Medical information is reliable Checked by Samoshkin Anton Aleksandrovich
Our clinic treats Parkinson's disease in Moscow using complex therapy. The best specialists find an individual approach to each person and select the best methods. Since the disease cannot be cured, the goal of providing assistance is to slow down its progression, reduce the severity of movement disorders and improve a person’s quality of life. Thanks to correct and timely actions, it becomes possible to maximize the period during which the patient can move independently, serve himself and perform feasible work.
What is Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is a degenerative pathology associated with disruption of the central nervous system (CNS). It has a chronic and gradually progressive course. In terms of frequency of development in older people, the disease is in second place after Alzheimer's disease. According to world statistics, this problem occurs in every 500 inhabitants on the entire planet. In children, the deviation is practically not observed; the risk group includes people after 40-50 years of age.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease must be carried out with a full understanding of the origin of the disorder and the reasons for its occurrence. Long before the first symptoms and abnormalities are detected, the destruction of CNS cells and associated disorders begins.
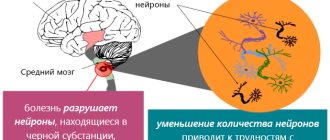
The basal ganglia of the central nervous system are responsible for all movements made by a person in the process of life. They are controlled by the cerebral cortex and help with drawing, writing, walking and other activities. These structures determine the muscle group that must be involved in order for everything to work out accurately and efficiently. The cortex gives them active impulses, and the basal formations slow them down a little through the release of dopamine. This allows movements to be precise and targeted in a normal healthy person.
Parkinson's disease occurs due to damage to certain areas of the ganglia, in which atrophy of nerve cells occurs and disruption of the structure and function of the fibers that conduct impulses to the muscles. At the same time, there is a decrease in dopamine, so the signals are not inhibited, but go directly to the muscles. The result is trembling, tremor, constant tension (rigidity), and difficulty making voluntary movements.
Parkinson's disease is not fatal
Today, out of every 1,000 people in the world over the age of 50, two suffer from Parkinson's disease.
It is extremely rare to experience symptoms of this disease even in people just over 16 years of age. In the case of this age-related disease, the statistics of identified cases are not in favor of men.
Perkinson's disease is not considered fatal, but can lead to the death of an already bedridden patient through many complications and pathologies of other vital organs and systems of an elderly person.
- Read in the article:
- What is Parkinson's disease?
- Symptoms of Parkinson's disease
- Parkinsonism syndrome
- Development of Parkinson's disease
- Nursing home for elderly people with Parkinson's disease
Causes of Parkinson's disease
For a still unknown reason, Parkinson's disease affects men more often. But among coffee and cigarette lovers it is less common. Currently, research is still underway to determine the exact cause of the disease. But the factors that provoke it are already well known:
- aging;
- hereditary predisposition;
- impact of negative factors;
- long-term use of certain drugs;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- infectious diseases of the brain;
- some have chronic pathologies;
- stress and poor nutrition.
Disruption of the structure of the nerve fiber very often occurs due to age-related changes. It is not uncommon for tremor to appear in people who have relatives with this problem, especially for young patients. The toxic effects of poisons, heavy metals, and radiation can also lead to atrophy of brain tissue. The use of antidepressants and antipsychotics helps reduce the level of dopamine and the sensitivity of nerve synapses to it.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease in Moscow begins with identifying and eliminating the main cause of the development of the pathology. Ganglion structures are affected after encephalitis, meningitis, or injury as a result of injury. Psycho-emotional overload, constant lack of sleep, eating low-quality foods, and lack of necessary substances also contribute to disruption of the central nervous system.
Why does Parkinson's disease occur?
According to experts, the main reasons contributing to the development of pathology are the hereditary factor and changes in the body associated with age. But sometimes an unfavorable external environment and concomitant physical diseases can trigger the onset of Parkinson’s disease. The mechanism of development of the disease is determined by the death of neuronal cells responsible for the production of dopamine, which gives the nervous system the ability to control muscle tone and body movements. In Parkinson's disease, the number of cells containing dopamine is only 20% of normal.
