The most valuable thing in the life of each of us is children, which is why their health should be monitored from birth, so as not to encounter numerous problems and complications that worsen the lives of children and parents. Pseudocyst of the brain in newborns, according to experts, is the safest complication that can appear during childbirth. Approximately one in 100 cases is diagnosed with this disease.
The appearance of such a formation does not entail serious consequences, but requires close monitoring by doctors. The pathology detected in infants is not reflected in the functioning of the brain. Moreover, it does not affect mental abilities or the appearance of mental problems.
The concept of pseudocyst
Formations of the cystic type are peculiar cavities, characterized by a round shape and having a small size. They are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (exudate or other substances). The bulges are concentrated on one or both sides at the same time. The mechanism of development of this pathology in infants has not been fully studied to this day. It may happen that, in the presence of alarming prognosis, a baby is born absolutely healthy, and a second newborn is born with damage to the nervous system, with completely normal prognosis.
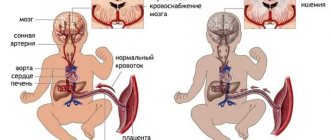
With the rather rapid intrauterine development of the brain, the vacated territory located in the area of the choroid plexuses is filled with a special fluid (cerebrospinal fluid). These are the processes that are observed during the development of a pseudocyst. It is safe for the life of the baby and is most often detected during an ultrasound scan of the fetus in the womb.
A large percentage of cystic formations resolve before birth. If this does not happen, then experts explain this by the presence of a herpes infection in the mother.
Reasons for appearance
The formation of a pseudocyst occurs during the intrauterine development of a child due to the influence of the following negative factors:
- Poor circulation in certain areas of the brain, caused by infection or malformations of the cardiovascular system.
- Insufficient oxygen supply to brain tissue (hypoxia), including in the last month of pregnancy.
- Previous hemorrhage in the brain (a subependymal pseudocyst is formed in a newborn).
Factors that increase the risk of formation include infectious or somatic diseases of a pregnant woman, exposure to stress factors, and excessive physical activity. The appearance of pseudocysts during intrauterine development is provoked by negative environmental factors, which include ionizing radiation (radiation), certain chemical compounds, including medications.
Often, a cerebral pseudocyst in newborns is formed due to the accumulation of fluid in the choroid plexus of the brain due to hypoxia. Typically, such formations resolve before the baby is born or during the first year of life.
There is a misconception among parents that cavity formation is provoked by vaccination. This is not true; the introduction of the vaccine has absolutely no effect on the development of the structures of the nervous system.
Diagnostics
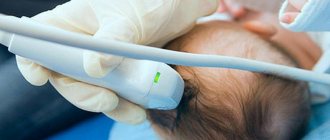
Ultrasound is most often used to confirm the presence of a false mass in the brain area. This method is the most popular, but it does not provide the opportunity to conduct a thorough inspection of the walls, as well as the internal space of the existing cavity. The emphasis is on specific areas where false benign formations most often form.
Particular attention is paid to the cerebral hemispheres. Also, emphasis is placed on the lateral ventricles, the area where the head of the nucleus (caudate) is located and some other areas. Features of the location of the pathology make it possible to distinguish it from a true cyst.
The presence of formations is confirmed by echo signs of a subependymal pseudocyst in the area of the right as well as the left ventricle. The use of ultrasonic waves is effective only in cases where the baby’s age has not reached 1 year. In this case, the fontanel located on the head is not covered by bones.
A newborn is examined for the presence of a pseudocyst if:
- the child was born prematurely,
- the birth was accompanied by serious complications,
- observation of insomnia, excessive tearfulness and anxiety in a newborn,
- the presence of convulsive muscle contractions, dizziness and other neurological signs.
When conducting research, the following methods for identifying the disease can be used:
- Doppler encephalography.
- Neurosonography.
- MRI and computed tomography.
- Cerebral scintigraphy and some other techniques.
If there is a suspicion that the fetus has genetic disorders, a chromosomal analysis of the fluid (amniotic fluid) may be prescribed. This intervention is invasive and is therefore used in very rare cases.
Diagnosis of cysts and pseudocysts of the brain
Ultrasound scanning of the brain parenchyma is a safe and informative diagnostic method. Indications for examination:
- Hypoxic conditions;
- Traumatic brain injury;
- Complication of childbirth;
- Restless behavior of the baby;
- Suspicion of pathology of intracerebral circulation.
Detection of pseudocystic cavities in newborns is not difficult. If the fontanelles become overgrown, tissue examination is carried out using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (CT and MRI).
Headaches, dizziness, muscle cramps with the combined presence of cystic cavities require combined diagnostics using neuroimaging methods:
- Positron emission tomography (PET);
- Neurosonography;
- Doppler encephalography;
- Cerebral scintigraphy;
- Computed tomography and MRI of the head.
