- Gallery
- Reviews
- Articles
- Licenses
- Vacancies
- Insurance partners
- Partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule for receiving citizens for personal requests
- Online consultation with a doctor
- Documentation
Dizziness – apparent rotation of objects inside the head or surrounding objects around one’s own body and a feeling of loss of balance.
Dizziness in children is a separate issue; it is very difficult to identify. The fact is that children cannot always describe this symptom. Until a child learns to speak, recognize his feelings and describe them in words, adults do not take his complaints seriously.
How can you suspect dizziness in a child?
Children's behavior changes. They usually close their eyes and lie face down, pressed tightly against the wall or headboard of the crib and unwilling to move. Older children do not want to get out of bed after suffering from illnesses.
As soon as you notice any unusual behavior in your child, you need to consult a doctor. Only he will be able to identify the causes and type of dizziness in a child and prescribe adequate treatment. If this is not done in time, then a banal ailment can develop into a serious illness.
Dizziness in children of all ages.
| Child's age | Causes of dizziness |
| Up to 3 years | Frequent causes of dizziness in young children are infections, parasites or hypoxic lesions of the brain. |
| 3-10 years | Paroxysmal vestibulopathies are quite common and resolve on their own within 10 years, even without the participation of doctors. However, one should not turn a blind eye to a child’s complaints of dizziness, because this can be an alarming signal of a serious illness. |
| 10-15 years | Possible causes of dizziness and nausea may be: poisoning with toxic substances or heavy metals when drinking alcohol, etc. Dizziness is often caused by injuries to the head and inner ear. In addition to physiological reasons, well-being is strongly influenced by natural hormonal processes in the body associated with growing up, stress and neuroses. |
Symptoms
If hypotension manifests itself in a newborn, then the parents do not have any special problems, because it is difficult to determine from his condition that there are health problems. This is explained by the fact that the child sleeps a lot, rarely cries, and is in constant peace. Children who have decreased muscle tone, legs and arms can extend more than 180 degrees at the joints. In addition, the following symptoms are observed: a delay in the rate of motor development and impaired swallowing and sucking. Dizziness, fainting, nosebleeds, emotional lability, decreased performance, joint and muscle pain, sudden deterioration in health, and headache may also occur. With a slight increase in blood pressure, the child’s health may be good. Although the child may quickly get tired and irritated. But if the pressure rises strongly, the child will always feel unwell. Among his complaints are the following: headache, dizziness, pain in the heart, palpitations, memory impairment. If a hypertensive crisis occurs. Symptoms such as severe headache, nausea, blurred vision, convulsions, impaired consciousness and others may be observed.
Diagnostic methods
The most popular and effective diagnostic methods are considered to be such procedures as:
- Brain electroencephalography (EEG) – examines brain activity, allows you to assess the child’s development and identify any abnormalities. This procedure is painless, safe and can be performed at any age.
- Electrocardiography (ECG) - examines the condition of the heart, allows you to identify disturbances in the functioning of this organ, heart defects, angina pectoris, etc. The procedure is also safe and can be performed at any age.
- Rheoencephalography (REG) - it is often confused with EEG, because studies are also carried out by placing electrodes on the head. However, REG does not examine brain activity, but evaluates the condition of blood vessels, their ability to expand and contract, their condition under stress and tone. Like previous diagnostic methods, it is carried out at any age.
In addition to these procedures, it is necessary to do a general blood test to look at the level of hemoglobin and donate blood for sugar. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe an MRI of the brain, an examination by an otolaryngologist, an examination of the fundus, etc.
There are also other materials about dizziness:
- among women;
- in older people;
- in teenagers;
- those who smoke or quit a bad habit;
- after training;
- with VSD;
- with osteochondrosis;
- after a stroke;
- before, during and after meals.
