The best medications for therapy
For all the measures described above to be effective, you need to support the sick body with special medications. Doctors have mixed opinions about which medications are best to use to treat cerebral gliosis. But they agree on one thing - treatment should be medicinal, not folk. The five most popular prescribed drugs include the following:
| Drug name | Active substance | Manufacturer |
| Cavinton | Vinpocetine | Hungary |
| Cinnarizine | Cinnarizinum | Bulgaria and Russia |
| Actovegin | Deproteinized calf blood haemoderivative | Austria |
| Glitsed | Glycine | Ukraine |
| Vinpocetine | Vinpocetine | Russia, India, Belarus |
To the described vasoactive drugs, you need to add antiplatelet agents to improve blood flow, amino acids, and nootropics. Vitamins E or B provide good support for treatment. But the most important thing is to choose the right main medicine. To do this, you should familiarize yourself with contraindications and side effects, and also consult your doctor. As stated earlier, his decision should be based only on complete brain studies.
Cavinton
Cavinton increases the consumption of glucose and oxygen by the tissues of the frontal lobes. That is why it is used in the treatment of the consequences of ischemic stroke, vascular dementia, atherosclerosis and other diseases. Sometimes the drug is used in ophthalmology: it treats chronic diseases of the blood vessels of the eye and its retina. The medicine should only be used after consultation with a doctor, otherwise the risk of side effects is too high. Know that:
- distributed in the form of tablets or concentrates for infusion;
- the dosage is determined strictly on an individual basis;
- the medicine costs from 228 to 850 Russian rubles.
With the correct dosage, the drug rarely produces side effects. But sleep disturbances, dizziness, tachycardia, nausea, and heartburn may occur. Less common are increased sweating, rapidly passing allergic skin reactions and general weakness. By the way, it may be a manifestation of an underlying disease.
The medicine does not have a negative effect on patients with kidney or liver diseases.
Cavinton is strictly prohibited for patients with severe coronary heart disease, serious arrhythmias, and the acute phase of a stroke. It is dangerous to prescribe it to pregnant women or nursing mothers. But this is acceptable if the risk to the mother’s health is more serious than the likely side effects for the child. Pregnant women may experience placental bleeding from taking it, and there is a risk of spontaneous abortion.
Cinnarizine
A selective blocker of slow calcium channels called Cinnarizine is used not only in the treatment of gliosis and its consequences. It is used in the treatment of post-stroke conditions, traumatic brain injuries, migraines, vestibular disorders, kinetosis, and encephalopathy. The medicine quickly relieves dizziness, tinnitus, nausea and vomiting. Cinnarizine has the following characteristics:
- Available in the form of tablets of 50 milligrams;
- tablets are taken orally after meals, the exact dose depends on the severity of the patient’s condition;
- It is difficult to answer exactly how much Cinnarizine costs, but usually its price ranges between 37 and 101 rubles.
Cinnarizine has few contraindications. It is not given only to pregnant, lactating women, and people with allergies. The medicine should be used with caution if a person is diagnosed with Parkinson's disease. But side effects are possible. Among the most common are drowsiness, lack of hunger, fatigue, dyspepsia and dry mouth. In exceptional cases, lichen planus and serious weight gain are recorded.
- Treatment of cerebral vessels: folk remedies, traditional medicine
Actovegin
This medicine is prescribed for cognitive impairment, which includes dementia and the consequences of strokes. It is occasionally used for diabetic polyneuropathy or circulatory disorders. Thanks to the active substance, the medicine increases the rate of blood flow in the capillaries. After systemic use, it improves the morphological and physiological state of the central nervous system. Remember, that:
- Available in the form of digestible tablets or injection solutions;
- first, the body should receive 10-20 milliliters of Actovegin, and then five milliliters per day;
- packaging of the drug will cost 568-1928 Russian rubles.
Actovegin rarely leads to side effects. But in particularly sensitive patients, drug fever, symptoms of shock, urticaria, and sudden redness in the injection area are recorded. Sometimes doctors observe myalgia, but the exact frequency is unknown. Actovegin is prohibited in case of pulmonary edema, decompensated heart failure, oliguria, anuria or long-term fluid retention in the body.
