Author Andrey Belyakov
05/25/2007 11:49 (Updated: 05/28/2021 19:47)
Health » Health and prevention
The combination of the words “concussion” leads, on the one hand, to sad thoughts, and on the other, you console yourself: “Who doesn’t it happen to?” What actually happens when our brains get shaken? Candidate of Medical Sciences, neurosurgeon at the multidisciplinary clinic CELT Andrey Khodnevich Pravda.Ru about this .
The child has a headache
“Despite the fact that this injury is not considered severe, there are quite a few social, medical and rehabilitation problems associated with it. The fact is that there are many structures in the brain that are most vulnerable to this kind of influence: the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland stalk, the brain stem.
They are located between the immobile spinal cord and the more mobile hemispheres of the brain, which means they can be most deformed.
Symptoms of a concussion are:
- firstly, after hitting the head, a person loses consciousness for a short time (sometimes the fainting is so short-lived that the victim himself does not have time to realize it).
- secondly, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, loss of visual fields appear (with both eyes a person can see only a third or half of the overall picture in front of him).
But such symptoms also appear when the activity of other organs is disrupted, sometimes completely unrelated to brain activity. On the other hand, more severe brain injuries (bruise, hematoma, etc.) produce the same consequences.
Therefore, in practice it is very difficult to objectify such symptoms. As a result, doctors resort to overdiagnosis - the patient has not yet had time to fall, and he has already been diagnosed with a concussion.
This is fraught with the fact that behind the mass of such patients (mainly antisocial elements), the doctor may miss a really severe case or not recognize another disease in time.
Why does a lump appear?
A bump on the head from a blow appears due to damage to small vessels. At its core, it is a type of hematoma. Upon impact, the capillaries rupture and blood flows out. When other parts of the body are bruised, a bruise appears on the skin, but there is usually no swelling. This is due to the fact that the subcutaneous tissue absorbs blood on the body and limbs. Therefore, swelling does not form.
There is no fiber on the head. Blood pours out under the skin. In this case, the liquid is not absorbed, but only accumulates. For this reason, a head injury leads to the appearance of a lump. This does not exclude the simultaneous formation of a bruise if the blow was strong enough.
Surgical intervention for hallux valgus
Classic surgery to correct hallux valgus is highly traumatic and requires a long recovery period for the patient. The operation is performed in an open manner - the surgeon makes a tissue incision with a scalpel down to the bone and then removes it.
Anesthesia can be used both local and general. The standard surgical procedure involves sequentially performing the following stages of the operation:
- Incision of soft tissues using a scalpel inside the surface of the phalanx of the thumb;
- Surgical dissection of the capsule of the first metatarsophalangeal joint (capsulotomy);
- Exostosis ectomy is a procedure for removing callus;
- Osteotomy – sawing of the first metatarsal bone;
- Changing the axis of the deformed area of the finger and correcting any degree of curvature;
- Arthrodesis is a strong fixation of the resulting position of joint tissues with metal pins and staples. The joints must be in close contact with each other to allow rapid fusion of tissues;
- The first articular metatarsophalangeal capsule of the finger is sutured;
- The surgeon applies a sterile bandage to the operation site and secures the foot with a tight fixing bandage.
Depending on the severity and severity of joint deformation, the operation can last up to 2 hours.
Causes
A hematoma on the head does not occur with every bruise. In order for a lump to appear, a fairly rough mechanical effect on the skin is necessary. Swelling usually occurs as a result of the following injuries:
- Bumps on a child’s head from an impact are most often caused by falls. Small children often fall out of strollers. Such injuries also occur when a child learns to walk.
- Adults are more likely to get bumps when hitting hard surfaces. This happens with awkward movements or when an object falls on a person from above.
Actions to reduce and remove the consequences of the impact
The first necessary actions after a bruise to prevent the growth of the lump. At the first stage, it is important to stop the flow of blood from the vessels. To do this, it is necessary to achieve their narrowing. And this needs to be done as quickly as possible. Therefore, first aid consists of providing cold exposure to the site of impact.
A suitable item may be a rag soaked in cold water. You should apply it for a few minutes until it warms up. As necessary, it is necessary to replace the lotion that has become warm with a cold one.
You can use what you have in the refrigerator. It could be ice. You can put it in a plastic bag. The bag should be wrapped in cloth and applied to the bruise. To prevent hypothermia, which can result in complications and illness, it is necessary to apply at intervals.
