Features of the nervous system
The psyche and body of the adze are interconnected. Any change in one system leads to changes in another. All this is reflected in the internal state. In neurology there is a separate direction - psychosomatics, with the help of which it is possible to establish a certain connection between mental reactions and their impact on human physiology.
As soon as a person becomes depressed or experiences stress, a protective reaction of the body immediately occurs - muscle tension. The body is constantly in tension, while the soul calms down. If such situations happen very rarely, then nothing harms the body.
But if this becomes regular, a psychosomatic illness may appear, which is difficult to identify. Physical ailments begin to actively manifest themselves, and the psychological causes are “deeply” hidden. As a result, doctors can spend years eliminating the effects without knowing exactly the main cause.
All processes inside the body occur smoothly and smoothly, controlled by the central nervous system. But if there is a chronic focus of excitation in the brain, which is caused by negative emotions, the nervous system no longer performs its main function.
When the body is left without a commander-in-chief, failures gradually occur that lead to the collapse of the unified system. The work of every organ is disrupted. As a result, a person develops diseases of the heart, stomach, etc. In addition, other ailments appear: poor appetite, insomnia, apathy, irritation, lack of interest in what is happening and in one’s life. In addition to the body, the psyche suffers. A feeling of anxiety and restlessness appears. From this observation it is clear why the nerves and psyche need to be strengthened. There are a huge number of special techniques for this, which are divided into 2 main groups: for the psyche and the body.
Stress bath
The bathhouse is a wonderful source of strength and positive emotions. We have already talked about it, but its importance is simply invaluable. Bath procedures will help you relax, get rid of stress and put your body in order. We have already spoken more than once about the fact that our emotions and the state of our body are connected. The pleasant muscle relaxation provided by the sauna brings peace of mind, calms the emotions and psyche. Water washes away dirt not only from the skin, but also from the soul.
In the bath, toxins and stress hormones are removed from the body. Tea made from dried berries and raspberry leaves, chamomile flowers and mint leaves will enhance this cleansing.
No good bath is complete without the use of a broom. As a “cure” for stress, you should use a birch, juniper or oak broom. In order for the procedure to be as pleasant as it is useful, the broom must be steamed. Broom does not like boiling water; he steams it with hot water an hour before the procedure. Before using a broom, you need to warm up your body in a steam room. Then, lightly patting the body with a broom, “walk” over the arms, legs, and torso. Gradually increase the strength of the pats. After the procedure you should drink tea with honey. This will help induce increased sweating. While resting from the steam room, you should wrap yourself in a terry towel to increase sweating. The number of approaches depends on your desire and the condition of the blood vessels.
A cosmetic procedure will bring a positive charge. After the steam room is the ideal time to use a scrub. As a scrub, you can use a mixture of honey and sea salt (1:1). By rubbing the body with a scrub, all deposits are removed and the pores open. After the scrub, you can visit the steam room again, applying a broom to your face, thereby creating the effect of an aromatherapy treatment. Finally, green tea with honey. After the bath you need a good rest. A full trip to the bathhouse helps cleanse the body of toxins, reduce weight up to two kilograms, and facilitate the functioning of the kidneys and vascular system. But the most important thing is that after the bath, the bad mood “goes away”, and peace and tranquility takes its place. After the bath, sleep and memory improve.
Body strengthening
To restore your body and mind, you need to follow simple tips:
- Physical activity has a positive effect on the body. Constant movement, sports and other physical activity have a positive effect on the condition of the body, and, consequently, the nervous system improves;
- control your diet. The body must receive the required amount of vitamins, minerals and other beneficial substances found in food products every day;
- rejection of bad habits. Despite the fact that many are accustomed to starting the morning with coffee and a cigarette, this habit should be forgotten. It’s better to completely give up all bad habits, such as alcohol, cigarettes, stimulants. The excitement that occurs due to receiving a dose of nicotine is quickly replaced by an inhibitory reaction;
- sauna and bathhouse. Such methods help cleanse the body and soul. Elevated temperatures and hot steam together help cope with many diseases, the body and nerves relax;
- harden. Water has a positive effect on the nervous system. If you harden yourself, you can strengthen your immune system. It invigorates and strengthens the body. There is a more extreme way to harden yourself - winter swimming. It may seem strange, but the health and calmness of walruses can only be envied. If you go down into an ice hole, your body will be very grateful;
- drink as much water as possible. Many people know the 8 glasses method. This is how much water a person should drink per day. This cleanses the body well, removing toxic substances;
- massage. A great way to get rid of many ailments and relieve stress. The body gradually loses its flexibility, the joints become less mobile. A good massage will speed up blood circulation and trigger metabolic processes.