Glitsed
Glitsed is prescribed for cerebral circulatory disorders, traumatic brain injuries, and neurocirculatory dystonia. It helps in the fight against psychological overload, improves memory, relieves insomnia and facilitates vigorous physical activity. As part of the treatment of cerebral gliosis, the drug has only an auxiliary effect. A brief description of Glitsed is as follows:
- sold in the form of flat white or cream tablets;
- as a rule, one tablet is prescribed three times a day;
- the cost starts from 136 rubles, but you can find cheaper offers on the Internet.
The medicine rarely has side effects, especially if used in the treatment of cystic glial changes in the brain. But allergic reactions on the skin are possible; indigestion, headache, and nausea occur less frequently. In exceptional cases, increased irritation and poor concentration are observed. The overdose was either not recorded or not observed.
Vinpocetine
According to the instructions, Vinpocetine is prescribed for insufficient cerebral circulation, for damage to the blood vessels and retina. Sometimes they treat vegetative-vascular dystonia against the background of climatic syndrome. For patients with gliosis of the brain, Vinpocetine is prescribed to improve metabolism in the affected organ and normalize blood flow. It is important to remember the following characteristics of the medicine:
- the drug is available in the form of tablets for oral administration or solution for injection;
- The dosage regimen is individual, since the dosage varies depending on the severity of the patient’s condition;
- the average price is 50-164 rubles.
Vinpocetine is contraindicated in case of coronary heart disease, stroke or severe signs of arrhythmia. It is dangerous to give it during pregnancy or lactation. Even if the dosage and rules of administration are followed, side effects are possible. Typically, adults experience insomnia, dizziness, increased heart rate, surges in blood pressure, profuse sweating, or allergic reactions.
Symptoms
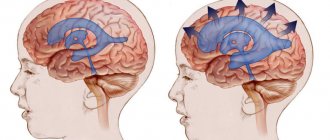
The clinical picture of gliotic foci of vascular origin is determined by the localization of the replaced tissue. The modified tissue does not cause gross disturbances, however, in the presence of large-scale foci, gliosis “reduces” the general background of life, worsening its quality.
Localization:
Frontal lobes
- Single supratentorial foci of gliosis of vascular origin
Leads to a general decrease in cognitive abilities: the pace of thinking slows down, control over one’s behavior is partially lost. Patients have difficulty learning new information and skills. Causal relationships are more difficult to establish. The patient is slower to think.
With deep lesions of gliosis, complex motor patterns are forgotten: patients forget how to tie shoelaces or how to play a musical instrument. The vocabulary becomes poor: sentences are monotonous, there are few or no synonymous words in speech.
The emotional-volitional sphere is upset. Emotions “dull”: all feelings lose their expression and color. Motivation decreases: the desire to explore the world around us is lost.
Temporal, parietal and occipital region
Hearing, speech and vision are affected. The perception of complex compositions is impaired. The sense of rhythm is disrupted. Visual accuracy deteriorates. The threshold of general sensitivity increases: the senses of tactile touch lose their sharpness. Memory deteriorates.
Single supratentorial foci of gliosis of vascular origin
The presence of foci in the cerebellar structures forms a picture of coordination disorder. Gait is disturbed. It is called “drunk” walking: balance is disturbed, the patient spreads his legs wide apart to maintain balance and not fall.
Limbs are shaking. This happens at rest and during movement. Individual fingers also tremble. Vision is impaired. Nystagmus appears - a synchronous rotation of the eyeballs to one side with a frequency of 60 movements per minute.
Muscle tone is impaired towards weakening. At the same time, tendon reflexes decrease. Muscles decrease in size. The synchronicity of the work of the flexor and extensor muscles is disrupted. Handwriting becomes disordered: the patient’s letters are difficult to read and spell out.
- Vascular genesis of the brain: what is it and how to treat it
The clinical picture of single supratentorial foci of gliosis of vascular origin also affects speech disorder. It loses its smoothness and becomes scanned. For example, a person speaks slowly and in syllables: “mo-lo-ko.” At the same time, the speech rhythm is observed.
Symptoms of focal white matter gliosis
Clinical symptoms are determined by the size, location, and progression of neuroglial accumulations:
- Severe headaches - diffuse type;
- Instability of blood pressure, frequent hypertensive crises;
- Unsteady gait, lack of coordination;
- Decreased mnestic functions;
- Memory impairment.
Therapeutic techniques are ineffective in the presence of diffuse periventricular lesions. Large accumulations in a child are rarely observed, so symptoms do not occur.