According to statistics, the risk of developing such a pathology in people with a hereditary predisposition doubles. Among the factors contributing to the development of Parkinson's syndrome are atherosclerosis of the arteries of the brain, the toxic effects of drugs or heavy metals, carbon monoxide or narcotic substances. A similar syndrome can be caused by head injuries and brain tumors, encephalitis and various degenerative pathologies.
Parkinson's disease symptoms and treatment
Treatment of Parkinson's disease is best started when the first symptoms of the disorder appear, this will slow down the progression of the pathology. The patient's relatives should closely monitor his condition. The initial stage of the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- decreased expressiveness of facial features;
- slowing down of movements while walking, blinking, eating and dressing;
- difficulty performing precise actions using fine motor skills (fastening buttons, tying shoelaces);
- change in handwriting (it becomes smaller and more illegible);
- decreased energy and fatigue;
- difficulty getting up from a sitting or lying position;
- choosing a shower when washing, since you need to get into and out of the bath;
- difficulty chewing and swallowing;
- increased salivation (salivation) and constant need to wipe your mouth with a napkin;
- drowsiness during the day and problems falling asleep at night;
- slow speech and monotonous pronunciation of phrases;
- decreased ability to learn and perceive new things.
Some people in the early stages of the disease experience symptoms that are in no way associated with parkinsonism. They experience constipation, decreased sense of smell, and absent-mindedness. Relatives notice the patient's unusual behavior during the REM sleep stage (he begins to actively move his arms and legs).
During the period of manifestation, Parkinson's disease is characterized by the presence of the following symptoms:
- Tremor.
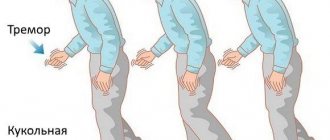
Trembling of the upper extremities predominates; it is much less common in the legs. Unlike other neurological pathologies, there is practically no head tremor with this disease. But fine vibration of the tongue and jaw is often observed, especially at a later stage. The maximum severity of the symptom is observed at rest, for example, when a person’s hands lie on the knees or the arm of a chair. If movement is made, the shaking is greatly reduced.
- Rigidity and slowness of movements.
An important symptom of Parkinson's disease is muscle rigidity. It manifests itself in increased tone and the appearance of constant resistance during passive movement. Here a differentiation should be made with spasticity, in which resistance occurs only at the beginning, that is, the “jackknife” syndrome is observed.
Rigidity in Parkinsonism most often affects all muscles of the body. But a number of patients have a predominant disorder of the flexor muscles. This determines the characteristic posture of a person with bent arms and legs (at the knees and elbows), while the arms are pressed tightly to the body (the “petitioner” pose).
Together with increased muscle tone or even in its absence, the “gear wheel” symptom is often observed. It manifests itself during the examination, when the doctor, when flexing and extending the patient’s limb, feels uneven resistance, similar to the sliding teeth of a gear.
- Balance disorders.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease in Moscow and its diagnosis begins with studying the safety of the so-called postural reflexes. In a healthy person, they allow you to stand upright, sit down or stand up, and maintain your posture when exposed to external influences (a push, a stumble). A patient with Parkinsonism is characterized by imbalance. He often falls, and when he sits down, he immediately leans back in the chair or armchair. It is this deviation that leads to a change in gait.
At the same time, the upper part of the body seems to go forward, and the lower part catches up with it, taking quick and short steps. If there is a need to stop immediately, it becomes difficult for the patient to do this, and he may fall. Typically, imbalance, up to the inability to move independently, is observed at a late stage of the disease.
