Leptospirosis is a severe infection in half of the cases and is found in all countries, except in the North and South Poles. People get sick especially often in tropical countries, from where tourists carry the pathogen around the world. The migration of infection is facilitated by the growing popularity of water sports. Leptospirosis affects more than a hundred species of wild and domestic animals - the main source of human disease.
Our expert in this field:
Nagibina Margarita Vasilievna
Infectious disease doctor, doctor of medical sciences, professor
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Causes of infection
At the Medica24 international clinic, the entire range of therapeutic and rehabilitation measures is performed at a guaranteed high professional level, which reduces recovery time.
The causative agents of the infection are spirochetes, there are more than 250 variants of them. Spirochetes produce toxins and enzymes; these substances destroy cells and disrupt the structure of the blood. Spirochetes are delicate, but can live up to 3 months in water and soil, and a month on food.
Spirochetes are carried in the urine by rodents and animals. A person becomes infected by consuming food and water that contains the pathogen through animal urine. Livestock gets leptospirosis, and dogs get it too, passing the spirochete to their owner. Human susceptibility to infection is very high. The disease is almost never transmitted from person to person.
Leptospirosis follows a seasonal pattern - in summer the incidence of the disease increases, but you can get infected from an animal at any time. In recent years, the main contingent of Russian patients are young men who are fond of water sports.
The international clinic Medica24 has everything necessary for the early detection of pathogens of infectious diseases and diagnosis of pathological changes, which allows you to make the correct diagnosis and begin therapy as soon as possible.
Causes of the disease and sources of infection
Leptospirosis is caused by the spiral-shaped aerobic bacillus Leptospira interrogans. Today, more than 230 groups of microorganisms have been identified. Leptospires are moderately stable in the environment and die when exposed to ultraviolet rays and high temperatures. In water, some strains can exist from several hours to a month, in swampy soil - up to 10 months.
The main reservoir of leptospirosis in nature are wild and domestic animals, primarily rodents (mice, rats), insectivorous mammals (hedgehogs, shrews), as well as pigs, cows, horses, dogs and sheep. A sick animal poses a danger throughout the entire period of the disease.
Leptospirosis is transmitted through foodborne illness by consuming contaminated food and water. Less common is contact transmission; infection occurs when caring for farm animals and when swimming in polluted water bodies.
Note! The probability of transmission of infection from a sick person to a healthy person is extremely low, since leptospirosis belongs to the group of zoonoses - infectious diseases whose pathogens parasitize the body of animals.
Symptoms of leptospirosis in humans
Leptospirosis goes through four periods, their duration is variable, lasting a total of 4-6 weeks.
The incubation period from infection to the first symptoms of leptospirosis lasts from two days to a month, more often – one to two weeks. It is impossible to find the site of entry of the pathogen; the spirochete passes “through” the skin and is carried throughout the body by blood.
The period of onset of the illness is no more than a week, the onset is so acute that the patient can name the hour when he fell ill. Severe intoxication with high fever, muscle and headaches, nausea and palpitations is caused by the production of toxins by spirochetes. Severe pain in the calves and lower back, aggravated by movement, is typical. The appearance is specific: a red and puffy face, herpes rashes on the lips and nose, the eyes are also red due to dilated blood vessels.
State Autonomous Institution "Shilkinskaya Central District Hospital"
Leptospirosis in humans is a natural focal bacterial zoonotic pathology characterized by anemia, fever, hemorrhagic damage to the liver, kidneys, mucous membranes of the oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, as well as disorders of the central nervous system. Leptospirosis is widespread on all continents except Antarctica, but it is most common in tropical countries.
The causative agent of leptospirosis is the aerobic gram-negative motile bacillus Leptospira interrogans; most of the microorganisms die quickly enough under the influence of high temperatures and sunlight. In dry soil, Leptospira can survive for about two hours, and in swampy soil - up to 10 months. The pathogens are able to tolerate freezing, so they easily survive the winter in frozen soil. Leptospira survives on food products for two days. In this case, these microorganisms die in a quarter of an hour under the influence of a half percent solution of phenol and one percent hydrochloric acid.
The main sources of infection are a variety of animals (rats, shrews, cattle, wood mice, water rats, pigs, voles, dogs and others). At the same time, a person with leptospirosis is not the source of the disease.
Human infection occurs when the skin and mucous membranes come into contact with moist soil contaminated with animal feces and water, when eating products containing feces of infected rodents, as well as through contact with the blood of infected animals during their slaughter or cutting of meat. In most cases, leptospirosis is of an occupational nature: workers in slaughterhouses, livestock farms, milkmaids, shepherds, veterinarians and people forced to work in wet fields are more susceptible to it.
