without harm to the patient’s health, and the second can be performed no more often than a regular x-ray. At the same time, CT, unlike MRI, is not performed in a confined space, which makes it more preferable for claustrophobics.
In addition, MRI shows the chemical structure of the tissues being studied, and CT will tell us about their physical state.
Another important difference is that MRI is more effective for examining soft tissue, while CT is more effective for examining bones and joints.
The price of a brain MRI is not much different from the cost of a CT scan.
Sign up for diagnostics Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Contraindications to brain tomography
MRI is not recommended for:
- pregnancy up to 12 weeks;
- previously installed pacemaker, inner ear prostheses;
- the presence of various metal fragments in the body: shavings, bullets, shot;
- various conditions of the patient, when it is impossible to maintain a motionless body position throughout the study.
A contraindication is also the presence in the body of implants that contain ferromagnets. This is because such structures can reach high temperatures depending on their size.
To clarify information related to the presence of any implant, you can order a call back on our website. After a few minutes, a call center specialist will answer your question or invite a doctor for a free consultation, if necessary.
Before registering for the study, please note that the patient’s weight should not exceed 130 kg. This limitation is due to the technical features of the tomograph.