General tips for recovering from stress
Prolonged stress contributes to the occurrence of diseases, initially of a functional nature, and then more serious. For this reason, quick relief from severe stress will help save the body from health problems.
- And so, the first way to recover from stress is to get good, long sleep. After experiencing stress, it is important to relax. This is what sleep is designed to help with. You need to sleep as long as possible so that you get tired of sleep.
- Immediately after stress, it would be nice to take a walk in the fresh air. It is better if this walk is long, allowing you to enjoy the healing air and the beauty of nature.
- After severe stress, a saline solution of one teaspoon of salt and half a liter of slightly cool water will restore peace of mind. This solution should be rubbed all over the body during the day and not washed off for two hours.
- Smile more often. Make it a habit to start your day with a smile. During the day, smile at your friends; if smiling is not appropriate, smile mentally. In the evening, as you prepare for bed, smile your most sincere smile at your reflection in the mirror.
- Clean up the house, sort out things in the wardrobe, in the workplace. There is an opinion among psychologists that in this way you can “put things in order” in your head.
- Immediately after stress, no later than 15 minutes, draw your emotions using colored pencils and burn or tear the “masterpiece.”
- After stress, a hobby will help you regain your strength. Surely there is some activity that you have only dreamed of: crocheting an openwork collar, carving a horse figure out of wood, learning to dance tango or swim. Thus, you abstract from stress and set new goals, albeit not on a global scale.
Proper diet
Nutritionists have developed a special diet for those who want to stop being nervous and start enjoying life. If the body lacks potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus and iron, then the nervous system and the entire body will suffer. It is especially important to ensure that the body receives the required amount of magnesium.
- You need to eat buckwheat, oat and wheat porridge more often.
- Phosphorus relieves muscle tension and stabilizes the functioning of the nervous system. The trace element is present in milk, cereals and beans.
- Calcium – regulates the functioning of muscles and nerves. Contained in milk, nuts and cabbage.
- Iron – contributes to the normal functioning of the thyroid gland, ensures normal metabolic processes. Present in seafood, river fish, fruits, green vegetables, baked goods.
- Potassium – normalizes the smooth functioning of nerves and muscles, prevents stress and nervous breakdowns. The lack of microelements can be compensated for by vegetables, fruits, lean meat and fish, and dried fruits.
How to strengthen the nervous system and psyche, stop being nervous over trifles
Nervousness, irritability, internal tension, irritable weakness, anxiety, sleep disturbances, decreased performance - these are the flowers that almost each of us encounters with varying frequency.
Not everyone gets berries in the form of chronic diseases of the nervous system, internal organs and psyche, narrowing of social contacts or isolation, but they still exist. And all this vinaigrette, seasoned with the light, crazy flair of modern life, is now commonly blamed on chronic stress. Let's try to figure out what it really is, what it is eaten with, and how to get rid of it effectively and painlessly.
When love leaves, the blues remain
- During the time of the ancient Greeks and other Hippocrates and Galens, all human behavioral characteristics were explained by the presence of a predominance of one of the four bodily fluids, which determined the type of temperament. There is a lot of lymph in a person - he is slow and calm, bile predominates - he is aggressive and hysterical if it is yellow or gloomy and gloomy if it is black. And only blood makes its owner cheerful and active.
- Later, everyone suffered from spleen and blues interspersed with hysterical fits. From them they went to the waters, shot themselves, went to the active army and drowned themselves. What serfs, European guild workers and American Indians did at this time in cases of life difficulties is not known for certain. It seems they drank bitters and smoked in their free time from back-breaking plowing.
- A little later, enterprising psychiatrists Freud and Jung explained everything by the suppression of the ego by a ruthless environment and public opinion and took up the emancipation of the suffering Self, one at great expense, and the second at a very high cost, successfully covering the whole of Europe with their psychoanalysis.
