What are the main manifestations of MIA-Lambert-Eaton syndrome (MLES)?
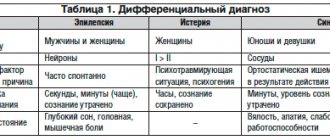
The main symptoms of MSLI are weakness and pathological fatigue of the proximal muscles, hip muscles and pelvic girdle, weakening or loss of tendon reflexes. Muscle strength and tendon reflexes can increase for a short time after physical activity (post-exertional relief). Although ptosis may occur in MSLI, the extrinsic oculi and tabulus muscles are usually minimally affected. Moderate autonomic dysfunction may be observed, which is primarily manifested by dry mouth.
Read also
Rehabilitation after stroke
It is very important to begin rehabilitation after a stroke as early as possible, since further recovery and the ability to avoid disability depend on this.
For rehabilitation after a stroke in the clinic “First… Read more
Myasthenia gravis
MYASTHENIAS – a disease associated with a disruption of the immune system, as a result of which antibodies are produced against the body’s own tissues involved in the transmission of nerve impulses, which...
More details
Sudden memory loss/transient global ischemia
Transient, that is, temporary memory loss occurs in elderly patients and people suffering from migraines. At the same time, memory for past and present events disappears. But the person is conscious, accessible...
More details
Sports injuries
Contrary to the popular belief that all athletes are completely healthy people, this particular group of patients is subject to colossal physical stress on various organs and systems, which...
More details
Weakness and numbness in the arm and leg
The appearance of general muscle weakness and numbness in the body, arm or leg is a very serious syndrome, and if it occurs, you should consult a neurologist as soon as possible. Connected…
More details
What tumor is associated with MSLI?
Approximately 50-66% of patients with MSLI are diagnosed with cancer, usually small cell lung cancer. A malignant neoplasm can be diagnosed when neurological symptoms appear or later, but usually within the first 2 years. Although immunological evidence suggests that tumor may play an important role in the pathogenesis of MSLI, a minority of patients with MSLI never develop a malignant process.
What experimental data indicate the autoimmune pathogenesis of MSLI?
Passive transfer of IgG from patients with MSLI to animals leads to electrophysiological abnormalities characteristic of MSLI. In the IgG fraction in MSLI, antibodies against potentiometer-dependent calcium channels are detected.
Basic diagnostic tests for myasthenia gravis
If symptoms of myasthenic syndrome appear, you should visit a neurologist. A comprehensive examination of the patient includes several methods:
- To exclude an enlargement or tumor of the thymus gland, CT and MRI of the chest and mediastinal organs are performed;
- if Lambert-Eaton syndrome is suspected, an examination by an oncologist is necessary for timely detection of the oncological focus;
- electromyoneurography (EMNG);
- proserine or kalamine test (subcutaneous injection of an indicator substance to monitor the reaction); helps identify familial infantile myasthenia.
Describe the pathophysiology of the autoimmune process in MSLI.
The main antigen against which an autoimmune attack is launched in MSLI is found in the area of the terminal end and small cell lung cancer cells. Antibodies in MSLI cross-react with N- and L-type voltage-gated calcium channels and synaptotagmin in presynaptic terminals, reducing the number of voltage-gated calcium channels, which prevents the activation of the cascade leading to the release of ACh from presynaptic vesicles. Decreased ACh release reduces depolarization in the muscle endoplasty, resulting in the muscle fiber activation threshold not being reached.
Causes
The reasons for the development of this syndrome are not fully understood, but some results are already available, in particular, Eaton Lambert syndrome can develop due to:
- genetic predisposition;
- the presence of malignant tumors in the body (cancer of the bronchi, stomach, ovaries, prostate, breast, etc.);
- autoimmune diseases (Sjogren's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.);
- thymic hyperplasia (tumors);
- dermatomyositis.
All of the above is a kind of trigger that provokes antibodies to attack their own cells. Most of all, as with ordinary myasthenia, acetylcholine suffers, the deficiency of which leads to the described syndrome. The pathogenesis of the syndrome is similar to the pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis.
What happens inside a nerve cell
The most dangerous thing about Eaton Lambert syndrome is that the symptoms may become noticeable only after a few years, and until then they will not manifest themselves in any way.
How is MSLI treated?
The release of acetylcholine from presynaptic terminals is enhanced by guanidine hydrochloride, 4-aminopyridine and 3,4-diaminopyridine. Amino-pyridines, especially 4-aminopyridine, lower the epileptic threshold. In some patients, the condition may improve with anticholinesterase drugs. In the case of paraneoplastic syndrome, the best option is to treat the underlying disease, which can lead to complete remission. Although improvement has been described with intravenous immunoglobulin and other types of immunotherapy (plasmapheresis, oral corticosteroids), the results of such treatment are often disappointing.