In addition to ice, there may be some frozen food products in the refrigerator, such as meat. It can also be placed in a bag, wrapped in a cloth or towel and applied to the bump. If you have a cold drink bottle, that can also come in handy.
However, cold objects may not be nearby. For example, the following situation may happen: a man hit his head, a lump appeared, what to do if applying cold is not possible?
In this case, vegetable oil can be of significant help. You need to thoroughly soak a piece of gauze or cotton wool with it and cover the bruised area for 30-35 minutes. The redness that appears after such a compress should go away, but the lump may not appear at all.
Symptoms
How to distinguish a hematoma from other types of edema and tumors? Bumps on the head from a blow have the following features:
- A hematoma always forms exclusively in the place that has been subjected to mechanical stress. For example, if a person hurts himself on the top of his head, the bump cannot appear in the frontal region.
- The size of the formation may vary. It depends on how severe the bruise was.
- The color of the cone may vary. Sometimes it does not differ from the rest of the skin color, but it may also be bluish due to hemorrhage. But in the head area there are no bruises of such a bright color as on other parts of the body.
- The skin around the lump looks swollen.
- When you press on the lump, pain is felt.
On average, swelling can last from 2 to 7 days. With intensive treatment and proper first aid, the lump goes away quite quickly.
When to see a doctor if you have a head injury
If the symptoms of a bruise are only swelling of the lump and pain at the site of the impact, which gradually subsides, then it is not necessary to go to the hospital; it is enough to use the remedies described above. But sometimes the situation can be much more serious. The injured person may experience not only a bump on the head from a blow, but also signs of a sharp deterioration in their condition as a result of a concussion, intracerebral bleeding, or a fracture of the skull. Urgent medical assistance is absolutely necessary.
Signs of such particularly severe conditions of the injured person are
- The appearance of open wounds and bleeding from them, which does not stop for more than 10 minutes.
- Feeling of severe pain in the head and neck area.
- Increasing nature of pain.
- Simultaneously with severe pain, attacks of nausea are observed.
- Blood or other fluid is leaking from the ears and nose.
- Increase in body temperature to a value greater than 38 degrees.
- Speech impairment.
- There is a feeling that there is “floating” in the eyes; the pupils are of different sizes.
- Confused consciousness.
If these signs occur, the victim must be taken to the hospital as soon as possible, and until the ambulance arrives, the person should be ensured complete rest and closely monitor his breathing and consciousness.
A bump on the head from a blow may appear to a lesser extent or not appear at all. It all depends on how quickly the situation is assessed and the necessary actions are taken to improve the condition of the injured person.
Features of bruises in children
A bump on the head after a blow in a child is a very common occurrence. After all, children love a mobile and active lifestyle. Babies have delicate scalp, so a hematoma can form even with a minor blow.
However, head injuries in children are often accompanied by concussion and other unpleasant consequences. Therefore, you need to pay attention to the baby’s well-being. Many children cry a lot when they are bruised, but most often this is due to fear rather than pain. You need to let the baby calm down, and then take a closer look at his condition. If you have the slightest doubt, you should contact a pediatric traumatologist.
The size of the hematoma does not always indicate the danger of injury. For example, with forehead bruises, huge bumps always form. However, the frontal bone is the strongest and protects the brain well, so unpleasant consequences from bruises in this area are rare.
Cold
Let's say that a child or adult has a bump on their head from a blow. What to do first? A few minutes after the injury, blood continues to flow from the burst vessels, and the lump grows. If the blow was very strong, then the swelling increases right before our eyes.
First of all, you need to stop the subcutaneous hemorrhage. To do this, apply cold to the damaged area. Its effect will help narrow blood vessels and reduce hematoma, as well as reduce pain. The following available tools are suitable for this purpose:
- Ice. If the injury occurred at home, you can take ice from the refrigerator, put it in a bag and wrap it in a towel. Apply an ice compress to the bruised area. This procedure must be repeated several times during the day. Instead of ice, you can use freezer items or a bottle of cold water.
- Compress with cold water. You need to moisten the cloth with cold water and apply it to the bump. As soon as the compress warms up, it must be replaced. This procedure is repeated several times.
- If you don’t have anything cold on hand, regular vegetable oil can help. It should be applied to cotton wool or a bandage and applied to the bruise for half an hour. With the help of such a folk remedy, you can completely avoid the appearance of a bump if the blow was not too strong.
Cold must be applied within the first 24 hours after injury.
