Causes of the disease
Birth trauma is a pathological condition characterized by damage to tissues and organs in a newborn during childbirth, which is accompanied by disruption of their functions.
Traumatic injuries become possible when the size of the child does not correspond to the birth canal, during the provision of manual or instrumental assistance or cesarean section. They are also recorded in post-term pregnancy, large fetal mass, malformations, anomalies of presentation, vacuum extraction, narrow maternal pelvis, exostoses and old age of the postpartum woman.
Erb-Duchenne palsy occurs when the spinal cord is damaged at the C5 and C6 level or the superior brachial plexus.
Erb-Duchenne palsy occurs in newborns due to birth trauma, with traction on the arm, head, pelvis or leg of the fetus.
In this case, a rupture, tear, tension in the trunks of the brachial nerve plexus may occur, as well as rupture of the scalene muscles, fascia, and bleeding may occur.
After some time, scar formation occurs around the nerve plexus of the brachial column, causing secondary compression of the plexus, disrupting the conduction of nerves, disrupting blood circulation and the formation of neuromas inside the trunk.
Erb-Duchenne palsy is a disease that occurs in stages, in three stages during which the nerve is restored. The first stage is the acute period of injury (from birth to one month of the child’s life), the second stage is the recovery period (from a month to a year), and the third stage is residual effects (from a year).
Symptoms and course of the disease
The clinical picture of Erb-Duchenne palsy depends on the degree of damage to the nerve fibers. In any case, there is a violation of the innervation of the muscles that raise the shoulder above the horizontal line, the muscles that rotate the shoulder outward. The affected arm is usually extended in all joints and is tightly attached to the child's body. In this case, there is no movement in large joints, there are no tendon reflexes in the affected arm. Sometimes there is a groove between the shoulder and chest as a result of misalignment of the affected arm. In this case, they talk about the “doll hand” symptom.
The most severe cases of upper paralysis involve the higher segments of the cervical spine, the fourth, and sometimes the third. In this case, damage to the phrenic nerve may occur, and breathing disorders are added to the clinical picture, which can in some cases be life-threatening for the newborn.
Treatment of the disease
Diagnosis and treatment of Duchenne-Herb's palsy by orthopedic doctors, neurologists and neurosurgeons. Treatment of paralysis, depending on the severity of the disease, can be surgical or conservative combined with physiotherapeutic procedures.
Conservative treatment of Erb-Duchenne palsy occurs in stages and begins immediately after the birth of the child. Treatment is long-term using various techniques. First of all, the injured limb is immobilized using a removable splint.
The splint is used for a year and is removed only in case of hygiene measures and medical procedures. In severe cases of this disease, the splint is used during the first three years of the child’s life, and is used only at night.
The treatment complex for Erb-Duchenne palsy also includes drug therapy, massage of the injured limb, physiotherapeutic procedures and activities (electrical stimulation of the arm muscles), passive therapeutic exercises, acupuncture and reflexology.
If the child does not noticeably improve the functionality of the affected arm within the first six months, surgical correction is usually indicated.
In the most severe cases of this disease, neurosurgical operations may be prescribed, which are performed on the nerve plexuses, and orthopedic operations on bones, muscles and joints.
In severe untreated cases, they resort to surgical treatment - muscle transplantation or arthrodesis of the shoulder joint; the latter intervention is performed in children no earlier than 10-32 years of age.
When operating on the shoulder joint, surgeons use arthroscopy. This is a new surgical method that allows operations to be performed using optical fiber.
Any surgical intervention is carried out using endoscopic devices, which ensures minimal trauma, is easily tolerated by patients, speeds up the rehabilitation period and significantly reduces the risk of complications. Throughout the rehabilitation period, specialists continue to monitor their patients and help carry out the necessary exercises and procedures.
Description of the disease
Duchenne-Erb's palsy is a degeneration of the nerve plexus in the shoulder area. As the anomaly develops, there is a violation of muscle tone, loss of sensitivity and atrophy of the muscles in this area. The most common is the secondary congenital form of the disease, which develops after injury to the child during obstetrics. Clinical manifestations include stiffness when trying to abduct, lift, or bend the upper limb at the elbow. Sensitivity and motor functionality in the fingers are preserved.