The entry gate into the human body for Leptospira is the epithelium of the nasopharynx and digestive tract, sometimes the mucous membrane of the genital organs and urinary tract, as well as areas of damage to the skin. No pathological changes are observed in the area of pathogen penetration. Leptospires spread throughout the body with the lymph flow, settle in the lymph nodes, multiply there and disperse throughout the organs and systems using the circulatory system. Often the pathogen accumulates in the tissues of the liver, lungs, kidneys and spleen and causes local inflammation in them.
Symptoms of leptospirosis in humans
The latent period for leptospirosis lasts from four days to two weeks. The disease begins suddenly, acutely, without warning and is characterized by:
- chills;
- injection of scleral capillaries;
- increased temperature;
- severe headache;
- insomnia;
- constant thirst;
- severe pain in the calf and other muscles;
- myalgia accompanied by skin hyperesthesia;
- puffiness and hyperemia of the neck and face;
- loss of appetite.
On the fourth day after the first manifestation of signs of the disease, the symptoms are supplemented by icteric staining of the skin, the appearance of exanthema, hypotension, bradycardia, muffled heart sounds, as well as pathological changes in the epithelium of the respiratory tract. During the same period, in almost all patients the liver and spleen noticeably increase in volume, and symptoms of kidney tissue damage appear.
In severe cases of leptospirosis, toxicosis increases in patients, associated manifestations appear, and symptoms of uremia appear.
Treatment of leptospirosis in humans
A person infected with leptospirosis must be placed in a hospital if there is a high probability of complications occurring and developing in him, as well as in situations where doctors consider it appropriate to establish laboratory control over the general condition of his body over time.
Patients are prescribed strict bed rest until the fever disappears. In addition, when symptoms of kidney failure appear, patients also remain in bed. For functional disorders of the kidneys and liver, patients may be prescribed diet therapy.
Treatment of leptospirosis involves the use of antibiotics. In particular, patients are prescribed intramuscular benzylpenicillin, intravenous ampicillin, or doxycycline (for severe disease). In addition to all of the above, a specific anti-leptospirosis heterologous immunoglobulin is often included in the treatment complex.
Nonspecific therapy for leptospirosis includes the prescription of symptomatic medications, detoxification, and monitoring the general condition of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
In most cases, leptospirosis has a favorable prognosis. Deaths are mainly due to untimely or inadequate medical care and the general weakness of the infected person’s body.
Prevention of leptospirosis in humans
Prevention of leptospirosis includes the following measures:
- control over the level of disease in farm animals;
- vaccination (administration of a special leptospirosis vaccine to persons who constantly work in contact with animals, or to persons located in the epicenter of the epidemic during an outbreak of leptospirosis);
- constant control over the condition of water sources (including places where water resources are taken for the needs of the population, public places for swimming);
- limiting the reproduction of rats, mice and other rodents (deratization of agricultural farms, urban facilities).
Symptoms at the height of the disease
The peak period of leptospirosis lasts up to two weeks, the pathogen is “located” in the internal organs, which leads to disruption of their function, and multiple organ failure develops. The entire period is high temperature, which ends with a sharp decrease almost within a few hours upon recovery.
Liver cells are damaged and jaundice develops. The larger part of the organ is affected, the brighter the color. The kidneys are always affected, leading to renal failure. Capillaries are damaged, which leads to hemorrhages and bleeding in the organs and nose. Hemorrhagic syndrome and hepatic-renal failure can lead to death.
By the end of the second week of the peak, a bacterial infection may occur with the development of bacterial inflammation in the organs and even sepsis.
We will call you back
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Treatment of leptospirosis
Patients with leptospirosis must be hospitalized in the infectious diseases department. They are prescribed bed rest for the entire period of fever. The basis of drug therapy for leptospirosis is antibacterial drugs. The complex of therapeutic measures also includes specific anti-leptospirosis immunoglobulin.
To relieve intoxication, patients are given intravenous infusions of water-salt solutions, and depending on the leading clinical manifestations, symptomatic treatment is prescribed. In case of development of acute liver, kidney or heart failure, intensive care measures are resorted to.
When does recovery begin?
By the end of the fourth to sixth week, from the appearance of the first signs of infection, recovery begins with a gradual fading of symptoms - a period of convalescence. But full recovery will not happen soon; weakness remains for a very long time.
In half of patients, recurrent infections are possible because the spirochetes take refuge inside the kidneys. The return is manifested by an attack of high fever with muscle and headaches, a red face with bloody eyes, that is, symptoms of the onset of the disease, but a little milder and disappear in just a few days.
