Home » Department of Neurology » Diseases » Minor chorea
Minor chorea is a disease of rheumatic etiology, characterized by movement disorders.
Damage to the body by the rheumatic process begins with the penetration of group A hemolytic streptococcus bacteria into the body. This microbe from foci of infection (for example, in chronic tonsillitis from the palatine tonsils) penetrates the bloodstream and spreads in various tissues. The pathogenesis of rheumatic lesions is based on connective tissue pathology. Damage to heart valves and joints may develop. Penetration of the pathogen into the central nervous system can provoke dysfunction of the cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and basal ganglia (neurorheumatism). Large and small vessels of the brain are damaged with the development of vasculitis and thrombusculitis. As a result of the development of degenerative processes, coordination of movements and muscle tone are disrupted in these areas of the nervous system.
After the discovery of antibiotics, the incidence of chorea minor is up to 10% of all neurological diseases. The disease develops more often in girls than in boys, and mainly in the autumn-winter period. The duration of the disease is from 3 to 6 weeks. Short-term relapses may occur over a long period of time after the height of the disease (for example, during pregnancy). In rare cases, deaths have occurred due to pathological effects on the cardiovascular system.
Lesser chorea - Types
Depending on the clinical course, the following are distinguished:
- Classic version of the course of minor chorea
- An atypical variant of the course of chorea: erased, low-symptomatic, sluggish form of the disease
- paralytic minor chorea
- pseudohysterical minor chorea
The course of the disease can be:
- Latent (hidden)
- Subacute
- Acute
- Recurrent
Signs of chorea
All types of chorea have one common feature - the appearance of violent movements in the skeletal muscles. The remaining symptoms differ somewhat in the minor, senile varieties and Huntington's chorea.
The British say that a child with chorea has to be punished three times before a diagnosis can be made: once for being restless, once for breaking dishes, and a third for making faces at his grandmother.
A. S. Nikiforov, A. N. Konovalov, E. I. Gusev
Clinical Neurology 2002
Signs of chorea - photo gallery
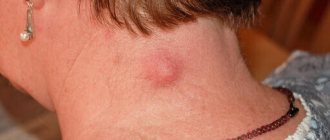
Chorea most often affects the facial muscles
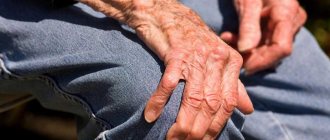
With all types of chorea, gait changes
Huntington's chorea is a progressive disease
Symptoms of various forms of chorea - table
| A type of chorea | Minor chorea (Sydenham's chorea) | Chorea of pregnancy | Huntington's chorea | Senile chorea |
| Symptoms of damage to the basal ganglia | ||||
| Changes in gait and voluntary movements of the arms and legs |
|
|
| |
| Changes in facial expressions and speech |
|
|
| |
| Changes in the nature of muscle tension (tone) in a calm state | muscle tone is reduced | stiffness when moving the trunk and limbs | muscle tone is reduced | |
| Mental and emotional disorders |
|
| not typical | |
Minor chorea - Causes
Among the reasons for the development of chorea minor and the risk factors for this pathological process are the following:
- Hereditary predisposition
- Female
- Rheumatism
- Age from 6 to 15 years
- Previous streptococcal infection (for example, sore throat)
- Asthenic physique
- Psychological trauma
- Increased excitability of the child's nervous system
- Frequent sore throats
- Chronic tonsillitis
- Respiratory diseases
- Rheumatism
- Decreased immunity
- Carious teeth
Classification of chorea
The name chorea is given to a whole group of diseases of the extrapyramidal system, united by common characteristics.
