Phlebologists never tire of repeating that the treatment of varicose veins must be comprehensive. This includes surgical removal of pathological veins, taking medications, influencing blood vessels with external medications, and compression therapy. In addition, it is extremely important to adjust your lifestyle. Including making it a habit eat right.
By introducing foods that have a beneficial effect on the condition of the veins into your diet, you will provide invaluable assistance to your health.
The diet should be aimed at:
- Reduced swelling
- Normalization of body weight
- Normalization of stool (since constipation also contributes to the development of varicose veins and its complications)
- Strengthening the connective tissue that makes up the vascular wall
- Blood thinning
What foods should be included in the diet
Foods rich in vitamin E. Vitamin E (tocopheryl acetate) is also called the “vitamin of youth”. It strengthens the walls of blood vessels, making them more elastic - and also participates in the formation of collagen and elastic fibers of the intercellular substance.
In addition, vitamin E ensures tissue regeneration and maintains normal levels of blood clotting - which is especially important in the context of preventing the development of thrombosis.
Vitamin E also has an anti-carcinogenic effect and helps strengthen the immune system. It also protects the cell structure from destruction by free radicals - in a word, a real little guardian of our health!
At-risk groups
Patients with the following problems are most susceptible to vascular diseases of the lower extremities:
· Long history of smoking;
· Diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2;
· Alcohol abuse;
· Prolonged physical inactivity;
· High blood pressure;
· Hypercholesterolemia (increased concentration of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood);
· High level of non-proteinogenic amino acid homocysteine in the blood;
· Obesity;
· Severe hormonal imbalance.
Pathologies of blood vessels and arteries of the legs mainly affect people who have crossed the threshold of fifty years of age, but in the last few years their active spread has also been observed among the young population. Men are more susceptible to such diseases than women.
It should be emphasized that most vascular dysfunctions are of a psychological nature, and people with a stressful type of character are most susceptible to them.
It is important to have a family history of disorders. This is especially true for atherosclerosis and varicose veins.
To provide your body with vitamin E, be sure to eat:
- vegetable oils
- flaxseed (as a dietary supplement)
- milk
- cereals
- soy
- beef liver
- egg yolk
- green salad
- nuts
Foods rich in vitamin P. Vitamin P (aka rutin) is a whole group of plant bioflavonoids that are effective antioxidants and have a pronounced capillary-strengthening property.
Rutin ensures elasticity of vascular walls, helps reduce swelling and maintain normal blood pressure, and also strengthens the walls of blood vessels among themselves, preventing their destruction.
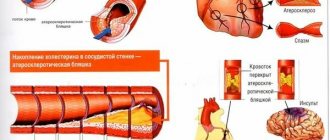
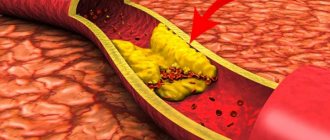
About healthy and diseased vessels
Healthy vessels are elastic, they respond to changes in the intensity of blood flow and, if necessary, expand or contract. If the vessels remain narrowed, then all other organs and tissues will receive less blood than needed, and, consequently, their nutrition will be disrupted. Also for this reason, the pressure “jumps”, since its normalization depends on the elasticity of the arteries and veins.
In addition to elasticity, the smoothness of the vascular walls is very important. If cholesterol plaques appear on the walls, blood flow will be disrupted, blood clots and other very serious consequences will appear.
Everyone probably knows about the consequences. These include:
- cardiac ischemia;
- cerebrovascular diseases;
- diseases of peripheral arteries (supplying blood to the legs and arms);
- rheumatic heart disease;
- thrombosis (threatens further pulmonary embolism);
- heart attacks;
- strokes.
To compensate for the lack of vitamin P in the body, pay attention to the following foods:
- Citrus fruits
- Tomatoes
- White cabbage
- Grape
- Dog-rose fruit
- Green tea
- Walnuts
- Seafood
- Sea kale
Foods rich in vitamin C. Vitamin C not only protects our body during cold season, but also strengthens the walls of blood vessels (connective tissue) and helps reduce swelling. In a word, it is simply irreplaceable for varicose veins - so do not under any circumstances ignore the “ascorbic acid” that is familiar to all Soviet children.
