The prevalence of lesions of the nervous system (CNS) in newborns has recently become almost epidemic. More and more children under one year of age are turning to pediatric neurologists and pediatricians with complaints of hyperactivity and developmental delay, which are nothing more than the consequences of pathology suffered during childbirth.
Many diseases of older children occur due to the fact that damage to the nervous system during the neonatal period was not recognized in time. In 80-85% of dead newborns, the section reveals a spinal cord injury; brain injuries are 2 times less common.
The consequences of damage to the nervous system during childbirth can be hydrocephalus, developmental delay, paresis and paralysis, visual and hearing impairment.
Causes of central nervous system damage in newborns
Suppression of the central nervous system of a newborn during and after childbirth can occur for three main groups of reasons: ischemic-hypoxic lesions, traumatic and infectious-toxic. Let's look at each group in more detail.
- Ischemic and hypoxic lesions of the central nervous system in newborns
are caused by a lack of oxygen in the child’s blood during childbirth. This may be due to long and protracted labor, weakness of labor, abnormalities of the placenta and umbilical cord. With ischemia (complete absence of oxygen), brain cells die, and the further picture of the disease depends on which part of the cortex this happens. - Traumatic lesions of the central nervous system
- in the vast majority of cases occur during childbirth. The immediate cause may be an early birth (the baby’s head is born very quickly and is injured), a large fetus, unskilled actions of the obstetrician, etc. - Infectious and toxic lesions
can be associated with viral infection, alcohol, smoking during pregnancy, etc.
Brain lesions most often have an ischemic-hypoxic nature, while the spinal cord is more often affected by physical trauma to the child’s neck during childbirth. To prevent this, it is very important to give birth in a good maternity hospital with a competent obstetrician, and in the first days after discharge, go to see an osteopath.
Mom, school or kindergarten: who is to blame for neurosis in children?
Have you started to notice that your child is biting his nails? Or maybe he is going to kindergarten or school in tears? Or did you start washing your hands with soap very often?
The manifestations of this disease (or rather of a whole group of them) are varied. As well as the reasons leading to them.
The many faces of neurosis. We are talking about it today with our regular consultants from Clinic Expert Tula - neurologist Anna Georgievna Sycheva and psychologist Kristina Yuryevna Shereshevskaya.
— There are many myths and fears around this disease. Most parents are sure that if a child is often capricious or sleeps poorly, then he has a neurosis. What actually lies behind the diagnosis of “neurosis”?
Neurosis is a disorder of mental activity caused by factors that traumatize the psyche. Neurosis is a collective concept that includes a number of disorders. There is no such diagnosis in the International Classification of Diseases. However, it is still used in medical practice to this day. Neurotic disorder is reversible and has a functional nature.
Read material on the topic: How to prepare for school after the summer holidays: advice from a child psychologist
— At what age can a child be diagnosed?
If we consider neuroses as broadly as possible and include among them the so-called constitutional childhood nervousness, then the diagnosis can be made soon after birth.
— Is neurosis a neurological or psychiatric disease?
It is located on the “border” of neurology and psychiatry. His treatment is carried out by neurologists, psychiatrists and psychotherapists. Psychologists can provide some help.
— What is neurosis and which type of disease occurs more often in children than others?
There are three main types of neurosis. These are neurasthenia, hysterical neurosis and obsessive-compulsive neurosis. Each of them consists, in turn, of other disorders.
The so-called systemic neuroses are relevant for clinical practice. Usually these are mononeuroses. These include neurotic ones: stuttering, tics, enuresis, encopresis, sleep disorders. These are their most common forms in children.
Neurotic disorders also include pathological habitual actions. For example, biting nails, twisting something on your finger.
The most common type is obsessive-compulsive disorder.
— What are the symptoms of neurosis in children?
Based on the numerous types of neurotic disorders, the manifestations are extremely diverse. These are frequent blinking, sniffing, smacking, coughing, biting nails, throwing hands, twisting something on a finger, etc. Such actions are characterized by repetition.
With neurasthenia, self-doubt, low self-esteem, and fear may be noted.
Read the material on the topic: Fairytale therapy for children's problems. Fear of needles
Phobic neurosis (fear neurosis) can be part of other forms of neurosis.
— Could neurosis be a mask for some other diseases?
Yes. For example, a psychotic disorder can be “masked” as neurosis.
— We all come from childhood. And if this is so, does this mean that parents shape psychological and psychiatric illnesses in children? Can the atmosphere in the family and parental upbringing serve as a trigger factor in the development of neurosis in children?
Yes. The fact is that the type of upbringing in the family largely determines the development of the child’s personality. Excessive care or rejection, authoritarianism or hyper-socializing upbringing - these and other points can influence the child, his temperament, and can be a kind of factor provoking the development of neurosis.
Read the material on the topic: Benjamin Spock: revolutionary innovator or hypocrite?
At the same time, the influence of the family should not be taken into account. There are, of course, other reasons for the formation of a neurotic disorder. How many children, frightened by a dog, will start to stutter? Of course, not all. And many such examples can be given. A certain “biological” basis also matters - predisposition, strength of the traumatic factor, etc.
