Ultrasound of cerebral vessels is an absolutely painless technique that helps to identify possible pathological processes. It has been scientifically proven that ultrasonic waves do not have a negative effect on organs and tissues, therefore such manipulation can be carried out not only for diagnosis in adults, but also in children. The number of procedures and frequency of examinations are not limited - ultrasound can be performed as often as necessary. Brain examination using ultrasound is carried out both according to the doctor’s indications and at the request of the patient. Let's look at how an ultrasound is performed and how to properly prepare for it.
In what cases is ultrasound of the brain prescribed?
Of course, you can undergo the examination without any complaints. But there are a number of symptoms that indicate that the procedure should not be postponed.
Be sure to consult your doctor if any of the following concerns you:
- Constant feeling of drowsiness and weakness;
- Dizziness, darkening of the eyes with a sharp rise;
- Noise in ears;
- Regular headaches or headaches that occur in the morning;
- Flashing “flies” before the eyes;
- Difficulty in perceiving information (reading or listening);
- Problems paying attention or remembering;
- Blood pressure surges;
- Episodes of incoordination;
- Apathy or low mood;
- Unreasonable nausea and vomiting;
- Deterioration of vision or hearing.
For preventive purposes, ultrasound is also indicated for those people who have high cholesterol or blood sugar levels, as well as people suffering from obesity, the elderly and those who have previously suffered a heart attack or stroke.
Sometimes ultrasound of cerebral vessels is prescribed before an upcoming operation, for example, if tumors in the head area are to be removed.
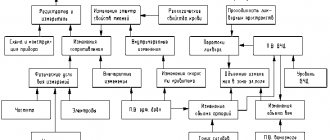
Brachiocephalic vessels
Brachiocephalic vessels (BCVs) are arteries that are responsible for supplying blood to the brain, tissues of the head, neck and shoulder girdle. This:
- 2 carotid arteries;
- 2 vertebral arteries, which at the base of the brain stem merge into one artery - the basilar;
- brachiocephalic trunk;
- 2 subclavian arteries.
They all form the so-called Circle of Willis at the base of the brain, thanks to which blood is evenly distributed throughout all parts of the brain. Therefore, the occurrence of pathological changes in any of the brachiocephalic vessels leads to disruption of the blood supply to the brain.
The Circle of Willis got its name in honor of the English physician and anatomist Thomas Willis, who became the first to describe it back in the 17th century.
Quite often, one or both vertebral arteries, which run along the lateral surfaces of the cervical vertebrae in a special bone canal, are affected. The main reason for impaired blood flow in them is pathobiomechanical changes in the cervical spine. They can lead to mechanical compression of the vertebral arteries and thereby create difficulties for the flow of blood through them into the circle of Willis and, accordingly, the brain. Also, with pathologies of the cervical spine, the cervical sympathetic nerve plexus can be irritated. This causes a spasm of the walls of blood vessels and also causes a decrease in their lumen, and therefore a decrease in the amount of blood entering the brain. In addition, when the nerves of the cervical plexus are irritated, limited neck mobility and acute pain are observed. All this together is called vertebral artery syndrome.
Thus, the cause of a decrease in the lumen of one or both vertebral arteries may be:
- functional blocks, i.e. the occurrence of a slight limitation in the mobility of the spine, including with osteochondrosis;
- instability in spinal motion segments of different locations of the cervical spine;
- tension in individual neck muscles, especially the anterior scalene and oblique muscles of the head;
- protrusion and herniation of the intervertebral disc;
- thickening of the atlanto-occipital membrane;
- bone growths, including those caused by uncovertebral arthrosis;
- spondyloarthrosis (a chronic disease accompanied by degenerative processes in the facet intervertebral joints).
Also, the cause of circulatory disorders in the brachiocephalic vessels can be atherosclerosis, i.e. the formation of plaques of different sizes in the walls of blood vessels, which also leads to a decrease in their lumen. In such cases, patients are found to have high levels of cholesterol in their blood. But often this is combined with disorders in the cervical spine.
In any case, if blood flow in the BCS is disrupted and vertebrobasilar insufficiency develops, the following may occur:
- headaches in the occipital, parietal and temporal regions;
- dizziness when turning the head;
- unsteady gait;
- visual disturbances;
- noise in ears;
- numbness of one half of the face;
- weakness, numbness of one or both hands;
- sleep disorders;
- fluctuations in blood pressure;
- heaviness in the head after sleep;
- deterioration of memory, ability to concentrate.