- The subsequent world wars, however, proved that in comparison with the world revolution, female hysteria was complete nonsense, and led scientists to a more detailed study of the theory of stress, since the representative sample of those who came from the war fields was very decent for a whole century.
What kind of bitch nerves do they have, and why don’t we have these nerves?
The theory of stress tells us that the body defends itself from any external factor that we perceive as an irritant and a violator of the constancy of our internal environment by mobilizing all regulatory systems. Since it is vital, first of all, to avoid death, the system of catecholamines (adrenaline and norepinephrine) and cortisol is activated, working within the framework of the “fight-flight” paradigm. It is responsible for raising blood pressure, increasing heart rate and breathing.
The meaning of stress is to allow the body to adapt to the changed external world and maintain the constancy of the internal environment, even against the background of infection or injury, even against the background of negative emotional influence from the outside. Whether you're sick with the flu or your boss yelled at you at work, your body needs to mobilize some of its potential to restore balance. That is, stress is not just emotional excitement or irritation, but an adaptive mechanism.
Chronic stress leads to depletion of the body's adaptive capabilities. The system starts to glitch. Instead of an adequate prompt response, paradoxical reactions appear:
- heartbeat at rest from bad thoughts
- or shortness of breath from a heavy foreboding,
- heart rhythm disturbances,
- sweating,
- fear of death,
- pallor of the skin from habitual exercise,
- muscle tension at rest,
- dry mouth,
- spasms in the stomach and intestines.
The main thing here is not to miss the signs of real diseases, which are practically indistinguishable from vegetative storms without additional diagnostic methods. But if everything has been checked more than once, and the suspicion of illness still persists, obsessive-compulsive neurosis is highly likely to occur.
Consequences of stress
- subjective (anxiety, aggression, weakness, fatigue, low self-esteem, bad mood),
- physiological (rising blood sugar, blood pressure, dilated pupils, feeling hot or cold),
- behavioral (risk of accidents, alcoholism, emotional outbursts, substance abuse, smoking, overeating), cognitive (weakened attention, decreased mental performance).
The mechanisms of stress development, adaptation to it, and failure of adaptive capabilities are almost identical for all people.
Only the threshold of perception is different. What is an ordinary trifle for one person is a whole tragedy for another.
Variants of group stress are also possible, when groups of people find themselves in unfavorable similar conditions. Moreover, the higher the load to achieve adaptation to difficult conditions, the more likely people react to it.
The study of stress resistance of different population groups and individuals allows for predictive diagnostics, identifying those who, under stress, are likely to react inappropriately or atypically and who are not shown types of work with high requirements for stress resistance.
More than half of the Russian population constantly live under stress. Up to 80% of them develop chronic fatigue syndrome and feel unwell in the morning, have problems falling asleep and sleeping at night, and have difficulty coping with physical and mental stress during the day
Physical manifestations of stress
- Decreased ability to concentrate.
- Irritability, bad mood.
- Sleep disorders.
- Growing appetite.
- Deterioration of organizational abilities (fussiness, absent-mindedness).
- Lethargy, apathy, fatigue.
- Sexual disorders.
- Increased anxiety.
- A feeling of an insurmountable obstacle or crisis.
- Feeling out of control.
- Poor health (muscle pain, headache, heartburn, increased blood pressure).
And now about panic
A panic attack is a rather painful complex of manifestations of autonomic disorders, which can be provoked by anything. That is, it is an unreasonable fear, triggered without objective signs of danger and in the absence of real pathologies of internal organs. The most popular triggers are: being in a cramped or stuffy room, climbing to a height, and indeed any discomfort in the body.
Predisposed to the following attacks:
- genetics,
- psychotype,
- emotional stress,
- chronic stress,
- experience of using psychotropic drugs.
At the moment of panic, a person may experience a feeling of lack of air, palpitations, pressing pain in the chest without connection with the load, trembling, sweating, heat or cold, tingling of the skin or crawling goosebumps, dizziness, nausea, a feeling of the unreality of what is happening. The fear of death from heart problems or stroke comes first.
What to do
- If chest pain, palpitations, sweat, shortness of breath occur for the first time, a call to the emergency room is indicated to rule out a life-threatening condition.
- If episodes recur, it is wise to consult a physician to rule out chronic diseases of the heart, lungs, or endocrine system.
