Brain heart attack and stroke are dangerous and insidious diseases. In the modern world, about one billion people suffer from high blood pressure. Hypertension causes the development of cardiovascular diseases, strokes and cerebral infarctions. Patients often ask the doctor the question: “What is the difference between a heart attack and a stroke, if in both cases there is a violation of cerebral circulation? What measures should be taken?
Heart attack and stroke, differences
A heart attack develops due to vascular thrombosis. The formation of blood clots in the vessels leads to blockage, the flow of blood into the tissues of the organ is disrupted, and necrosis develops, leading to the destruction of the affected tissues. A heart attack can affect not only the brain, but also the heart, liver and intestines.
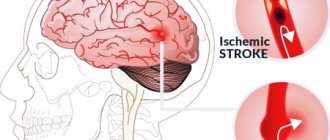
A stroke occurs due to a circulatory disorder, characterized by bleeding in the brain; in most cases, the functions of the affected area are taken over by other parts of the brain. A stroke can occur in the form of ischemic cerebral infarction or hemorrhagic cerebral stroke. Hemorrhagic stroke differs from ischemic cerebral infarction in the following manifestations:
- With a hemorrhagic stroke, a vessel wall ruptures or blood leaks through the vessel walls. Blood begins to flow into the brain tissue - a cerebral hemorrhage occurs.
- An ischemic stroke, or cerebral infarction, develops when blood vessels are blocked or there is insufficient blood flow to the brain, and the affected area of the brain dies.
At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors with extensive experience diagnose, treat and rehabilitate neurological patients. The clinic is located in Moscow on Nagornaya Street. The neurological department of the Yusupov Hospital accepts patients in any condition, even the most severe. The Neurology Clinic treats:
- hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes;
- multiple sclerosis;
- epilepsy;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- Parkinson's disease;
- consequences of traumatic brain injuries;
- diseases of the nervous system.
Prevention
- Primary prevention consists of proper nutrition, exercise, giving up bad habits and stress, adequate sleep and rest, and regular medical examinations.
- Secondary prevention of stroke includes the elimination of risk factors - treatment of concomitant pathologies, regular monitoring by the attending physician, elimination of risk factors. This approach will help not only prevent stroke, but also improve overall health. According to WHO estimates, the creation of an adequate system of care for patients with stroke will make it possible in the coming years to reduce mortality during the 1st month of the disease by 20% and ensure independence in everyday life 3 months after its onset in at least 70% of patients.
Symptoms of diseases
Ischemic stroke is characterized by dizziness, dark vision, numbness in the limbs - a feeling of numbness appears in the arm or leg, in some cases symptoms appear on one half of the body. The patient's speech becomes incoherent or he cannot speak at all for some time. The face and lips may become distorted - facial paralysis develops. This occurs due to damage to a part of the brain and its failure to perform its functions. With timely assistance, functionality is restored - healthy areas of the brain begin to be responsible for speech, muscle function and other functions.
Hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by an acute course of the disease, the appearance of the following symptoms:
- a sharp decrease in visual acuity;
- loss of consciousness;
- photophobia;
- tinnitus;
- headache;
- vomiting, severe nausea;
- redness of the face and body;
- unsteady gait;
- convulsions;
- paralysis of one side of the face;
- paralysis of one side of the body;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- the patient speaks poorly, gets confused in words;
- coma.
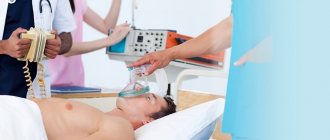
It is very important to provide first aid for a brain stroke as early as possible. The patient is admitted to the hospital, diagnostics are carried out, seizures are eliminated, brain swelling is relieved, and the patient’s condition is stabilized. On the basis of the Yusupov Hospital there is a hospital, an intensive care unit, and a rehabilitation unit for patients after serious illnesses. If necessary, resuscitation measures will be carried out at the Yusupov Hospital and the seriously ill patient will be cared for.
Stroke: sudden symptoms
A stroke can also develop with abnormal development of cerebral vessels, with uncontrolled arterial hypertension, with atherosclerotic damage to the arteries supplying the brain.
The main manifestations are speech impairment, sudden facial asymmetry, weakness or decreased sensitivity in the limbs. The main symptoms of acute cerebrovascular accident are associated with the development of acute ischemia of the part of the brain that is responsible for certain functions of the human body.