Parskinson's disease, in addition to impaired movement, stiffness and tremors, is accompanied by other non-motor abnormalities:
- depression;
- cognitive problems;
- vegetative symptoms;
- high fatigue;
- lack of sleep or drowsiness;
- dementia and personality changes;
- apathy;
- muscle pain syndrome;
- respiratory disorders.
Sometimes Parkinson's disease develops atypical symptoms, which can make it difficult for even an experienced specialist to diagnose the disease. These include dystonia and dyskinesia. In the first case, contractions of muscle fibers are observed, accompanied by painful sensations. This sign requires differentiation from arthritis. Dyskinesia manifests itself in involuntary twitching and movements of the arms and legs, which decrease somewhat after taking drugs with dopamine.
24/7 CONSULTATION BY PHONE: +7
Classification of the disease and rate of development
Treatment for Parkinson's disease depends on the stage of development of the disease. To determine it, the Hoehn-Yahr classification is used, based on the severity of the manifestations of pathological symptoms:
- Zero.
Some parts of the brain cells begin to deteriorate, but no obvious abnormalities are observed. A manifestation of absent-mindedness is possible, which many at a young age take as a sign of overwork, and at an older age – as normal aging of the body. Sometimes the perception of smells may change slightly.
- First.
The first manifestations begin in the form of trembling of the limbs on one side of the body (hemiparkinsonism), increased tremor is noted after stress. Some deviations can be found in the pronunciation of words, gestures, and posture. The precise movements required when grooming (shaving, combing hair) begin to take longer than before. There is a decrease in mood, loss of strength, and depressive symptoms.
- Second.
The progression of the disease leads to damage to both parts of the body (bilateral parkinsonism), mild postural instability appears, coordination is impaired, and significant fatigue occurs when performing physical activity. Shaking of the head becomes noticeable, the face loses expressiveness, and speech becomes monotonous.
- Third.
All signs and symptoms characteristic of the previous stage become even more pronounced. The balance is noticeably disturbed, but the opportunity for free movement and self-service still remains. The patient's gait changes, it becomes uncertain, and he moves in small mincing steps.
- Fourth.
A person almost completely loses the ability to act independently and care for himself and requires constant care and supervision. He can stand and move with difficulty only with support.
- Fifth.
There is a complete loss of independence and ability to move. The person constantly lies in bed or sits in a wheelchair. Due to impaired swallowing, exhaustion occurs; nutrition is most often provided parenterally.
The transition from one stage to another cannot be determined by a time frame, since it is an individual process. It depends on age and treatment method. In young people, life expectancy after the manifestation of pathology can be up to 40 years, in middle-aged people - up to 20 years. In an elderly patient, the period will be up to 7 years. If you do not take medications or use other methods of assistance, your life time can be significantly reduced.
The duration of each stage can be measured from several months to ten years. There are often cases when a jump occurs from the first stage of stasis to the third, bypassing the second. With the correct selection of treatment, it is possible to transfer the patient with this disease to a lower stage for some time.
Forecast
If the patient's dominant symptom is tremor (shaking), then the prognosis will be much more favorable than in persons suffering from motor slowing. Today, the statistics are such that, due to active pharmaceutical development of the latest drugs, it is possible to prolong the life of patients and significantly improve its quality.
It is impossible to completely cure the pathology, and its specific prevention has not yet been developed. If contact with specialists was timely, and auxiliary treatment was chosen correctly, then further progression of the process can be stopped, maintaining working capacity and prolonging the patient’s life for a long time. If the disease is started by the lack of adequate therapy and self-medication, then this is fraught with a reduction in life expectancy to 7-9 years.
Diagnostics
Treatment of Parkinson's disease is impossible without making a correct diagnosis. He diagnoses clinically based on the symptoms of the disease. In this case, three main features are taken into account:
- tremor at rest;
- muscle stiffness;
- hypokinesia.
