Symptoms and warning signs after a stroke
You can get a strong blow to the back of the head when practicing martial arts.
Injury to the back of the head can be accompanied by a decrease in the quality of visual function, since this area is connected to the optic nerves. In some cases, loss of consciousness or a feeling of numbness in the extremities (especially the lower ones) is provoked. This sign is explained by a possible concussion. It is not recommended to neglect a bruise of the occipital part. In medicine, there are cases where damage made itself felt after many years.
Symptoms may vary depending on the degree of injury and the exact location of the injury. With minor damage to soft tissue, a hematoma forms. A strong blow to the back of the head usually causes a concussion (ICD-10 code S06.0).
The main signs of mild damage are:
- drowsiness;
- pain;
- diplopia;
- loss of consciousness.
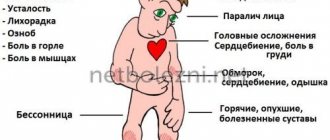
In case of severe trauma, a person experiences:
- loss of consciousness;
- headache;
- nausea;
- noise in ears;
- fear of light and sounds;
- nystagmus;
- asthenia;
- change in heart rate;
- sweating;
- sleep disorders.
Serious damage can be caused by hitting the back of your head against a wall or ice. The injury is characterized by clouding of consciousness, short-term loss of speech and paralysis of facial muscles. The person may feel very dizzy.
If someone hits a child on the back of the head and he has a headache, this is particularly dangerous.
Does protective equipment help prevent injury?
One of the most common misconceptions is that you can rely on protective equipment to completely avoid injury. In fact, protective equipment cannot guarantee perfect safety for a fighter. Some damage is actually reduced due to specialized equipment. This, in particular, reduces the force of the impact and slows down its speed of movement.
But protection cannot protect the central nervous system from damage during blows to the head , since there are many nerve endings under the vault of the skull. For this reason, head protection has become more common in martial arts. For example, in a form of martial arts such as wrestling, special headphones are required.
Basically, of course, they protect the ears, since the cartilaginous parts of the ears break quite easily, but they can also somewhat soften the force of a blow to the head. In boxing, protective helmets are often used, which reliably protect against various impacts, and at the same time provide sufficient visibility. This innovation is believed to have contributed to a significant reduction in injuries among boxers. Important: An athlete may lose consciousness due to a strong blow to the neck or to the area of the so-called solar plexus. The latter is a particularly vulnerable point on the human body. If the abdominal muscles are relaxed at the moment of impact, then the likelihood of shock from pressing the nerve endings to the spine is very high.
Diagnostic methods
The degree of damage is assessed using MRI images.
In order to diagnose damage caused by trauma to the occipital part, it is necessary to consult a neurologist. The specialist will evaluate the biomechanics of the cervical spine, determine range of motion and muscle tone.
Clinical diagnosis is based on examination results. If it is impossible to clarify it, additional procedures are carried out. MRI, CT and echoencephalography are usually prescribed.
First aid
If a person hits the back of their head, it is recommended to apply a cold compress to the affected area. You can use ice wrapped in a cloth or a bottle filled with cold water. You need to keep the compress for 15-20 minutes, then take a half-hour break and repeat the procedure. It is extremely important to monitor your pulse and breathing. If blood appears, the wound should be disinfected and bandaged.
A severe concussion is accompanied by poor circulation and severe hematomas around the eyes. The injured person should be kept at rest. The victim may feel sick, so it is necessary to turn him on his right side so that the vomit can come out freely and air can enter the lungs. It is recommended to tilt your head back slightly and tilt your face closer to the floor. Limbs should be placed at an angle of 90 degrees to prevent fractures during convulsions. It is necessary to call an ambulance and not take any action until the doctor arrives.
It is not recommended to give painkillers, as they interfere with the diagnosis of the injury.
Consequences and treatment of hitting the head (back of the head)
A head injury can occur in both adults and children. But most often there are cases when it is the child who hits the back of the head. After all, children are distinguished by an enviably large supply of energy, which they splash out through jumping, running, climbing trees and similar children's activities.
During such games, they often fall and hit their heads on a hard surface, be it asphalt, concrete floor or furniture.
The consequences of a blow to the back of the head or just the head in both adults and children are relatively the same, so if you see that a person has symptoms of a bruise or concussion, he urgently needs first aid, because people in such a state cannot fully control themselves.