Article on the topic
Stroke and methods of its treatment. What you need to know about anticoagulants
In young patients, an acute ischemic attack in the brain or myocardium is malignant, often leading to disability and even death. This is due to the fact that with age, the number of small vessels supplying blood to the myocardium and brain increases. During the acute period, “bypass” small vessels begin to function, which help to nourish and replenish oxygen deficiency, saving the affected organ from total death. Young people do not have such “donors”.
It is worth paying special attention to a person’s subjective feelings. Signs of a stroke are associated with dysfunction of the muscles of the head and body. This means that if a person has an unnatural smile - with a distortion in the corners of the lips due to the impossibility of normal muscle contraction, he cannot raise his arms normally, and his handshake is weak, there are problems with speech, it is worth showing him to the doctor as soon as possible. It must be remembered that in case of a stroke, assistance should be provided in the next couple of hours.
Article on the topic
One step before a stroke. How to recognize the symptoms of the disease in time
Causes of heart attack and stroke
Causes of development of ischemic cerebral infarction:
- increased blood viscosity;
- blood clots;
- decreased cerebral blood flow due to diseases of the heart, vascular system, and blood;
- age;
- physical inactivity;
- bad habits;
- pathology of the vertebral and carotid arteries.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke increase gradually. Over time, a cyst forms at the site of the area affected by ischemic cerebral infarction.
The main causes of hemorrhagic stroke:
- high blood pressure (hypertension);
- microangiopathy (pathological condition of the vessels responsible for metabolism).
First signs and symptoms
Before a stroke, drowsiness, headache, numbness of the limbs, fatigue, spots before the eyes, nausea, dizziness, temperature fluctuations, and blood pressure jumps appear. These are the harbingers or first signs of a stroke that appear several hours or days before the disaster. Most often, these symptoms are ignored, or they are attributed to fatigue and overwork.
Symptoms of a stroke themselves are divided into general cerebral and focal. They can be of varying degrees of severity depending on the prevalence of the pathological process.
- General cerebral symptoms: headache, impaired consciousness up to loss of consciousness, stupor, agitation or weakness, disorientation in space and time, sweating, feeling hot, convulsions. Makes you feel sleepy and sometimes chills.
- The focal abnormalities of a stroke depend on which area of the brain is affected. They can be unilateral or bilateral. This group includes disturbances in speech, vision (visual hallucinations), gait, movements up to paralysis, and sensitivity.
Symptoms of ischemic cerebral stroke develop gradually, with focal symptoms predominant.
With a hemorrhagic stroke, the onset is rapid, with a predominance of cerebral symptoms.
There are several stages in the development of a stroke: the acute period (from the moment of the stroke to 3 weeks on average), the recovery period - from 2 weeks to 24 months.
Course of the disease
Cerebral infarction most often occurs in older people. Before an ischemic cerebral infarction, patients do not always complain of surges in blood pressure or any pronounced symptoms of trouble in the functioning of the blood vessels of the brain. Ischemic cerebral infarction occurs in people with normal blood pressure after nervous stress or heavy physical activity. Depending on the volume of the affected area and its location, brain function is restored. If the affected area is large and vital centers are affected, the patient may lose speech, and the consequences in the form of paralysis, tremors and other disorders of the nervous system will last a lifetime. Most often, the prognosis after an ischemic stroke (cerebral infarction) is favorable - patients recover within a few weeks, can live a long life, work, and take full care of themselves.
Hemorrhagic stroke is acute; about 70% of patients receive surgical treatment - low-traumatic puncture operations are performed to remove brain hematomas. The severity of the patient's condition depends on the location of the hemorrhage and the degree of vascular damage.
Highly qualified medical staff provide effective treatment and good care for patients after heart attack and stroke. Rehabilitation of patients takes place using high-quality European equipment - patients are helped to restore social skills with the help of exercise machines and special equipment, blood circulation in tissues is improved with the help of massage, psychologists and speech therapists work with patients after a stroke. For seriously ill patients after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, the Yusupov Hospital operates a rehabilitation department. You can make an appointment with a neurologist by phone.