- In the absence of such pathologies, do not neglect a visit to a psychotherapist or psychiatrist.
- Stop waiting for an attack, since listening to yourself responds to any slightest irritant with a release of adrenaline into the blood, which triggers panic.
- Taking sedatives or beta blockers that slow down the heart rate is a way to only temporarily eliminate symptoms. They do not fight the cause of panic, and besides, sedatives, for example, Corvalol, which contains the barbiturate phenobarbital, are easy to get used to.
- In severe cases, specialists prescribe antidepressants. It is better not to start taking tranquilizers that can cause severe addiction after only 3 weeks of use.
- Cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy and auto-training should be aimed at creating attitudes that a panic attack is not dangerous to physical health and it is quite difficult to die in the process. By supporting all this with breathing exercises, walking and meditation, you can achieve quite acceptable results.
Physiology
If you look at a person from the point of view of primitivism and analyze him as a visual biological model, it will become obvious that the nervous and endocrine systems are simultaneously responsible for his full functioning in a changing external environment.
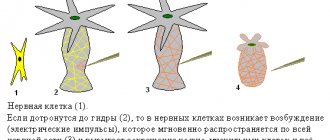
The nervous system is represented by:
- Central part (brain and spinal cord). In the cerebral cortex, the neurotransmitters dopamine and serotonin are responsible for emotionality and mood.
- Periphery in the form of nerves and nerve ganglia. Here the reception of external irritations, their implementation, processing and issuance of a response occurs. The main types of response are the conduction of an electrical impulse along a nerve fiber and a chemical process in synapses with the participation of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
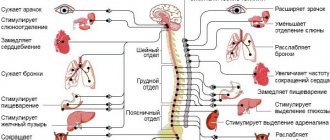
- There is also a vegetative part - these are like automatic transmissions or autopilots for the heart, breathing, and digestion. Only yogis can control this with the power of thought, but an ordinary healthy citizen does not need this.
The endocrine system, with the help of hormones entering the blood, regulates body temperature, energy, plastic metabolism, the functioning of the cardiovascular, reproductive, and digestive systems, and also interferes well with the functioning of the brain. Emotions and nervous tension are most actively influenced by adrenal hormones (adrenaline, norepinephrine, which are also neurotransmitters, and cortisol), sex hormones, and thyroid hormones.
Therefore, if a person complains of excessive irritability, mood instability, especially in combination with fatigue, sweating, weight loss, he is checked for the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH alone or in combination with T4-thyroxine) to exclude increased activity of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism).
For women, fluctuations in the background of sex hormones are a completely separate issue.
And this is not only the notorious PMS, which turns a quiet office woman, an easy-going girl or a respectable mother of a family into a fury, sobbing and screaming at the same time, but also the emotional instability of pregnant women and irritability, coupled with vegetative symptoms in women during menopause. By the way, not only women in menopause, but also men in a testosterone crisis are at risk of becoming characters in jokes. Their moods can also change ten times a day, and this is not at all a sign of their bad character.
- Dopamine
Its peak, as all readers of women's magazines know, for women occurs in the middle of the cycle - this is generally a paradoxical thing. On the one hand, if a lot of it is produced in those parts of the cerebral cortex that are responsible for reward motivation, then the person is overwhelmed with inspiration and can work tirelessly. If in the insula, which covers part of the frontal and parietal lobes and is responsible for emotions, the person experiences an aversion to all types of physical or mental labor. That is, a low level of dopamine in general is a lack of anticipation of joy as such from any type of activity, from making money to sex. In other words, dopamine is the anticipation of a high and the engine of creative progress, interest in learning and conquering new frontiers.
Prolactin is responsible for the high itself, and oxytocin is responsible for attachment. Dopamine is the opposite of prolactin, and when there is a lot of it, a person begins to look for adventure and his brakes fail.
It’s interesting how neurotransmitters work in the process of emotional burnout, when an enthusiast who is literally burning at work or in any field of activity is left with only horns and legs emotionally, and he himself becomes first apathetic and then completely aggressive at the mere suggestion of doing something once a favorite activity.
- First, at the stage of interest in a new business, a dopamine surge is formed, provoking enthusiasm.