Treatment
Treatment can be medicinal or non-medicinal. If arterial hypotension occurs in a labile form, then preference is given to the second type of treatment, which includes several methods. It is necessary to normalize the daily routine, which includes the child’s correct combination of study and rest. It is important to take timely breaks. This also includes quality sleep at night, as well as daytime rest. Don't forget your daily walks. A child should be in the fresh air for about two hours a day. Meals should be taken four to six times a day. At the same time, there should be a sufficient amount of salt in the food. It is important that the products contain a sufficient amount of nutrients and microelements, which are very important for the child’s body. It is important to maintain optimal water regime. Massage has a good effect. Recommended area: hands, collar area and calf muscles. If such methods are insufficient or childhood hypotension has progressed to a more serious method, the doctor will prescribe the necessary medications. Treatment of hypertension depends on many factors. If arterial hypertension in children and adolescents is accompanied by a slight increase in pressure, non-drug therapy is used. If a child is overweight, it is necessary to reduce body weight. This is achieved by increasing physical activity and normalizing nutrition. If the school assigns a lot of homework, you need to make sure that this does not affect the health and condition of the student. If lifestyle changes do not lead to a decrease in blood pressure or the levels are high, drug treatment is prescribed. Antihypertensive therapy is also prescribed for those children who suffer from diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney diseases. Most of the drugs prescribed for adults are also used for younger patients. But doses and medications are always selected individually.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, first of all, blood pressure measurements are needed. This is usually done in a sitting position for the first half. The measurement occurs three times, the interval between these is three minutes. Also, it is not done immediately after mental or physical stress, but after an hour has passed. In addition, the following diagnostic methods are used: ECG, ECHO-kg, ABPM, study of autonomic homeostasis, EEG registration, psychological testing, clinical and biochemical blood tests, consultation of the necessary specialists in order to exclude secondary arterial hypotension. To confirm the diagnosis of arterial hypertension, daily monitoring and tests with different types of stress are used. During the study, it is important to identify the cause of the increase in pressure if hypertension is secondary. This is what helps the doctor prescribe effective treatment. If the cause of hypertension is not eliminated, treatment measures will not give the desired effect, the result will be temporary.
SICK IN TRANSPORT - WHAT TO DO?
How nice it is to visit your grandmother in the village, to travel by car with your baby. But trips are not always a joy - sometimes during a trip the baby feels sick, feels sick, gets motion sickness, and the whole family gets a bad mood instead of pleasure. The cause of this is kinetosis or motion sickness. The condition can manifest itself when driving any type of transport - your own car, ship, bus, trolleybus and tram, on a train or plane. In children, in addition, kinetosis can also occur when riding on swings or carousels, various attractions, and even when rotating around its axis.
In fact, from the point of view of the anatomy and physiology of the body, kinetosis is not a disease - the body simply does not know how to adequately react in such conditions, and the vestibular apparatus becomes uncoordinated.
By the way, not only people suffer from kinetosis. According to scientists, many animals are susceptible to this condition - dogs, cats, cows, horses and even fish.
The problem of motion sickness becomes more acute every year, because more and more families are purchasing personal cars and carrying their children in them; parents and children have begun to make longer and longer trips using different types of transport.
Who does this threaten...
Kinetosis can be an independent syndrome that occurs as a result of motion sickness, but it can also be a symptom of serious diseases. Therefore, do not neglect contacting a doctor - only a pediatrician or neurologist will be able to figure out whether the baby is really prone to motion sickness or whether this is a manifestation of pathology of the ENT organs, nervous system, diseases of the stomach and intestines, or heart problems. And, of course, you shouldn’t be guided by the principle “it’s age-related - it will outgrow”, or “we had it too - be patient”, you need to help the baby and this can be done quite effectively.
We will talk in more detail about helping a child in case of motion sickness - but still, before using all the methods and medications we have listed, consult your doctor - not all medications may be suitable for your baby!
It is believed that children aged 2 to 11-12 years are susceptible to motion sickness, and the problem goes away with age. Although, according to world statistics, up to 70% of the population is susceptible to motion sickness to one degree or another, for some reason the problem is not given due attention and no active measures of assistance are taken. The tendency to kinetosis is inherited, and girls are affected twice as often as boys.
In addition - it all depends on the type of transport - some people tolerate swings and merry-go-rounds well, but feel terribly sick in the car, other kids can take long trips by car, but feel sick on a ship or trolleybus. And there is a category of children whom kinetosis can overtake even when riding in a children's rocking chair!
Where does it come from...
Of course, from the point of view of classical medicine, kinetosis is not a disease, but a protective-adaptive reaction to sudden changes in environmental influences. However, the baby feels no less bad from this than from any illness. All these troubles arise due to the vestibular apparatus, which is located in the inner part of the ear. The outer and middle ears are responsible for hearing, but the inner part is also responsible for body positions in space. Its structure and functioning are much more complex and interesting than the outer part - although it is very small in size and fits in the temporal bone. Let's talk a little about its structure and work to better understand the cause of kinetosis.