A comprehensive study reveals concomitant pathology that occurs during complicated pregnancy or childbirth. Using intravenous administration of a contrast agent, the condition of the cerebral arteries is monitored, areas of hemorrhage and hematomas are identified.
If chromosomal abnormalities are suspected (Edward's disease, Down's disease), amniocentesis is performed - taking material from the amniotic fluid for genetic examination.
Difference between cyst and pseudoplasm
False formations that appear in the brain area have significant differences from the true ones. They are distinguished by:
- Place of appearance. In most cases, pseudoformation is located in the zone of the subcortical nuclei, or rather between them. The pseudocyst is localized near the lateral ventricles or in the area of the cerebral hemispheres.
- Reason for appearance. The disease can be secondary or acquired. An accurate diagnosis is made through instrumental diagnostics. If a specialist has directed you to undergo an examination, you should not abandon this step, since timely detection of pathology will prevent the occurrence of serious violations.
Pseudocyst of the brain in newborns and adults
Cystic pseudocysts are cavity formations with liquid contents and a thin wall that limits the size of the structure.
The false cavity differs from the true analogue by its formation from the germinal matrix, which is clearly visible on MRI of the brain. Nosology refers to developmental anomalies. The most common location of a cystic cavity formation is between the head of the caudate nucleus, the optic thalamus, and the lateral angles of the lateral ventricles. In adults, the main cause of cystic cavities is brain infections (Toxoplasma, Cryptococcus).
Is a pseudocyst dangerous and why?
The existing pseudocyst in the head of a newborn in all cases has a second cause of development. The following reasons may act as a catalyst for the appearance:
- lack of oxygen,
- problematic childbirth,
- presence of injury.
A false cyst in an infant is not dangerous to health. This pathology should cause alarm in cases where the formation rapidly increases in size.
There is no need to perform any specific therapeutic procedures in the treatment of pseudocysts in infants. All that is necessary is to regularly visit a neurologist and carry out restorative therapy designed to combat the emergence of possible complications that often appear against the background of injury.
If after 12 months the formation and the baby have not gone away, doctors diagnose a true cyst. In such situations, you should be observed by a neurologist throughout your life.
How to identify a pseudocyst
A highly accurate, informative and safe method for diagnosing brain-related abnormalities in infants is neurosonography. Indications for the study are:
- Asphyxia of the baby.
- Birth injuries.
- Fetal hypoxia.
- Protrusion or retraction of the fontanel.
- C-section.
- Infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy (rubella, chickenpox).
- Prematurity.
- Difficult birth.
The following studies may also be prescribed to the baby:
- Doppler encephalography, which allows you to assess the condition of the arteries of the brain and neck.
- Two-photon emission tomography is an effective way to examine internal organs. Used to detect various tumors and monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
- Cerebral scintigraphy is a modern type of diagnostics used to assess the condition of the brain, liver, heart, kidneys, and thyroid gland.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This examination is performed on infants under general anesthesia.
But the main method for detecting cystic formation is ultrasound. With its help, any formations in the body are determined, for example:
- Cyst on the tailbone.
- Cyst in the kidney.
- Popliteal tumor (Becker's cyst).
In case of a false cyst, repeated examination must be carried out over time in order to track the dynamics of growth of the formation. If its size has not changed or, on the contrary, increased, a therapeutic course or surgery is prescribed.
Treatment
The course of pathology observed in a newborn child should be monitored by a pediatric neurologist. The following techniques can be used during therapy.
Medicines
As a rule, doctors prescribe a number of drugs to children, the action of which is aimed at improving blood circulation in the brain, and also prescribe antihypoxants:
- Mexidol,
- Cytoflavin,
- Vitamins belonging to group B,
- Mildralex.
If hyperactivity is observed, the use of drugs such as:
- Glycine,
- Pantocalcin, as well as Pantogam.
To strengthen the musculoskeletal system, you should attend massage sessions, but only if they are recommended by your doctor.
If the false cyst was not subject to resorption during the first year of the child’s existence, and it increases in size, surgery will be required. Removal of the formation is carried out through craniotomy using endoscopy and shunting techniques.
Relationship between pseudocyst and other pathology
It is believed that a pseudocyst in a baby’s head is a consequence of changes at the genetic level. Often the pathology is accompanied by the development of other defects in the body. When detecting changes in the brain, the doctor must pay attention to possible changes in the functional state of other organs. A study is being conducted to identify disorders of the heart, blood vessels, internal organs, structures of the urinary and reproductive systems.
A subependymal pseudocyst on the left in the brain is often accompanied by the development of Edwards syndrome, which is a chromosomal disease. In this case, multiple developmental defects are noted, which are formed against the background of trisomy 18 chromosomes. These include abnormalities of the facial and cerebral skull, changes in the shape of the chest, ventricular septal defect, pulmonary artery aplasia, hypoplasia of the cerebellum and corpus callosum of the brain. In this case, complex surgical treatment is required; the prognosis usually remains unfavorable.