Which medicine is best for veins?
Is it possible to effectively fight varicose veins, popularly called simply “varicose veins”? This topic is especially relevant for young women who attach great importance to the beauty and health of their legs. Varicose veins and CVI provoke frequent cramps and swelling of the legs, nightly fatigue and pain in the lower extremities. Timely treatment can prevent the development of varicose veins and the occurrence of complications - such as venous thrombosis - which are much more difficult to cope with than the initial symptoms of varicose veins. It is equally important not only to start treatment in a timely manner, when even minor symptoms appear, but also to choose the right approach to it, which allows you to influence all disorders of the venous circulatory system that cause varicose veins.
On a note
Relentless statistics claim: in our country, approximately 30 million people suffer from CVI pathologies[1], while from 35 to 60% of patients are people of working age[2].
Often, potential patients do not attach importance to the first symptoms-harbingers of the disease, since in the initial stages they can be mildly expressed. What are these symptoms?
- Swelling of the ankles, feet, and lower legs indicate congestion in the blood vessels, due to which blood plasma enters the tissues through the walls of small capillaries. Swelling is often accompanied by a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the legs. The symptom most often appears in the evening.
- Vascular “webs” or “stars” - telangiectasias.
- Paresthesia. The patient periodically feels numbness, burning and tingling in the legs - the so-called goosebumps. This usually occurs after a long and significant static load on the lower limbs.
- Night cramps are another harbinger of the disease. They can also occur due to stagnation of blood in the veins of the legs. The body needs such involuntary and very painful muscle contraction in order to push blood from bottom to top through the vessels.
In addition, the development of varicose veins is indicated by a constant feeling of tired legs. If treatment for varicose veins is not started in the initial stages, then later large veins begin to protrude from the patient, forming nodes and twisted cords under the surface of the skin. Trophic disorders accompanying varicose veins and CVI lead to dryness and hyperpigmentation of the skin of the legs, thinning and constant itching. Complications of the disease can include trophic ulcers, trophic dermatitis, eczema, acute thrombophlebitis and pulmonary embolism.
Therapy for venous diseases is aimed at eliminating the causes of the disease, alleviating symptoms and correcting complications in the later stages of the disease.
Compression therapy is based on the action of special therapeutic knitwear or bandaging with elastic bandages. They tightly and evenly fit the patient’s thigh and lower leg, narrowing the lumens of the superficial veins of the leg, which eases the load on the walls of the veins, reduces the likelihood of their stretching and thinning, and eliminates the risk of blood clots. In addition, compression products alleviate the patient’s physical condition, relieving bursting pain and a constant feeling of heaviness in the legs.
Surgical methods are used in the later stages of the disease. Thus, phlebectomy involves the removal of dilated superficial veins in situations where all other methods of therapy have proven ineffective. Sclerotherapy is similar to phlebectomy, but in this case the vein is removed not with the help of surgical instruments, but by injecting special drugs. After such a drug is injected into a vein, it glues its walls and stops blood flow in the vein.
However, the basis for the treatment and prevention of varicose veins is still drug therapy. The combination of drug therapy with non-drug methods (lifestyle correction, gymnastics, diet) and concomitant therapy (compression hosiery) allows for maximum impact on both the cause of the development of varicose veins and the reduction of its symptomatic manifestations (pain, heaviness, swelling, cramps in the legs) .
The leading role in modern drug treatment and prevention of varicose veins is played by systemic venotonics (venotonics), taken orally. The mechanism of their action is aimed at correcting disturbances in the functioning of the venous circulatory system, which are the cause of the development of varicose veins, namely:
- disturbances in venous tone (the operation of vascular valves, which normally prevent the reverse flow of blood in the legs);
- thinning and weakening of the walls of blood vessels (under blood pressure in the veins);
- blood thickening (increasing its viscosity and tendency to form blood clots).
The therapeutic effect of the use of venotonics in tablets is systemic in nature - that is, it helps to improve the health of blood vessels throughout the body, affecting the venous system as a whole. Due to this, systemic venotonics, as a rule, have a more pronounced and long-lasting effect on the symptoms of varicose veins - in contrast, for example, to external venotonics in the form of gels and ointments, which act for a short time and only at the site of application.