Often the vertebral arteries are pinched during movement, in particular turning or throwing back the head. Therefore, symptoms of cerebrovascular accident often occur after performing a trigger movement.
Dangers of cerebrovascular accident
For normal functioning of the brain, a large amount of energy is needed, which it receives from nutrients and oxygen delivered to its cells by blood. It enters the brain through 4 main or main arteries: 2 carotid and 2 vertebral. Therefore, if the blood flow in one of them deteriorates, it is possible to compensate for this due to the work of the remaining three blood vessels. But the body’s compensatory capabilities are not limitless.
Initially, when blood supply to the brain decreases, headaches, dizziness, memory loss and increased fatigue occur, which leads to deterioration in performance. After some time, patients experience more pronounced neurological symptoms, which already indicate multiple brain damage. And the reason for such phenomena is chronic cerebral circulatory failure, which is also called discirculatory encephalopathy.
Circulatory disorders provoke the gradual death of neurons (nerve cells) in different parts of the brain, which causes the development of neurological symptoms with a predominance of asthenic manifestations: weakness, irritability, sleep disturbances. This is often accompanied by depressive states, which may subsequently give way to apathy.
Once it begins and is not diagnosed in time, cerebrovascular accident progresses. During its course, there may be periods of sharp deterioration and gradual worsening of symptoms. The main danger of such phenomena is a sharp increase in the risk of developing severe diseases, one of which is a stroke or acute disruption of the blood supply to the brain.
Every year, strokes are diagnosed in more than 400,000 residents of Russia, and 35% of patients die within the first 3 weeks, and only 50% live longer than a year after suffering a stroke.
Types of ultrasound of cerebral vessels
Various techniques can be used to study cerebral vessels:
Doppler ultrasound
- used to assess blood flow in vessels, allowing to identify its nature and speed.
Duplex ultrasound.
This technique is a variation of the technique described above. Duplex examination allows you to visualize blood vessels, assess their condition, identify blood clots, plaques, aneurysms and other pathological processes. During this technique, the direction and speed of blood flow are also determined.
Triplex ultrasound.
With its help, an image of the arteries is obtained, colored in different shades, depending on the direction and speed of blood movement. The ophthalmologist can also set other parameters for staining - this opportunity is provided by a computer program. Ultrasound of cerebral vessels using triplex scanning allows you to obtain maximum information about the state of the circulatory system.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Which diagnostic technology will be chosen is determined by the specialist, depending on what parameters are important to him for diagnosis.
Duplex scanning of BCS
To assess the condition of the brachiocephalic vessels and the quality of their functioning, ultrasound diagnostics, namely Doppler ultrasound (USDG), is used. The method is based on an effect discovered by physicist Christian Doppler. The essence of the diagnostic procedure is that the ultrasound wave is reflected from different tissues with different intensities. This allows you to determine the density and homogeneity of the studied area of the body or an individual organ from the image displayed on the monitor of the ultrasound machine. Based on this, the correct structure of a particular tissue or organ and the quality of its functioning are assessed.
Doppler was able to develop special programs that were able to recognize ultrasonic waves reflected from moving objects, namely from erythrocytes, i.e. red blood cells. This discovery significantly expanded the capabilities of ultrasound diagnostics and made it possible to analyze the speed and direction of blood flow, as well as provide data on the quality of blood supply to the tissues and organs being studied.
The first and most important advance was the development of Doppler ultrasound, or Doppler ultrasound. It is used to assess and determine the characteristics of blood circulation and allows you to obtain a two-dimensional image of blood flow in the examined area, assess its speed, the presence of blood flow deficiency, and the nature of vascular resistance. The disadvantage of this method is the inability to assess the condition of the vessel walls, so it is usually prescribed to determine the effectiveness of treatment for an already established diagnosis.
Duplex scanning of neck vessels (USDS) has wider capabilities, so this type of diagnosis is used most often. With its help, it is already possible to study the structure of the walls of the brachiocephalic vessels, their course, as well as the characteristics of blood flow dynamics in real time. Therefore, duplex scanning makes it possible to accurately detect various circulatory disorders in the BCS at the early stages of development and select their most effective treatment. Although recently the concepts of ultrasound dopplerography and ultrasonic scanning doppler scanning have already merged into a single concept, and doctors themselves, when prescribing ultrasound of the vessels of the neck, mistakenly indicate ultrasonography and ultrasound doppler scanning, implying ultrasonography.