— Do the causes of neuroses in children of preschool and school age differ or are they the same?
In general, there is one reason - a psychotraumatic factor. Some of them will be common to children of any age, others will be different.
For example, a schoolchild has disproportionately higher mental loads, expectations from him, and the need to develop a sense of responsibility. To some extent, such general moments also exist in the preschool period, but they are not so intense.
— Which children are at risk for developing neurosis?
Children with a hereditary predisposition. In particular, tics do not appear out of nowhere. When interviewing the parents of such a child, it may reveal, for example, that the mother has anxiety.
The next point is problems in the area of relationships between parents.
A certain background for possible neuroticism can be created by the style or model of behavior of parents. For example, if a mother has increased anxiety, then it can be “transmitted” to the child.
Errors in upbringing can contribute to the appearance of a neurotic disorder.
— What specialty does a doctor treat neuroses in children?
Neurologist, psychiatrist, psychotherapist, pediatrician.
— Does neurosis necessarily require treatment, or is it enough to remove provoking factors and create a calm atmosphere for the child?
Treatment of neurosis in children is not necessarily medicinal. Anyway? psychological work is required with the child and his parents to find out the provoking moments, the traumatic factor, etc. Often this work is enough to fix the problem.
In some cases, medications are used. The treatment regimen is always determined by the doctor.
— What is the most important thing in the treatment of neurosis? How can parents and their immediate environment help their child cope with the disease?
It is necessary to find out the cause of neuroticism. It is very important for parents to participate in the treatment process. It is recommended to work with a psychologist who will understand possible problems within the family and give appropriate recommendations.
— What is the prevention of neurosis in children?
First of all, this is the harmonization of family relationships. Easy to say, hard to do. Therefore, clarification is necessary.
It is important to adhere to the general principles of education for the whole family (unity of prohibitions, requirements, reactions to various actions of the child).
Discuss “what is good” and “what is bad.” It is not enough to simply prohibit; it is important to be able to convincingly show why. This can be done as early as 3 years old.
Read fairy tales with positive moral content. It’s good to role-play appropriate situations (including using toys), explaining along the way what and why is permissible or prohibited.
More of our articles every day on social networks: VKontakte, Facebook, Odnoklassniki
Parents need to communicate competently with their child. Authoritarianism can have a negative impact. Ideally, a democratic, partnership style of relationship is optimal. It is important to be able to listen to a child, understand him and help him understand himself. For example, if a child is crying, the correct thing to do is not to ask him “Why are you crying?” but to say “I know you are upset. Tell me why".
In the process of communication, it is important to form eye-to-eye contact with the child, and, if possible, position yourself at his height level: squat down or sit the child higher. It should be remembered that partnership is not a synonym for permissiveness, but a respectful attitude towards the child.
It is necessary to properly dose intellectual and physical activity. Neurosis often develops due to its inconsistency with the child’s real capabilities. School with its number of lessons, plus several clubs with the need to keep up everywhere may well become a factor provoking the development of neurosis. A similar situation can occur when a child is preparing for school.
Read the material on the topic: What to do if a child has a stomach ache?
The work of parents on themselves is of great importance. It has been shown that anxious parents have anxious children. If a parent knows about their increased anxiety and fears, they need to work with this problem - independently or with the help of a specialist. The principle “Educate yourself, because the child will be like you” works here.
Other materials on topics:
Are toads to blame? Why do warts appear in children?
Are unvaccinated children the healthiest?
Fairytale therapy for children's problems. Fear of the dentist
For reference:
Sycheva Anna Georgievna
In 1981 she graduated from the pediatric faculty of the Astrakhan State Medical Institute (today Astrakhan State Medical University).
From 1981 to 1982 she completed an internship at the I-Moscow Medical Institute named after. THEM. Sechenov, specializing in Pediatrics.
In 1995, she underwent professional retraining at the St. Petersburg State Pediatric Medical Academy, specializing in Neurology.
Currently he holds the position of neurologist at Clinic Expert Tula. Receives at the address: st. Boldina, 74
Shereshevskaya Kristina Yurievna
In 2010, she graduated from the Faculty of Pedagogy and Psychology at Oryol State University with a degree in Preschool Pedagogy and Psychology, and in 2021 she graduated from graduate school with a degree in Educational Psychology.
In 2021, she completed a master’s course in the field of “Special (defectological) education”, profile “Psychological support for the education of persons with developmental problems.”
Teacher of preschool pedagogy and psychology, educational psychologist, candidate of psychological sciences.
Main complaints
Pathology of the nervous system in newborns does not appear immediately, and this is its insidiousness. After all, the longer the disease remains unrecognized, the more difficult it is to treat it in the future. Only very pronounced disorders make themselves felt in the first days of the baby’s life, usually manifesting themselves in convulsions. Seizures that occur in the first 24 hours after the baby is born are especially dangerous.
Most often, parents pay attention to the child’s hyperexcitability, restless behavior, and sleep disturbances. Also often associated symptoms are excessive regurgitation and choking. Some mothers manage to notice disturbances in motor functions. As a simple home test, you can use a child's skills screening test depending on age.