Types of damage
The faster a hematoma forms, the more difficult the recovery. Injuries of this type are divided into:
- lungs that develop within a day, accompanied by mild pain and not requiring special treatment;
- moderate severity, the appearance of which requires no more than 5-6 hours, accompanied by noticeable swelling and pain, worsening the motor function of the limb;
- severe, forming within 2 hours after a bruise, accompanied by dysfunction of the limb, acute pain and noticeable swelling.
Treatment of moderate and severe hematomas should be carried out under the supervision of a physician to eliminate possible negative consequences of injury.
In addition to the severity of the damage, there are other criteria for classifying hematomas:
- by depth of location - under the skin, under the mucous membrane, deep in the muscle tissue, under the fascia, etc.;
- according to the state of spilled blood - uncoagulated (fresh), coagulated and lysed (filled with old blood that is not capable of clotting);
- by the nature of blood distribution - diffuse (blood permeates the tissue and spreads quickly), cavitary (blood accumulates in the cavity between the tissues) and encysted (over time, the cavity filled with blood is surrounded by a “bag” of connective tissue);
- according to the condition of the vessel - pulsating (blood flows freely from the vessel and flows back) and non-pulsating (the rupture of the vessel is quickly sealed by a thrombus).
Almost always, hemorrhage poses a health hazard, so to eliminate its consequences, you need to seek medical help immediately after the injury.
Exposure to heat
Cold is a first aid remedy for bumps on the head from a blow. How to treat the hematoma further? Many people limit themselves to only cold compresses on the first day. However, this is not enough. On the second day, the sore spot must be warmed up. Under the influence of heat, the swelling subsides and the lump begins to dissolve.
You can apply a warm boiled egg to the bruise. Table salt, heated in a frying pan and wrapped in a cloth, is also suitable. You should not use compresses that are too hot, so as not to burn your already injured skin.
In the following days, the lump is treated with pharmaceutical ointments or folk remedies.
First aid for injury
This type of injury is more common in children (see Head injuries in children). Good microcirculation and tissue metabolism allow the resulting hematoma to quickly resolve. To do this, you need to follow some recommendations.
What to do if you hit your head and a bump appears? Cold should be applied to the injury site. To do this, you can use a cold compress, a regular metal spoon, ice from the refrigerator, a special gel pad, a cold element for the freezer, a bottle of cold water, a rubber heating pad with ice or cold water. It is important to keep the cold for a long time, and the greater the blow, the longer the contact with the cold should be.
Recommendation! Take a break periodically so as not to overcool the bruised area and cause local frostbite.
What to do if a child has a bump on the head from a blow? As a rule, this consequence of a head injury goes away in 1–2 days. Pain and swelling only bother you on the first day. Over time, the lump resolves without leaving any changes behind.
The lump in an adult causes virtually no discomfort, except for a short-term cosmetic defect. But children endure their trauma much more emotionally. Firstly, they constantly touch the site of impact and thereby cause painful stimulation. Secondly, they can be repeatedly injured in the same place.
Which doctor should I contact if I have a hard lump on my head? Find out who will help you.
Read what to do if a bump appears on the head of a newborn. Identifying the cause.
Ointments
How to anoint a bump on the head from a blow after first aid? In pharmacies you can buy various local remedies for bruises. Let's look at some of them:
- "Troxerutin." This is a drug in the form of a gel that helps resolve swelling after a bruise. The product is well absorbed into the skin, but it is not recommended to apply it to damaged epithelium. The treated sore spot should be protected from exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
- "Troxevasin". The gel strengthens the walls of damaged blood vessels and promotes their healing. It reduces swelling and relieves pain. The cone should be treated with gel in the morning and evening.
- "Rescuer". This gel stops the inflammatory reaction and heals the injured area of the skin. In addition, it has disinfectant properties.
- "Heparin ointment." The product is intended to combat thrombosis. However, it is also effective for bumps on the head from a blow. The ointment acts as an anticoagulant and promotes the resorption of hematomas.
- "Lyoton 1000". This gel also has anticoagulant properties and dissolves blood mass under the skin after a bruise.
- "Mirralgin." The product is a plant-based balm. It improves blood circulation in damaged tissues, relieves pain and swelling. This harmless herbal remedy is especially indicated for young children.
These medications must be used until the lump disappears completely. Treatment may take varying periods of time, depending on the severity of the injury.
Medicines to get rid of lumps
Gel "Troxevasin"
The product strengthens capillaries and vascular walls, has an effect against swelling and emerging inflammation. The bump on the head is lubricated with gel in the morning and evening. In this case, the medicinal product is smoothly rubbed into the skin until absorbed.
