The causes of Parkinson's disease are those factors that influence the occurrence and development of this disease throughout human life. Typically, this disease is chronic; as the pathology develops, permanent degenerative changes occur in the body as a result of the death of brain cells.
The reasons why these processes occur have not been fully studied to this day. Medicine at this stage can only talk about those factors that directly or indirectly influence the development of Parkinson's disease. They are considered to be the causes of this disease. In order to more accurately begin to talk about what provokes parkinsonism in a particular case, it is necessary to understand the basis of the pathology and how it affects the processes in the human brain.
Death and damage to dopaminergic cells
Content:
- Death and damage to dopaminergic cells
- Heredity in parkinsonism
- Genetic predisposition
- Brain injury
- Brain diseases
- The presence of harmful and lack of beneficial substances
- Spiritual reasons
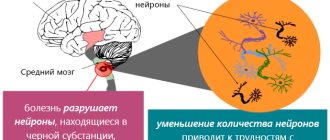
Typically, the pathology manifests itself in the fact that in the midbrain the composition of the black substance begins to actively change. This substance in its normal state contains cells capable of producing the substance dopamine. Dopamine is necessary for the connection of nerve processes or neurons of the substantia nigra with the striatum of the brain. With a lack of dopamine, a disturbance in the coordination of movements occurs, motor ability decreases, all this progresses until the person completely loses his ability to work and independence. The synthesis of dopamine decreases, and as a result, the neurotransmitter function with which a person coordinates his own movements decreases.
When dopaminergic cells in the brain are damaged or killed, dopamine production drops sharply, which leads to a lack of interaction between the substantia nigra and the striatum in the human brain. When 80% of dopaminergic cells are lost, symptoms of Parkinson's disease begin to appear. As their synthesis in the body decreases, the disease progresses to more complex stages.
Experts still cannot accurately answer the question about the causes of damage and death of nerve cells that provoke parkinsonism. According to experts at the University of Cambridge, genetic mutations that undermine the natural process of rejecting defective mitochondria may be to blame for this process. As you know, mitochondria act as a kind of battery for the cell, destroying and creating energy for them. If defective mitochondria are detected, they need to be eliminated. However, there are defects in the genetic code of Parkinson's disease that interfere with the process of repairing mitochondrial defects. This study suggests that if patients are given medications to remove unnecessary mitochondria during therapy, the development of parkinsonism can be prevented.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease
This disease is practically untreatable, but modern medicine, as well as high achievements in the field of neurology, help cope with severe symptoms of the disease. Each specific case of treatment of a disease is considered by a doctor individually. The following treatment methods are currently used in medicine:
- drug therapy,
- surgical intervention,
- physical therapy and massage.
Medicines
Medicines help overcome difficulties with walking, movement and tremors. These drugs increase or replace dopamine, a specific signaling chemical (neurotransmitter) in the brain that is deficient in patients with Parkinson's disease. But dopamine cannot be given directly because it does not enter the brain. Let's take a closer look at what a disease such as Parkinson's disease is like and its treatment.
To increase dopamine levels, the following are prescribed:
- Carbidopa/Levodopa, the most effective antiparkinsonian drug. The substances included in its composition penetrate the brain, promoting the production of dopamine.
- Carbidopa-levodopa infusion is a combined drug in the form of a suspension; is supplied to the duodenum via an infusion pump. Recommended to alleviate the condition of patients with advanced disease.
- Dopamine agonists. Unlike levodopa, they are not converted into dopamine, but reproduce dopamine effects in the brain. Their effectiveness is not as high as that of levodopa, but the effect is longer.
Often prescribed together with levodopa to smooth out the side effects of the latter.
- Dopamine agonists: pramipexole (Mirapex), ropinirole (Requip), and rotigotine (Neupro). A short-acting dopamine agonist, apomorphine (Apokyn), has been developed for rapid relief.
- MAO-B inhibitors. These include selegiline (Eldepryl, Zelapar) and rasagiline (Azilect). They slow down the destruction of dopamine by inhibiting brain monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B).
When added to carbidopa-levodopa, these medications increase the possibility of hallucinations.
- Catechol-o-methyltransferases (COMT inhibitors). Entacapone (Comtan) is the main drug in this class. It gently prolongs the effect of levodopa by blocking the enzyme that breaks down dopamine.
- Tolcapone (Tasmar); another COMT inhibitor that is rarely prescribed due to the risk of serious liver damage and liver failure.
- Anticholinergics. Helps control limb tremors. Several anticholinergic drugs are available, such as benztropine (Cogentin) or trihexyphenidyl.
Their modest benefits are often offset by side effects: memory loss, confusion, hallucinations, constipation, dry mouth and urinary problems.
- Amantadine. Doctors may prescribe amantadine alone to provide short-term relief from symptoms of mild, early-stage Parkinson's disease. In later stages, they may be prescribed together with carbidopa-levodopa to control involuntary movements (dyskinesias) caused by carbidopa-levodopa.