Varieties of chorea - table
| A type of chorea | Minor chorea (Sydenham's chorea) | Chorea of pregnancy | Huntington's chorea | Senile chorea |
| Mechanism of disease development |
| hormonal changes | hereditary gene defect | cerebral atherosclerosis |
| Commonly Affected Gender | female | female | men and women | men and women |
| Age of disease onset | any | reproductive | after forty years, less often from 20 to 30 | after 60 years |
| Reversibility of symptoms | reversible | reversible | irreversible | irreversible |
Lesser chorea - Symptoms
The development of minor chorea is accompanied by the following clinical signs:
- Twitching of arms and legs (trochaic hyperkinesis) on one side or symmetrical
- Twitching of facial muscles (grimacing, blinking, twitching of the corner of the mouth, wrinkling of the forehead)
- Muscle weakness
- Gait disturbance
- Shoulder Jerking
- Movement coordination disorder
- Head twitching
- Handwriting disorder
- Sleep disorders
- Seizures
- Speech impairment (lingual hyperkinesis)
- Difficulty swallowing (hyperkinesis of the laryngeal muscles)
- Intermittent breathing (diaphragmatic hyperkinesis)
- Emotional excitability
- Memory and attention disorders
- Increased fatigue, irritability
- Psychoses with auditory and visual hallucinations
Changes in the functioning of the nervous system with chorea
The nervous system is the main regulator of all body activities. The spinal cord and brain ensure the coordinated functioning of skeletal muscles, internal organs, processing of information coming from outside and emotional response to the environment.
The ability to voluntarily control your body is one of the main components of a quality life. There are several levels of regulation of conscious movements. Skeletal muscles are controlled by nerve cells (neurons) located in the gray matter of the spinal cord. They, in turn, are completely subordinate to a special part of the brain - the cortex. It is here, in a small area of the cerebral convolutions, that nerve cells are present, which are the beginning of the path of voluntary movements.
The parts of the brain provide various aspects of the body's vital functions.
Most voluntary motor activity is a set of complex movements: walking, speaking, running, writing. Their clarity is ensured not by one cell, but by a group of different structures located in several parts of the brain. One of the centers for coordination of movements is located in the cerebellum. However, its neurons are entirely subordinate to a special part of the brain - the extrapyramidal system.
The central level of regulation of voluntary movements is located deep in the brain and consists of several anatomical structures - the basal ganglia. Each is an island of gray matter containing neurons connected to other parts of the brain. There are several similar clusters of neurons:
- pale globe;
- amygdala;
- caudate nucleus;
- shell and fence.
The basal ganglia are the main part of the extrapyramidal system
Normally, these nuclei are firmly interconnected with the cerebral cortex. The neural connections of these cells ensure the implementation of long-mastered voluntary movements - speech, walking, writing, in which many muscle groups are involved.
Chorea is a medical term denoting a neurological disease, which is based on damage to the nuclei of the extrapyramidal system of various natures. Both adults and children are susceptible to pathology. In some cases, the negative effects of chorea are reversible, in many cases they progress and inevitably lead to an unfavorable outcome.
Lesser chorea - Diagnosis in Israel
Diagnosis of minor chorea begins with collecting an anamnesis of the patient’s life and illness. The diagnosis is confirmed by a characteristic clinical picture in combination with certain research methods:
- Blood test - allows you to identify the content of markers of streptococcal infection in the body: antisteptolysin-O, rheumatoid factor, cyclic citrullinated peptide, C-reactive protein.
- Electromyography is a method that allows you to study the biopotentials of skeletal muscles. When recording the electrical activity of muscles during chorea minor, an elongation of potentials and asynchrony in their appearance are revealed.
- Electroencephalogram - reveals diffuse slow-wave bioelectrical activity of the brain.
- Computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, positron emission tomography help identify focal changes in the brain.
Symptoms of pathology
Modern medicine has identified two main forms of the disease:
- classic Huntington's chorea - progression begins after 40 years, the clinical picture is characterized by decreased muscle tone and excessive movements;
- juvenile form - manifests itself in childhood, accounting for 10% of all cases of the disease.
The development of the disease is rapid, but gradual. Symptoms of minor chorea in children:
- smacking your lips while talking;
- frequent and deep sighs;
- constant sniffing;
- spontaneous protrusion of the tongue.
