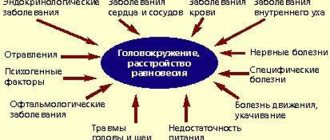
What is unsteadiness of movements?
Unstable movements – permanent or temporary loss of coordination. If they occur systematically, this indicates the presence of abnormal disorders in the body. Extra-systemic indicate that inflammatory processes are occurring in the body.
Most often, unsteadiness of walking manifests itself in combination with other symptoms:
- headache;
- unexplained sudden weakness;
- tingling in the legs;
- dizziness.
To better understand, it is necessary to know why a person may stagger when walking and why this is so important.
Movement is achieved through a healthy bone structure, developed muscles and healthy joints. The cerebellum is the part of the brain responsible for coordination; it is also controlled by vision and the vestibular apparatus.
Impulses pass through the spinal cord, sending a signal to the lower parts of the body that a movement needs to be performed. Only after this the muscles begin to work.
When these impulses are disrupted, the entire system is disrupted. This is where the gait disorder comes from. A transmission failure causes the legs to become unresponsive.
Failures in the musculoskeletal system lead to exactly the same result. The legs cannot correctly carry out the necessary “commands”.
If the functioning of the cerebellum is disrupted, the impulse itself does not reach, therefore, the command does not arrive at all. Consequently, a person cannot move, his legs do not obey.
Causes of VSD: the essence of the diagnosis
In the human body, as I prefer to say during my appointment, there are three sections of the nervous system: central (brain and spinal cord), peripheral (spinal cord roots and individual nerves) and autonomic (including the vagus nerve - emerging from the structures of the brain, autonomic nerve plexuses, including the solar-celiac plexus and carotid glomerulus, as well as individual vegetative cells). So, the functions of the central nervous system are the mind, information processing, most of the sensory organs due to the cranial nerves (vision, hearing, taste, etc.), integrative tasks, as well as the development of a command to act. The peripheral nervous system provides control over the human body, facilitates the collection of information (temperature sensitivity, tactile sensitivity, etc.), and also ensures the execution of commands for action. The autonomic nervous system is practically independent of our consciousness and controls autonomic functions: vascular tone, including the brain, blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, production of exocrine and internal secretion glands (including sweat glands). All this provides a double and sometimes even triple system of control of important functions of the human body. At the same time, in the autonomic nervous system there are inhibitory and excitatory influences in balance, which, by changing the strength of these influences, regulate the functions described above.
However, the autonomic nervous system is in close relationship with other departments, in particular, through the work of the vagus nerve, which is a cranial nerve. The vagus nerve nuclei, in turn, interact to some extent with the limbic structures of the brain responsible for emotions and perceptions of stress. In general, the human body is a single and very complex structure. Therefore, an imbalance in one part of the nervous system can lead to disturbances in another part. Thus, the presence of chronic or simply severe acute stress, congenital structural features of the autonomic nervous system, the influence of debilitating diseases, hormonal changes (during puberty, as well as during menopause in women), as well as some other factors lead to an imbalance of inhibitory and excitatory influences and the development of various types of disorders, including changes in cerebral vascular tone. This is exactly how, due to this imbalance and changes in vascular tone, a symptom complex of such a condition as vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD, vegetative dystonia, vegetative dystonia syndrome, these are all synonyms) is formed.
So, VSD is not a disease in the full sense of the word, “in the West” there are no separate codings according to the ICD 10 system for various forms of VSD, this is what led to the appearance of information about the absence of such a diagnosis in European and American practice. At the same time, psychological and psychotherapeutic assistance is very well developed there, and since one of the most important factors in the development of vegetative dystonia is stress, very often this problem is dealt with there more often not by doctors, but by psychologists, and, less often, by psychotherapists (and the diagnosis implies somatoform autonomic dysfunction, which is encrypted in class F and cannot be made as the main diagnosis by a therapist or neurologist).
In domestic realities, going to a psychotherapist for a patient means the presence of a certain “stigma”, and psychological support is unsatisfactorily developed and is quite expensive. Therefore, neurologists often deal with these problems. And they are forced to make a diagnosis due to the bureaucratic aspects of paying for visits, diagnostic procedures, etc. In this case, the generally accepted ICD 10 system is used, which still contains the term other disorders of the autonomic nervous system - code G90.8. And it is the code G90.8 that is the ICD 10 code for autonomic dysfunction. At the same time, according to the data I have, in the near future, with the adoption of ICD 11, a whole list of codes for this classification system will appear, responsible for coding this diagnosis. And there is a whole section 8D** responsible for coding these diagnoses.
