Familiarize yourself with other diseases starting with "P": Felon, Panic attack, Pancreatitis, Papillomas, Paralysis, Bell's palsy, Paranoia, Paraproctitis, Facial nerve paresis, Periodontitis, Periodontal disease, Paroxysm, Paroxysmal tachycardia, Scab (favus), Pediculosis, Spermatic cord torsion , Bone fracture, Rib fracture, Hip fracture, Post-term pregnancy
How to detect facial nerve paresis
This neurological disease, diagnosed with weakness of the facial muscles, leading to immobility and asymmetry of one part of the face, occurs due to disruption of the passage of impulses of the facial nerve. Outwardly it manifests itself in the patient’s inability to speak clearly, smile normally, or close an eye. With timely contact with a neurologist, the mobility of the facial muscles can be restored.
There are 3 forms of the disease:
- Congenital facial nerve paresis occurs in only 10% of cases. With this pathology, the newborn also experiences other damage to the nerve branches. With this form, the child requires surgical intervention;
- The first syndrome in peripheral paresis is pain in the postauricular area. On one half of the face, swelling of the nerve fibers and muscle hypotonicity occur;
- With central paresis, the eyes and forehead do not suffer from pathology, which preserves the patient’s ability to blink normally. Under the influence of pathology of brain neurons, the muscles of the lower part of the face are affected.
In addition, paresis is classified into stages: acute, subacute, chronic.
Diagnosis and treatment of facial paralysis
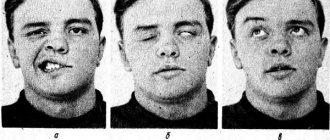
You can identify violations at home (note the presence or absence of facial expression disorders and movements of facial muscles), you just need to take a test - see if the movements are performed equally on both sides (close your eyes; close alternately first one and then the other eye; close your eyes; raise your eyebrows; frown your eyebrows; wrinkle your nose; bare your teeth; puff out your cheeks; blow, whistle; form a fold on the neck). If suspicions are confirmed, you should consult a specialist to diagnose the extent of damage to the facial nerve.
In diagnosis, the main importance is to conduct research to determine the level and depth of nerve damage - the development of indications for surgical intervention, and therefore the success of the operation, depends on this. The set of diagnostic procedures includes a mandatory visual inspection, determination of the level and threshold of sensitivity. instrumental studies in the form of myography, ultrasound of blood vessels and, if necessary, tomography. Only after receiving complete information about the location and extent of damage to the nerves and muscles of the face, a treatment plan (reconstructive operations) is drawn up, the essence of which is the reinnervation of the affected muscle fibers or the transposition of muscle fibers.
Surgical treatment of facial nerve paralysis is carried out by Mikhail Leonidovich Novikov, a reconstructive microsurgeon, a leading specialist in Russia in the treatment of congenital pathologies of the peripheral nervous system.
Treatment is provided free of charge with the support of Rusfond. In order for treatment to be free, parents of sick children need to collect documents from the list, send them (can be scanned to the address) for verification and registration, and then wait for a call for treatment.
You can make an appointment with a specialist by phone: 8 on weekdays from 9.00 to 19.00 Moscow time Or through the form on the website Sign up for a free consultation
Causes
The disease can be caused by various factors, which differ depending on the age of the patient. Facial nerve paresis can be affected by:
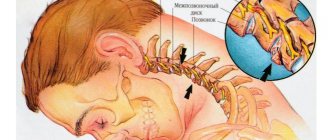
- Nerve damage due to surgery or otitis media;
- Hypothermia of the head and behind-the-ear area;
- ARVI of the upper respiratory tract;
- Herpetic infections;
- Head injuries;
- Mumps;
- Tuberculosis;
- Polio;
- Syphilis.
The severe inflammatory process that accompanies these pathologies provokes disruption of the facial nerve. In addition, poor blood circulation in the face can affect it. Contributes to this:
- Ischemic stroke;
- Hypertensive crisis;
- Diabetes;
- Multiple sclerosis.