Ultrasound scanning is often used to study the arteries and veins of the neck in combination with triplex scanning of blood vessels. The latter method allows you to study the direction of blood flow, coloring it red and blue depending on the direction of movement: towards or away from the ultrasound sensor.
Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the neck and head, in particular the brachiocephalic vessels, can detect:
- wall-occlusive pathologies of blood vessels, i.e. leading to a decrease in their lumen or complete closure;
- level and degree of vascular lumen obstruction;
- deformations, tortuosity, abnormalities in the development of blood vessels;
- aneurysms (protrusion of walls) and vascular spasm;
- venous blood flow disorders;
- changes in the condition, elasticity of blood vessels and their hemodynamic significance.
An x-ray examination of the cervical spine is also prescribed.
The results of the study make it possible to accurately determine the cause of impaired blood supply to the brain and the appearance of other symptoms that bother the patient, assess the severity of existing changes and select the optimal treatment tactics. In the future, ultrasound examination is prescribed to monitor the dynamics of changes and evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy.
Possible contraindications
There are no contraindications to ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels. The exception is severe damage to the skin in the area being examined. In this case, the procedure can be postponed until complete healing.
Another nuance may be an allergic reaction to silicone, which is part of the contact gel. If you have already had cases of allergic reactions to silicone, be sure to notify the doctor who ordered the test and the doctor who will conduct it. A specialist may recommend taking antihistamines to reduce allergies, or purchasing another gel without silicone.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage of the diagnostic procedure is its high information content and 100% safety. Since the manipulation does not imply invasiveness, it has no contraindications. The study has other benefits:
- It doesn't hurt at all;
- Ultrasound does not cause discomfort;
- The ability to study both the physical state of blood vessels and their functionality.
One of the disadvantages is the low accessibility of blood vessels in certain areas of the brain for diagnostics using ultrasound.
What pathologies can be diagnosed?
Doppler ultrasound has certain limitations in diagnosing diseases. For example, she will not be able to study small veins - for this she needs to perform angiography. But there are a number of pathologies that can be identified:
- Atherosclerosis. By examining the head and neck using ultrasound, it is most often possible to diagnose atherosclerotic disorders. This condition is indicated by echogenicity, the presence of plaques, and thickening of the vascular walls. Moreover, if the lumen of the artery narrows by more than 20%, then the patient is diagnosed with “stenosis.”
- Thrombosis. Thrombosis is characterized by blocking of the arterial lumen by a blood clot. On Doppler ultrasound, inflammation of the vessel wall with a homogeneous formation inside is clearly visible.
- Compression of blood vessels. The examination allows you to see areas where blood flow is impaired due to the impact of swollen tissue on the channels. This allows you to diagnose cervical osteochondrosis and identify problems with blood circulation after injuries.
In addition, these ultrasound examinations can detect a number of other diseases, including vasculitis, post-traumatic dissections of the arterial walls and other pathologies.
Doppler ultrasound is a safe diagnostic method that can be performed in any case if there is a medical need for it. Timely implementation of the procedure allows you to identify the disease at an early stage of its development.
Preparing for the study
If you want to get the most accurate results, you need to properly prepare for the upcoming test. Let's consider the most important stages of preparation:
- Since we are talking about checking blood vessels, it is important three days before the upcoming procedure to give up alcohol, energy drinks and additives that can affect the functionality of blood vessels and the speed of blood flow;
- Try to completely relax and breathe freely at the time of diagnosis;
- Do not engage in sports or physical activity for at least 2 hours before the ultrasound.
- If you are constantly taking any medications, be sure to discuss this with your doctor. If it turns out that the pills affect blood pressure and blood vessels, the doctor may stop them for a day, or postpone taking the drug to a later time;
- 3 hours before ultrasound diagnostics you need to refrain from smoking;
- Before the procedure, long hair must be collected so that nothing interferes with the examination process.
If the examination is being carried out on a child, you should prepare him mentally. Explain to your child that this procedure is completely painless and does not cause discomfort, persuade him to lie still - movements during the diagnostic process can distort the results of the study.
Indications for the procedure
Doppler sonography is indicated in the following cases:
- Problems with coordination and other symptoms indicating a malnutrition of the brain (the patient is dizzy, has tinnitus, etc.).
- Unstable heart rhythm.
- Hypertonic disease.