Folk remedies
For the complex treatment of this disease, herbal decoctions are used. They are used both externally and internally. Decoctions of fern roots are used for foot baths, and hands are rubbed with jasmine flower oil. Depending on what symptom of the disease you want to cope with, various medicinal herbs are used.
It is also important to maintain an active lifestyle during the treatment period, supplement your diet with vegetables and fruits, and stop drinking and smoking. The diet must contain foods that will activate the brain (for example, nuts, seafood). In the absence of contraindications, you can increase the amount of fluid consumed. Failure to eat a balanced, proper diet can overload the body.
Physiotherapy
The effectiveness of physical therapy in treating the disease has been proven by many. It increases blood circulation and motor activity of the limbs. Good for relieving limb tremors. When treating Parkinson's disease, you can perform the following simple exercises:
- stretching,
- circular movements of the hands and shoulders,
- twisting the body in a standing and sitting position,
- tilts of the head, body,
- raising your legs parallel to the floor,
- neck stretch.
Doctors recommend several useful approaches to treating the disease that will help cope with the further development of the pathology. This includes frequent stay in the fresh air, physical activity; to control speech, you can read books out loud to monitor the correct pronunciation.
Massage
With an integrated approach to treating the disease, it is effective to undergo massage sessions, which are carried out using special techniques and techniques. This makes Parkinson's disease easier. The impact on different muscle groups of the limbs helps restore their activity and has a positive effect on the nervous system.
Surgical intervention in treatment
Often Parkinson's disease, regardless of the causes and methods of treatment, progresses. In this case, deep brain stimulation (DBS) is used. Electrodes are implanted in the brain and connected to a generator, which is implanted in the chest near the collarbone. The device transmits electrical signals to the brain; as a result, symptoms become less severe.
The doctor adjusts the settings depending on the patient’s condition. Surgery comes with risks, including infection, stroke or brain hemorrhage.
DBS can stabilize the effects of medications, reduce or stop reflexive movements (dyskinesias), reduce tremors, and improve and slow movements. But although DBS relieves the symptoms of Parkinson's disease, the procedure is not able to stop the development of the disease.
Heredity in parkinsonism
According to many studies, it has been found that Parkinson's disease also has a hereditary cause. If you carefully study your family history, you can identify signs of a gene mutation, although scientists have not yet been able to identify the gene itself. The inheritance pattern of this disease has also not been identified to date, so heredity is still only an assumption in the theory of the development of Parkinson's disease.
It is believed that the most likely type of inheritance of parkinsonism is autosomal dominant. This type suggests that in each generation the manifestation of Parkinson's disease will be noticeable. However, the likelihood of an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance is also high. He says that the disease is inherited through several generations. Men are more often affected by this disease. In order to determine a more accurate mode of inheritance, many tests were carried out, as a result of which experts began to doubt the hereditary factor in the occurrence of the disease in principle. Based on the results of the research, it turned out that only in 5% of cases of Parkinson’s disease there is a related predisposition to the disease.
Parkinson's syndrome: diagnosis
At the first manifestations of the disease, you should rush to consult a specialist. Based on the complaints, the neurologist will conduct an examination and predict the possible risks of developing the disease. Additionally, studies should be conducted to rule out problems in the functioning of muscle tissue. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is used as the most informative method.
A doctor can make a diagnosis based on typical treatment for the disease. Having prescribed a classic course, he monitors the patient’s condition over time. If the condition clearly improves, the diagnosis is confirmed.
It is imperative that a study of the condition of the vessels be carried out for atherosclerosis, as a factor that increases the risk of worsening the patient’s condition.
Genetic predisposition
From assumptions about the hereditary factor of parkinsonism, there follows an assumption about a person’s genetic predisposition to this disease. Parkinson himself suffered from this pathology, along with several other members of his family. Various studies over different periods of time have confirmed the likelihood of a genetic factor as the cause of the disease in the range from 2.5 to 94.5% of all cases of the disease. Such a scatter could not but cause disagreements among neurologists around the world regarding their view of the issue being studied.
The basis of such disagreements is the fact that parkinsonism syndrome may be part of the clinical picture of other neurological pathologies with a hereditary nature of transmission.
Parkinsonism is most often detected in elderly people, to which not all relatives live.
In addition, in the absence of exogenous factors, some metabolic disorders caused by parkinsonism may not appear at all. Therefore, the use of clinical data to establish a genetic predisposition to Parkinson's disease does not allow us to draw reliable conclusions about the causes of the disease.
Less often in medical circles you hear about a recessive type of genetic predisposition to Parkinson's disease, linked to sex characteristics. However, any study reveals a genetic predisposition to the disease in no more than 3-8% of cases. At the same time, this pattern turns out to be different in populations of different countries. It is important to mention here that in Sweden a pattern of predominance of the so-called 0 blood group in patients with parkinsonism has been identified. The same trend is emerging in Norway, but in Finland it is completely absent. Therefore, experts conclude that a possible cause of parkinsonism is the hereditary transmission of a defect in the tyrosine hydroxylase fragment.