Screening test. Normal full-term baby:
- By 2 months he can hold his head while lying on his stomach.
- By 6 months, sits independently and steadily.
- At 12 months – the beginning of independent walking.
Children with traumatic lesions of the spinal cord at the neck level are delayed by 1-2 months, however, their developmental delay is not as severe as with damage to the cerebral cortex.
Based on the pace at which the child develops, one can approximately judge the presence of neurological abnormalities and consult a doctor in time. The doctor will conduct more detailed studies that will show the diagnosis and level of damage to the nervous system.
Symptoms of neurological diseases
Symptoms may vary depending on the severity of the disorders and their causes. Alarming symptoms for parents are:
- sleep disturbances in a child, constant headaches;
- problems with headaches when the weather changes;
- decreased academic performance, memory impairment;
- fast fatiguability;
- hyperactivity, mood swings;
- nervousness;
- various speech disorders;
- impaired mental function;
- problems with urination (enuresis);
- general weakness;
- the appearance of weakness in the limbs;
- obsessive behavior, tics;
- loss of previously acquired skills;
- convulsions.
In order for parents to have a reason to visit a neurologist, it is not necessary to wait until all of the listed symptoms appear. Usually the child has a specific problem. This could be a sharp decline in academic performance, the appearance of nervousness, or behavioral disturbances. Young children may lose previously acquired skills and develop speech disorders. If a child does not speak at 2 years old, this is also a reason to visit a specialist who will conduct the necessary diagnostics and prescribe treatment.
Osteopathic examination
An examination by an osteopathic doctor involves not only a neurological examination, but also a search for anatomical abnormalities in the structure of the skull, cervical vertebrae, sacrum, ribs, etc. All this is of great importance for the child’s health, since the slightest deviations in anatomy are projected on an enlarged scale into the future life of the baby. Osteopathic diagnosis is carried out by a doctor and includes:
- Examination: determination of the arch of the body, position of the limbs, behavior of the child.
- Assessing the amplitude, strength and rhythm of the primary respiratory mechanism.
- Assessment of the pattern of the craniosacral system.
- Testing the mobility of the cervical and lumbosacral spine.
- Global skull test, assessing the mobility of each of the bones of the arch and base.
- Diagnosis of intraosseous injuries of the skull and sacrum.
After the examination, the osteopathic doctor gets an idea of all the anatomical disorders in the child’s body and immediately begins treatment.
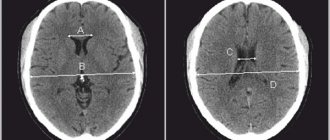
Diagnosis of perinatal lesions of the central nervous system
The diagnosis of perinatal brain damage can be made only on the basis of clinical data; data from various research methods are only of an auxiliary nature and are sometimes necessary not to make the diagnosis itself, but to clarify the nature and location of the lesion, assess the dynamics of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment.
Often, one child has several types of perinatal lesions of the central nervous system. In this regard, it is important to conduct a comprehensive examination of the child.
In recent years, there has been a significant improvement in the diagnostic capabilities of children's medical institutions. Additional research methods have appeared in the diagnosis of perinatal lesions of the central nervous system:
- Neurosonography (method of echoographic visualization of the brain of a newborn and a child up to 1 year old, while the fontanelle is open)
- Electroencephalography (a method for studying the functional activity of the brain, based on recording electrical potentials of the brain.)
- Ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels
- Echospondylography of the cervical spine
- Electroneuromyography (study of nerve signal conduction and muscle response)
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Biochemical blood tests
- Consultations with specialists (endocrinologist, orthopedist, speech therapist, psychologist, etc.)
It should be noted that there is no need to apply all additional diagnostic methods at once. The specific research methods for your child will be determined by a specialist from our center based on the neurological status at the time of examination.
Osteopathic treatments
Osteopathic treatment of central nervous system lesions in newborns is aimed at eliminating anatomical dysfunctions in the newborn’s body, restoring normal biomechanical relationships of all bones and joints, as well as soft tissues damaged during traumatic birth. Examples of techniques that are included in the osteopathic course of treatment for newborns:
- Fascial decompression of the sacrum, sacrolumbar joints.
- Removal of blocks at the level of the articulation of the first cervical vertebra and the skull.
- Balancing the tone of the thoracoabdominal diaphragm.
- Release (normalization of muscle tone) of the upper aperture of the chest, collarbones, shoulder blades, first rib.
- Decompression of sphenobasilar synchondrosis.
- Balancing the mutual tension membranes of the cranial cavity and spinal cord.
- Elimination of intraosseous damage to the occipital, temporal, and sphenoid bones resulting from injuries during childbirth.
- Correction of blood outflow and cerebrospinal fluid circulation in the cranial cavity.
- Balancing and balancing techniques.
The goal of treatment is to ensure that there are no tensions, blocks, or dysfunctions in the newborn’s body, so that it functions as an ideally tuned biomechanical system. The entire future life of the baby and diseases that may appear due to missed birth injuries depend on this.