Mimic spontaneous movements on the face gradually become more intense, they are joined by dancing, nodding the head out of place, waving the arms, and swaying the body from side to side. The child will be diagnosed with tic hyperkinesis and observation by a neurologist will be recommended.
As the child grows, the above symptoms may disappear, but there is a general slowness in behavior. Subsequently, muscle tone becomes as high as possible and the patient is not even able to take care of himself - fasten buttons, put on trousers, and so on.
A striking symptom of Huntington's chorea is a mental disorder - at first it is increased irascibility and emotionality, sleep disturbances. As the pathology progresses, unmotivated aggression appears, and at an older age, hallucinations, delusions and even suicidal thoughts are noted. At the same time, patients cannot be critical of their own condition and behavior and consider themselves absolutely healthy.
The result of a genome disorder is dementia and dementia, when a person needs constant care. The progression of the disease lasts for 10-20 years. The juvenile form of Huntington's chorea develops quickly, with death occurring within 8-10 years.
Lesser chorea - Treatment in Israel
Israeli doctors have extensive experience in the treatment of chorea minor and can offer you the following treatment methods:
- Penicillin antibiotics (bicillin) are used to combat streptococcal infections.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (sulindac, ketorolac, salicylic acid derivatives) - reduce inflammatory syndrome in tissues.
- Glucocorticoids (prednisolone) – prevents the development of edema and inflammation in tissues, and an allergic reaction.
- Sedatives, tranquilizers (benzodiazepines, barbiturates) - relieve neuropsychic tension.
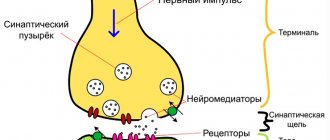
- Neuroleptics are drugs that inhibit the transmission of dopamine (one of the neurotransmitters). Haloperidol is used in combination with aminazine and reserpine, which block the transport of dopamine in nerve endings.
- Dopamine competitor drugs (dopegit) - when taken, the drug binds to dopamine receptors, which prevents the attachment of the endogenous transmitter.
- Antihistamines (suprastin, diphenhydramine) - eliminate the allergic component of the disease.
- If there are risk factors (for example, chronic tonsillitis), preventive lavage is indicated, and if it is ineffective , removal of the tonsils.
- When stopping the acute stage of the process, a stay at the sanatorium resorts of the Dead Sea, famous for its healing and restorative effects, will have a positive effect on the patient’s body.
Lesser chorea is a disease that requires special attention from a doctor when identifying and treating it.
Attention! All form fields are required. Otherwise we will not receive your information. Alternatively use
Treatment of Huntington's chorea
Modern medicine does not have clear treatment tactics; this disease is considered incurable. In some cases, the following are prescribed as a treatment for hyperkinesis in children:
- Tetmodis – reduces movement disorders;
- neuroleptics (Haloperidol, Azaleptin and others) – reduce muscle tone, inhibit the progression of mental disorders;
- Amitriptyline is an antidepressant that reduces the intensity of motor and facial disorders.
No other therapeutic prescriptions are made because any intervention does not produce any results. Patients are literally doomed, because as a result they become completely uncontrollable, do not orient themselves in space and time, lose their memory and do not recognize any of their relatives. They must be under constant supervision, which is why they are most often placed in specialized psychiatric clinics.
Huntington's chorea is a genetic disorder. Therefore, when such a patient appears in the family, all family members must be examined, and pregnancy planning is best done under the strict supervision of geneticists. Modern scientists can offer people who are at risk of having such a baby to undergo IVF or ICSI - it will be possible to implant a healthy fertilized egg into the mother.
More complete information about the pathology and the disease rheumatic chorea can be found on the pages of our website.