Old age
Often, older people (over 60 years old) experience swaying, as well as “floaters” before the eyes. It is also common to experience tinnitus and dizziness when walking. Headaches appear sharply, and sometimes even fainting occurs. As a rule, all these symptoms are ignored and blamed on age.
In some cases, this may indicate problems with the body, so you should consult a doctor. This way you can ensure your usual full life.
One of the reasons is a malfunction of the cardiovascular system of the brain. Atherosclerosis appears (as mentioned above, a disease of the second category).
With age, the functioning of the vestibular apparatus is impaired.
Gait disturbance may also be due to heart disease. For example, ischemia can reduce blood circulation in the area of the ear where the organ responsible for balance is located. Also, insufficient blood circulation leads to uncertain movements. Other diseases also have a detrimental effect (arrhythmia, hypertension).
It has a great influence on gait and blood viscosity, because it supplies oxygen to the organs. How quickly it reaches the desired place, including the cerebellum, depends on its speed.
Injuries and diseases of the spine also make it difficult to transmit signals. Therefore, movement disorders are possible. Elderly people are often susceptible to sleep disorders, which leads to diseases of the third category.
The most common occurrence of maladaptation is observed. The person feels extremely insecure, there is a feeling that no one needs him, inexplicable fears and anxiety. As a result, he may skid when walking, become dizzy, have dark vision, and his condition worsens every day. For treatment, you must definitely contact professionals and it is better not to delay, because the consequences can be disastrous.
Based on all of the above, we can conclude that many factors can lead to an unsteady gait and they should not be ignored.
If the cause is eliminated, the consequences will also be eliminated. Life will be familiar, fulfilling and healthy. Therefore, it does not matter how old a person is, treatment is necessary regardless of age.
What diseases cause gait disturbances?
The main coordinators of normal gait and balance are the human eyes and inner ear. Accordingly, poor vision, infectious diseases of these organs often disrupt balance and, as a result, change his gait. The use of alcoholic beverages, drugs, and uncontrolled use of medications, including sedatives, also occupy a significant place among the causes of impaired gait.
Any pathology in the human nervous and muscular system can lead to gait disturbances. We are talking, first of all, about pinched intervertebral discs.
If we talk about more serious causes of changes in gait, then diseases such as multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, and Parkinson's disease come to the fore. Loss of sensation in both limbs in diabetes leads to loss of balance and instability.
There are a number of different diseases that are accompanied by gait disturbances.
Spastic hemiparesis causes a hemiplegic gait. In the case of such a disorder, the patient experiences a change in the position of the upper and lower extremities relative to the body. Those. the elbow, wrist, fingers are bent, the shoulder is turned inward, the leg in the joints - knee, hip and ankle - is extended. In milder cases, the arm is in a normal position, but its ability to move when walking is still limited.
Paraparetic gait can be observed in people with varying degrees of spinal cord lesions and spinal cord injury.
Limited flexion of the foot on the dorsal side causes a gait with a very sonorous name - rooster gait. Due to full or partial foot drop, the toes brush the surface during a step and the person must lift the foot as high as possible to avoid this.
Weakness in the proximal muscles of the leg, which occurs with myopathies and spinal amyotrophy, causes a person to walk waddling from side to side. This disorder is called the duck walk.
Parkinsonian (akinetic-regid) gait can be recognized by the following signs: the patient’s back is hunched, his legs are bent, and his arms are bent, while a resting tremor can be noticed. The patient begins to move by leaning forward. While walking, a person takes mincing steps that make a shuffling sound.
Apraxic gait can usually be observed in patients with bilateral frontal lobe lesions. The symptoms of gait disorders in this case are very similar to parkinsonian ones. But there are a number of differences: the patient is easily given some of the movements that make up the process of walking - while he can lie or stand. But as soon as one needs to start walking, a person is not able to do it. Having finally moved forward, the patient stops again. Such attempts to move are repeated several times.
Choreoathetotic gait - it is characterized by disruption of the walking process by sudden movements, made as if through force.
Legs set wide apart and steps of different lengths and speeds are signs of a cerebellar gait. A patient with this disorder can close and open his eyes and still be able to remain balanced. However, as soon as he changes his position, his balance is immediately lost.
