Risk factors for ischemic stroke
Stroke in an elderly person is characterized by a severe course, which entails various disorders of neurological and cognitive functions. The main cause of stroke is blockage of blood vessels in the brain by a blood clot. In medicine, there are several types of stroke:
- lacunar;
- atherothromboembolic;
- cardioembolic.
In addition, there are strokes caused by such reasons as a migraine attack, dissection of the arterial wall, and hereditary vascular diseases.
Risk factors contributing to the occurrence of pathology:
- arterial hypertension;
- diabetes;
- excess body weight (obesity);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system, accompanied by arrhythmias of various etiologies;
- age over 55 years;
- bad habits (alcohol abuse, smoking).
In most cases, stroke in older people begins suddenly. According to statistics, the peak of hypertensive crises and strokes occurs at night or early in the morning.
Symptoms
Stroke in older women and men is manifested by the following symptoms:
- loss of visual fields;
- high blood pressure, dizziness;
- paresis of a limb or half of the body;
- dysarthria (unintelligible and incoherent speech);
- distorted face;
- confusion;
- loss of coordination of movements (partial, complete).
As a rule, when a stroke occurs, a combination of these symptoms occurs, and to make sure that a person is developing this particular disease, you need to do a simple test before doctors arrive:
- ask to repeat any phrase. If speech is unintelligible, it is a stroke;
- ask to smile. If the patient has a stroke, the smile will be asymmetrical;
- ask to raise your arms, bending them at an angle of 45 degrees, and hold in this position for several seconds. If one arm does not lower, then it is a stroke.
Important! If even one of these signs appears, you should immediately call an ambulance. It is strictly forbidden to give a person any medications, as this can only worsen the situation!
Before the ambulance arrives, you need to lay the patient down, raising his head slightly. Provide him with a flow of air: open the window, unfasten his collar, free him from his belt and tie. If vomiting begins or the victim loses consciousness, carefully turn his head to the side and remove his tongue from the mouth so that it does not fall back.
How to help a person with hyperthermia?
It is worth noting that treatment of stroke at home is not possible - hospitalization is mandatory. However, it is useful to know that regardless of the cause of the stroke itself, the patient is often left alone in the room. If there are signs of fever, on the advice of a doctor, you can only take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (analgin, ibuprofen).
In case of hemorrhagic stroke in a hospital setting, other methods of combating hyperthermia can be used, after which the patient’s condition improves. They use narcotic, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and sedative drugs.
Cooling occurs exclusively through the skin. Ice packs, wet bandages, or special helmets placed on the patient's head can be used - coolant constantly circulates inside the helmet.
- For this purpose, intravenous infusion of cooled saline solution is used. The method is convenient because it allows you not only to quickly cool a person, but also to warm you up if the need arises.
- Intravenous catheter temperature management. The essence of the method is to install a special catheter that has its own cooling system. A temperature sensor is installed in the patient's urinary catheter, based on the readings of which the temperature of the intravenous catheter changes. This is a rather complex, but highly effective system that allows you to constantly monitor and adjust the patient’s temperature.
Consequences of a stroke
The transferred disease has consequences that, depending on the type and course of the pathology, can remain for many years, or may disappear after a certain period of time.
Manifestations of the disease are divided into several groups:
- speech disorders. A stroke affects different parts of the brain, so the patient may experience changes in articulation or speech production;
- motor disorders. An elderly person may have impaired mobility of the limbs or mobility of the face;
- cognitive disorders. They are characterized by absent-minded attention, decreased intelligence, memory loss;
- emotional-volitional disorders. A person with such manifestations after a stroke becomes “tearful”, as a result of which he can plunge into a prolonged depressive state.
These consequences arise only after the end of the acute period of pathology. In the first weeks after a stroke, the patient has symptoms such as speech impairment, frequent headaches, unstable blood pressure, and arrhythmia. In some cases, high body temperature, tremors, and convulsions are noted.
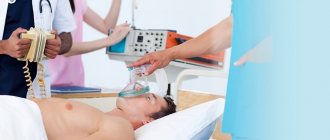
Surgical assistance for stroke is a guarantee of the patient’s life
The main symptoms of acute cerebrovascular accident include the following:
- headache, often severe;
- dizziness;
- neurological symptoms that appear immediately after the stroke occurs
- increase in body temperature of varying intensity.
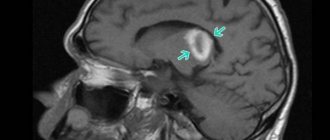
Early signs of stroke
If an experienced doctor is diagnosing a stroke, then body temperature must be monitored, which almost always increases after an acute disorder. In the future, this indicator often becomes a means of monitoring the patient’s condition. Of course, thermometry is far from the only diagnostic method, but if the temperature rises to critical values, most often this indicates extensive hemorrhage in the brain tissue.
If we are talking about an ischemic stroke that develops without hemorrhage, a constantly elevated temperature may indicate pathologies such as:
- cerebral edema;
- an inflammatory process in the body caused by bacteria or viruses;
- thrombosis of arteries or veins;
- pneumonia or exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Temperature during a stroke is an important diagnostic criterion, which cannot be ignored.
Ischemic stroke is often characterized by low-grade fever
Treatment
The main goal of emergency physicians is to stabilize the victim’s condition and support the functioning of brain cells before hospitalization. For this purpose, basic therapy is carried out, which includes activities such as:
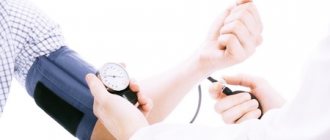
- control and/or correction of blood pressure;
- temperature control;
- relief of seizures;
- control of heart rate and glucose levels;
- maintaining water-salt balance.
