Why do organic lesions develop?
The causes of organic damage to the central nervous system include:
1. Peri- and intranatal pathology (brain damage during pregnancy and childbirth). 2. Traumatic brain injuries (open and closed). 3. Infectious diseases (meningitis, encephalitis, arachnoiditis, abscess). 4. Intoxication (abuse of alcohol, drugs, smoking). 5. Vascular diseases of the brain (ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, encephalopathy) and neoplasms (tumors). 6. Demyelinating diseases (multiple sclerosis). 7. Neurodegenerative diseases (Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease).
A huge number of cases of the development of organic brain damage occurs due to the fault of the patient himself (due to acute or chronic intoxication, traumatic brain injury, incorrectly treated infectious diseases, etc.)
Prevention
So far, brain pathologies in children cannot be prevented in any way. But we can diagnose them in the early stages of development and prevent more serious complications. And sometimes even save the baby’s life. Therefore, it is very important to see a child from a competent, experienced specialist from infancy. There are such specialists in Russia! And it will help you choose the most experienced specialized doctor. You can also choose a clinic where seeing this specialist will be affordable for you and your little one will like it.
- Daria Bogdanova
- Neurology,
- Neurosurgery
Let us consider in more detail each cause of central nervous system damage.
Peri- and intrapartum pathology
There are several critical moments during pregnancy and childbirth when even the slightest impact on the mother's body can affect the health of the child. Oxygen starvation of the fetus (asphyxia), prolonged labor, premature placental abruption, decreased uterine tone and other reasons can cause irreversible changes in the fetal brain cells.
Sometimes these changes lead to the early death of a child before the age of 5-15. If life is saved, then such children become disabled from a very early age. Almost always, the disorders listed above are accompanied by varying degrees of severity of disharmony in the mental sphere. With reduced mental potential, positive character traits are not always sharpened.
Mental disorders in children can manifest themselves:
- in preschool age : in the form of delayed speech development, motor disinhibition, poor sleep, lack of interest, rapid mood changes, lethargy; - during the school period : in the form of emotional instability, incontinence, sexual disinhibition, impaired cognitive processes.
Traumatic brain injuries
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a traumatic injury to the skull, soft tissues of the head and brain. The most common causes of TBI are car accidents and household injuries. Traumatic brain injuries can be open or closed. If there is communication between the external environment and the cranial cavity, we are talking about an open injury; if not, it is a closed injury. The clinic presents neurological and mental disorders. Neurological include limitation of limb movements, disturbances of speech and consciousness, the occurrence of epileptic seizures, and damage to the cranial nerves.
Mental disorders include cognitive impairment and behavioral disorders. Cognitive disorders are manifested by a violation of the ability to mentally perceive and process information received from the outside. Clarity of thinking and logic suffer, memory decreases, and the ability to learn, make decisions and plan ahead is lost. Behavioral disorders manifest themselves in the form of aggression, slow reactions, fears, sudden mood swings, disorganization and asthenia.
Infectious diseases of the central nervous system
The range of infectious agents that cause brain damage is quite large. The main ones among them are: Coxsackie virus, ECHO, herpes infection, staphylococcus. All of them can lead to the development of meningitis, encephalitis, and arachnoiditis. Also, lesions of the central nervous system are observed during HIV infection in its final stages, most often in the form of brain abscesses and leukoencephalopathies.
Mental disorders due to infectious pathology manifest themselves in the form of:
- asthenic syndrome - general weakness, increased fatigue, decreased performance; — psychological disorganization; — affective disorders; — personality disorders; — obsessive-convulsive disorders; - panic attacks; - hysterical, hypochondriacal and paranoid psychoses.
Intoxication
Intoxication of the body is caused by the use of alcohol, drugs, smoking, poisoning with mushrooms, carbon monoxide, salts of heavy metals and various medications. Clinical manifestations are characterized by a variety of symptoms depending on the specific toxic substance. The development of non-psychotic disorders, neurosis-like disorders and psychoses is possible.
Acute intoxication due to poisoning with atropine, diphenhydramine, antidepressants, carbon monoxide or mushrooms most often manifests itself as delirium. In case of poisoning with psychostimulants, intoxication paranoid is observed, which is characterized by vivid visual, tactile and auditory hallucinations, as well as delusional ideas. It is possible to develop a manic-like state, which is characterized by all the signs of a manic syndrome: euphoria, motor and sexual disinhibition, acceleration of thinking.
Chronic intoxication (alcohol, smoking, drugs) manifests itself:
- neurosis-like syndrome - the phenomenon of exhaustion, lethargy, decreased performance along with hypochondria and depressive disorders; - cognitive impairment (impaired memory, attention, decreased intelligence).