Gel "Troxerutin"
Used to relieve swelling. Well absorbed through the top layer of skin. The product can only be applied if there are no open lesions or wounds. Places treated with gel should be protected from exposure to active sunlight.
Heparin ointment
The product promotes the resorption of blood clots and prevents the formation of new ones. Reduces pain. The ointment is applied in a thin layer in the morning, afternoon and evening until the symptoms of the bruise disappear.
Gel "Rescuer"
Promotes active cell growth and rapid restoration of injured skin. Has an antimicrobial effect. Quickly absorbed. Apply 1-2 times during the day. Apply a thin layer.
Folk remedies
Bumps on the head from a blow can also be cured using folk remedies. Everyone knows the wound-healing properties of aloe and Kalanchoe juice. These plants can be used to make a compress that will help reduce tissue swelling. You need to take a leaf of the plant, remove the top layer from it, put it on the sore spot, and then cover it with film and cotton wool. The compress is kept for about 2-3 hours.
You can use regular cabbage leaves. They need to be crushed and boiled in milk. Then put the mixture on a napkin or cloth and apply it to the bruise. Keep the compress for about 1 hour. This remedy helps relieve swelling.
Bumps on the head from a blow in adults can be treated with a mixture of iodine and alcohol (1:1 proportions). This remedy is especially useful for swelling of a bluish and pinkish color, accompanied by severe subcutaneous hemorrhage.
Plants that help with bruises
Cabbage
It is an excellent remedy to help cope with swelling and bloating after an impact. First, its fresh leaves should be crushed. It is best to use a meat grinder for this. The resulting mass should be placed in a small volume of milk and boiled a little. Then, you should take the cabbage out onto a napkin and apply the resulting warm healing compress to the bump for 1 hour. Then the damaged area must be washed.
Thyme
This plant has healing and swelling properties. Its other name is creeping thyme. Its fresh leaves should be applied to the place where the bump is located on the head after a blow. It is believed that the healing plant even helps restore memory if its decoction is used to wipe the head.
Sagebrush
In a situation of bruise, the juice of the plant effectively helps. To obtain it, the grass should be thoroughly ground. The released juice must then be carefully applied to the bruised area.
Oak bark and daisy flowers
From these components you need to make a powder. Its amount should be equal to one tablespoon. Then you need to prepare a saturated composition by pouring a glass of boiling water over the powder. The solution must be infused for half an hour. A piece of cloth soaked in the resulting liquid is applied to the site of the injury and the consequences of the blow disappear faster.
Possible consequences
It should be remembered that a bump on the head from a blow is not always a harmless phenomenon. After all, the cranium contains the brain, many vessels and nerve nodes. Damage to these anatomical structures can lead to serious consequences:
- concussion;
- skull fracture;
- rupture of cerebral vessels.
It is important to remember that serious head injuries often lead to severe disruptions in the functioning of the central nervous system. Such pathologies often require long-term treatment. Therefore, everyone should know in what cases a lump can be dangerous.
Head injury
The main task of adults when a child has a head injury is not to panic, thereby further frightening the child and others, but to competently provide first aid and promptly consult a doctor or call an ambulance. This will not only alleviate the child’s condition, but will also speed up his subsequent recovery.
If a child hits his head and breaks the skin, that is, there is an open wound or bleeding, apply a clean, ideally sterile, bandage to it, and press the bleeding vessel with your hand through the bandage. The scalp and face have an abundant blood supply, so often even a small wound leads to significant bleeding. Pressing the wound with your hand and cooling with available means (a bottle or a heating pad with ice) will help stop the bleeding faster. A heating pad with ice should be wrapped in a piece of cloth or a towel, since direct contact of extreme cold with the skin can lead to frostbite. It is recommended to apply cold even if the skin is not damaged, but there is a soft tissue injury or hematoma (that is, a bump or bruise). In this case, the cold will not only help relieve pain, but also reduce swelling.
After providing first aid, consult a doctor at the emergency room. They will not only help you properly treat the wound and avoid further infection, but will also conduct the necessary examinations to determine how deep the damage is, whether the skull bones are affected, and whether further medical observation of the child in the hospital is necessary.