Symptoms of injury to the head and its occipital part
If someone around you hits the back of the head or any part of the head, after which he experiences dizziness, nausea, poor health, and drowsiness - these are the first signs of a concussion. The injured person needs first aid, and then emergency care to prevent the condition from worsening.
Symptoms for head injuries are quite varied, but there are some that can be used to fairly accurately determine which part of the head was damaged. This is especially true for bruises on the back of the head. Damage to this area often leads to visual impairment, since the occipital region of the head is responsible for control in space.
Headbutt
When you hit your head, you feel a strong pain that disappears after a while. When a person falls and hits any part of the head, within a few minutes a small “bump” forms at the site of the injury as a result of tissue swelling. This happens with a slight blow to the head. For more serious injuries, the following symptoms may occur:
- drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- mild nausea;
- double vision;
- partial numbness of the limbs.
With a strong blow to the back of the head, the following symptoms are observed:
- vomit;
- loss of consciousness lasting from several minutes to several hours;
- speech problems;
- temporary blurred vision; ;
- numbness of all limbs for some time;
- numbness of facial muscles.
First aid for head injuries
First aid for a blow to the back of the head is necessary for the victim immediately after the incident, without waiting for the ambulance to arrive. Of course, an ambulance also needs to be called, since in the future the wounded person will need professional treatment from doctors. What to do in this situation:
- Place the injured person on the floor or sofa (depending on location) so that he remains at rest.
- Apply a compress to the bruised area. This could be a frozen product from the freezer or a piece of ice wrapped in a towel; also use a bottle with cool liquid. The compress should be applied for no more than 15 minutes, then removed for half an hour and applied again.
- If the victim experiences a feeling of nausea, he must be turned on his side.
Note! You only need to do what will alleviate the condition of the wounded person, but you should not give painkillers immediately after a bruise until an ambulance arrives. This may interfere with the examination and diagnosis of the injury.
The consequences of injury to any head area are very serious. After all, the skull contains the brain - an important organ that “manages” everything that happens in the body. Therefore, if he is injured, there can be very serious consequences, namely:
- one-sided agnosia. This diagnosis implies a complete lack of perception of one side of the visual space. For example, if there is a bruise on the left side, a person ceases to perceive the left side;
- absent-minded attention, poor concentration, mild temper and irritability;
- disruption of normal sleep;
- memory impairment;
- weather dependence (when the weather changes, your health worsens);
- depression;
- frequent headaches, occasional dizziness;
- occasionally a person loses consciousness or his vision becomes dark;
- the appearance of hallucinations from time to time;
- frequent headaches;
- neck muscle spasm;
- blood pressure disturbance: when it rises, throbbing pain appears, and when pressure is low, morning dizziness is observed;
- poor performance.
Treatment methods
Heparin ointment is used to resolve the hematoma.
Treatment at home is justified in cases of minor injury. Experts recommend the use of external agents Heparin, Traumeel gel or Dolobene gel. In accordance with the instructions, ointments are applied 2-3 times a day.
A hematoma in the occipital region is eliminated with cold compresses. If a lump forms, it is recommended to use Troxevasin or Gepatrombin ointment.
During the treatment period, it is necessary to reduce the time spent watching TV or spending time in front of a computer monitor, and avoid physical activity. This regime should be followed for a month. It is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air.
In case of a concussion, the pathology must be treated in a hospital setting under the supervision of a neurologist, surgeon and traumatologist. The duration of rehabilitation for a child is 1 month, and for an adult - 2 weeks. It is extremely important to maintain bed rest and avoid bright lights and loud sounds.
To eliminate headaches, analgesics Ibuprofen, Noofen, Nimesulide, Maxigan are prescribed.
In some cases, the patient experiences sleep disturbance or drowsiness, sudden mood swings and memory loss. To improve the general condition, sedatives Adaptol, Novopassit, Persen are prescribed, as well as drugs that help optimize blood circulation in the brain. This series includes Piracetam, Cavinton, Sermion, Trental, Cinnarizine, Instenon. Neuroprotectors Cerebrolysin, Actovegin, Gliatilin, Mexidol, Neurox are also used. To improve memory, nootropics Phezam, Selank, Phenotropil are prescribed.