- Transient ischemic attacks.
- IOP.
- Previous stroke or heart attack.
- There are suspicions of atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes.
- Fatigue quickly for no apparent reason.
- Cervical osteochondrosis.
This procedure is also indicated if heart surgery is to be performed, if there are pulsating formations in the neck, or if thrombosis is suspected. In children, it is performed in case of serious postural problems and delayed development of the child.
How to do an ultrasound of the brain
The person lies down on the couch, his head resting on a low pillow. The desired area of the skin is lubricated with silicone gel. In order to determine the nature and speed of blood flow, several sensors are attached to the temples.
If it is necessary to study the condition of the veins and arteries of the brain, the specialist suggests conducting Doppler sonography, during which changes in the displayed sound waves from moving blood cells are recorded. To carry out the procedure, the sensor can be localized in the forehead, back of the head or temples.
In total, the manipulation lasts no more than 40 minutes. Next, the patient receives the test results in hand and goes to the attending physician to decipher the results.
Features of ultrasound examination
As a rule, Doppler sonography is planned in advance, but it can be performed urgently. The procedure itself is painless, so patients tolerate it calmly.
The examination is carried out according to the following scheme:
- The patient lies on his back. The head should be relaxed (a flat pillow is placed under it).
- You need to remain calm, breathe evenly and, if possible, not move.
- A special gel is applied to the area under study to prevent the penetration of air between the skin and the sensor.
- The movement of the sensors is controlled by a specialist. As a result, an image of the vessels appears on the monitor screen.
The study lasts no more than 1 hour. During the study, the doctor may ask the patient to do some action: turn his head, squeeze a vein in a certain place, breathe less often, etc.
Dopplerography of extracranial vessels begins with examination of the right lower segment of the carotid artery. The sensor is then moved up the neck. Next, the color mode is activated, which makes it possible to identify a number of pathologies: deformations of the walls of blood vessels, impaired blood flow in certain areas, etc.
Decoding the results
A neurologist interprets the results of an ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels. In order to establish an accurate diagnosis, the specialist takes into account the characteristics of the cerebral vessels and the patient’s medical history, because some changes may be an anatomical feature unrelated to pathology.
If everything is normal, the results should look like this:
- the lumen of the vessels is completely free, various neoplasms are absent;
- turbulent blood flow is not present in the branching of vessels;
- the thickness of the vascular wall is less than 0.9 mm (sometimes 0.9-1.1 mm is also a normal option);
- absence of foreign inclusions, cysts and various neoplasms.
Please note that a diagnosis cannot be made based on ultrasound alone. The disease is determined by a combination of pathological factors, which are indicated by various studies.
Ultrasound of head and neck vessels
This is a modern ultrasound diagnostic method, which makes it possible to most accurately determine the condition of the neck vessels that supply the brain, shoulder girdle and arms.
The article was prepared by our ultrasound diagnostics doctor Irina Alekseevna Romadova.
When a person is prescribed a study of the brachiocephalic arteries (BCA), he has questions:
— what will he have to deal with?
- How effective is this method?
- isn't it harmful?
— and won’t this procedure cause discomfort?
What is ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck.
Duplex ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries (USD BCA) is a modern ultrasound diagnostic method that makes it possible to most accurately determine the condition of the neck vessels that supply the brain, shoulder girdle and arms.
These vessels are called brachycephalic. These include the carotid, vertebral, subclavian arteries and their connection, which forms the brachiocephalic trunk.
The BCA study allows the doctor to determine the presence of a violation of the blood supply to the brain , and to predict the likelihood of worsening the disease in the future.
Types of vascular studies
Vascular examination can be carried out in three ways:
- Ultrasound Dopplerography or Dopplerography . The research is based on the Doppler effect, named after the Austrian scientist Christian Doppler who discovered it.
- Ultrasound scanning or duplex scanning of the vessels of the neck and head is a combination of both the Doppler effect and B-mode (regular gray ultrasound image). That is, the doctor can evaluate the movement and speed of blood flow , as in Dopplerography, as well as the internal walls of blood vessels , deposits on them, the presence of atherosclerotic plaques, thickening, and developmental anomalies. With this method, two functions are examined at once, hence the name duplex. Ultrasound scanning shows a complete picture of the movement of blood through the arteries and veins, which makes it possible to make a more accurate diagnosis.