It is important for the doctor to obtain objective information about the medical history. Therefore, when contacting the clinic, the patient or his relatives must provide the following information:
- at what age deviations began to be detected;
- the first signs of disturbances (handwriting, behavior, facial expressions, gait, tremor);
- gradual or sudden onset;
- absence or presence of cognitive problems (depression, hallucinations);
- whether there are other people in the family with neurodegenerative disorders;
- the presence of traumatic brain injuries, infectious pathology;
- working conditions and hazards;
- established other diseases;
- name of medications taken.
To confirm the disease, you must contact a neurologist; in case of cognitive disorders, you may need to consult a psychiatrist. The basis for establishing a diagnosis is the following criteria:
- unilateral initial manifestation;
- tremor at rest;
- progressive course;
- positive dynamics after taking levodopa;
- course of the disease for 10 years or more.
For differential diagnosis, it is enough to confirm three or more signs. MRI, CT, and ultrasound of brain vessels are used as instrumental methods. They are required to exclude other diseases and concomitant pathologies.
Treatment methods for Parkinson's disease
Treatment of Parkinson's disease in Moscow and other cities should begin with its first manifestations. It is best to involve experienced specialists in this problem who will help you choose the best methods of assistance and rehabilitation.
The lack of therapy or the wrong approach to it significantly shortens the life of a patient suffering from Parkinson's disease. After ten years, and sometimes earlier, he becomes disabled or dies, and after 15 years from the onset of the disease, the mortality rate is already 80%. And even with a sluggish form, without taking medications and using modern techniques, strong everyday disadaptation quite soon occurs, a person’s ability to work and socialization decreases. The quality of life suffers greatly, and the patient himself becomes a heavy burden for family and friends.
Treatment for Parkinson's disease includes:
- taking medications;
- physiotherapy;
- psychological assistance;
- therapeutic exercises;
- special diet.
To correct dopamine, drugs are used that help:
- increase dopamine levels;
- stimulate dopamine receptors;
- inhibit the reuptake of this substance;
- reduce its destruction.
The following medications are used for this:
- Levodopa drugs.
They are among the most effective medications for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, which are used in both early and late stages of the disease. They are recommended in case of disorders associated with functional adaptation, and to a lesser extent these drugs affect tremor. The dose is selected individually; the patient needs to monitor the condition during therapy, since levodopa drugs have multiple side effects.
- Dopamine agonists.
They allow direct stimulation of dopamine receptors and are also recommended for use at any stage. Treatment of Parkinson's disease with their help is carried out in combination with levodopa drugs. Recent studies indicate that the use of dopamine agonists early in the disease helps reduce the likelihood of dikinesia or significantly delay its onset.
- Anticholinergic drugs.
They help reduce the manifestation of tremor and do not have a special effect on the phenomenon of bradykinesia. They are preferable to start treatment of Parkinson's disease in young patients and middle-aged people with a predominance of limb tremors and the absence of cognitive impairment.
- COMT inhibitors.
These medications can increase the concentration of levodopa drugs in the blood plasma. This allows you to achieve the desired effect of therapy using lower dosages of the main drug. Recommended for treatment at any stage of the disease.
- Antidepressants.
This group of drugs helps with depression and decreased social activity of a person. Best used in conjunction with the work of a psychotherapist.
If the disease is at an early stage, the person may not be prescribed medications. His normal activity is maintained with the help of physical therapy, massage, and physiotherapeutic procedures. Psychological assistance is provided to the patient and his environment with the help of experienced specialists.
24/7 CONSULTATION BY PHONE: +7
Stages of Parkinson's disease - symptomatic, duration and prognosis
Parkinson's disease is a common, slowly progressive disease of the central nervous system.
It manifests itself in damage to the stem structures of the brain, accompanied by disorders of the synthesis of a special neurotransmitter - dopamine. Unfortunately, it is incurable. It is sluggish and typical for older people.
It is possible to roughly predict life expectancy in the presence of Parkinson's disease only by symptoms, taking into account the treatment used.