Classification of leptospirosis
The classification of leptospirosis is based on clinical manifestations, leading syndromes, course of the disease and severity. A detailed classification with explanations is presented in the table.
| Classification sign | Form of leptospirosis | Comments |
| Clinical manifestations | icteric | occurs with yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes |
| anicteric | the skin and mucous membranes retain their natural color, other symptoms of the disease come to the fore | |
| Leading syndrome | renal | characterized by kidney damage, patients complain of lower back pain, urine becomes dark, sometimes mixed with blood |
| hepatorenal | Symptoms of kidney damage include pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea and vomiting, yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes | |
| meningeal | the leading symptoms are signs of damage to the nervous system: severe headaches and muscle pain, sleep disturbances, nervous agitation, anxiety | |
| hemorrhagic | accompanied by the appearance of multiple hemorrhages on the skin and mucous membranes, blood in the urine | |
| Flow | acute | in the acute form, the duration of the disease is 3-4 weeks, in the protracted form - 2-3 months |
| protracted | ||
| with relapses | relapses of infection are observed in 20-30% of patients, in other cases the disease proceeds without exacerbations | |
| no relapses | ||
| with complications | with timely treatment, the likelihood of complications with leptospirosis is low; as a rule, complications develop in the absence of medical care and in weakened patients | |
| without complications | ||
| Severity | light | the degree of severity depends on the massiveness of the lesion, the state of immunity and the age of the patient; Most adults have mild or moderate leptospirosis |
| moderate severity | ||
| heavy |
Diagnosis of the disease
The general blood test shows a very high level of leukocytes, many band neutrophils, and a very high ESR. Urinalysis with large deviations. Biochemical blood test showed high bilirubin, AST and ALT, creatine phosphokinase.
The diagnosis is made by a characteristic clinical picture and identification of the pathogen in biological fluid - blood or urine. The infection is also looked for in contact pets. The recognized diagnostic standard is the microagglutination test or PMA of Leptospira.
Classification
There are two forms of the disease - icteric and anicteric .
- Jaundice - the incubation period in this case lasts 1-2 weeks. It begins acutely, body temperature can rise to 40 degrees, and a pronounced feeling of weakness appears. Around day 2-3, the liver enlarges, and in some cases, the spleen. I am worried about pain in the calf muscles, icterus appears in the sclera and skin. Oliguria develops around day 4-5 , later anuria . Hemorrhagic syndrome appears. Tachycardia is a concern , infectious myocarditis . This form of the disease is sometimes called “infectious jaundice.”
- Anicteric - the incubation period lasts 4-10 days. The patient experiences weakness, body temperature, weakness, develops meningeal signs, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, oliguria, and liver enlargement.
According to the severity of the disease, three degrees are distinguished:
- mild – mild intoxication, internal organs are not affected;
- moderate – severe intoxication, all the symptoms of leptospirosis are present;
- severe - damage to internal organs occurs.
Treatment and prevention of leptospirosis
Due to the high probability of multiple organ failure, even with a mild course, the patient must be hospitalized. They are treated with penicillin and, of course, against the background of active intravenous symptomatic therapy.
There is a vaccine, it is well tolerated, but vaccinations are done according to indications during an outbreak or in a natural source of infection. Repeated vaccination is done after a year. Dogs must be vaccinated. In case of contact with an infected animal, antibiotics are prescribed.
You can learn how to speed up recovery and ensure the fastest possible recovery from an infectious disease specialist at the international clinic Medica24, who has completed training and internship in the best centers in the country. Contact the Center for Infectious Diseases by phone 24 hours a day +7 (495) 230-00-01
The material was prepared by an infectious disease specialist at the international clinic Medica24, Doctor of Medical Sciences Margarita Vasilievna Nagibina.
Complications
The most common complication of leptospirosis is kidney failure. In severe cases, it can develop already in the first week of the disease, increasing the risk of death to 50-60%. Leptospirosis can also be complicated by:
- liver failure;
- hemorrhages in various organs (lungs, adrenal glands);
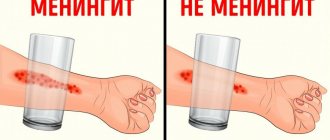
- meningitis (inflammation of the brain);
- pneumonia (pneumonia).
Note! The risk of developing complications is higher in people with weakened immune systems and young children. Reluctance to seek medical help and self-medication can lead to serious consequences for leptospirosis.
Tests and diagnostics
During the diagnostic process, the doctor examines and interviews the patient, assesses the presence of visual signs of leptospirosis.
To establish a diagnosis, the following studies may be performed:
- General analysis of urine and blood, biochemical blood test.
