Instrumental research methods make it possible to broadly and completely study the state of the brain, the functioning of its cells and parts, as well as diagnose disorders of other organs. How does an EEG differ from an Echo-EG is a question that is asked by almost everyone who has encountered certain disorders of the central nervous system in their life.
EEG and Echo-EG are reliable and safe methods for diagnosing central nervous system disorders. Thanks to both studies, reliable information about the state of the brain can be obtained in the shortest possible time.
EEG
The abbreviation EEG in the medical community refers to electroencephalography of the brain: one of the methods for studying the state of the brain, which is used when one or another pathology or malfunction is suspected. Using EEG, you can also track the degree of participation of the central nervous system in pathologies of other systems and organs. The principle of the study itself is simple, and is based on the study of electrical impulses emitted by individual areas of the brain.
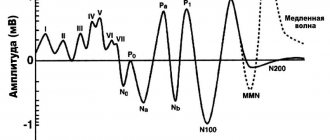
Reference. The “product” of such an analysis will be an electroencephalogram: a graph of the biopotentials of the brain. From the curve of this graph, an experienced specialist can determine how coordinated the work of individual brain zones is and how actively it functions.
The specialist refers the patient to an EEG if:
- dizziness and headaches;
- neuroses, mental disorders;
- neurotoxin poisoning;
- paroxysmal hemicrania;
- sleep disorders, insomnia;
- epileptic seizures;
- panic attacks;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia, etc.
As for the diagnostic procedure itself, it is carried out absolutely painlessly for the patient who lies or sits in a relaxed position with his eyes closed. Sometimes an EEG is performed directly during sleep, so the patient must fall asleep either naturally or with the help of special medications before the procedure.
Once the patient is ready for the procedure, a “helmet” equipped with electrodes is placed on his head, capable of recording electrical activity in various areas of the head. Diagnostic results are displayed on paper or simply on a computer screen. By deciphering the result obtained in the form of a graph, the doctor determines the presence or absence of certain deviations from the norm.
What is the difference between head MRI, EEG and ultrasound?
The main differences between ultrasound, MRI and EEG are the principles of their influence on the human body and the way the equipment operates. MRI has shown excellent results in a comprehensive study of intracerebral disorders and detection of all kinds of tumors in the patient’s head. When an MRI of the cervical spine or head is performed, a special coil is installed to enhance the effectiveness of the image.
The result of the diagnosis is a three-dimensional image that can help the treating doctor establish the correct diagnosis. Ultrasound is performed using sound waves at such a high frequency that the human ear cannot perceive them. When penetrating through the human body, echo signals with different speed parameters are reflected. The processes occurring inside the human body are diagnosed.
Often during examination, an ultrasound technique called neurosonography is used, which with high accuracy determines the size of individual areas of the head, the presence of various anomalies, and cancerous formations.
EEG (electroencephalography) records the bioelectrical activity of the brain, which is processed by a device, displayed in the form of wave oscillations on a paper tape or recorded as a separate file on a computer.
An EEG is performed using a machine called an electroencephalograph. Special electrodes are distributed over the head area, recording electrical signals from brain cells and processing them into an electrical oscillatory process. The result of electroencephalography is an image that is displayed on paper, looking like waves with different amplitudes. EEG is not able to determine the type and location of an organic disorder, but is ready to provide data on the presence of pathology and identify the area of the brain that contains it. Compared with MRI, the method makes it possible to detect mental disorders in brain activity.
To correctly answer the question: what to do with ultrasound of blood vessels and cerebral cortex or MRI, you need to focus on the positive aspects of both examination methods.
Ultrasound makes it possible to study children with lack of attention. The process is carried out quickly. There is no need to lie still for a long time during scanning. Proper preparation for MRI of the brain can prevent complications.
MRI examination is one of the best ways to diagnose organic brain pathologies; it is more effective in detecting cancerous formations in the initial stages of development and correctly prescribing a treatment method.
When compared with ultrasound, MRI encephalography has one important distinguishing feature. Ultrasound of the brain or MRI involves diagnosing anatomical disorders, and EEG is aimed more at examining the functional state of the brain. MRI and EEG pose completely different tasks.
Features of ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels
When performing an ultrasound, the doctor is able to find out the structure of the vessel being examined, make a decision about the functional capacity, the presence of pathological abnormalities, and defects. The diagnostic method is called Dopplerography. The procedure is divided into three types: Standard form, which looks like a two-plane examination - the method makes it possible to carry out a full examination, examining the vessels to the point where they enter the canals, noticing neoplasms. Duplex form - the scan results (display of the vascular system of the brain) are given to the person in the form of a color image. The doctor has a detailed picture of both the extracranial and intracranial structures, which radically simplifies the diagnosis. Three-dimensional ultrasound examination makes it possible to create an image of vessels comparable in information content to photographic images for further analysis of the state of verification of structural disorders. There is one drawback that will not allow the doctor to obtain data on the functional state of the blood supply.