- Triplex scanning is a type of duplex assessment. However, it provides even more information because it uses the additional technique of color Doppler mapping. A color image of the movement of blood in the vessels makes it possible to more accurately determine changes in blood flow.
Unlike conventional ultrasound, which shows organs in a static state, Doppler ultrasound shows the movement of blood flow and its speed. This is made possible by the difference in speed at which Doppler ultrasound reflects and receives waves.
Undoubtedly, duplex scanning is the most modern research that provides a complete picture of changes in blood vessels. The ultrasound machine in our clinic belongs to the expert class and is equipped with all vascular programs. This makes it possible to most effectively visualize and evaluate pathological changes in the vascular bed.
Doctor's qualifications
We all know that the results of the study directly depend on the qualifications of the doctor performing the study. Our doctor Irina Alekseevna Romadova completed a full course of training in ultrasound angiology (examination of all vessels) at the Northwestern State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov, and masters all methods of vascular research. This is undoubtedly a big plus for our patients , because if there is damage to various vessels, then she can evaluate them all, besides, Irina Alekseevna is a former surgeon and is well versed not only in physiology, but also in anatomy .
Safety
Ultrasound examination is completely safe and painless for the patient. The use of this technique has no restrictions or contraindications. Ultrasound scanning can be used repeatedly, both for diagnosis and for monitoring the course of the disease at various stages of treatment.
What pathologies
The most common pathologies diagnosed with ultrasonography are:
- atherosclerotic lesions of the vascular wall
- vascular obstruction
- aneurysms
- deformations and abnormalities of vascular development
- dilation and incompetence of the venous bed
- thrombosis
- damage to the walls of blood vessels
The sensitivity of the method is very high , with ultrasound even minor, initial manifestations of atherosclerosis in the walls of blood vessels are visible, the identification of which will allow timely measures to be taken and prevent the formation of atherosclerotic plaques .
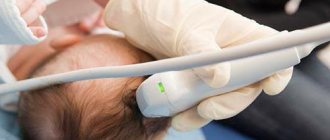
In some situations, it is necessary not only to examine the vascular bed, but also to evaluate the elasticity of the vessels, their elasticity, and ability to respond to changes in blood pressure and oxygen content in the atmosphere ( resistance ). For these purposes, the Carbonik , which is equipped in the ultrasound room at the Smart clinic. It has been clinically proven that with the help of a breath test using the Carbonik device, the most reliable information about changes in the resistivity of the vascular bed is obtained.
This photo shows the process of conducting a study of cerebral vessels with the Carbonik apparatus.
Who is this procedure indicated for?
As a measure to prevent serious complications of cerebrovascular accidents, such as stroke, BCA ultrasonography is recommended to be performed on individuals at risk at least once a year.
- People over 40–45 years of age.
- Patients with diabetes mellitus.
- Persons with a family history of stroke.
- If abnormalities are detected in the lipid profile.
- Patients with pathology of the heart and vascular system.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Patients with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
- Autoimmune vascular disease (hemorrhagic vasculitis)
This study is also indicated for all people with complaints indicating changes in the vessels of the neck.
- constant or recurrent headaches;
- migraine
- dizziness;
- sensation of noise or ringing in the ears;
- absent-minded attention;
- impaired coordination of movement;
- decreased vision;
- memory change;
- blood pressure problems;
- fainting;
- neck injuries;
- condition after a heart attack or stroke.
Preparing for the study
BCA ultrasound does not require , but on the day of the examination it is better to exclude from the diet foods that can change the tone of the vascular wall, such as coffee, strong tea, alcohol, energy drinks, cola. It is advisable to refrain from smoking two hours before the test. If you are taking medications that affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system, be sure to tell your doctor.
Carrying out the procedure
The procedure takes about 30-40 minutes, the patient lies on his back, the chin should be raised up and slightly turned in the direction opposite to the one being examined. The doctor may press a little on the patient’s neck during the examination, but in general this does not cause any discomfort. Our clinic has a “ platinum ” version of the device, including a device for heating the gel , which makes the procedure even more comfortable. The ultrasound scanner will record all the indicators, and the doctor will enter them into the study protocol.
Summary: Duplex ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries is accessible and effective diagnostic method. In addition to high resolution, the method is absolutely safe . The Smart Clinic has an expert level ultrasound machine installed, and our doctor, Irina Alekseevna Romadova, is an experienced specialist, which together gives our patients timely and effective diagnosis, and therefore, subsequently, the correct treatment.