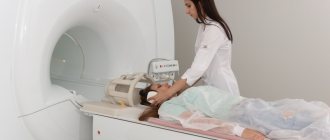
When a patient is prescribed magnetic resonance imaging of the head, he has a completely reasonable question: isn’t MRI of the brain dangerous? Yes, patients have heard about the dangers of radiation in the field of radiation diagnostics, but in the case of MRI, it should be understood that this method is fundamentally different from the x-ray method. X-ray examination uses ionizing radiation, which occurs when exposed to radioactive rays, which, of course, can cause harm to the body. However, MRI is an absolutely safe method, since it is based on the principle of the influence of magnetic fields on internal organs. Magnetic radiation during MRI is completely safe for the human body: we all live in conditions of magnetic fields, from the Earth’s magnetic field to household appliances.
Is MRI safe?
The main advantage of MRI, in addition to its high informativeness for diagnosis, is the absence of ionizing radiation .
The MRI method is based on the electromagnetic characteristics of hydrogen atoms, which quantitatively predominate over other particles in human tissue. A constant high-power magnetic field is maintained inside the tomograph; radio signals with a frequency close to the vibration frequency of hydrogen pass through it. Due to resonance, the radio wave is amplified, which is recorded in a special matrix and converted by a computer into an image.
Since different tissues of the human body contain different amounts of hydrogen, the outgoing signals from different organs and tissues differ significantly, which makes it possible to obtain fairly accurate images.
There is no medical evidence that this procedure is harmful to health or causes any complications. Among the millions of people who have undergone magnetic resonance imaging, there have been no cases of ill health or harm to the body after the examination.
The only inconvenience for the patient when conducting magnetic resonance imaging is the duration of the study. An MRI scan can take anywhere from 15 minutes to 1 hour. During this period, the patient should lie still . The examination itself is an absolutely painless procedure ; the effect of magnetic waves does not cause any discomfort to the patient.
Types of MRI examinations
Magnetic resonance imaging of the head is performed with or without a contrast agent. In the first case, the subject is injected with special substances (usually based on gadolinium salts), which make it possible to create a contrast between different tissues. In some cases, the contrast agent may cause allergic reactions. The type of study (with or without contrast) is determined by the specialist.
How often can an MRI be done?
MRI is prescribed for various pathologies of the substance and blood vessels of the brain, paranasal sinuses, diseases of the spine and spinal cord, joints, abdominal and pelvic organs. This study is carried out as necessary. As a rule, an initial MRI allows you to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe treatment. A repeat MRI examination is prescribed to clarify the condition of an organ or system after surgery, to monitor the treatment process, and for a more refined diagnosis using a contrast agent.
Since electromagnetic waves do not cause radiation exposure to the human body, unlike X-ray examinations, MRI can be done as often as required for diagnosis and effective treatment. Thanks to the constant improvement of computer technology, the MRI procedure has become absolutely safe for the public, and at the same time the most informative for the doctor.
Radiation during MRI: description of the method, radiation level, contraindications - MEDSI
Table of contents
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – what is it?
- Radiation level on MRI
- Magnetic resonance imaging in oncopathology
- How often can magnetic resonance imaging be done?
- Tomography - operating principle
- Contraindications
- Are there any complications?
- Advantages of MRI at MEDSI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – what is it?
Magnetic resonance imaging is a modern method for studying the structure, condition and functioning of internal organs.
The operation of an MRI device is based on the phenomenon of resonance of magnetic fields and on the different images of tissues of different structures as a result. The signals are sent to a computer, which decrypts them and converts them into an image. The data obtained is analyzed and assessed by a specialist - a radiologist. Modern equipment makes it possible to obtain images of internal organs, making the study highly informative. MRI helps identify a large number of diseases that are not diagnosed as accurately using other methods.
MRI has great advantages over invasive and radiographic research methods, as it is a safe and comfortable procedure. Thanks to this, the study is used in the diagnosis of diseases of many organs and systems:
- brain
- cerebral vessels
- temporomandibular joint
- joints
- spinal cord
- spine
- abdominal organs
- pelvic organs
- reproductive system,
- hearts
One of the most common applications of magnetic resonance imaging is the diagnosis of diseases of the nervous system. MRI of the brain allows you to identify tumors and determine the stage of their development, diagnose problems with blood vessels, multiple sclerosis and other pathologies.
Many patients are interested in what dose of radiation the body receives during the examination, and whether MRI is dangerous for health.
Radiation level on MRI
Unlike X-rays and computed tomography (CT), patients receive zero radiation dose from MRI because the test is magnetic rather than ionizing radiation-based.
The effects of an MRI scanner are comparable to those of a cell phone or microwave oven. MRI does not cause disturbances in the structure, condition and functioning of tissues and organs, while being a highly accurate diagnostic method.
Therefore, you can be sure: there is no radiation exposure during MRI.
Magnetic resonance imaging in oncopathology
The absence of radiation makes it possible to use MRI for cancer patients with confirmed diagnoses of various malignant tumors for whom radiographic examination methods are contraindicated. X-rays and computed tomography can cause harm to body tissues due to ionizing radiation: cause changes in DNA and negatively affect existing pathological processes. Electromagnetic effects during MRI are safe for both tumors and healthy tissues and organs.
For patients with cancer pathology, MRI is prescribed with the use of a contrast agent to increase the information content of the study, this allows for a detailed study of the tumor and the vascular network that feeds it.
How often can magnetic resonance imaging be done?