Systemic venotonics are a fairly large group of drugs. As a rule, most of them are obtained by processing medicinal plant raw materials, because the most active angioprotectors are precisely the components of plant origin: flavonoids (diosmin, hesperidin, avicularin, quercetin, rutin and others), horse chestnut extract (containing escin), rose hip extract (containing vitamin C) and others. Based on the number of active angioprotectors in the composition, all systemic venotonics can be divided into single preparations (for example, containing only flavonoids, only escin or only rutin) and combined ones, consisting of several active angioprotectors - for example, flavonoids enhanced with escin and vitamin C. The advantage of combined venotonics is that they are able to provide the entire complex of actions necessary for the treatment of varicose veins “in one tablet”: venotonic, angioprotective (strengthening the walls of veins and capillaries) and antiplatelet (reducing blood viscosity).
This is interesting
Active study of bioflavonoids began in the late 90s of the last century. The impetus for this was the “French paradox”. The fact is that a large-scale international study showed that among the French, mortality from atherosclerosis is significantly lower than among representatives of other European nations. This was due to their consumption of red wine, which contains large amounts of various types of flavonoids. Scientists have proven that flavonoids not only prevent the development of blood clots, but also have a venotonic effect, which means they can be effectively used in the treatment of varicose veins[3].
Some other drugs can also be used as an auxiliary (concomitant) therapy for varicose veins.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: based on acetylsalicylic acid, diclofenac, as well as the Ginkgo Biloba plant. They are prescribed for the treatment of concomitant inflammatory processes or for symptomatic treatment aimed at eliminating pain symptoms in the legs due to varicose veins.
External venotonic agents. These include ointments, gels, and creams for external use, which help alleviate the symptoms of varicose veins: fatigue, heaviness, swelling of the legs. The most popular external venotonics are conventional gels and ointments based on heparin, troxerutin, etc.
Further in the article we will consider systemic venotonic agents for the treatment of varicose veins in the form of tablets.
Drugs for the treatment of blood vessels: which ones to choose?
The variety of means for the treatment and prevention of varicose veins often leads to the fact that a person is lost and does not know which drug is best to choose. Without a doubt, any medicine must be prescribed by a doctor, and in the case of varicose veins, consultation with a specialist is simply necessary. In this case, the doctor must be informed about all medications taken at the time of treatment so that he can prescribe adequate treatment, taking into account the preservation of the therapeutic effect of all medications simultaneously taken by the patient.
According to Russian and European phlebological standards, systemic treatment of varicose veins requires an integrated approach, which was already mentioned above in the article.
- Venotonic effect . Makes it possible to combat the incompetence of the valvular apparatus of blood vessels. Normally, blood moves through the vessels of the legs from bottom to top - against the force of gravity. This occurs due to the contraction of the calf muscles during movement and physical activity, as well as due to the presence of special valves on the inner surface of the vein wall, which prevent the reverse flow of blood. However, under the influence of various kinds of provoking factors, the valves weaken and begin to let blood through in the opposite direction. As a result, excess blood volume accumulates in the superficial veins, which leads to a gradual stretching of their walls.
- Angioprotective effect. Aimed at strengthening the stretched walls of blood vessels - restoring their firmness and elasticity. Under the pressure of venous reflux (pathological discharge of blood from top to bottom), blood stagnates in the veins, the walls of the vessels become thinner and the fluid is able to penetrate into neighboring tissues. Swelling occurs, which, in turn, leads to impaired trophism.
- Antiplatelet effect . Aimed at combating trophic disorders and restoring rheological parameters of the blood (reducing its viscosity and the risk of blood clots). So-called thick blood is a very common companion to the disease, because varicose veins themselves are not so dangerous as the venous thrombosis that appears against its background. Disruption of blood flow contributes to the accumulation of metabolic products in small blood vessels, this causes blood thickening and provokes the appearance of free radicals and mediators of the inflammatory reaction. All these factors in combination worsen the fluidity of the blood and lead to its thickening.
Ideally, a systemic venotonic drug should work simultaneously in all directions to achieve the best effect without taking additional drugs. As a rule, this advantage also provides a more compact course of treatment (since it acts on all aspects of the varicose vein problem at once) and good cost savings.