The vestibular apparatus has been studied by scientists for a long time and closely, but still, much remains a mystery, although most of its structure and work have already been clarified. It is also called the balance system, it reacts to the earth’s gravity (gravitational forces), is responsible for the self-perception of the position of the head and body in space, and for the directions of movement. It consists of a vestibule and a system of three semicircular canals located in three planes - perpendicular to each other, like the coordinate axes in mathematics - X, Y and Z. They give us the feeling of a “three-dimensional world”. With their help, the baby can move left and right, up and down, back and forth and in a circle. Each semicircular canal contains hairs (cilia) and fluid that changes its flow when the body position changes. Due to irritation of these hairs, the brain receives sensations of movement, gravity and sound vibration. Simultaneously with receiving information from the vestibular apparatus, the brain receives information from the organ of vision and, superimposing it on each other, gives a coordinated reaction.
With kinetosis, during movement or rocking, the baby’s senses receive conflicting information - the eyes see a static picture, the child does not move, and signals from the vestibular apparatus about changes in body position occur - therefore, discoordination and irritation of various organs and systems occurs. If in an adult a cerebral cortex and a well-developed coordination system also help cope with pitching, then in a baby all structures are still just being formed and are being trained. Therefore, the occurrence of motion sickness occurs more often in them. By the way, motion sickness in children under 2 years of age is rare because they have not yet formed spatio-temporal connections and the brain still has a fragmented picture of the world. And the vestibular apparatus in children under 2 years of age is still poorly developed.
The degree of severity of kinetosis varies in different children - it all depends on the individual sensitivity of the body. Overstrain of the visual analyzer in the form of horizon movements, stuffy, hot rooms, adult smoking, high humidity, as well as emotional mood - the child’s anxiety or fear of traveling, his excitement - can increase the severity of the manifestation of kinetosis.
How it develops and how it manifests itself...
Due to an excess of impulses coming from the vestibular apparatus, irritation of the baby’s internal organs occurs. In this case, three types of different body reactions can develop:
- emotional - a feeling of fear, panic, less often euphoria or delight is formed,
- vegetative - redness or pallor of the skin, increased sweating, hypersalivation (increased salivation), nausea and vomiting, disturbances of consciousness, fainting.
- muscular - contractions of individual muscle groups, forming deviations of the body in different directions, accompanied by swaying, unsteadiness of gait, loss of the sense of support under the feet.
These three forms can be combined differently in different babies and, therefore, give so different reactions.
Kinetoses are divided into four main forms, although this division is rather arbitrary and the forms can be combined.
There is a nervous form of the disease, which can manifest itself in a baby with dizziness, heaviness in the head, weakness, headaches, weakness and lethargy.
The gastrointestinal form will manifest itself as a disturbance or distortion of the sense of taste, the appearance of an unpleasant taste in the mouth, and in addition there may be nausea, vomiting, stool disorders, abdominal pain and increased sensitivity to odors.
In the clinic of the cardiovascular form, tachycardia (increased heart rate) or, less commonly, bradycardia (decreased heart rate), increased blood pressure, and heart rhythm disturbances are observed. The baby's pulse pattern changes - as the attack progresses, it slows down, yawning occurs, breathing becomes shallow, and blood pressure drops sharply - the baby may suddenly turn pale and faint.
However, more often than others, a mixed form develops - in which most of all symptoms appear; all children experience increased sweating and pallor.
If the attack begins...
With all your appearance, reassure the baby, convince him that everything is fine and nothing terrible has happened. It is better, of course, if the trip is not during rush hour and in cool weather. But, in any case, provide the baby with access to fresh air, if possible, stop the transport and go out to stand on the ground, walk a little. Ask your baby to breathe rarely and deeply, sometimes this helps to cope with an attack of lightheadedness. You can offer your baby to suck on a sour candy or lemon. Ask him to look at stationary objects - at his finger, at the house, at the toe of his shoe. If there is no vomiting, but the baby complains of weakness and dizziness, you can give him a special remedy.
Always keep several plastic bags, some water for washing or wet wipes and a set of clean clothes on hand - the baby may not always have time to tell you that he feels bad and something bad might happen, the baby might vomit. Then you will need to help him get himself in order.
Where is the best place to go...
The very first thing you need to remember is that in case of repeated attacks of motion sickness, be sure to show the child to the doctor, as we discussed earlier - a serious illness may be hidden under the mask of kinetosis. But if the cause of the baby’s suffering is precisely the problem of motion sickness, there are quite a few ways to help the baby and ease the suffering of the baby and the whole family.