What is dangerous about gliosis - prognosis for life and health
Life prognosis depends on the underlying cause of the disease. Clinical symptoms are determined by the severity of white matter damage. Affecting the functional centers of breathing and blood circulation can lead to death. Encephalitis and meningitis are dangerous, which often lead to an unfavorable prognosis and death.
Minor symptoms, favorable outcome for gliosis in the frontal lobes of the brain. Subcortical species are dangerous if they spread diffusely.
Traditional treatment
- To inhibit the processes of sclerosis of blood vessels and neurons:
400 gr. mix crushed leaves of 5-year-old aloe with 650 mg of honey and 650 g. red Cahors. Let it brew in a dark place for at least 5 days. Take 1 teaspoon 3 times before meals. The course of treatment is 2-4 weeks.
- To dilate blood vessels in the brain:
2 tbsp. Mix dill seeds and a glass of crushed valerian root with 1.5-2 glasses of honey, pour 1 liter of boiling water. Let it brew for a day. Before meals, take a tablespoon of the mixture for 4-6 weeks .
150-250 gr. Pour boiling water over hawthorn fruits. Let it brew for 30 minutes. Take the infusion 1 tbsp. half an hour before meals. The course of treatment is up to 1.5 months .
Diagnostics and MRI
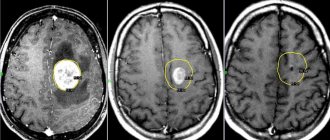
Diagnosis of cerebral gliosis is based on CT and MRI data:
- Magnetic resonance imaging is a priority method for identifying such abnormalities. Using this method, a specialist will see foci of gliosis in the brain, determine the degree of prevalence and determine the exact cause of the disease.
- Computed tomography can also be used as a way to diagnose gliosis of the white matter of the brain, but this method does not provide such an accurate clinical picture as MRI, and in addition, CT can be irradiated with X-rays, which does not have the best effect on overall health.
Sometimes, for a more complete picture of the disease, it is necessary to conduct additional examination in the form of tests and other manipulations. Always, after diagnosing gliosis, there is a need to treat the disease that provoked the death of neurons.
MRI results
Today MRI is considered the most popular method for studying many diseases:
- In the case of gliosis , usually the MRI report may say “a picture of a gliosis focus in the left (right) frontal lobe.”
- If there are multiple foci , then this technique will reveal all the locations of their localization and the extent of neuronal death.
- Also, a magnetic resonance imaging scanner will determine the cause of such lesions.
- If the culprit for the death of nerve cells is a vascular disease, then the MRI report will say “a picture of single (multiple) foci of gliosis in the white matter of the brain, probably of vascular origin.” Read more about vascular genesis of the brain and what it is in our similar article.
- In addition, a specialist can identify additional abnormalities in the brain, such as hydrocephalus, hematomas and other diseases.
Signs of gliosis
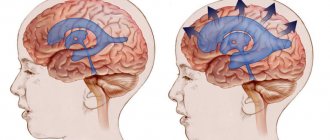
The human brain consists of an ependymal membrane, glial cells and neurons. The latter transmit nerve impulses throughout the body. Pathological processes affecting the central nervous system (CNS) in some cases lead to the death of neurons.
Glial cells in a normal state perform protective, trophic and secretory functions and are responsible for cellular metabolism. They make up 40% of the total mass of the brain matter. The destruction of neurons stimulates the process of filling the resulting voids with glia, which provide nutrition to the cells of the nervous tissue. In this case, the quantitative ratio of cerebral elements changes.
The process of replacing neurons with neuroglial cells is called gliosis and is considered a secondary disease of the central nervous system. The causes of the pathological phenomenon can be age-related changes, trauma, demyelination and ischemia of cerebral structures.
Microangiopathy of the brain, focal changes on MRI (axial projection)
In the early stages, gliosis has no clinical manifestations; the deviation can be diagnosed with a magnetic resonance scan of the brain. As the process progresses, characteristic symptoms arise:
- headache;
- paresis, paralysis;
- speech disorder;
- hearing loss;
- loss of visual acuity;
- lack of coordination in space;
- memory loss;
- decreased concentration;
- development of hypertension.
In newborns, loss of the swallowing reflex, hearing and vision impairment, and symptoms of hydrocephalus are noted.
The clinical picture depends on the type of gliosis, the localization of the process and the nature of the disease that caused the death of nerve cells. Supratentorial focal changes (located above the cerebellum) lead to impaired motor activity and fine motor skills.