Atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities leads to narrowing of the lumens of blood vessels. Such atherosclerosis is called obliterating (the abbreviation OASNK is used - obliterating atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities).
What is atherosclerosis
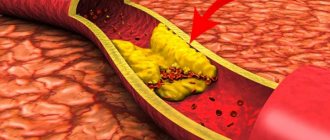
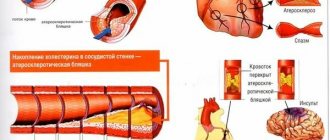
Atherosclerosis is a chronic systemic disease in which pathological changes occur in the arteries - the vessels through which oxygenated blood is carried from the heart throughout the body. The disease is associated with the deposition in the vascular walls of arteries of modified lipids - low molecular weight, water-insoluble substances, primarily fats, of which cholesterol plays the largest role in the development of atherosclerosis. Lipid deposits form plaques that narrow the lumen of blood vessels, as a result of which the flow of arterial blood is hampered and may even stop completely (vascular blockage).
Atherosclerosis is a systemic disease, that is, with the development of favorable factors, the formation of lipid plaques can occur in various parts of the arterial system. However, as a rule, at the stage of manifestation of symptoms, the disease occurs with primary damage to one or more groups of vessels.
More information about atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities
is a type of disease characterized by predominant damage to the terminal (end) section of the abdominal aorta and its main branches, including the femoral arteries.
If pathological changes lead to a narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, then such atherosclerosis is called obliterating (the exact medical diagnosis of OASNK
is
obliterating atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities
).
Obliterating atherosclerosis is the most common disease of the arteries of the lower extremities. It appears mainly in men, starting from 50-60 years, in women - from 60-70 years. At the age of 65 years and older, obliterating atherosclerosis of the lower extremities is detected in approximately 10% of the population.
Causes of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities
Atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities
There is a complex of factors that contribute to
atherosclerotic vascular damage , including the arteries of the lower extremities. There are non-modifiable (that is, unchangeable) and modifiable (modifiable) risk factors. Non-modifiable risk factors include:
- age (the older you are, the stronger the manifestation of atherosclerosis);
- gender (men suffer from atherosclerosis much more often than women);
- genetic predisposition (if there are strokes and cardiovascular diseases in the family history, atherosclerosis is more likely).
Main modifiable risk factors
:
- disorders of lipid metabolism (increased levels of total cholesterol in the blood. A distinction is made between low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. The threat of atherosclerosis increases with an increased content of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and, conversely, with a reduced content of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.);
- smoking;
- diabetes;
- obesity, overweight;
- high blood pressure (accelerates the development of atherosclerosis);
- sedentary lifestyle (leads to metabolic disorders);
- poor nutrition;
- renal failure.
For the development of atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities, smoking and diabetes mellitus are of greatest importance.
Alcohol
A study at the University of Illinois at Chicago among middle-aged and elderly people found a link between heavy drinking and stroke. Excessive alcohol consumption can damage your arteries.
Alcohol also provokes the development of thrombosis inside the vessels.
Of course, it will be better if the above products are completely excluded from the diet. But most likely, this is simply impossible to do. But at least minimize their consumption, try to choose a healthier alternative. And then your vessels will be in excellent condition.
zen.yandex.ru
Symptoms of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities
Symptoms of atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities
Atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities at an early stage can be practically asymptomatic. However, the absence of pronounced symptoms does not guarantee that atherosclerotic lesions are insignificant. Since lipid deposits in the walls of arteries do not immediately lead to disruption of blood flow, the development of atherosclerosis can go unnoticed for years.
If atherosclerosis develops slowly, the body compensates for the difficulty in blood flow through the main arteries with the help of collateral circulation, in which blood flows through the lateral branches of the arterial system. In this case, even a significant degree of atherosclerotic damage may not produce pronounced symptoms. The most striking symptom - intermittent claudication occurs only when the lumen of the artery is blocked by 80%.