Brain injury
Even the mildest single brain injury can increase the likelihood of developing neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s disease, as American doctors have repeatedly stated. Neurologists trace the relationship between any concussion and the occurrence of senile dementia, based on a study of 300 thousand older Americans over 12 years. Data showed that when patients suffer brain injuries, they develop parkinsonism in 71% of all cases of the disease. Moreover, out of 300 thousand case histories, half contained records of tuberculosis incidence.
Doctors noted that when suffering a moderate concussion, the risk of developing pathology is about 56%, and when suffering a concussion along with tuberculosis - 83%. Experts suggest that a concussion reduces the resistance of this organ to the factors of aging. Along with mechanical concussion, depressive states also have a negative impact on the stability of the human brain, which has been proven by Canadian scientists.
Brain diseases
Another factor that can provoke the occurrence and development of Parkinson’s disease is a number of diseases and their complications in the human brain. Often, after suffering viral or infectious processes in the brain, complications can occur, for example, meningitis, encephalitis and others. These infectious processes weaken the immune system, can destroy brain cells and, as a result, lead to secondary parkinsonism.
Pathology can be caused by various vascular diseases, for example, atherosclerosis of blood vessels, circulatory disorders in the body. Tumors in the brain area can also play an important role in the development of Parkinson's disease.
Symptoms
The development of Parkinson's disease is directly related to a lack of dopamine - this is one of the neurotransmitters that ensure the transmission of signals in interneuron connections. That is, the conductivity of nerve fibers.
A lack of dopamine leads to the fact that signals in interneuron connections “freeze”, the speed of their transmission sharply decreases, this leads to impaired motor functions and mental abilities.
This is why Parkinson's disease is always accompanied by both motor and mental impairments.
The first signs of the disease are rarely a cause for concern - stiffness of movement in the right half of the body, twitching (trembling) of the hands, oily skin and hair, frequent depression, constipation.
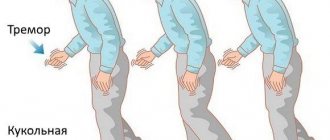
Over time, pronounced tremor occurs - trembling of the arm, leg, and then the head, involuntary movements of the fingers.
At an early stage, the tremor affects only one arm (leg), and then spreads to the second. Tremors always begin in the limbs, and head tremor joins with the development of the disease.
The person’s movements become slow, the gait is shuffling. He moves in small steps, before turning around, marking time.
The back is bent in an arch, the head is lowered, the arms and legs are bent, and a characteristic stoop is formed - the “petitioner pose.”
Facial expressions are becoming increasingly impoverished. The face becomes motionless and loses expression. The impression arises that the person does not react to anything.
The muscles become less and less mobile, rigid, it becomes difficult for a person to make movements, their volume is increasingly limited. He cannot fasten buttons, tie shoelaces, shave, brush his teeth, and over time he completely loses the ability to take care of himself in everyday life.
Speech changes - it becomes unintelligible, quiet, monotonous.
Over time, the clinical picture is supplemented with new symptoms:
- dementia develops
- impotence occurs,
- urination increases,
- swallowing is impaired,
- the skin becomes dry,
- sweating increases,
- sense of smell worsens,
- sleep is disturbed
- blood pressure decreases,
- salivation increases.
Forms of the disease
The forms of Parkinson's disease are determined depending on which of the symptoms is most severe.
1. Trembling form - trembling (tremor) predominates in the arm, leg or both arms, legs, head, and the most pronounced tremor is at rest. With movement, it may weaken or even disappear.
2. Rigid form – characterized by stiffness in the muscles, especially when starting to move, and limited mobility.
3. Akinetic form - characterized by slowness of movements, impoverishment or complete absence of facial expressions.
Along with these three main forms, mixed forms are distinguished: rigid-tremorous, tremulous-rigid, akinetic-rigid, etc.
The presence of harmful and lack of beneficial substances
With severe intoxication in the body, brain tissue is poisoned by toxins, which also sometimes causes a pathological process. The occurrence and development of Parkinson's disease can be influenced by poisoning with manganese, heavy metals, drugs, carbon monoxide and other substances. A striking example of the occurrence of Parkinson's disease in young people is the discovery of a massive incidence of this disease in 1977 among a group of young people who used synthetic heroin.
There is no direct relationship between the incidence of Parkinsonism and alcohol consumption, but in medical circles it is believed that alcohol abuse, as well as drugs, provokes weakening of brain cells and creates a favorable environment for the development of Parkinson's disease.
Sometimes the disease can be caused not only by the presence of harmful substances in the human body, but also by insufficient levels of beneficial ones, for example, vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D in the human body is responsible for the formation of a protective barrier aimed at combating free radicals and toxins. Therefore, with its deficiency in old age, all of the above substances freely enter the brain and have a detrimental effect on its cellular structure, which is a prerequisite for the occurrence of Parkinson’s disease.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?