However, even if the head impact does not cause any damage to the skin, there is still a risk of a concussion or even more serious, life-threatening injury. Its symptoms are not always obvious, especially in the first minutes after injury. But this is where the main danger of head injuries lies. Particular attention should be paid to those head injuries that were accompanied by loss of consciousness, amnesia (“memory lapses”), subsequent vomiting, dizziness, slurred speech, double vision, bleeding from the nose, ears, and the appearance of asymmetry of the face or pupils. Increased drowsiness, lethargy or, on the contrary, irritability, headache are signs of brain suffering. All these symptoms require mandatory and prompt consultation with a doctor. Do not try to solve the problem yourself by giving your child painkillers and hoping that everything will go away on its own. This could result in wasted valuable time. Remember that even with outward well-being, immediately after an injury, symptoms of a concussion and brain damage can appear within 24 hours, which is why the doctor may suggest that you hospitalize even an apparently healthy child for observation in the department for 1-2 days.
If, as a result of a head injury, a child nevertheless has a concussion and the doctor recommends rest, bed rest, and protective rest, the parent is obliged to strictly monitor the implementation of these recommendations. The absence of strong sound and visual stimuli (TV, computer, loud music), limitation of visual stress (reading books, drawing, handicrafts) in the first time after a concussion, strict adherence to the daily routine, limitation of physical activity is the key to a speedy recovery and the prevention of headaches and dizziness , behavioral disorders and other long-term complications of head injury.
When a doctor's help is needed
It is necessary to consult a doctor if the bump on the head after the blow does not go away within a week. If swelling does not disappear for a long time, this may indicate trauma to the bone tissue.
Seek immediate medical attention if a child or adult experiences the following symptoms:
- pain in the head and neck area;
- dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- blurred vision;
- strabismus;
- discharge of blood or clear fluid from the nose or ears;
- increase in pain syndrome;
- disorders of speech and consciousness;
- pain that increases when turning the head;
- seizures;
- bleeding from the wound that does not stop for more than 10 - 15 minutes.
These warning signs may indicate a severe head injury. It is necessary to put the patient to bed, call an ambulance and monitor his consciousness and breathing until the doctors arrive.
Is a lump always associated with a bruise?
A soft bump after a head hit is not dangerous if there are no signs of trauma to the brain or bones of the skull. It is important to remember that a hematoma from a bruise never has a solid structure. If the lump looks like a lump, it is most likely not related to an impact.
Very often, people associate tumors on the head with the fact that they accidentally hurt themselves. However, such bumps may have a completely different origin.
The following formations may occur in the forehead and scalp area:
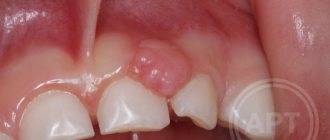
- Atheromas (wen). They look like balls filled with greasy contents. Festering wen can be painful.
- Hemangioma. This tumor of blood vessels is very similar to a lump after a bruise. However, such a neoplasm has a more intense color than a regular hematoma.
- Fibroma. The tumor consists of connective tissue and is benign. With trauma, malignant degeneration is possible.
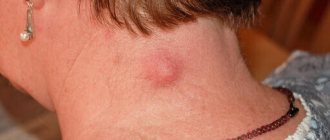
- Lymphadenitis. In children, lymph nodes often become enlarged due to inflammation and infections. They look like red, painful bumps. They are usually located on the back of the head or behind the ears.
The appearance of a bump on the head should not be associated solely with the blow. Many of the above tumors require surgical removal. Therefore, if you are not sure that the lump is caused by a bruise, then you need to consult a specialist. Only a doctor can determine the exact cause of the tumor.
What diseases are manifested by a bump on the head?
If the bump on the head from the blow does not go away within 3-4 days, then you need to consult a doctor to clarify the circumstances. Diseases that manifest themselves as a bump on the head, unrelated to a blow:
- Lipoma is a benign tumor of adipose tissue, which is why it is often called a “fat.” The formation has a soft consistency, it is mobile, not fused with the surrounding tissues, and grows slowly. Lipoma has different sizes from 0.5 cm in diameter to several centimeters. In rare cases, it can fester, and then surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
- Hemangioma is a benign formation of blood vessels. It differs in that it appears from the first days of birth and has a reddish tint.
- Lymphadenitis is inflammation of the lymph node. It may increase due to a respiratory infection or other somatic diseases and blood diseases.
- Fibroma is a benign tumor of connective tissue.
- Hematoma is a limited accumulation of blood due to vascular damage. A cavity is formed in which blood collects. If a small amount of blood has collected, then the hematoma goes away on its own, but if whole blood clots accumulate, then in this case it is only necessary to drain the hematoma.