Specific treatment in a hospital setting includes thrombolytic therapy, antiplatelet agents, mechanical thrombus extraction, and elimination of cerebral edema.
Thrombolytic therapy
Indications for such therapy: age from 18 to 80 years and no more than 4.5 hours from the onset of the stroke. The victim is administered an effective drug - tissue-type plasminogen activator, which dissolves blood clots.
Contraindications:
- Blood pressure is higher than 185/110;
- sensitivity to drugs of this type;
- erosion, gastrointestinal ulcer in the last 6 months;
- various brain pathologies;
- recent brain surgery;
- taking anticoagulants, etc.
Taking into account the extensive list of contraindications, thrombolytic therapy is performed in no more than 10% of patients.
Antiplatelet agents
These drugs are prescribed to patients on the second day after thrombolytic therapy. If it is not carried out, then on the first day. Aspirin is prescribed as a preventive measure against recurrent stroke, and its use significantly reduces mortality.
Mechanical thrombus extraction
This technique is the most effective. As a result of its use, blood supply to the brain is restored in the shortest possible period. The principle of mechanical thrombus extraction is the mechanical removal of blood clots using a special high-precision instrument. A stand is immersed in the artery and advanced to the site of blockage, after which it is removed with a catheter. All manipulations are carried out under radiographic control.
One of the main advantages of mechanical thrombus extraction is the ability to perform it within 6–8 hours after the onset of an ischemic stroke and a small number of contraindications. However, the use of this method is not possible in all clinics. This is due to the need to have in the arsenal of a medical institution the most modern equipment and a staff of vascular surgeons capable of performing this manipulation.
Elimination of cerebral edema
In some cases, stroke patients develop brain swelling. Its elimination is carried out with the help of diuretic drugs. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the patient's condition.
Why is hyperthermia dangerous during a stroke?
Hyperthermic syndrome is dangerous for any person, not to mention patients with strokes. Any increase in temperature leads to a sharp acceleration of all metabolic processes in the body. In acute cerebrovascular accident, hyperthermia increases the permeability of the blood-brain barrier, enzyme activity decreases, and brain cell death occurs faster.
If there are too many dead cells, the focus of the stroke increases with irreversible changes in the central nervous system, after which the person may become disabled. It is worth noting that the active death of brain cells due to circulatory disorders has already begun, so control of body temperature is very important during treatment. Hyperthermia is especially dangerous in hemorrhagic lesions of brain tissue.
Thermometry in patients with strokes should be carried out at least 2 times a day, even with a visible improvement in the condition. This is due to the inability of such a patient to adequately assess their condition - they may simply not notice the high temperature.
Patient care
In most cases, mortality in the first days after the onset of a stroke is caused by impaired blood circulation in the brain. In the subsequent period, patients die from various complications caused by prolonged immobility:
- pneumonia;
- bedsores and/or their infection;
- thromboembolism;
- thrombophlebitis.
That is why patient care must be thorough and regular. It is important to turn the elderly person from one side to the other every 2-3 hours, and also to ensure that the bedding does not bunch up.
Daily care for a person after a stroke includes important elements of rehabilitation, which are recommended to begin immediately after his life is out of danger. Early recovery from this pathology has a beneficial effect on the patient’s condition and contributes to his speedy recovery.
Massage
Passive gymnastics and massage are mandatory activities aimed at preventing the development of bedsores. In addition, these procedures help prevent contracture (limited mobility in the joints) caused by the patient's immobility.
At the initial stage, the patient's muscles are stretched, joints are extended and flexed. Such manipulations should only be carried out by a specially trained person. The time and number of sessions are individual and determined by the attending physician.
Important! The massage must be performed by a specially trained person. The number and time of sessions is determined by the doctor.
If the elderly person is conscious, passive stimulation of the muscle frame and speech gymnastics are prescribed.
The right diet
Caring for an elderly person after an ischemic stroke includes a special diet containing foods rich in potassium. This trace element is found in large quantities in bananas, legumes, fish, seafood, spinach, dried fruits, kefir, and low-fat yogurt. It is recommended to include vegetable salads with vegetable or olive oil and light vegetable soups in the menu.
Coffee, strong tea (all varieties), and alcoholic beverages should be excluded from the diet.
In addition, you should limit your use of:
- red meat dishes (no more than 150 g per day);
- smoked products;
- spicy, salty dishes;
- baking.
Food must be boiled, stewed or baked.
Leisure after a stroke
The patient's time after an ischemic stroke should be devoted to improving mood and returning to an active life.
To improve motor skills and cognitive disorders, it is recommended:
- collect puzzles;
- draw, sew, knit;
- listen to the radio, read books, communicate with people.
Such hobbies promote recovery and significantly increase the chance of returning to a full life.
Doctors are unanimous that a nursing home after a stroke is an excellent opportunity to return to normal life as quickly as possible. The patient is surrounded by care, and qualified staff guarantees proper care, adequate nutrition and round-the-clock supervision.
Temperature indicators for stroke
Temperature readings during a stroke are not the main sign of the disease. Neurological manifestations come to the fore in symptoms and treatment.
The stroke itself in the first minutes usually does not cause a critical or diagnostically significant deviation in body temperature.
During the first hours from the onset of a brain stroke with a hemorrhagic form of the disease, the temperature gradually rises, and after 2-3 hours it can reach 38 degrees. A temperature of 37.2 degrees is considered the norm for a hemorrhagic stroke; exceeding this indicator worsens the patient’s chances of recovery.
With the ischemic type of disease, body temperature usually drops to 36 degrees. If the readings do not fall below this level, you can hope for successful treatment of the stroke.