- Then, when the novelty has worn off, a smooth dopamine plateau allows you to plow without stopping and get everything done. When work consumes all our time, and there are no new impressions, positive emotions, and time for sleep, food, and communication with loved ones is saved, dopamine tells us “bye,” and first a slight, and then more and more confident irritation with the world around us appears. Adrenaline and cortisol levels are high here.
- And then comes drowsiness, a sharp decrease in working capacity, and a feeling of anxiety due to loss of control over the situation.
- Later, intolerance, aggression, and indiscipline are added to this. And these are already undoubted signs of exhaustion.
- Serotonin
But the feeling of quiet happiness is already serotonin, this is prolonged satisfaction with life. It is serotonin that says that everything is fine and let it always last as it is. Serotonin is blocked by dopamine. And chronic stress blocks both mediators.
Therefore, after a breakup, the one who switched to a new object, impressions or interests is warmed by the rays of dopamine and on the rise, while the one who remained in the position of the sufferer has lost both serotonin well-being and dopamine short-term anticipation of pleasure.
Goals and objectives
We needed the entire previous dreary excursion into neurophysiology solely in order to clearly define the strategy and tactics in the fight for calm nerves and a balanced nervous system.
The goal is already clear to us: to calm down and stop being nervous over trifles. It remains to show persistence in achieving it.
Leaving outside the scope of all issues related to major psychiatry, let's talk about the hygiene of the nervous and endocrine systems, as well as practical skills for bringing your emotions and psychological status into a divine form.
Statistical calculation
Dear Russians, get rid of stress with the following simple and affordable folk remedies:
- 46% watch TV,
- 43% listen to music,
- wash down stress with about 20% alcohol,
- seize -16%,
- relieve tension through sports 12%,
- sex – 9%, while more than half of those surveyed in sociological surveys note the negative impact of stress on their sex life.
How not to destroy the endocrine system ahead of time
Like other adherents of a healthy lifestyle, we strongly recommend not to test your body’s strength, but to wisely exploit the resources given at birth. Of course, if you inherited early menopause or a low level of production of endogenous opiates, the person is a victim of circumstances and is forced to make more efforts than others to live a full life. But, if initially everything with the hormones was in perfect order, there is no need to do everything to make the system fail.
- Get enough sleep
Tales about Napoleon, who slept for four hours and was distinguished by his bright head and remarkable capacity for work, should not confuse you. Our hormones are produced in a certain daily regime and are quite dependent on the time of day. Focus on your own needs (see why it is so important to maintain a daily routine). If your body is screaming that getting up at six in the morning is unrealistic, try to understand it: perhaps your adrenal glands produce cortisol not at 4-5 in the morning, like a person who easily gets up at half past six, but with a delay of couple of hours. This is very common for those receiving glucocorticosteroid therapy.
Lack of sleep of just one hour a day in the short term reduces the ability to concentrate and remember information. In the long term, it threatens problems with cerebral circulation, the cardiovascular system, diabetes mellitus, and immune disorders (see lack of sleep increases the risk of heart attack and stroke).
In 2007, a University of California study was published on the effects of lack of sleep on emotionality. The results were disappointing: the emotional centers of the brain of the sleep-deprived subjects reacted 60% more actively to the negative images shown. That is, lack of sleep leads to an irrational emotional response to the world around us.
- Go to bed before 24 hours
It is known for certain that people suffering from neuroses (and especially neurasthenia) feel worse in the evening and at night. If you are accustomed to anxiety, suspiciousness without objective reasons, night terrors, episodes of self-pity and chronic resentment towards others, go to bed as early as possible. In addition, neuroscientists say that falling asleep before midnight allows the brain to rest better.
The habit of falling asleep early will also get rid of the addiction to eating your negativity at night with sweets and fatty foods.
- Physical activity
- Walk for at least an hour every day (see Nordic walking).
- Sleep in a ventilated area. Oxygen starvation of the brain is a poor assistant in regulating emotions.
- The paths of healthy lifestyle and sports diverge at a certain stage. Sport should be more like physical education with dosed exercise without stimulants, hormones and diuretics (see lazy people live longer).
- Sex is a good option to relieve stress if it is not a long-distance race and does not give additional reasons to be nervous and worried.
Smoking is absolutely not recommended, as a potential culprit of a large number of somatic diseases and vegetative disorder.