In order to optimize the functionality of the nervous system, it is recommended to take B vitamins Milgamma, Neuromultivit, Benevron BF, Neurobion, as well as vitamins containing magnesium Magne B6, Magnelis B6.
For constant apathy, a course of antidepressants Tsitol, Stimuloton, Fluoxetine is recommended. Treatment is carried out under the strict supervision of a neurologist.
Massage
Massage helps improve blood circulation and normalize the functions of the neck and brain.
Procedures are prescribed for impaired motor functions after a severe brain injury. First of all, the back is massaged, then the limbs and abdomen. Stroking, rubbing and kneading are used. The duration of exposure is 10-20 minutes. The course includes 15-20 procedures.
For mild to moderate concussion, massage can be done 2-3 days after the injury. The back of the head, neck and forearms are warmed up while the patient is sitting. Then the back and shoulder blades are rubbed. Also, during the first 3-5 days, cryomassage is used, which involves the use of liquid nitrogen. The duration of the procedure is 5 minutes. The course includes 8-10 procedures.
Physiotherapy and spa treatment
Physiotherapeutic methods are indicated for severe bruises. They serve as an adjunct to drug treatment. Helps optimize cerebral circulation and metabolism.
Among the main procedures it should be noted:
- electrophoresis with vasodilators and cerebral circulation stimulants;
- galvanization of the brain and its segments;
- transcerebral UHF therapy;
- laser therapy;
- oxygen baths.
Patients who have suffered a mild form of concussion, after two months from the onset of the disease, can be sent to climatic and balneological resorts in Kislovodsk, Pyatigorsk, Essentuki, Solnechnogorsk.
Resort rehabilitation is not indicated in the acute phase of the disease, in the presence of contraindications and mental disorders.
Treatment with folk remedies
Ginseng root in the form of a decoction helps normalize blood circulation in the brain.
To speed up therapy, they often resort to using traditional medicine recipes. For example, it is recommended to add aloe juice to medications. Stimulation of blood circulation is facilitated by an infusion based on string, St. John's wort or ginseng. If apathy is present, taking valerian or motherwort is indicated.
Before using traditional medicine, you should consult a doctor. A specialist can choose the appropriate combination of medications and herbs.
Nutrition
When restoring the nervous system, honey, potato or cabbage juice, and flax oil are useful. It is recommended to include nuts and dried fruits in your diet. Nutrition should be varied, but not heavy. You should consume more citrus fruits and drink plenty of water.
It is necessary to completely eliminate alcoholic beverages, caffeine, and nicotine.
Pain in the temporal part of the head after a blow
If a head injury occurs, it is important to immediately begin rehabilitation measures at home, which will help prevent serious complications - intracranial hemorrhages, swelling and dislocation of brain structures.
If a person falls and hits their head hard, the consequences can range from a mild concussion to coma and death. Statistics show that the prevalence of head injuries is about 200 cases per 100 thousand population annually. For 30% of patients, brain damage is fatal.
Every year, severe head injuries and associated disorders of vital and brain functions lead to the death of 1.5 million people in the world. Another 2.5 million people become disabled.
The child hit the back of his head, what to do?
06.07.2021
Hello, dear parents. We have already discussed the topic of head impacts during falls, for example, what to do if a child hits his ear, or a child hits his nose when falling. Today we will talk about what to do if a child falls and hits the back of his head.
In this article, you will learn what such a fall can lead to, what consequences can occur if you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, and what symptoms indicate the seriousness of the toddler’s condition.
You will also learn how to provide first aid and what to do to try to prevent possible bruises on the back of the head.
Alarming symptoms
It is possible that a blow to the back of the head will pass with virtually no characteristic symptoms appearing. Or maybe the bruise will just hurt. But parents should know that if any signs and characteristics appear in the behavior and well-being of the baby, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor, and sometimes call an ambulance immediately.
- The baby's limbs were numb.
- In the eyes of the little one, everything splits into two.
- Nausea occurs, which may be accompanied by severe vomiting.
- Detection of differences in pupil sizes, short-term eye twitching.
- The skin became pale. A blue tint may appear.
- The child cries a lot, do not calm down for more than 15 minutes.
- Convulsive attacks appeared.