Related services: Consultation with a neurologist
Symptoms of chorea
Clinical manifestations resulting from damage to the body by a neurological disorder include many types of problematic patient conditions. Doctors note the presence of paroxysmal activity of a hyperkinetic nature, which is replaced by adequate behavior and complete stabilization of general well-being. In many patients, specialists in the field of neurology identify the appearance of:
The main signs of damage to the body can last for many weeks or even longer. A person suffering from the described disease is able to produce sounds uncharacteristic of a healthy individual (occurs as a result of disorders in the larynx). This phenomenon frightens people around and causes constant curiosity, and therefore creates negative conditions for most children, since they cannot study calmly in an educational institution. In case of regular repetitions of anomalies, the child is transferred to home study of basic knowledge.
Hyperkinesis can spread to the muscular part of the facial area, upper and lower extremities, and in some cases can affect the entire body. With this disease, in addition to the main manifestations, a person may experience mental disorders:
- Emotional lability develops.
- High degree of anxiety.
- Reduced level of memorization of certain events.
- Difficulty concentrating.
The symptoms described above develop at the initial stage of the disease and accompany the patient between attacks of a hyperkinetic nature. The severity of disorders in this area has different indications. In some situations, a sick child has no differences from his peers. Children with a similar diagnosis are similar in behavior to patients suffering from attention deficit and hyperreactivity, that is, children cannot sit in one place or do one thing for a long time, they are constantly worried and lead an overly active lifestyle.
In some patients, doctors notice problems with swallowing and pronouncing words. Common disorders that occur against the background of minor chorea include acquired heart defects. Also, body weakness, difficulty sleeping, neuropsychic seizures and more are attributed to the consequences of the disease.
Symptoms
In medicine, there are several symptoms that are characteristic of any type of chorea:
- involuntary movements of the limbs (an important diagnostic symptom);
- head twitching;
- decreased muscle tone;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- grimacing;
- gesticulation is increased;
- if you ask a person to write something, you can notice a change in handwriting;
- memory loss;
- hyperkinesis in this disease disappears during sleep;
- dancing gait;
- temperature increase;
- all the movements that a person tries to control, he performs with great difficulty.
Choreic hyperkinesis
Rare species of trochees
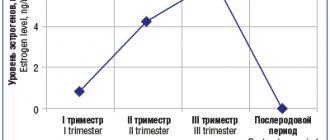
- chorea of pregnancy. Occurs due to an increase in the amount of estrogen. Typical for first-time mothers who have a history of minor chorea or rheumatism. Treatment is prescribed with extreme caution so as not to harm the fetus. In severe cases, haloperidol is prescribed. All symptoms disappear after childbirth;
- when using oral contraceptives: symptoms appear in the 3rd – 4th month after using the drug and disappear immediately after cessation. Hyperkinesis of low intensity, usually on one side;
- with systemic lupus erythematosus: there is no clinical inflammatory process and pronounced neurological symptoms are characteristic. In most cases, it gradually resolves without residual symptoms;
- medicinal chorea occurs due to the side effects of neuroleptics, psychostimulants, antidepressants, anabolic steroids, calcium antagonists. A special feature is the long-term preservation of the clinic after discontinuation of the drug;
- vascular chorea is easily differentiated: a rapidly developing clinical picture after a cerebrovascular accident, symptoms are one-sided, pathological foci in the brain are visualized on CT or MRI;
- chorea with polycythemia (increased number of red blood cells). An acute condition, mainly manifested by hyperkinesis of the facial muscles. Treatment: adjustment of blood viscosity;
- chorea with brain damage during pregnancy or childbirth, or in the first days of a child’s life. The main cause is cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy) with a clinical picture of neurological disorders;
- neuroacanthocytosis includes chorea and red blood cell pathology. It is a hereditary disease, the first symptoms appear in infancy. The progression of the disease is slow, therapy is ineffective and mostly only symptomatic;
- Lesch-Nychen syndrome. A rare hereditary disease manifested by choreatosis (fast, sharp, convulsive movements combined with slow movements). At the clinic: uncontrollable vomiting, large amounts of urine and feces. Treatment: allopurinol.
Medicines
Photo: grud.guru
The main drugs used in the treatment of chorea are tranquilizers and antipsychotics. They are prescribed exclusively by a doctor and are issued at a pharmacy strictly according to a prescription. These groups of drugs have their own characteristics; in particular, when taking them, a lot of side effects can occur, so they are prescribed with some caution. In this regard, it is especially important that the patient strictly follows the instructions of his doctor and does not self-medicate.