The term and definition of pathology were introduced and described by European doctors in the early 70s of the 19th century. The disease was named after them. Both specialists identified a direct connection between motor function disorders in the superior brachial plexus in infants and assisted births. In modern medical literature there is also such a definition as “proximal upper paralysis”. According to statistical data, the disorder has an incidence of 1-2 cases per 1000 children born. A number of specialists from various fields of medicine are developing methods to prevent injury to infants: neurologists, orthopedists, traumatologists, pediatricians, neonatologists, gynecologists and obstetricians.
Diagnosis of the disease
To diagnose Erb-Duchenne palsy, the child is examined by an orthopedist and a neurologist. They also collect anamnesis, which should contain information about the course of pregnancy and childbirth.
To obtain additional information, additional research methods are used: ultrasound examination of the shoulder joint and cervical spine, computer myelography, electromyography, magnetic resonance imaging, vascular Dopplerography of the brain and spinal cord, dynamometry, electroneuromyography, rheovasography and radiography.
Etiology of Duchenne-Erb's palsy
As stated earlier, the most common occurrence is upper obstetric paralysis, which develops as a result of birth injury to the fetus. In other age categories, the disease can be caused by damage to the brachial spinal roots located in the area of the 5th and 6th vertebrae. Nerve fibers can be damaged by a strong upper blow, a fall to the side of the arm, a bruise on a static object, by “pulling” the arm to the side, or a penetrating wound into the specified area.
Infantile paralysis is formed when the nerve trunk of the brachial plexus is stretched during turning by the leg, pulling the fetus by the arms, releasing the shoulder from the birth canal, or traction by the pelvis. The described manipulations are necessary in case of incorrect presentation of the child, insufficiently intense labor, a protracted period of delivery, narrow anatomy of the mother’s pelvis, or a large fetus. Often, along with acquired paralysis, there is a combination with torticollis.
The primary manifestations of the injury are inflammation and hematoma in the damaged area. A tear or complete rupture of nerve fibers, vascular walls, and muscles occurs. Over time, acute manifestations disappear, however, at the site of the violation of tissue integrity, scars form, which put pressure on the nerve plexus and the vessels feeding the department.
Prices
| Disease | Approximate price, $ |
| Prices for diagnosing migraine | 7 060 — 8 260 |
| Prices for diagnosing childhood epilepsy | 3 100 — 4 900 |
| Prices for brain shunting for hydrocephalus | 33 180 |
| Prices for treatment of Parkinson's disease | 58 600 |
| Prices for migraine treatment | 9 680 |
| Prices for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | 6 550 |
| Prices for diagnosing epilepsy | 3 520 |
| Prices for rehabilitation after a stroke | 78 300 — 82 170 |
| Prices for treatment of childhood epilepsy | 3 750 — 5 450 |
| Prices for treatment of multiple sclerosis | 4 990 — 17 300 |
| Disease | Approximate price, $ |
| Prices for diagnosing childhood arthritis | 2 000 — 3 000 |
| Prices for diagnosing childhood epilepsy | 3 100 — 4 900 |
| Prices for pediatric neurosurgery | 30 000 |
| Prices for treatment of childhood epilepsy | 3 750 — 5 450 |
| Prices for treatment of umbilical hernia in children | 9 710 |
| Disease | Approximate price, $ |
| Prices for hip replacement | 23 100 |
| Prices for clubfoot treatment | 25 300 |
| Prices for Hallux Valgus treatment | 7 980 |
| Prices for knee joint restoration | 13 580 — 27 710 |
| Prices for scoliosis treatment | 9 190 — 66 910 |
| Prices for knee replacement | 28 200 |
| Prices for treatment of intervertebral hernia | 35 320 — 47 370 |
| Disease | Approximate price, $ |
| Prices for pediatric neurosurgery | 30 000 |
| Prices for craniotomy | 43 490 — 44 090 |
Treatment of Duchenne-Erb's palsy
In the acute period of the disease, doctors resort to complete restriction of movements in the affected limb. To do this, an immobilization splint is applied. Parallel restorative manipulations are:
- visiting a massage therapist;
- exercise therapy classes;
- physiotherapeutic measures.
At this stage, pharmacological painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, medicinal substances that improve blood circulation and metabolic processes can be prescribed.
If therapeutic measures are poorly effective, the patient is referred for consultation to a neurosurgeon. The specialist evaluates the feasibility of surgical intervention. In childhood, instrumental correction is best performed at 6-7 months of life. Therefore, after three months of conservative treatment, you need to think about possible surgery. During neurosurgical manipulations, corrective plastic surgery of the nerve trunk is performed. Only microsurgical techniques are used.