In 1967, scientists found out how many separate stages of development of Parkinson's disease are and what their dynamics are, which made it possible to develop a scale that includes 5 stages, taking into account the duration of the disease and disturbances in motor activity.
Later it was finalized and included three more transitional stages, reflecting borderline states. The detailed information collected helped doctors understand how to treat early Parkinson's disease and whether it can be treated at all.
- stiffness in one hand;
- slight tremor of one hand when excited;
- depressed mood;
- insomnia;
- bouts of unexplained fatigue.
A little later, if treatment was not started at the first signs of the first stage of Parkinson's, the disease will develop to stage 1.5. The tremor of one limb will become constant and will stop only during sleep.
Also a sign of the onset of transitional stage 1.5 is a feeling of stiffness in the cervical region and upper back. Trembling throughout the hand affects handwriting. Activities requiring fine motor skills also suffer.
For many, it is easier to ignore the illness than to begin treatment for Parkinson’s disease at the initial stage. Stage 1 Parkinson's disease usually lasts up to 3 years if left untreated.
Second stage
Stage 2 Parkinson's disease is characterized by symptoms affecting both sides of the body and complicated treatment.
The disease gradually intensifies and new symptoms appear:
- decreased joint mobility;
- tremor of both hands;
- decreased mobility of facial muscles;
- speech deteriorates, the person speaks more slowly and quietly;
- the lower jaw or tongue trembles;
- swallowing function is impaired;
- the flow of saliva is not controlled;
- problems with sweating: the skin becomes either very dry, parchment-like, or too oily.
As with stage 1 Parkinson's disease, stage 2 has a good prognosis. The patient is still able to control changes in the body, but begins to move much more slowly. It requires extra effort to perform simple operations.
Treatment for stage 2 parkinsonism, like stage 1, is carried out with the help of physical education, medications and a special diet. It allows you to slow down the development of pathological phenomena and prolong a person’s working capacity. Also, with proper treatment, a noticeable improvement in the condition is possible.
Stage 2.5 is characterized by deterioration in motor activity. Problems arise with balance during sudden movements, and walking speed slows down. However, people are able to resist a push to the chest, which is a good sign for possible rehabilitation.
At stage 3 of Parkinson's development, a person is still relatively independent.
But he is no longer able to work, disabled. He copes with everyday needs, spending much more time on it than usual. Sometimes he needs help caring for himself.
Most often this concerns dressing, since it is difficult for a person suffering from Parkinsonism to get his hand into a sleeve or deal with small fasteners.
Signs of stage 3 onset:
- Severe slowing of speech. There is a tendency to constantly repeat words.
- The facial muscles are very limited in movement, which brings the face closer to a frozen mask.
- Mincing gait, slow movement in small steps with feet parallel to each other.
- Severe constant jerking of the head.
- Joints work slower and worse.
- Constant posture changes. A person moves with his head constantly tilted forward and his limbs bent at the joints.
Life expectancy at stage 3 of Parkinson's disease is not affected; a person can live with similar symptoms for decades.
Older people experiencing stage 2 and 3 Parkinson's are quite capable of living independently with a little occasional help from others.
Stage 4
With Parkinson's disease stage 4, all the symptoms described above are noticeably intensified. A person loses independence. Carrying out simple household needs now requires the help of loved ones.
The main symptoms of Parkinson's stage 4:
- Postural instability develops. The patient easily loses balance even with slow movements. Falling when trying to get up from a sitting position or quickly turn around becomes a very real threat. However, the person is still able to walk independently and even take short walks on good days.
- Mental changes are inevitable. This is partly a consequence of dementia, partly a psychological reaction to a physical condition. A patient with stage 4 parkinsonism thinks about suicide, becomes depressed, and often cries.
During this period, it is necessary for someone close to be with the sick person at all times. The goal is to protect you from injury and provide moral support, as well as help you stick to a proper diet and monitor your medications.