The place for the trip needs to be thought out in advance - if it is a ship, you need to be located closer to the center, and if it is a bus, try to position yourself in the front and close to the opening windows. If the trip is long, go for walks at stops more often, open the window more often and ventilate your seat. Be sure to seat your baby in the direction of travel.
If you travel in a personal car, there are also certain rules. The seat next to the driver has the least amount of motion sickness. However, according to traffic rules, children under 12 years old cannot be seated there, so place the baby in the middle of the back seat. By the way, it is worth fastening a child into a car seat not only according to traffic rules, but also to reduce the manifestations of kinetosis. A baby fastened in a seat will experience less inconvenience, because kinetosis occurs in children at those moments when they are overly active, if they jump around the cabin, lie on the seats, or look out the rear window of the car. In addition, the correct sitting position makes it possible to breathe deeply and look in the right direction - the child will look forward and pay little attention to the side windows, where the picture changes very quickly, which helps alleviate the manifestations of motion sickness. It is the irritation of the vestibular apparatus and the image flashing strongly before the eyes that provokes lightheadedness. Many children find it helpful to travel at night; because of the darkness, movement outside the window is not visible, but it is best on the road if the baby sleeps, although it will not be easy to persuade the restless one to sleep. If the baby does not agree to sleep, keep him busy with games or entertainment - this way he will not get hung up on his feelings, and this will make it possible to cope with lightheadedness.
You need to prepare for a long trip in advance - take your baby with you on trips over short distances at different periods of time, so he will get used to the movement. Ventilate the cabin before the trip, do not close the windows, and in winter do not turn on the stove at full power - intense heat with dry air will negatively affect your well-being. Try to drive smoothly, without making sudden changes in speed, making sharp turns, or sudden braking. Irritating and pungent odors have a significant impact on the child’s condition - remove air fresheners and strong-smelling products from the cabin, and under no circumstances smoke in the cabin!
Shouldn't we eat...
Many parents believe that it is worth eating before a long journey - this is fundamentally wrong; a hearty breakfast or lunch on the road will only intensify the manifestations of kinetosis. However, you shouldn’t carry your baby hungry either - you need to snack on easily digestible food. Moreover, this should be done at least an hour before the trip, and not right before leaving the house. You should not reproach your child with fatty, fried, meat products and fast foods. The optimal pre-trip meal is pieces of fish, cottage cheese, yogurt with a bun or salad. Sour and salty foods help well, although you should not abuse them. You should not take milk and carbonated drinks with your baby on the road, and it is also not recommended to eat while traveling. Do not eat on the road yourself, so as not to provoke the child; you can only give the child non-carbonated cool water.
If you travel far, it is better to organize lunch on the road, stopping somewhere to rest, and after eating you should not immediately hit the road - take a walk for 30-40 minutes - this will help your child cope with motion sickness.
Let's try it the folk way...
There are many recommendations and ways to relieve suffering from motion sickness, which have been formulated among parents over the years. Many recommendations have proven themselves well, and it makes sense to try to use them in practice. The only thing I would like to immediately note is that all further recommendations are not a panacea for kinetosis - they can really help someone, but there are kids for whom none of the advice is suitable, and you need to be prepared for this.
Citrus fruits are good helpers against the symptoms of motion sickness, in particular nausea - you can give the baby a slice of lemon or orange, or you can just put a lemon peel on the cheek. In addition to citrus fruits, any sour fruits and peaches are suitable. Sucking on a pitted olive, a piece of pickled cucumber, a slice of tomato has a similar effect, or you can give the baby a sour candy to suck.
Ginger is considered a very effective remedy for nausea; it can be cut into small slices and sucked on the road. However, the baby may not like the taste - so you can give him ginger cookies or candy, mix ginger infusion into his drink or give him ginger tea.
Essential oils of peppermint or chamomile help well with motion sickness - they should be applied in a small amount to a clean scarf or napkin and inhaled while moving. Spinach juice or oat infusion has an antikinetic effect - but you need to start taking them a few days before the trip - a quarter glass twice a day, half an hour before meals. When traveling, in order to prevent motion sickness, you can give your child a small amount of sour juices or still mineral water.
You can wipe your baby's face and hands with a damp towel or apply a damp, cool bandage to the forehead. Unfasten all the tight fasteners and loosen the elastic bands, place the baby on your lap and talk to him gently, lulling him to sleep; sleep is the best remedy for motion sickness.
What if we go to the pharmacy?...