The stage of development of atherosclerosis can be determined by how quickly pain occurs:
- Stage I
: pain in the legs occurs with significant physical activity. When walking calmly, pain occurs no earlier than after 1 km. ways. - Stage II
: pain occurs earlier than after 1 km. Moreover, if it arose more than 200 m later, we speak of stage II (A), and if less than 200 m later, we speak of stage II (B). - Stage III
: pain occurs every 25-50 m. At this stage, the legs hurt even at rest, especially at night. Patients usually lower their leg off the bed to improve blood flow and reduce pain. - Discomfort at rest is a critical indicator. The presence of discomfort indicates a high degree of stenosis or occlusion (complete closure of the lumen of the artery).
- Stage IV
is characterized by the appearance of ulcerative-necrotic changes. Feet become cold. Their hair falls out and their nails become deformed. Blackening of the skin occurs on the fingers and heels. Trophic ulcers develop. Possible gangrene.
Intermittent claudication
Intermittent claudication is pain in the calf muscles (less commonly, in the buttocks and thighs), as well as numbness and coldness of the lower extremities, forcing the patient to stop walking. It is enough just to stand in one place, the symptoms go away, and movement can continue.
What it is?
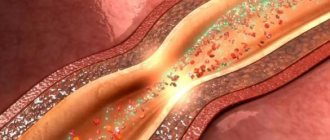
Blockage (or occlusion) is a sudden occurrence of vascular obstruction, which is a consequence of pathological processes occurring in the tissues. As a rule, the reasons for the onset of the development of the disease are the appearance of a blood clot or traumatic exposure. At critical moments, when the patient requires urgent surgical intervention, it is the cause of the disease that will be the main criterion in determining the strategy of action of health workers. Weakening or cessation of blood circulation in any part of the circulatory system leads to ischemia (oxygen starvation) of organ tissues and the onset of necrotic processes (we are talking about cell death and tissue necrosis). Therefore, in the event of a complete blockage of a vein or artery, emergency medical care is an absolute necessity.
Symptoms of vascular blockage
If the vessel is passed less than halfway, the person begins to feel obvious discomfort. The symptoms of the disease will depend on where in the circulatory system the clogged fragment is located.
- Blockage of heart vessels. In case of damage to the coronary vessels of the heart, the development of coronary artery disease (CHD) begins. At the initial stage, it is indicated by angina attacks, the duration of which does not exceed 10 minutes.
- Blockage of blood vessels in the legs. If there are such deviations, the patient feels pain and discomfort in the legs. In addition, patients often complain of constant coldness of the legs and pallor or cyanosis of the tissue.
- Blockage of cerebral vessels. In this case, the intensity of the attack will depend on how much the internal cavity is dug. The patient may experience periodic or constant headaches, accompanied by increased blood pressure. Dizziness, vomiting, nausea, or confusion may also occur.
Get a free consultation Consultation on the service does not oblige you to anything
Consequences of the disease
A decrease in patency can have the most unpleasant consequences for the patient. The consequences of a developing disease can be very diverse and, again, will depend on the location of the damaged vessel.
So, at the initial stage * blockage of blood vessels in the extremities * is fraught only with the appearance of pain and pulling sensations in the legs. Prolonged obstruction entails the formation of trophic ulcers and complete tissue necrosis. With such a diagnosis, the patient is indicated for limb amputation. Otherwise, he may develop gangrene.
Prolonged ischemia of the heart vessels often causes the development of myocardial infarction. The extent of tissue damage in this case will depend on the volume of the area affected by the obstruction.
Long-term blockage of blood vessels in the brain is no less dangerous. Increased blood pressure and headaches caused by ischemia of brain tissue often indicate the onset of an ischemic attack, the final stage of which may be a stroke.
Diagnostics
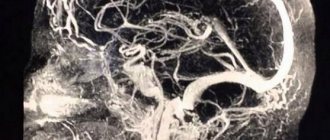
A patient whose complaints indicate the alleged presence of poor patency will have to undergo a series of general and specific examinations to confirm or refute the diagnosis. Along with laboratory blood tests and other standard manipulations, the patient may also be prescribed an MRI of the heart and blood vessels related to the area affected by the disease. The resulting three-dimensional image will allow you to determine the degree of vascular patency and identify the presence of plaques or traumatic injuries to veins and arteries.
MRI of the brain vessels will allow the doctor to get a complete picture of the state of the brain tissue and take timely measures to exclude death or permanent disability.