Sensory ataxia - This disorder exhibits features similar to cerebellar gait. They differ in that the patient loses his balance as soon as he closes his eyes.
If a person falls on one side while walking, we are talking about vestibular ataxia.
Hysteria is also often accompanied by gait disturbances. It is typical for her to have simultaneous disturbances in balance and walking. A person suffering from hysteria is simply unable to stand without outside help, much less move.
When should you sound the alarm?
Impaired coordination in some cases is a consequence of serious illnesses. It is recommended to consult a specialist if:
- stumbling has become more frequent, often occurring even out of the blue;
- falls due to weakness in the legs;
- impaired control of movements;
- unnatural gait;
- after a long walk there is a sudden stop, then there is a feeling that it is impossible to move your leg;
- feeling of “cotton” legs;
- difficulty walking on stairs;
- when moving, most of the weight increasingly moves to the heel area;
- when trying to get up, a person falls;
- difficulty raising a leg or starting to move after a long rest;
- the appearance of dizziness, pounding in the temples, darkening in the eyes.
Often a person begins to be afraid and panic.
It is absolutely impossible to ignore such symptoms, since they indicate the presence of diseases.
Doctor's help
It is impossible to make a diagnosis yourself when it sways from one side to the other. This is done exclusively by specialists. To begin with, doctors monitor the patient’s movements using the following methods:
- observation of movements directed forward with the face and forward with the back;
- doctors watch how the patient moves in a straight line with his right and left sides;
- alternate change of step rhythm;
- comparison of walking with eyes closed and with eyes open;
- watching a person climb stairs;
- movement around an object (for example, a chair);
- making turns while driving;
- It is also suggested to walk on your toes and heels.
Based on the results, the doctor prescribes further examination and treatment:
- undergoing magnetic resonance imaging;
- X-ray;
- CT scan;
- blood donation (general analysis and biochemical);
- A biopsy of muscle tissue is performed.
In addition, the patient should be examined by other doctors:
- ENT;
- ophthalmologist;
- endocrinologist
After going through all the stages, the doctor can diagnose the patient and prescribe the necessary treatment.
You should turn to traditional medicine only after examination and consultation with a doctor.
Any medications are prescribed only by a certified specialist! All drugs are prescribed based on the individual characteristics of each organism. Medicines that help one person can cause irreparable harm to another.
Who should I contact?
There are often situations when the patient himself understands that he needs the help of a specialist. However, he has no idea which doctor to see. To do this, you need to carefully monitor the symptoms and act in accordance with them:
- Cardiologist. It is worth contacting him if, along with impaired gait, there is also increased blood pressure or in the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Neuropathologist. A neurologist is consulted if a person often experiences stress, nervous or other mental disorders.
- Traumatologist/orthopedist. You have been injured, there is pain in the muscles or joints.
- Surgeon. You should see a surgeon if you receive serious injuries.
If it is impossible to identify the symptoms on your own, you should consult a general practitioner.
Often the cause of symptoms is sought using magnetic resonance imaging. This diagnostic method allows you to identify the cause of the development of pathology, as well as make an accurate diagnosis.
Choosing a clinic is easy to do using the service. A single registration center for MRI or CT allows you to select a medical center based on specified parameters: type of examination, metro station, and also sort the search results by price, rating, work schedule.
Patients have access to online registration through the website or telephone registration with a discount on the study in the amount of up to 1,000 rubles.
Treatment
Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia is the subject of enormous controversy in the scientific community. Who should make this diagnosis? Neurologist, therapist or psychiatrist? How to treat this condition and how – symptomatically or try to find the mechanisms of pathogenesis of this condition?
But disputes are disputes, and on this site I share my opinion. The most important thing is non-drug therapy, namely psychological support, stabilization of lifestyle (sleep, work conditions, family situation, bad habits, etc.); in the presence of panic conditions, consultation with a psychiatrist and the prescription of anti-anxiety therapy are indicated. In all cases, restorative therapy will not be harmful (including B vitamins, their derivatives, in particular Enerion, such “soft” drugs as Mexidol, Neurox, Ethoxidol, Armadin, Fnibut, etc.). In the presence of dizziness, the prescription of vertigolytics (Betaserc, Vestibo, etc.) is controversial, because there is usually no substrate for their work. It is more important to use vestibular rehabilitation and vestibular gymnastics techniques than drug treatment.