- About nutrition
- Do not neglect iodized products (milk, salt) if you live in areas where there is little of this element in the water. Lack of iodine leads to decreased thyroid function. The result of this may be weakness, lethargy, decreased ability to work, fatigue, depressed emotional background, and bad mood.
- Don't overeat. Control of eating behavior is not fasting or mono-diets, but balanced meals three to four times a day in small portions.
- Products that strengthen the nerves are lean meats, beef liver, fish and seafood, unpolished cereals, cottage cheese, bananas, herbs, citrus fruits, asparagus.
- Synthetic vitamins today have a very narrow range of use for laboratory-proven hypovitaminosis. In addition to vitamin D in northern latitudes, it is better not to use vitamins in preparations for preventive purposes. Vitamins that strengthen the nervous system are group B, ascorbic acid, PP and vitamin D3.
Physical anti-stress barrier
- Water treatments
They are able to normalize the tone of the nervous system due to temperature and reflex mechanical effects. Even at home today it is quite possible to take advantage of a relaxing bath, hydromassage or contrast shower. It is traditionally believed that a bath relaxes, and a shower tones the nervous system.
- In everyday life, baths with a water temperature of 35-37 degrees Celsius are shown. It makes sense to add solutions or decoctions of herbal sedatives (valerian, motherwort) to the water. The duration of the bath is from 15 minutes to half an hour.
- Among the physiotherapeutic variations of baths, pearl ones are known (with hydromassage, creating the effect of many bubbles). The massage effect can be achieved through the flow of water or air, which allows you to eliminate muscle tightness and not worry about trifles.
- For depressed states, chronic fatigue syndrome and a tendency to depressive disorders, starting with the French neurologist Charcot, contrast showers are used in different versions. Its purpose is to stimulate and relax certain areas of the skin with a water jet of different temperatures, training blood vessels and nerves to adequately respond to stressful needs.
- Bath
This is not just an antediluvian variation of temperature stimulation of the skin, but also an entire ritual that allows a person to tune in to cleansing the soul and body and getting rid of everyday negative emotions (see the benefits and harms of baths and saunas). Combines physiotherapy and meditation.
- Hardening
This is a stressful variant of temperature exposure. Trains the body to respond adequately to cold stress. mobilizing all possibilities. With long-term practice, it leads to a paradoxical vascular response: instead of spasm, the vessels respond to cold by expanding their lumen. You need to start hardening yourself gradually, first by giving up indoor shoes. Gradually moving on to dousing with cool water and doing gymnastics in the fresh air. Terminal hardening options: dousing with ice water in the cold, swimming in an ice hole and walking barefoot in the snow.
Physiological wrestling techniques
- Breathing exercises
This is the simplest and most effective method of controlling autonomic reactions. Strelnikova’s breathing exercises give good results.
The most popular and well-known system of breathing exercises is the Buteyko method, whose adherents claim that they were able to get rid of even bronchial asthma and use forced breathing for any reason. In general, any exercise to prolong exhalation can reflexively reduce the heart rate due to inhibition of the sympathetic nervous system. Also, breathing more rarely or deeply can calm and strengthen the nerves. To do this, you need to alternate a short inhalation with an extended exhalation and pauses after it.
- The formula for relaxing breathing, where the first number is the duration of inhalation in seconds, with the “+” sign is the length of exhalation, and in brackets is the pause between breaths: 2+2(2), 4+4(4), 4+6(2) , 4+7(2),4+8(2), 4+9(2), 5+9(2), 5+10(2), 6+10(2), 6+10(3), 7+10(3), 8+10(3), 9+10(4), 10+10(5).
- It is useful to take several exhalations through tightly compressed lips or long exhalations with an open mouth for the combination: “ho” or “he”.
- Rhythmic walking will also help establish a rhythm for proper breathing. For four steps you need to take a full breath, for the next two you need to hold your breath, for the next four you need to exhale completely.
- You can also perform gymnastics while lying down or sitting against a wall with a straight back.
- Lie on the floor, place your arms extended along your body, palms down. Breathe relaxedly for a minute, then take a maximum breath and hold your breath for 4 seconds, then exhale as much as possible, trying to push all the air out of your lungs. Do five approaches.