Methods of treating atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities
Bypass surgery
Treatment of atherosclerosis begins with the elimination of factors contributing to the development of the disease. Doctors at the Family Doctor recommend regular exercise and quitting smoking (treatment of a patient who continues to smoke is futile). Patients are prescribed a special diet to improve lipid metabolism. Treatment also includes measures to normalize blood pressure.
- At the first stage of the disease, conservative (medicinal) treatment is possible.
- Starting from stage II of obliterating atherosclerosis, surgical treatment is performed. The main methods used are bypass surgery, prosthetics, balloon angioplasty and stenting.
The bypass method assumes that blood flow is directed around the artery affected by atherosclerosis - through a shunt. The patient’s own vein is most often used as a shunt (the absence of a vein is easily compensated by the body). In some cases, synthetic prostheses in the form of a hollow tube are used. During bypass surgery, the affected artery is usually not removed. In the treatment of atherosclerosis of the lower extremities, femoral-popliteal or femoral-tibial bypass surgery is used.
If you experience symptoms indicating atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities, you should definitely consult a doctor to undergo examination and begin treatment. If surgery is indicated for you, it should not be postponed. Atherosclerosis is a progressive disease and at an advanced stage cannot be treated. If gangrene develops, amputation may be required. Seeing a doctor at an earlier stage of the disease will allow you to save the limb and restore its function (eliminate intermittent claudication). Vascular surgeons at “Family Doctor” have extensive experience in treating obliterating atherosclerosis at various stages, including performing femoropopliteal and femoro-tibial bypass surgery.
Conservative treatment
Conservative (drug) treatment can be effective only at the first stage of the disease. It includes the use of vasodilators, as well as drugs that reduce blood viscosity and normalize metabolic processes in the body.
Femoropopliteal bypass surgery
Femoropopliteal bypass is the main method of restoring blood supply to the lower limb in case of occlusion of the femoral artery.
More information about the treatment method
Femoral-tibial bypass
Femoral-tibial bypass surgery is indicated if femoral artery occlusion is accompanied by popliteal artery occlusion.
More information about the treatment method
Prosthetics
Prosthetic replacement is a method in which the blocked artery is removed and replaced with a synthetic prosthesis (or the patient's own vein). Prosthetics are more difficult for the patient to tolerate and therefore are used less frequently than shunting.
Stenting
To treat atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities, balloon angioplasty and stenting are also used to expand the lumen of the vessel. However, the applicability of these methods is limited. They are effective only if the occlusion is observed in a separate, relatively short section of the artery.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Diagnostics
To diagnose atherosclerosis, both laboratory and instrumental methods can be used:
- general blood analysis;
- blood cholesterol level test;
- angiography (injection of a contrast agent into the blood, which reflects X-ray radiation and gives the specialist a detailed map of the condition of the vessels of the entire body);
- CT, MRI;
- coronary angiography (to study the coronary arteries);
- ECG, echocardiography (echocardiography);
- Holter ECG monitoring (to detect disturbances in heart rhythms);
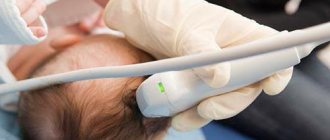
- Ultrasound (to study the condition of the aorta, kidney vessels, heart).
Diagnostics usually does not cause problems for an experienced doctor - for this, our center has all the necessary equipment. After all, modern high-tech devices will be required - the better the equipment, the more detailed the examination data will be, which will help the doctor choose the optimal treatment method.
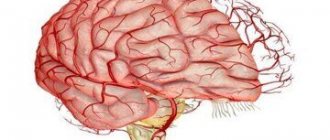
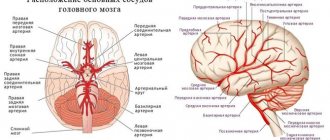
Atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries
When cholesterol plaques form and the arteries of the brain narrow, the brain cells experience a lack of blood and nutrients. The following symptoms may indicate this condition:
- periodic dizziness,
- noise in ears,
- headache,
- increased fatigue,
- disturbances in coordination of movements.
The narrowing of the main carotid artery supplying the brain is identified as a separate diagnosis - carotid artery stenosis. Damage to the vessels supplying the brain carries the threat of a serious disease - ischemic stroke of the brain.