Of course, today any pharmacy is replete with a huge selection of medications for any ailment, and pharmacists’ recommendations are often in favor of the price of the drug rather than its effectiveness. And many drugs cannot be used by children. Therefore, you need to know approximate recommendations for the use of certain medications, but make the final choice only together with your doctor.
All medications must be taken in advance so that they have time to be absorbed and produce their immediate effect - usually 30-45 minutes before the trip. They can reduce the sensitivity of the vestibular apparatus, eliminate dizziness and nausea. However, doctors recommend using medications only in extreme cases and only if the baby always gets motion sickness while traveling. For the purpose of prevention, they should not be used.
All medicines are divided into several groups. The first are specially developed groups of drugs that can help combat the symptoms of kinetosis. These include "Dramina" used from one year, "Ciel" from two years, "Kinedryl" from two years, "Bonin" from 10-12 years. The main effect of the drugs is their penetration into the central nervous system and the reduction of excitation in it coming from the vestibular apparatus, suppressing the center of vomiting. In addition to positive effects, they also have a fairly large list of side effects - dry mouth, temporary visual disturbances, increased intraocular pressure, tachycardia, so discuss the dosage of these drugs with your doctor. In addition, they should not be taken together with alcohol-containing medications or sedatives; they have a pronounced sedative effect.
The second group of drugs are homeopathic remedies, the most common of which are “Kokkulin”, “Vertigohel”, “Avia-more”. The principle of action of this group of drugs is that in large doses they themselves would cause symptoms of kinetosis, but in small doses they help the body fight it. They have practically no contraindications or side effects, except for allergies and individual insensitivity. Many of them are available in a form convenient for kids - in the form of caramels, granules or drops. They are also not recommended for prevention, but are used half an hour before departure.
In case of severe motion sickness, the doctor may recommend a nonspecific group of drugs - these are antihistamines (antiallergic), antiemetics, sedatives (sedatives). The thing is that in addition to their main effect, they also have an inhibitory effect on the nervous system and prevent motion sickness. True, side effects in the form of lethargy, lethargy, and drowsiness are also inevitable. But if every trip for the baby ends with vomiting, it’s better to be drowsy! Your doctor will determine the dose and specific medicine.
In addition, the pharmaceutical market now offers a variety of various dietary supplements (dietary supplements) that help reduce kinetosis. But it’s difficult to give recommendations here - there are many manufacturers, there are even more fakes - be careful. Well-known and well-proven dietary supplements include “Ginger in capsules”, “Zangvil” and “Vazoleptin”. The methods of using them are similar to all other drugs, and the dosage of each drug should be discussed with your doctor or specified in the instructions.
But it doesn’t help us...
If you gave your child a drug and it had no effect, there is no need to increase the dosage or give the drug again - this is dangerous! Most likely, this phenomenon is an individual insensitivity to these drugs. In your case, you will have to be patient and just help the baby cope with the move easier. Try to put him in a position of complete rest - horizontally on the seat and ask him to relax and sleep if possible.
Train….
To make the life of a little traveler easier, you can train the body, because with age, the symptoms of kinetosis fade away because the vestibular apparatus adapts, becomes trained and can cope with troubles. If you often travel by car or other transport, you need to train your baby from early childhood.
Those parents are right who begin to take their little ones with them on trips - the main thing is that the first trips are short distances and initially carried out in a car seat. Then the baby adapts to the movement and trains his vestibular apparatus regularly.
In addition, you can practice at home, but also regularly. It is recommended to use simple exercises - spin the baby, swing on a gymnastic ball or hands, spin and turn over. Many dads, when playing with their babies, throw them in the air and spin them, the main thing is not to overdo it. We can recommend placing the baby on your shoulder and circling him around the room back and forth, changing the position of his body in space.
If the baby is older, teach him to somersault and roll sideways, walk along curbs or a log. It is useful to ride on a swing or carousel, jump on a trampoline, and go swimming.
The most important thing is kinetosis, an unpleasant condition, it can ruin the start of your vacation. But, knowing in advance about the ways we have described to alleviate the condition, you can make travel full of positive emotions and enjoyable for the child.