An ultrasound examination is necessary if there are complaints of symptoms indicating vascular disorders in the brain area. The main signs include increased pain, causeless dizziness, weakness, which can reach the point of loss of consciousness.
Another important aspect when answering the question of which is better than MRI or ultrasound of the brain is the price factor. Ultrasound is very much inferior in price to magnetic resonance scanning.
EchoEG
This concept refers to the term “echoencephalography”, which is based on the study of the state of the brain using the ultrasound method. The method is based on the fact that different tissues of the human body (skin, bone, etc.) can reflect ultrasonic waves differently.
Using this study, doctors identify various hemorrhages, abscesses, edema and tumors, as well as hydrocephalus and intracranial hypertension. The study itself is carried out by applying a special sensor to various points of the head and analyzing the results displayed on a computer screen. The patient should be in a sitting or lying position at this time.
Reference. An echoencephalogram is a diagram of ultrasound signals converted into electrical impulses.
What common
In fact, there is not much in common between these two methods of studying the brain and central nervous system activity. Both of them have the same “object” of research, but different goals. Both studies require the patient to be at rest (the latter should sit or lie in a relaxed state). The results of both studies need to be deciphered, and only a qualified specialist can identify this or that pathology.
Both procedures are absolutely safe and painless for the patient. They can be prescribed to both adults and children, pregnant and lactating women, etc.
Indications of echo-EG of the brain
Echoencephaloscopy is indicated when alarming symptoms appear: migraine, fainting, dizziness of unknown etiology, loss of balance, tinnitus, nausea and vomiting, prolonged insomnia, decreased concentration, constant fatigue.
People in whom the attending physician suspects the occurrence of lesions and other processes in the brain need diagnosis: intracranial hypertension, cervical injuries, traumatic brain injuries, circulatory disorders in the brain, tumors (benign and malignant) in the skull, hydrocephalus, idiopathic parkinsonism syndrome , tuberculosis, pituitary adenoma, brain abscess, neurotic diseases, meningitis or encephalitis.
The specialist gives a referral for Echo-EG to young children when there is: sleep disturbance (drowsiness or insomnia), neurotic disorders, nervous tics, stuttering, head injuries, hyperactive behavior in which the child constantly demands attention, increased muscle tone, enuresis, slowdown in physical development, encopresis.
It is advisable to conduct a study when a diagnosis has already been made to assess the effectiveness of the course of therapy.
Indications for the study include: concussion, memory impairment, neurotic reactions, feeling of lack of oxygen, fainting, nausea not associated with eating, and others.
Echo-EG is often used to diagnose the brain before performing computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
The examination allows you to detect dangerous lesions in the brain: hematomas, tumors, foreign bodies, neoplasms, cysts, disruption of the functioning of the ventricles of the brain.
Advantages of the diagnostic method:
- safety;
- the possibility of performing the procedure on children, pregnant women and even the elderly;
- absence of adverse reactions and complications after manipulation;
- minimum of contraindications (echoencephalography is not done only if the patient has open wounds on the head, since sensors cannot be installed because of them);
- reliability and accuracy of graphic images;
- Not only the midline structures of the brain are examined, but also the periosteal space of the skull.
Echo-EG is prescribed to pregnant women to examine fetal parameters. The condition of the baby’s brain must be studied. The results of the procedure can be called positive if the brain hemispheres in the picture are symmetrical and look like butterfly wings.
What is the difference between EEG and EchoEG
The main and main difference between the research methods under consideration will be the nature of their impact on body tissues. If EEG works with electrical impulses, which any human or animal brain inevitably produces during operation, then EchoEG uses exclusively ultrasonic signals that are reflected differently from different tissues.
As a result, the goals of diagnosis also differ. In the case of an EEG, an assessment is made of brain activity and the degree of coordination of nervous processes (this way, for example, syndromes of developing epilepsy can be identified), while an EchoEG is aimed at detecting pathological formations of the brain (tumors, abscesses, etc.).
Reference. Since the ultrasound-based method involves external influence on the body, many patients believe that it is more harmful than EEG, but this is not the case. Ultrasound examination does not have any negative effect on organs and tissues; it is safe for both children and adults. EEG can also be called completely safe.
According to many modern doctors, echoEG has recently become outdated, and is being replaced by many more modern methods. However, echoencephalography is still used in many medical organizations and makes it possible to diagnose and prevent the development of many pathologies.
MRI, CT, ultrasound, EEG of the brain - which is better, what is the difference between head diagnostic methods
When choosing the type of diagnostic examination, you should always listen to the position of the attending physician.
The specialist will be able to give an accurate recommendation based on the results of a preliminary study or the patient’s medical history, and decide on a diagnostic method that can most accurately detect probable diseases. To say which is better than ultrasound of cerebral vessels or MRI, you need to know the effectiveness of the planned examination method, the degree of quality of the resulting images.