- Massage
A relaxing massage is preferable, including stroking, rubbing, and very light kneading of the extensors of the limbs. Therapeutic massage for the spine and vibrating massage for the chest. In addition to professional general or therapeutic massage, self-massage is indicated. For muscle spasms, you can use shaking the limbs (with or without holding the fingers). The fine vibration allows the muscles to relax successfully.
Relaxation practices may include:
listening to your favorite music,
aromatherapy,
yoga practices,
swimming pool, etc.
Psychological help
Since we have found out that anything can trigger anxiety and nervousness, and some of those suffering from neurasthenia even independently adapt external factors to their needs, then psychological training should move along two paths.
- Take control of circumstances.
- Soften the perception of traumatic factors and reduce their significance.
Thus, first you have to admit to yourself that the problem exists. And it’s not that as a child, dad used a belt, and mom was dissatisfied with her academic performance, that she wasn’t appreciated at work, and her loved one turned out to be a petty creature. There are many circumstances and they are everywhere, and a neurotic personality is ready to respond to any message from waiting for the end of the world to a rumbling stomach.
Since childhood is behind the horizon, you will have to take responsibility for your life without dumping it on your parents, spouses, loved ones, young offspring or random people around you. With such a perception, they cannot be to blame for all the misfortunes that happen to us. Maybe just a little bit, which we will also control.
- If possible, we will immediately stop communicating with everyone who is unpleasant to us. Or let’s reduce this communication to the necessary minimum in the most correct and neutral form: “Yes. No. Thank you. Sorry". And this will be our spacesuit against unpleasant people, and they will not be able to break through it.
- Assertive behavior is polite firmness. Allows you to correctly defend your interests and adhere to your line of behavior even under the pressure of external circumstances.
- Solving problems as they arise. We will stop waiting for something to happen at any moment that will justify our hopes for some nasty gift of fate. And we will solve problems as they arise. Now and today. The past will have to wave its hand and stop delving into it. Plans for the future should be plans, and not an attempt to find another reason to get excited.
- Imagine the worst possible outcome of the problem. If we are starting to worry, we should go all the way and think about the worst-case scenario. Then think about whether it is so scary and what can really be done to prevent this from happening.
- Learn to set goals and objectives. "What I want?" and “How to get it?” - quite reasonable questions to ask yourself that will help you develop an action plan and reduce the degree of neuroticism from not understanding what to do in the future.
- To stop worrying about your health, get a check-up and repeat the tests no sooner than your doctor recommends. By adhering to a healthy lifestyle, you will reduce the risk of developing serious pathologies, and non-serious pathologies can be treated or go away on their own.
- Write down everything that worries you on paper and, for each item, make a plan of real actions that will help get rid of the problem. It will be immediately clear where it really exists, and where they have made a mountain out of a molehill.
- Keep yourself busy with something interesting, something you love, something that brings you pleasure—a hobby. A passionate person has no time to delve into himself. He's just busy. Be aware of dopamine peaks, plateaus and declines. Give yourself a break and switch.
- Try to evaluate things and events correctly. Try to approach your assessments objectively. Many values cease to be so over time. Is it worth killing yourself and those around you for the sake of them?
- Accept yourself. If only the smartest, most beautiful and successful people actually reproduced, the Earth would not face the problem of overpopulation. Nature came up with everything much more cunningly than we thought. We are controlled by hormones and transmitters that are triggered for any reason, almost like our anxiety.
- Get rid of guilt. You do not have to be responsible for other adults and independent people. Let them solve their problems themselves.
- Reduce the significance of episodes that bother you. Don't get hung up. Switch your attention.
- Don't expect much from others and don't be afraid of their opinions.
- If no self-administered measures work at all, contact a professional medical psychologist, psychotherapist or psychiatrist.
Techniques
- Meditation
One of the most effective calming techniques that anyone can learn would be desire. Meditation is focused thinking that comes from Hinduism. More often it is a spiritual or health practice with elements of self-immersion with the goal of achieving perfection or, at least, peace.
It involves detachment from external stimuli by adopting a certain body position, listening to relaxing sound stimulants or music that help control concentration on sensations or internal visual images. In general terms, this is detached contemplation, which allows you to reduce the significance of external stimuli, stop being nervous and become calm.