Alena Paretskaya, pediatrician,
We thank the site https://www.detskydoctor.ru for the material provided
You can make an appointment or call a pediatrician at home by calling the Center in Moscow:
+7(495) 229-44-10, +7(495) 954-00-46
Previous
Next
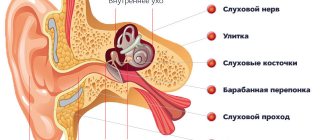
Classification of otitis media
Otitis media is divided into three large groups depending on which part of the hearing organ the inflammatory process has developed:
- Outer. In this case, predominantly the soft tissues of the external auditory canal are affected; sometimes the inflammation spreads to cartilage (chondroperechondritis develops) or bone tissue (osteomyelitis). External otitis is divided into diffuse and local. In the diffuse form, only the skin of the ear canal is affected; in the local form, specific skin lesions are present - boils, pustules, blisters.
- Average. The center of inflammation is located in the Eustachian tube, tympanic cavity and in the air cells of the temporal bone. Otitis media can be acute and chronic, perforated or non-perforated, catarrhal and purulent.
- Interior. This type rarely occurs as a primary pathology. There are two reasons for its formation: a complication of otitis media of the middle ear or a secondary pathology in other serious diseases of the body. Inflammation begins behind the eardrum and involves the cochlea and semicircular canals. Unlike other types of otitis media, inflammation of the inner ear often causes no pain. And the symptom by which it is diagnosed is hearing loss, tinnitus, and severe dizziness. In the case of purulent inflammation of the inner ear, the disease has a high risk of severe complications - sepsis, meningitis, encephalitis. In addition, this is accompanied by high fever, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, severe weakness, and headache.
What to do if a child has an attack of tachycardia before the doctors arrive?
Until the ambulance arrives, there are several ways to alleviate the child’s condition:
The most important thing is to calm the child down, open a window or vent so that fresh air can enter the room. The following measures can then be taken:
- Wipe the child's face with cold water, and then place a cloth soaked in cold water on his face.
- Have your child close his eyes and then gently apply pressure to his eyeballs for a few seconds. This will provoke a reflex in which the heart rate decreases.
- Perform a Valsalva maneuver - the child should close his mouth and nose tightly and strain as if he wants to exhale.
- Massage the carotid sinus, that is, the place where the carotid artery divides into two branches - external and internal. This place is located approximately where the thyroid cartilage is on both sides of the neck. It’s easy to feel the thyroid cartilage; in men it’s called the “Adam’s apple.” After this, move your fingers slightly downward, and immediately under the Adam’s apple you will feel the carotid sinus with a characteristic pulsation. Apply pressure and massage for a few minutes. Source: L.A. Balykova, I.S. Nazarova, A.N. Silence Treatment of cardiac arrhythmias in children // Practical Medicine, September 2011, No. (53), pp. 30-37
Causes
It is not always possible to find pathological reasons for a persistent decrease in pressure. This usually happens with primary hypotension, which, however, has its own reasons:
- asthenic physique;
- puberty;
- hereditary predisposition;
- problems during pregnancy and childbirth;
- features in the child’s character, for example, a tendency to depression;
- overwork;
- stress.
Secondary hypertension has causes that are associated with diseases of internal organs and systems: kidney disease, pneumonia, cardiovascular disease, adrenal disease, etc. Also, this form of hypotension can develop due to the use of certain medications, especially considering that children's bodies are most sensitive to medications. But a child’s blood pressure can increase for various reasons. This may depend on hereditary, external factors, and specific age. If a pregnant woman smokes during pregnancy, the risk that the breastfeeding baby will have health problems increases. Diseases of the endocrine system also cause hypertension. Children with VSD are considered potential hypertensive patients. An overdose of some nasal drops leads to a narrowing of blood vessels not only in the nose, but even in the arteries. Because of this, blood pressure increases. It has been noted that high blood pressure is often characteristic of those children who are obese or overweight. Poor nutrition, low physical activity, sedentary lifestyle, stress, school workload. All this can cause health problems.
Types of heart rhythm disorders
Tachycardia is divided into three main types :
- Sinus is the most common. With it, the heart rate in the sinus node increases. Most often appears during physical activity. However, it may be the first sign of vegetative-vascular dystonia of the hypertensive type and other diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Paroxysmal (ectopic) - a sharp increase in the number of heart contractions by two or three times. Manifested by shortness of breath, abdominal pain, cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes. Source: E.L. Boqueria Ectopic atrial tachycardia in children: clinical picture, diagnosis and treatment // Annals of Arrhythmology, 2006, No. 3, pp. 16-19
- Chronic – a condition in which a child’s blood pressure decreases, convulsions, suffocation, and chest pain occur. Treatment is usually lifestyle changes. Parents should protect the child from psycho-emotional and physical stress, monitor his daily routine, ensure proper nutrition and general hardening of the body.