The typical sign of late, end-stage Parkinson's disease is severe immobility, but other symptoms also occur.
The person is no longer able to move independently. He even needs help to stand up or sit down. As a rule, the patient spends the remaining time in bed or in a chair.
Characteristic symptoms of stage 5 Parkinson's:
- rapidly developing dementia;
- problems with bowel movements and urination;
- speech becomes slurred;
- swallowing function is impaired;
- Depression intensifies.
At stage 5 of Parkinson's, what many consider to be torture for both the patient and those around him happens to people. Often the intellect during this period is almost completely lost, the person suffers.
Non-drug methods
Treatment of Parkinson's disease in our clinic is not limited to the selection of medications. To improve the condition, it is recommended to use a diet. According to the research results, the patient has positive changes in motor function with certain dietary habits:
- reducing the amount of protein food;
- sufficient fluid intake (in the absence of contraindications);
- frequency of meals – up to 4-5 per day, in small portions;
- complete cessation of alcohol consumption;
- regular intake of caffeinated drinks;
- consumption of berries high in anthocyanins (strawberries, raspberries, currants);
- a decrease in vitamin D levels in Parkinson's disease requires constant intake of fish and seafood, as well as regular walks in sunny weather.
Great importance is given to doing exercises. Physical therapy for neurodegeneration helps:
- improve cerebral and peripheral blood flow;
- accelerate the production and action of dopamine;
- reduce oxidative stress;
- reduce the severity of tremor;
- strengthen muscle tissue and prevent its atrophy;
- prevent falls and injuries, normalize coordination.
The specialist selects certain exercises that should be performed regularly, for 20 minutes, 2-3 times a day, only in this case can you count on the formation of muscle memory. This complex includes stage plastique movements, training in relaxation and proper breathing. This takes into account the age and degree of endurance of the person, the presence of complications and other factors.
The frequency and duration of movements depends on the stage of the pathology and the person’s activity. They are selected in such a way that all muscle groups are trained, but with an emphasis on areas that require more correction.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease in Moscow involves the use of physiotherapy. Various methods of exposure can be used already in the first stages of the disease. They help reduce pain symptoms, remove hypertonicity of muscle fibers, and improve tissue trophism. The positive effect of physiotherapeutic treatment methods on the central, autonomic and peripheral nervous systems, as well as the condition of the musculoskeletal system, has been proven.
The following types of therapy are recommended for patients with parkinsonism:
- transcranial magnetic brain stimulation;
- pulsed electrotherapy on the cranial area;
- magnetic therapy;
- pulsed low-frequency electrostatic therapy on the lower leg muscles;
- pressotherapy in the lower extremities and lower back;
- electrophoresis with drugs to relieve spasms and pain;
- electrosleep;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- balneotherapy and mud therapy.
If you make an appointment at Dr. Isaev’s clinic, you can not only significantly improve the condition of a loved one. An important aspect of the treatment of Parkinson's disease is family consultations with a psychologist. The patient’s relatives are explained the features, causes and signs of the disease, told how to care for a person with this problem, and taught how to properly communicate with him.
Questions and answers
How quickly does Parkinson's disease develop?
This disease tends to progress very slowly, and therefore for years the person and his environment are not aware of his problem. The developmental stage with clinical manifestations occurs after the death of more than 60% of dopamine neurons. There are no early signs due to a compensation mechanism in which healthy areas take on the functional responsibilities of damaged ones. For young people, life expectancy with this diagnosis can be 20-40 years; for older people, the prognosis is less optimistic; they live on average 6-7 years.
Is it possible to cure this disease forever?
Currently, medicine does not have the means and capabilities to completely cure this disease. But with a competent and comprehensive approach, it is possible to significantly improve the patient’s quality of life and delay the development of motor and other disorders for a long time. It is almost impossible to do this on your own at home. Therefore, you should contact experienced specialists and follow their recommendations.