With prolonged treatment in the stage of residual effects, it is no longer possible to restore the full functionality of the limb. Orthopedic interventions aimed at restoring the anatomical position of the hand can improve the condition. Some motor abilities that were previously lost may also be restored.
Causes
The most common cause of Erb-Duchenne palsy is injury to the superior trunk of the brachial plexus in the neck during obstetrics. The fact is that sometimes during the birth process the obstetrician has to use additional manipulations to help the baby be born (thus saving his life): turning on the leg, traction by the handle, releasing the shoulder, traction by the pelvis. I would like to emphasize that such actions are carried out only if necessary, when the child is not able to be born on his own, and it is too late to talk about a caesarean section. During such manipulations the following are possible:
- excessive stretching of the upper trunk of the brachial plexus, tears and even ruptures of its bundles (the roots of the C5-C6 cervical segments are damaged);
- traumatization of the scalene muscles and nearby fascia on the neck (where the nerve trunks pass);
- slight bleeding in the area of the brachial plexus and scalene muscles.
Direct damage to nerve fibers is initially accompanied by impaired nerve conduction and the appearance of symptoms of the disease, and muscle injury and bleeding, after swelling and resorption of the hematoma decrease, leave behind scar changes that can compress the nerve trunks, thereby disrupting nerve conduction and also creating a picture of Erb-Duchenne palsy .
In addition to injuries during childbirth, the superior bundle of the brachial plexus can be damaged by:
- falling on an outstretched arm;
- sharp traction (jerk) on the hand;
- a strong blow from above on the shoulder;
- contusion of the shoulder joint and neck area;
- gunshot or knife wound in the brachial plexus.
The described situations, of course, are much less likely to cause Erb-Duchenne palsy compared to obstetric problems.
Forecast
How will Erb-Duchenne's palsy end: full recovery or disability? This depends on many factors:
- on the severity of damage to nerve fibers;
- from the timeliness and correctness of treatment;
- from scrupulously following all the recommendations of the attending physician (and therefore the patience of the patient and his parents).
With partial damage to the upper bundle of the brachial plexus, even 100% recovery is possible (according to statistics, up to 20% of patients with partial damage have such a chance). With a complete breakaway, unfortunately, the chances are much less. However, timely surgical treatment increases their percentage.
Thus, Erb-Duchenne palsy is a disease that can be overcome. Its main symptoms in the form of limited movement in the shoulder and elbow joints can be minimized if you seek medical help in a timely manner and do not let the situation take its course.
Prevention
Carrying out preventive measures is an almost impossible task. Prevention includes maintaining the health of women, vigilant management of pregnancy for the timely detection of pathologies, indications for caesarean section. An important task is to choose the right means of obstetrics, so as not to use obstetric manipulations. However, not all situations can be foreseen in advance. Even a cesarean section is not a panacea. It is difficult to ensure that shoulder injury does not occur during a cesarean section.
It is even more difficult to talk about prevention in the case of traumatic Duchenne-Erb palsy. The only recommendation is to try to protect yourself from injury as much as possible.
Symptoms
The superior bundle of the brachial plexus is the source of nerve fibers for such nerves as the musculocutaneous, axillary and partially radial. With Erb-Duchenne palsy, the function of the muscles controlled by these nerves (deltoid, brachialis, brachioradialis, biceps brachii) is impaired and sensitivity in the area of their innervation is lost. This is accompanied by the following symptoms:
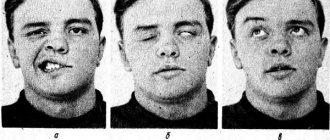
- the inability to actively (that is, independently) bend the arm at the elbow joint (passive flexion is not limited. Passive means “with someone’s help”);
- the inability to raise the arm to a horizontal level forward, or move it to the side, that is, restriction of movements in the shoulder joint. As a result, the hand “hangs” all the time;
- the inability to turn the affected arm outward, as a result of which the arm is brought into the body in such a way that the palm seems to turn away from the body and looks to the side and back;
- the dorsal extension of the hand is weakened, so the palm in a free state is in the position of palmar flexion (due to the prevailing tone of the flexor muscles);
- weakened finger extension;
- sensitivity on the lateral surface of the arm (outer surface of the shoulder and forearm) is impaired;
- the flexion-elbow reflex is not evoked;
- In children, grasping and palm-oral reflexes are also not evoked (in adults they are normally absent);
- muscle tone on the affected limb is reduced;
- the skin feels colder and paler to the touch compared to a healthy limb;
- painful pressure at Erb's point. The point is located above the collarbone outside the attachment point of the sternocleidomastoid (sternocleidomastoid) muscle.