- Faith
In difficult life situations, often turning to faith helps a person get support in a situation where secular methods do not work. The church provides an opportunity not only to find solace and an opportunity to cope with psychological trauma, but also offers socialization, which in a secular society is quite difficult for certain categories of people.
- Autotraining
This is a set of exercises for developing positive attitudes. Self-hypnosis aimed at relieving mental and physical stress without outside help. Combines with muscle relaxation techniques. For example, with breathing exercises. At the initial stages, the patient is asked to learn the state of warmth in the limbs, heaviness in the legs, achieving them independently by repeating certain speech settings. In the future, it is proposed to learn how to evoke vivid visual images or a contemplative state with closed eyes. The technique is aimed at creating a supportive state or reducing the significance of irritating factors.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy
This is a psychotherapeutic practice aimed at getting rid of stereotypical perceptions of reality and psycho-traumatic factors. It is important here that the work is carried out by the psychotherapist and the patient, whose active participation is mandatory. During therapy, it becomes clear what circumstances provoke the problem, which provokes uncontrollable thoughts. How this affects the patient in terms of beliefs, experiences and behavior. At the same time, situations and provocateurs that trigger the alarm are gradually recorded. The psychotherapist proposes a program of work on correction. Most often, it includes specific exercises that should be performed in a traumatic situation and are aimed at reinforcing new skills to combat anxiety. The goal of therapy is to change behavioral patterns and emotional states.
- Pets
Do not neglect the advice to seek help from your pets. First of all, this applies to aquarium fish. Observing them works better than any psychorelaxation technique.
All methods presented in the article can be considered both in combination and separately, depending on existing contraindications or preferences. Humanity has accumulated vast experience in the fight against nervousness, which you can only use in your own particular case.
What is a nervous breakdown?
Nervous breakdown is not a medical term and does not indicate a specific mental illness or condition. But this does not mean that such a condition is normal or physiological and does not require the organization of high-quality assistance to the person. On the contrary, such conditions require the organization of high-quality medical care with a complete diagnosis of the state of the nervous system.
Such a person’s description of his condition may indicate hidden mental health problems, and often requires particularly increased attention and even urgent medical attention. Since it is against the background of a nervous breakdown that various, more complex mental disorders can form. Signs and symptoms of a nervous breakdown or burnout syndrome are a sign that you have exhausted your mental and physical resources, they are depleted and require outside help. Burnout syndrome does not mean that you are crazy! Regardless of the symptoms that appear.
This is a turning point, a borderline moment. How your nervous system reacts, will it be able to withstand such large overloads. If you manage to help your brain in time and correctly, so that no mental illness begins to develop.
We hope that we can help you understand what happens at such turning points with the human nervous system.
Signs of a nervous breakdown always vary from person to person and depend on the cause, psycho-emotional status, culture, education and gender.
The concept of a nervous breakdown does not generally mean that a person is no longer able to function normally.
Burnout syndrome
On this page we take the position of the common use of the expression “I’m having a nervous breakdown” and from the position of many years of medical practice we will reveal this concept.
You've probably heard of burnout syndrome and wondered what it is? So let me explain. This is a term coined by psychologists to denote a state of exhaustion of nervous activity. This condition is popularly described as a nervous breakdown.
You may feel like you're going crazy right now, but you're not. These are just your sensations that are formed by the brain. We can help you recover. But this will not happen overnight, it will take some time.
The term "nervous breakdown" is sometimes used to describe a stressful situation in which someone becomes temporarily unable to function normally on a day-to-day basis.
This is usually well understood when the demands of life become physically and emotionally overwhelming. In the past, the term covered many different mental disorders, but is rarely used today. More often it is used in everyday life and implies a certain psychophysical discomfort of a person, and not a specific mental state.
Irritation and discomfort
When we are nervous, we begin to get lost, when we are lost, we become nervous. You need to be able to break this vicious circle. Make it a habit to breathe deeply whenever you feel irritated. This will help you calm down quickly enough to make the right decisions.
Pay attention to yoga. This activity is designed to ensure internal harmony, and this is precisely what is lacking in people exposed to stress. A few tens of minutes a day, and you are already quite capable of controlling your emotions and easily escaping discomfort. Breathing techniques, correct postures and thoughts are all aimed at enabling you to achieve absolute calm.