Functions of the facial nerve
The facial nerve innervates (provides communication with the central nervous system) the facial muscles, which are responsible for the movement of facial muscles and the expression of all our emotions. There are only 2 facial nerves: right and left, each of which is responsible for the corresponding half of the face. The facial nerve has five branches: the 1st branch innervates the muscles of the upper third of the face, the 2nd and 3rd innervate the muscles of the middle third of the face, the 4th branch is responsible for the movements of the lower third of the face and the 5th branch activates the facial muscle of the neck. – m. platysma. The facial nerve exits the skull as a single trunk through the stylomastoid foramen of the pyramid of the temporal bone. Division into branches occurs in the area of the parotid salivary gland. Violation of the integrity of the nerve will lead to paralysis of the facial muscles that it innervates. Accordingly, if the nerve damage occurred in the cranial cavity, in the canal of the temporal bone and also before the branches depart, then paralysis will manifest itself on the entire half of the face corresponding to the side of the damage. If one of the branches or several branches of the facial nerve is damaged, then paralysis will occur only in those areas where the muscles that innervate these branches are located. The most severe degree of paralysis of facial muscles is damage to the facial nerve at the level of the trunk.
How does facial paralysis manifest? Symptoms of facial paralysis
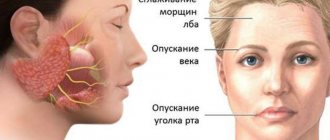
This manifests itself as follows: half of the face, or some part of it, does not express any emotions, there are no movements. A person cannot smile, be surprised, etc. At rest, asymmetry of the face is observed, and the side on which the facial nerve is damaged is lowered (the eyebrow, lower eyelid, corner of the mouth are lower, the cheek tissues sag). With facial expressions, the asymmetry intensifies. All this leads to a decrease in the social activity of people with this disease, and difficulties arise when communicating with people. But this problem is not only an aesthetically unsatisfactory appearance. There are also a number of functional disorders:
1) Impaired diction, the pronunciation of many sounds is difficult, speech is slurred, due to the lack of tone of the orbicularis oris muscle and the muscles of the buccal region; 2) Difficulty eating, especially liquids; 3) Difficulty brushing your teeth; 4) Drooling is not uncommon; 5) Complaints about the absence of tears, incomplete closure of the eyelids, which leads to the development of keratitis, conjunctivitis, which may result in the loss of the eyeball. In this case, quite often they resort to blepharorrhaphy (stitching of the eyelids), in which it is necessary to constantly use eye drops and ointments; 6) The opposite situation may also occur, in which there is constant lacrimation associated with the lack of adherence of the lower eyelid to the eyeball; 7) The appearance of difficulty in nasal breathing due to the fact that the nasal muscles do not work and a valve effect is formed.
All of the above symptoms significantly reduce the quality of life of a person with this diagnosis.
Causes of facial paralysis:
- Benign and malignant brain tumors, most often associated with acoustic neuromas;
- Diseases and neoplasms of the middle ear;
- Injuries and surgeries in the temporal region;
- Injuries and operations of the parotid region, which is often an iatrogenic complication when removing a pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid salivary gland;
- Malignant formations of the parotid salivary gland;
- Viral infections, including human herpes virus;
- Idiopathic lesions - Bell's palsy.
Treatment of paralysis of facial muscles
Treatment for paralysis of facial muscles cannot be delayed! In this case, time is running out! This is not due to the nerve itself, but to the changes that occur in the facial muscles. The nerve can be restored 25 years after the first signs of paralysis appear, but the ability to move muscles cannot be restored. Modern research shows that facial muscles completely lose the ability to contract after 2 years of lack of movement. Muscles that do not receive functional load atrophy, muscle tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue, and such tissues are not able to contract.
Operations performed for this disease:
Neuroplasty: masticatory nerve, hypoglossal, cross plastic, combination of methods.
This method is suitable for patients with a disease duration of no more than 1.5-2 years. The essence of this method is to reinnervate the facial nerve (the nerve that conducts the impulse is sutured to the “non-functioning” facial nerve) with another motor nerve (usually the masticatory nerve or hypoglossal nerve is used). The operation is performed using modern microsurgery. This operation is performed in a hospital under anesthesia and is classified as high-tech medical care (HTMC). The fibers of the working nerve grow along the facial nerve, so the impulse reaches the facial muscles and they begin to contract. As a result, facial movements appear and a certain amount of facial expression is restored.
The cross nerve is a nerve autograft taken from the sural nerve (n. suralis) through a mini-incision in the ankle area. This autograft is sutured to the facial nerve on the healthy side and passed through a tunnel (without visible incisions) and sutured into the facial nerve on the damaged side. Through this graft, a nerve impulse passes from the healthy side to the diseased side, causing the muscles on the damaged side of the face to move. In this case, the donor area (leg) does not suffer functionally, the function is not impaired. This method is often used in clinical practice in combination with other treatment methods.