In the absence of contraindications, MRI can be prescribed (depending on the disease and the characteristics of its course) as often as necessary to develop an effective treatment plan or adjust it. Since the procedure is safe for the body, it can be carried out with minimal time intervals.
Only a doctor can determine the frequency of MRI. If there is an urgent need or in accordance with the developed follow-up plan, the study is carried out several times within one day. MRI does not pose any health risks.
Tomography - operating principle
The subject lies down on a retractable table, which slowly passes inside the magnet tunnel. It creates a magnetic field that affects the hydrogen atoms in the patient’s body, causing them to line up parallel to the resulting field. The radiofrequency pulse emitted by the tomograph causes resonance in the hydrogen atoms. This “feedback” is recorded by a computer, which converts the response vibrations into an image. This operating principle of the tomograph is called nuclear magnetic resonance.
An MRI is performed within 15–20 minutes, during which time the computer analyzes a sufficient amount of information obtained as a result of the interaction of the magnetic fields of the tomograph and the patient’s body.
During an MRI, the patient does not experience any discomfort. You must lie still, as the quality of the images obtained and the accuracy of the diagnosis depend on this.
In order not to disrupt the operation of the tomograph, which is based on electromagnetic resonance, all metal objects and electronic accessories and devices must be removed before the examination. There should be no metal parts on clothing.
No prior preparation for MRI is required.
Contraindications
MRI, being a safe and painless diagnostic method, has a number of contraindications, which are associated not only with the supposed negative influence of electromagnetic waves, but also with the psychological factor, and with cases of individual reactions to contrast agents.
MRI is contraindicated:
- during pregnancy in the first trimester (due to the possible negative effects of electromagnetic waves on the fetus)
- patients with metal implants (pacemakers, hearing aids, clips on blood vessels, joint prostheses, etc.)
- patients with allergic reactions
- patients suffering from claustrophobia and other mental disorders
Are there any complications?
Numerous studies on MRI have not revealed any negative consequences of this diagnostic procedure for the body. The influence of electromagnetic waves emitted by a tomograph is comparable to radiation from a cell phone. We are under the influence of the latter for a much longer time.
Therefore, we can say with confidence that there are no side effects during the study.
Advantages of MRI at MEDSI
- Equipment from global manufacturers
- Interpretation of studies by experienced radiologists
- Conducting research for adults and children
- Conducting studies under sedation (in a state of medicated sleep) for patients suffering from claustrophobia
- Safety
Contraindications for MRI
In some cases, MRI can cause some harm to health, and therefore doctors do not prescribe this research method to the patient. Common reasons for refusing magnetic tomography include:
- The first trimester of pregnancy (absolute contraindication), the second and third trimesters - for health reasons, strictly individually;
- The presence in the patient’s body of various metal implants for medical purposes (pacemakers, hemostatic clips applied to the vessels of the brain, wires in the bones, orthopedic structures, artificial joints, etc.);
- Fear of closed spaces (claustrophobia);
In addition, there are a number of absolute and relative contraindications to MRI.
What is the essence of MRI of the brain?
The brain is one of the most complex organs of the human body. Any surgical procedure can be dangerous, so it is important to make the most accurate diagnosis possible. MRI of the brain is a non-invasive examination method.
The procedure is carried out using a special device that creates a magnetic field. X-rays are not used during the examination. Electromagnetic waves affect human cells. The hydrogen atoms contained in the cells are arranged in a certain way and then returned to their original place. These movements are recorded on the computer monitor after automatic processing of the transmitted signals. The doctor can independently adjust the frequency of electromagnetic waves for a higher level of image detail.
The radiologist receives layer-by-layer images in a three-dimensional projection, which are further analyzed for the presence of a particular pathological process.
Diagnostics using a tomograph is carried out for the following purposes:
- determination of the disease and the stage of its development;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
MRI for a child
For young children, MRI examinations are performed according to strict clinical indications in specialized clinics, usually using anesthesia. If it becomes necessary to have an MRI performed on an older child, parents should explain to him that the examination does not cause pain. The only inconvenience can be the loud sound of the tomograph (earplugs are required) and the duration of the examination procedure, during which it is necessary to lie still.
If diagnosing a disease in a child is possible without magnetic resonance imaging, then pediatricians try not to prescribe the study due to the inconvenience that is difficult for the baby to bear. If the study is still necessary, and the child is unable to remain motionless, sedatives and anesthetics are used. An MRI of a child under anesthesia is possible strictly after consultation with an anesthesiologist .
Recommendations from experts
When identifying and monitoring the development of a disease, the optimal frequency of magnetic resonance scanning is that which allows the doctor to receive timely information about changes in the patient’s condition. If a stroke is suspected, the frequency of the study reaches 3 times in 2 days. Even in severe cases, the procedure is carried out repeatedly over 7 days. The frequency of MR imaging for some diagnoses is shown in the table.
| Diagnosis | Multiplicity of research (if the patient's condition is stable) |
| encephalopathy | Once a year (once every 4-5 years) |
| brain tumors | up to 4 times in the first 12 months (then every 6-12) |
| hydrocephalus | newly diagnosed or unoperated - on the recommendation of the attending physician; for non-obstructive form and after surgical correction - once every 4-5 years |
| multiple sclerosis | 1-2 times a year |
| Alzheimer's disease | every 12 months |
| after operations | up to 4 examinations in the first year (every 1-1.5 years) |
It is advisable to carry out preventive examinations of the brain:
- persons under 30 years of age - according to indications or in the presence of alarming symptoms;
- up to 45 - once every 2 years;
- up to 60 years - every 12 months;
- for older people - once every six months (native and with the use of contrast).
MRI of the head