- Spinal tap.
- PCR or RT-PCR testing.
- X-ray of the chest organs.
- Microscopic analysis for leptospirosis in humans - a microscopic examination of blood, urine and cerebrospinal fluid is carried out in order to detect the causative agent of leptospirosis in them.
- Inoculation of biomaterial on nutrient media to determine the pathogen.
- A serological blood test for leptospirosis, during which the increase in the amount of antibodies to leptospira in the blood serum is determined.
- ELISA method for determining IgM antibodies.
- Coagulogram, ultrasound examination, lumbar puncture.
Causes
The causative agent of the disease is Leptospira interrogate. It is an aerobic, gram-negative, motile, spiral-shaped rod, the reservoir of which is animals. A person with leptospirosis is not a source of infection.
The gates of infection are the mucous membranes of the mouth, nasopharynx, and damaged skin. In the body, infection spreads through lymph and blood .
The risk zone includes those people whose activities are related to animals. These are veterinarians, farm owners and workers, meat industry workers, shepherds, milkmaids, etc.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of leptospirosis is established on the basis of epidemiological data, the clinical picture of the disease and data from laboratory research methods. Laboratory research methods include bacterioscopic, bacteriological, serological and biological methods.
Leptospira during the height of the disease can be isolated from blood, cerebrospinal fluid and urine, at later stages - only from urine.
The microscopic method of examination is effective in the early stages of the disease (from 1 to 5 days). The maximum number of leptospira is obtained after centrifugation of the material. Dark-field microscopy and Romanovsky-Giemsa staining of smears are used.
The bacteriological research method is the most effective. Blood cultures are carried out before 4 - 5 days of the disease, urine is cultured at 2 - 3 weeks. The results of the analysis are delayed, so the diagnosis of leptospirosis is based on serological research methods.
Serological research methods are used at the height of the disease. Microagglutination reactions (RMA), complement fixation (RSF) and passive hemagglutination reactions (RPHA) are used. The use of these methods is also delayed, since the study of paired sera is assumed, when the first sample is taken for examination at the beginning of the disease, the second - after 10 - 14 days. With PMA, titers of 1:100 are considered positive, with RSC - 1:10.
Biological testing is carried out in specialized laboratories. Laboratory animals such as rabbits and hamsters are used for infection.
Rice. 12. View of Leptospira under a microscope.
Prevention
There are the following measures to prevent leptospirosis:
- Vaccination is carried out from 7 years of age. In adulthood, vaccinations are given to people who, due to their profession, often come into contact with animals. We are talking about veterinary and agricultural workers, as well as those who work in slaughterhouses or live in epidemic-prone areas and have close contact with homeless animals.
- Very careful adherence to personal hygiene rules.
- Refusal to swim in untested bodies of water.
- Compliance with safety measures when working with animals.
- Correct and timely treatment of damage to mucous membranes and skin - for this you need to use special products.
- Immediately contact a specialist when the first symptoms of leptospirosis appear.
Epidemiology
Leptospirosis is a zoonosis, a natural focal disease. The reservoir of pathogenic Leptospira in nature are mammals, amphibians, reptiles, and birds. The source of infection for humans can be many wild and farm animals that secrete Leptospira in the urine for a long time. Nowadays, natural foci of leptospirosis are affected by intensive human economic activity (water reclamation work, construction of large livestock complexes, etc.), which leads to changes in the ecology of rodents and can contribute to both the attenuation of the epizootic process in the foci and the emergence of new natural and also anthropurgic (economic) and mixed foci of leptospirosis. In anthropurgic foci, the source of infection is farm animals, rodents, and dogs. A person with leptospirosis is practically not contagious.
According to the epidemiological classification of L.V. Gromashevsky, leptospirosis, according to the transmission mechanism, is classified as an intestinal infection. However, by type of intestinal infection, leptospirosis is transmitted mainly among animals, and humans are more often infected when Leptospira penetrates through the outer integument (percutaneous mechanism of infection). Leptospirosis is transmitted by contact, water and food.
The main factor in the transmission of infection remains water contaminated with the urine of infected animals. Human infection with leptospirosis occurs when swimming in open freshwater reservoirs, during fishing, hunting, during various agricultural work, working in coal mines, drinking water from open reservoirs and wells, consuming infected products, and through direct contact with sick animals. Possible occupational infection.
People are highly susceptible to leptospirosis, but mostly young and middle-aged men are affected. Most cases of infection occur in the summer-autumn period. Along with sporadic morbidity, epidemic outbreaks are also recorded. After the illness, persistent serovar-specific immunity remains.