Vascular diseases of the brain and neoplasms
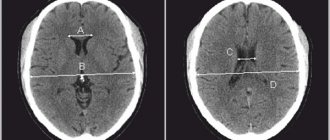
Vascular diseases of the brain include hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes, as well as dyscirculatory encephalopathy. Hemorrhagic strokes occur when brain aneurysms rupture or blood seeps through the walls of blood vessels, forming hematomas. Ischemic stroke is characterized by the development of a lesion that lacks oxygen and nutrients due to blockage of the supply vessel by a thrombus or atherosclerotic plaque.
Discirculatory encephalopathy develops with chronic hypoxia (lack of oxygen) and is characterized by the formation of many small foci throughout the brain. Brain tumors arise from a variety of causes, including genetic predisposition, ionizing radiation and exposure to chemicals. Doctors are discussing the impact of cell phones, bruises and head injuries.
Mental disorders in vascular pathology and neoplasms depend on the location of the lesion. Most often they occur with damage to the right hemisphere and manifest themselves in the form of:
— cognitive impairment (to mask this phenomenon, patients begin to use notebooks and tie knots “for memory”); - reducing criticism of one’s condition; - nighttime “states of confusion”; - depression; — insomnia (sleep disturbance); — asthenic syndrome; - aggressive behavior.
Vascular dementia
Separately, we should talk about vascular dementia. It is divided into various types: stroke-related (multi-infarct dementia, dementia due to infarctions in “strategic” areas, dementia after hemorrhagic stroke), non-stroke (macro- and microangiopathic), and variants due to disorders of the cerebral blood supply.
Patients with this pathology are characterized by slowing down, rigidity of all mental processes and their lability, and a narrowing of the range of interests. The severity of cognitive impairment in vascular lesions of the brain is determined by a number of factors that have not been fully studied, including the age of the patients.
Demyelinating diseases
The main disease in this nosology is multiple sclerosis. It is characterized by the formation of lesions with destroyed nerve endings (myelin).
Mental disorders in this pathology:
— asthenic syndrome (general weakness, increased fatigue, decreased performance); — cognitive impairment (impaired memory, attention, decreased intelligence); - depression; - affective insanity.
Neurodegenerative diseases
These include: Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. These pathologies are characterized by the onset of the disease in old age.
The most common mental disorder in Parkinson's disease (PD) is depression. Its main symptoms are a feeling of emptiness and hopelessness, emotional poverty, decreased feelings of joy and pleasure (anhedonia). Dysphoric symptoms (irritability, sadness, pessimism) are also typical manifestations. Depression is often combined with anxiety disorders. Thus, symptoms of anxiety are detected in 60-75% of patients.
Alzheimer's disease is a degenerative disease of the central nervous system characterized by progressive decline in cognitive function, personality disorder, and behavioral changes. Patients with this pathology are forgetful, cannot remember recent events, and are unable to recognize familiar objects. They are characterized by emotional disorders, depression, anxiety, disorientation, and indifference to the world around them.
Treatment of organic pathology and mental disorders
First of all, the cause of organic pathology should be established. Treatment tactics will depend on this.
In case of infectious pathology, antibiotics sensitive to the pathogen should be prescribed. For viral infections - antiviral drugs and immunostimulants. For hemorrhagic strokes, surgical removal of the hematoma is indicated, and for ischemic strokes, decongestant, vascular, nootropic, and anticoagulant therapy is indicated. For Parkinson's disease, specific therapy is prescribed - levodopa-containing drugs, amantadine, etc.
Correction of mental disorders can be medicinal and non-medicinal. The best effect is shown by a combination of both methods. Drug therapy includes the prescription of nootropic (piracetam) and cerebroprotective (citicoline) drugs, as well as tranquilizers (lorazepam, tofisopam) and antidepressants (amitriptyline, fluoxetine). To correct sleep disturbances, hypnotics (bromizoval, phenobarbital) are used.
Psychotherapy plays an important role in treatment. Hypnosis, auto-training, Gestalt therapy, psychoanalysis, and art therapy have proven themselves well. This is especially important when treating children due to possible side effects of drug therapy.
Mood disorders (depression and mania in children and adolescents)
The first signs of mood disorders can appear in children aged 5-6 years, but most often this type of mental disorder occurs in adolescents. This is due to the peculiarities of puberty and social adaptation during this period of life. There are two types of mood disorders:
- depressive disorders are characterized by attacks of depression (Episodes of low mood), without attacks of mania;
- Bipolar disorders are characterized by alternating episodes of depression and mania. The period of depression is followed by a period of elation, with a return to normal between attacks.
Cases where attacks of mania are observed without the presence of depressive periods are extremely rare.
Most often, the development of mood disorders is associated with stress, for example, the death of a loved one, constant criticism from parents or teachers, rejection by peers, or a series of tragedies. But the predisposition to the development of such conditions can be inherited.