To improve metabolic processes in the brain, drugs such as piracetam, Actovegin, and Cerebrolysin are prescribed. These drugs are in most cases well tolerated and rarely cause side effects (general weakness, dizziness, anxiety, dyspeptic disorders, sleep disturbances).
Sedatives are also used, which have a general calming effect on the central nervous system. The sedative effect manifests itself in the form of a decreased response to various external stimuli. This effect is achieved by regulating the functions of the central nervous system, that is, the processes of inhibition are enhanced or the processes of excitation are reduced. In addition, sedatives have a beneficial effect on sleep, facilitate the onset and increase the depth of sleep.
Of the B vitamin preparations, preference is given to thiamine (B1) and cyanocobalamin (B12). B1 carries out the conduction of nerve impulses along axons (peripheral processes of nerve cells), and participates in the regeneration of nerve processes. B12 is involved in the construction of the myelin sheath of nerves, reduces pain resulting from damage to nerve fibers (but is not used as a pain reliever). In addition, vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is often prescribed, which acts as an antioxidant and also ensures the transmission of electrical impulses at the point of contact of two nerve cells.
To treat infections of bacterial etiology, antibacterial agents are prescribed. The choice of a specific antibiotic depends on the type of infectious agent.
Glucocorticosteroids are used for systemic use. Most often, prednisolone is used in the form of tablets; in case of exacerbation of the process, injections are used.
The following changes may occur while taking prednisolone:
- increased blood pressure;
- menstrual irregularities in women;
- muscle weakness;
- decreased glucose tolerance;
- osteoporosis (decreased bone density, causing bones to become more fragile and prone to fractures);
- indigestion, nausea, vomiting, increased appetite;
- allergic reaction due to individual intolerance to the drug.
Despite such a wide range of side effects that occur while taking glucocorticosteroids, in some cases it is impossible to do without them.
Causes
The cause of the primary forms of pathology lies in genetic disorders. Certain chromosomal defects cause damage to various neurons of the basal ganglia and, ultimately, the development of one of the variants of primary chorea.
The following factors can lead to the development of secondary forms of the disease:
- infections: whooping cough;
- meningitis;
- borreliosis;
- viral encephalitis;
- neurosyphilis;
- HIV;
- multiple sclerosis;
- hypo- or hyperglycemia due to diabetes;
- neoplasms;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
Video: the nature of hyperkinesis
Treatment
Photo: econet.ru
To successfully treat chorea, it is necessary to know exactly the cause of the development of this disease. First of all, you should establish a daily routine, nutrition, and physical activity. It is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air and eat small and frequent meals. For people prone to hypertension, it is important to control their blood pressure levels. It is recommended to measure blood pressure at least three times a day, especially important in the morning and in the evening before bed. It is also necessary to monitor the intake of antihypertensive drugs and remember to take them on time.
To reduce the severity of involuntary movements underlying the manifestation of the disease, tranquilizers and antipsychotics are prescribed. In order to improve nutrition and brain function, means are used that improve metabolic processes. B vitamins are used to improve the transmission of nerve impulses from the brain to muscle tissue.
If chorea was caused by an infectious disease of bacterial etiology, antibiotics are prescribed, the action of which is aimed at destroying pathogenic microorganisms. For Wilson-Konovalov disease, medications are used that reduce copper absorption. With this disease, it is also important to strictly adhere to the diet, which implies the exclusion of products containing copper. Glucocorticosteroids are prescribed in cases where the etiology of chorea has an inflammatory component, for example, with vasculitis. Also, chorea can occur during long-term use of certain medications, so you should clarify what medications the person was taking. If one of the listed drugs is suspected to be responsible for the development of chorea, the use of this drug should be immediately discontinued.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is used in combination with drug therapy:
- galvanization;
- electrosleep;
- radon baths.