If a newborn baby is held horizontally in the arms, the affected limb will hang down (both in the prone and supine positions).
The severity of the symptoms described above depends on how severely the nerve fibers are damaged. If there is a complete rupture of the bundles, then there will be no movement completely, and if the tear was partial, then the movements will be limited in volume and strength.
In the clinical period of Erb-Duchenne palsy, three stages are distinguished:
- spicy;
- restorative;
- period of residual effects.
The acute stage lasts the first month from the moment of paralysis, the recovery stage lasts up to a year (according to some sources, up to three years), and then comes a period of residual effects that lasts for the rest of life. It is very important to take measures to treat Erb-Duchenne palsy in the acute and recovery stages, since in the period of residual effects radical changes in improving the condition cannot be expected.
By the end of the recovery period and during the period of residual effects, if the patient’s recovery is poor, the affected limb shortens, becomes hypotrophied (loses weight), and in severe cases looks underdeveloped, like a baby’s (and remains that way for life). It is possible to form contractures in the area of the shoulder and elbow joints. In severe cases, a “puppet” groove is formed - a line that limits the transition of the arm to the torso. Muscle atrophy can cause subluxation or even dislocation of the shoulder joint. The scapula on the affected side rotates, its edge seems to move away from the spine. Over time, due to the described changes, curvature of the spinal axis in the cervicothoracic region develops, that is, scoliotic deformity.
Symptoms of Duchenne-Erb paresis
Duchenne's paresis is characterized by dysfunction of several muscles: the brachialis, deltoid and biceps. Symptoms for this disease depend on the degree of damage to the nerve fibers, as well as the stage of the pathology.
The development of the pathological process occurs in several stages:
- The acute stage is characterized by the appearance of difficulties when bending the elbow, as well as a decrease in hand function. The duration of this stage is up to 3 days;
- recovery stage. With optimal treatment methods, swelling of the affected area decreases, and blood circulation gradually normalizes. However, complete restoration of lost functions may require long-term rehabilitation;
- stage of residual effects. Timely treatment allows you to avoid serous consequences, such as muscle hypertrophy and separation of the scapula from the spine. These processes occur at the stage of residual effects; treatment of the pathology is ineffective during this period.
Signs of the pathological process in children appear in the first days of life. Constant crying and restlessness of a child should be a serious signal indicating problems in the body. Thus, with Duchenne paralysis, children experience severe pain, which causes anxiety in the newborn. The following symptoms also indicate the development of a pathological process in children:
- decreased muscle tone;
- hand clenched into a fist;
- the arm is extended at the elbow;
- pale skin;
- weak breathing.
Only specialists can identify Duchenne's paresis and make a diagnosis, guided by research results. In the Yusupov Hospital, when examining a patient, European equipment is used, which is characterized by high accuracy of results and the ability to visualize details of the body.
Complications and prognosis
Obstetric Duchenne-Erb palsy, even with proper therapy and rehabilitation, can still have certain consequences, which are characterized by the following symptoms:
- Over time, children may develop shortening and dystrophy of the hand .
- In addition, underdevelopment of the scapula , which manifests itself in its reduced size and asymmetrical location.
- Due to the injury and, as a consequence, damage to the nerve fibers of the brachial plexus, symptoms of scoliosis , which mainly affects the cervical and thoracic spine.
- Despite the fact that in more than half of cases positive results can be achieved, some children develop a decrease in muscle strength in a relatively healthy arm .
- Also in practice, there have been cases where severe damage to the brachial plexus was accompanied by a slight narrowing of the eye on the side of the damaged limb . However, this consequence passed quickly enough with proper and timely therapy.
Duchenne-Erb's palsy is a very serious injury, and in order to avoid serious complications, it is extremely important to begin therapy immediately after the birth of the child.
Thanks to this, over time, the function of the damaged hand is restored, and the child can live a full life. Prevention of this birth injury consists in proper management of pregnancy and childbirth, adequate choice of method of delivery, thanks to which the risk of injury to the child will be minimized.