How it manifests itself
The symptoms of Lambert-Eaton syndrome are not specific and resemble the manifestations of some other myasthenia gravis, so it is quite difficult to make a correct diagnosis. The clinical picture is based on increased fatigue and weakness of the skeletal muscles, which predominates in the upper legs. The hips and pelvic area are mainly affected.
The patient's main complaint is weakness in the legs, unsteadiness while walking, which is especially noticeable when climbing stairs, as well as during long walks. Sometimes discomfort appears in the back or neck. There are muscle pains, sensory disturbances, numerous disorders of the autonomic nervous system - dry mouth, minimal tears, increased sweating of the palms, decreased blood pressure when suddenly standing up from the bed.
A duck's gait is typical and tendon reflexes are reduced. A distinctive feature is the fact that the more the patient moves, the faster muscle weakness passes. This is the main difference from classical myasthenia, in which this symptom does not exist.
Some patients may experience drooping of the upper eyelid. Swallowing problems and visual disturbances are very rare.
Diagnosis of the syndrome
Methods for studying Eaton-Lambert syndrome
Thanks to the use of modern diagnostic methods, great successes are achieved in the treatment of the syndrome:
- Initially, doctors analyze the patients’ subjective complaints and compile the most detailed anamnesis. The doctor asks the patient when the first symptoms appeared. If children are being treated, the information is provided by the parents. During the examination of the patient, the doctor determines whether he has vision problems in the form of double vision.
- To determine hereditary predisposition, the doctor determines whether his immediate relatives had malignant neoplasms or Eaton-Lambert syndrome.
- The patient is also examined to determine rheumatoid arthritis.
- To make the most correct diagnosis, the patient undergoes a general neurological examination. To do this, he must pass special tests, which involve repeating certain movements. This allows you to determine whether the patient has muscle weakness.
- In some cases, a proserine test is prescribed, with the help of which muscle contractility is assessed before and after the injection. This test is not reliable when screening children.
- Diagnosis also requires laboratory and special studies. They allow you to determine the level of specific antibodies to the effects of acetylcholine receptors.
- In some cases, patients may be prescribed electroneuromyography, which consists of an instrumental assessment of the level of muscle excitability. Also, using this method, you can determine the speed of transmission of nerve impulses. With this disease, the first criterion always has deviations, and the second is characterized by normal indicators.
- To make the most accurate diagnosis, patients are prescribed MRI of the anterior mediastinum. Using this method, a preliminary diagnosis is confirmed. MRI allows you to determine the presence of a tumor process on the thymus gland.
Thanks to a wide range of diagnostic methods, it is possible to most accurately establish a diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment, in accordance with the individual characteristics of the patient.
Treatment
Treatment for Eaton-Lambert syndrome is divided into two components. Treatment of paraneoplastic type and autoimmune type of disease.
In the first case, in order to relieve the patient of the symptoms of myasthenia gravis, it is enough to remove the malignant neoplasm. After which the symptoms of Eaton Lambert's myasthenia will gradually go away.
If the disease is of the autoimmune type, treatment in most cases consists of drug therapy, which may include taking the following drugs:
- suppress the immune system (glucocorticosteroids);
- provoking the production of acetylcholine (inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase, such as pirdostigmine ipidacrine);
- potassium salts;
- pulse therapy (consists in the use of hormones, which are initially administered to the patient in the maximum amount and the dosage is reduced each time).
Taking certain medications that stimulate the production of acetylcholine is associated with certain risks, including side effects, such as:
- convulsive processes;
- bradycardia;
- increased salivation;
- constriction of the pupils;
- development of cramps in the stomach or intestines.
Therefore, only a doctor should select and adjust the dosage of such medications.
This is what a patient with myasthenia looks like: Eaton Lambert
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures for this disease consist of extensive procedures that begin with interviewing a doctor. Thus, the patient or patient will have to tell the specialist in detail what worries him, the nature of the complaints, the time of their appearance, the presence of vision problems, and heredity.
Next, the doctor will conduct a series of neurological tests on the patient, including:
- Proserine test.
- Repetitive movement test.
You can read more about methods for diagnosing myasthenia gravis using neurological tests in our article - myasthenia gravis, what is it?
Naturally, diagnostic measures include instrumental and hardware diagnostics, including:
- blood test to determine the concentration of specific antibodies;
- blood test for tumor markers;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- computed tomography (CT);
- electroneuromyography;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
It happens that after the first examination it is not clear whether there is a similar disease in the body or not, but all the symptoms indicate its presence. In this case, repeated diagnostics are indicated in six months.