What to do if you have a stroke
There are techniques that allow you to identify signs of a stroke yourself. For example, they can be used if someone becomes ill on the street and you suspect a stroke. You need to ask the person to smile, speak, raise both hands. If the victim cannot comply with your request or there is asymmetry, you should immediately call for help and list all the symptoms.
At the same time, you need to provide first aid: lay the victim down, placing a small support under his head, and free him from clothes that are preventing him from breathing. He should not eat or drink or make sudden movements. When vomiting, turn your head to the side.
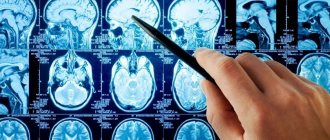
Further treatment is carried out in a hospital. First, diagnostics are carried out to clarify the diagnosis; computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, lumbar puncture and EEG (echoencephalography), angiography are prescribed. Then conservative (basic therapy, treatment of neurological complications) or surgical treatment is prescribed.
After the end of the acute period, rehabilitation is prescribed: massage, physical therapy and other activities, depending on the degree and type of disorder. The patient is observed by a neurologist, physiotherapist, speech therapist, and psychotherapist.
The brain has neuroplasticity: with the right approach, you can recover from a stroke, restore brain function and prevent stroke complications. The key factor is timely initiation of treatment, proper rehabilitation and regular exercise.
According to WHO, about 60% of patients do not require assistance by the end of the first year, and 30% of patients of working age can return to work.
What is more dangerous for humans?
The likelihood of complications and death is high in both cases. But the incidence and survival rate depend on gender. Infarction with damage to the heart muscle in middle age is more common in men; after 50 years, this difference smooths out.
The fact is that in a young woman, a high level of estrogen protects her from the development of atherosclerosis, and during menopause, hormonal levels change. The mortality rate due to myocardial necrosis remains higher in the stronger sex. Stroke occurs less frequently in women, but in them it is more likely to be fatal.
It makes no sense to talk about what is more dangerous: a stroke or a heart attack. The prognosis and outcome of each of these diseases depends on many factors:
- age and gender;
- degree of irreversible damage to organ tissue;
- presence of concomitant diseases;
- speed and accuracy of emergency care.
The probability of death of the patient in the first hours of acute vascular pathology is the same in both cases. But in this sense, my colleagues and I consider a heart attack to be more dangerous. Myocardial necrosis develops very quickly, and doctors simply do not have time to get to the patient. However, after a stroke, it takes much longer to recover and more often leads to severe disability: the prognosis for quality of life is less favorable.
Similarities and differences
Acute vascular disorders have common causes. Most often the problem occurs as a result of:
- thrombosis;
- embolism;
- atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- diabetes;
- systemic diseases with vascular damage.
Development factors: obesity, abuse of fatty foods, stress, bad habits and physical overload. The development of a stroke can also be triggered by anemia, hemodynamic disturbances, intoxication, skull trauma, and thinning of the vascular wall.
The main similarities and differences in the symptoms and methods of emergency care for impaired blood flow in vital organs can be clearly presented in the form of a table:
| Myocardial infarction | Stroke | |
| Signs | Pain behind the sternum radiating under the left shoulder blade, into the arm or lower jaw, rhythm disturbance, pressure surges, shortness of breath, weakness, panic attack and fear of death. | Numbness of the body, loss of control, paresis and paralysis, impaired vision, hearing, swallowing, coordination. Nausea and vomiting, without relief, severe headache, lethargy. |
| Basic diagnostic tests | Blood biochemistry with determination of necrosis markers, ECG, EchoCG. | Coagulogram, CT or MRI of the brain, encephalography, spinal puncture |
| First aid | Give Nitroglycerin, Validol, Corvalol, Aspirin. Place or lay in a bed with a high headboard. | Place on a horizontal surface; if you lose consciousness, turn your head to the side. Medicines cannot be given. |
| Possible complications | Rhythm and conduction disturbances, aneurysm, heart failure, cardiac rupture, cardiogenic shock. | Persistent or transient paresis (or paralysis), decreased intellectual abilities, memory loss, coma. |
Prevention methods for both diseases are not particularly different. It is recommended to walk in the fresh air, monitor your weight, follow a diet, and do exercises daily at a moderate pace and without overload. It is also important to constantly monitor blood pressure and sugar levels, take blood thinners and statins in order to normalize cholesterol levels.