The rehabilitation period takes from 4 months to 2 years. During this period, it is necessary to strictly follow the recommendations: daily myogymnastics, myostimulation, massage.
| Illustration of facial nerve neuroplasty using the masseteric branch of the trigeminal nerve: |
Autologous muscle transplantation (granus muscle, latissimus dorsi)
This method is suitable for patients with a disease duration of more than 1.5-2 years. The essence of this method is to transfer the muscle from the donor area (gracilis muscle - thigh, latissimus muscle - back) to the face, in which the vessels of the muscle flap are sutured into the vessels of the face using a microscope. Thus, this autograft is supplied with blood and “takes root.” The muscle is reinnervated through the masticatory (or hypoglossal) nerve and the cross nerve. This operation is performed in a hospital under general anesthesia, which is also high-tech. The transplanted muscle imitates contractions of the muscles of the middle zone of the face, that is, a smile appears. An invisible thin scar remains in the donor area, the function of which is not impaired.
The rehabilitation period takes from 4 months to 2 years. During this period, it is necessary to strictly follow the recommendations: daily myogymnastics, myostimulation, massage.
| Illustration of lean muscle autotransplantation: |
Autotransplantation of muscles (temporalis muscle).
This method is suitable for patients with a disease duration of more than 1.5-2 years. The essence of this method is to move the temporal muscle without disrupting its blood supply and innervation to the midface area, forming a nasolabial fold. This operation is performed in a hospital under general anesthesia. When this muscle contracts, a smile is formed. Also, this method achieves facial symmetry at rest. The rehabilitation period takes from 4 to 10 months. During this period, it is necessary to strictly follow the recommendations: daily myogymnastics, myostimulation, massage.
| Illustration of temporalis muscle transposition: |
Static facial correction.
This method is suitable for patients with any duration of the disease. Often used as an adjunct to previously described treatment options. The essence of this method is to move and fix the soft tissues of the face on the diseased side into a symmetrical position relative to the healthy side. The result is symmetry of the face at rest, movements do not appear (if this method is used separately, without combination with previously described methods). With this correction, threads, meshes, and fascia are often used for additional tissue fixation. The rehabilitation period takes from 1 to 6 months.
With all methods of surgical treatment, incisions are made, as in a facelift, in the scalp, along the natural fold in the pre-auricular area, behind the auricle. After such incisions there are no visible scars. The donor area, regardless of the method, does not suffer functional losses.
Characteristic clinical signs
Symptoms of the disease are:
- Smoothing the nasolabial fold;
- Drooping of the mouth on one side;
- Deterioration or loss of taste on the tip and sides of the tongue;
- Wide eyelid and lagophthalmos when closing the eye;
- Leakage of food from the mouth on the affected side of the face;
- Inability to stretch lips;
- In the first days of illness, noise phobia is present;
- lacrimation;
- Inability to wrinkle forehead;
- Facial asymmetry of varying degrees;
- Pain in the area behind the ear.
If these symptoms are detected, you should consult a neurologist.
Drug therapy
We list the medicine that is used to eliminate signs of paresis:
- An anti-inflammatory agent that helps relieve swelling.
- Vitamins.
- Blood thinning medications.
- Hormonal drugs.
- Corticosteroids.
- Moisturizing eye drops.
- Anesthetics.
Therapy
Facial nerve paresis requires a long course of treatment, which lasts about six months. It includes:
- Analgesics;
- Decongestants;
- Corticosteroids;
- Vasodilators;
- Sedatives;
- Vitamin and mineral complexes with a high content of B vitamins;
- If the eyes are affected, use artificial tears;
- Massage;
- Physiotherapy;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
If the nerve is completely severed, surgery is necessary.
Causes
Let's list the main ones:
- Neuritis or inflammatory process.
- Compression of a nerve branch after an injury.
- Infection.
- Hypothermia.
- Virus.
- Surgery to combat other disorders.
- Otitis.
- Sometimes paresis occurs after infection in the nerve tissue.
- Congenital syphilis.
- New education.
- Mumps.
- Polio.
- Osteitis is a disorder of sebaceous cells, problems with blood vessels or bone tissue.
- Central paresis occurs when the brain is damaged.
The congenital form occurs with various developmental defects of the child.