- There was a nosebleed and hemorrhage in the eyes.
- Changes in coordination of movements, imbalance.
- Clear discharge appears from the ears, mouth or nose.
- It is difficult for the child to turn his head to the side.
- Speech retardation.
- The child hit the back of his head, the lump grew very large - be sure to see a doctor.
Possible results of the impact
Parents should know what injuries, other than a minor bruise, their child may suffer as a result of a blow to the back of the head:
- Brain contusion. This can happen if the child hits the back of his head on the floor. Since small children have not yet fully formed and strong enough skeletal system, and in particular the bones of the skull, a brain contusion may occur after a fall. If the form of such an injury is mild, the doctor will prescribe medication; in the case of severe injury, surgery.
- Concussion. Occurs quite often with blows to the back of the head. As a rule, treatment takes place without complications, with the help of medications.
- Fracture. Often accompanied by discharge from the child’s ears or nose. They can be presented as clear liquid or blood. Treatment is conservative.
- Traumatic brain injury. Can be closed or open. The treatment process is the longest. Symptoms of this pathology are severe drowsiness, fainting, vomiting, and convulsions.
One day my son fell on the street and hit the back of his head. At the same time, there was even an abrasion with slight bleeding, which was successfully stopped. Everything worked out without drug treatment.
Once, when my friend and her daughter were returning home from kindergarten (in winter), they slipped, fell and hit the back of their heads. Everything turned out okay for the mother, but the girl was diagnosed with a concussion and appropriate treatment was prescribed.
There was also a case with a neighbor boy. He was visiting his grandmother and one day she washed the floor in the hallway and told him not to leave the room until it was dry. But then the cat Vaska jumped out from under the sofa and ran into the corridor. Sashenka, who had been trying to get the cat for a long time, ran after him, forgetting about his grandmother’s warning.
Possible consequences and complications
After a brain injury, it is necessary to check your vision.
The consequences of a blow to the back of the head during a fall in an adult and a child are dangerous and can be irreversible. Therefore, even with the slightest damage, it is important to contact a specialist in a timely manner.
The main complications include:
- the formation of visual-spatial agnosia (a person has a failure to perceive the left side of space);
- absent-mindedness;
- forgetfulness;
- irritability;
- decreased performance;
- sleep disorder;
- depressive disorder;
- hallucinations;
- clouding of consciousness;
- blurred vision;
- dependence on weather conditions;
- constant headaches;
- noise in ears;
- dizziness;
- decreased concentration.
Displacement of the occipital bone can cause circulatory problems in the brain.
Displacement of the occipital bone often provokes insufficiency of blood flow in the arteries of the spinal column. The person may lose coordination. The segment determines the topography of the temporal zones, and they, in turn, determine the location of the lower jaw. Therefore, one of the complications of the injury may be its sagging or displacement to the side.
Tension of the muscular system under the occipital area contributes to compression of the lymphatic vessels, which causes a violation of the outflow of lymph and swelling in the chin area. Too much damage can cause death.
Reasons for banning blows to the back of the head
As stated above, blows to the back of the head are prohibited, so such attacks usually occur either in connection with a gross violation of the rules, or when one of the opponents falls onto the ropes due to a blow to the lower jaw or forehead.
With such a fall, harmful processes occur in the brain, and the consequences are comparable to a blow to the back of the head - there is also strong pressure on the brain stem from the cerebellum and brain fluids - cerebrospinal fluid.
Damage to the cerebral hemispheres
The hemispheres of the brain begin to move, and when braking, they collide with the bones of the skull and are injured. The resulting movement of cerebrospinal fluid injures the main regulatory centers of the brain. On the contrary, when you fall on your back and there is a concomitant blow to the back of the head, a bruise of the cerebellum occurs on the occipital bone. Sometimes this is accompanied by rupture of the superior cerebral veins, which provokes subdural bleeding.
Damage to the eyes and ears, hands and joints of the arms
In addition to the brain damage already mentioned, blows to the head are characterized by other injuries. The most obvious are injuries to the eyes and ears. Sometimes injuries to the hands and joints of the arms occur. However, as you know, the eyes are one of the most sensitive and vulnerable human organs, as a result of which some doctors recommend ophthalmological examinations of fighters at least once every six months.