Types of lumboischialgia
According to the method of progression, lumboischialgia is divided into 2 forms:
- acute – characterized by acute lumbago that occurs for the first time;
- chronic - pain (they are nagging and dull) appears periodically and systematically, periods of exacerbation are replaced by remission.
Depending on the affected area, lumbago with sciatica occurs:
- unilateral – pathology covers the right or left side of the body;
- bilateral, or bilateral - inflammation spreads to both sides.
Depending on the cause, lumbar sciatica is distinguished:
- vertibral, or vertebrogenic – caused by diseases of the spine:
- discogenic – develops with intervertebral hernia;
- spondylogenic – caused by osteochondrosis;
- nonvertebrogenic – not associated with diseases of the spine:
- angiopathic - provoked by disruptions in the blood circulation of the lower back and lower extremities;
- myofascial – a consequence of damage to muscles and fascia;
- caused by pathologies of the peritoneal organs;
- caused by problems in the hip joints;
- idiopathic - the cause cannot be determined.
Treatment of the sciatic nerve according to Neumyvakin
According to Dr. Neumyvakin, it is almost impossible to treat sciatica and maintain the acid-base balance in the body with pharmaceutical drugs. Slags and toxins accumulate in the body over the years, when eventually a special imbalance arises between acids and alkalis.
The technique is based on hydrogen peroxide and baking soda. It is this combination of components that gives good results for sciatica. Neumyvakin points out that you need to take hydrogen peroxide orally. The body will begin to receive a fair portion of oxygen when the H2O2 solution decomposes into separate elements: free oxygen and water.
The technique is simple to implement:
- To support the immune system, hydrogen peroxide should be taken orally on an empty stomach (1 hour before meals).
- Start drinking an aqueous solution of peroxide with 2 drops three times a day, for which dilute 1 drop of peroxide in 350 ml of warm water.
- So, gradually increase the dose to 10 drops, adding one every day.
- After 10 days, take a break for 3 days and continue taking it, starting with 10 drops and reducing it to a minimum, up to 1 drop.
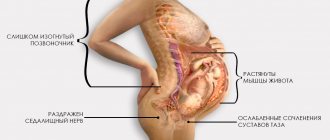
Causes of pathology
The disease develops when the sciatic nerve is pinched, injured or inflamed.
A variety of factors can cause this situation:
- injury to the back area;
- radicular syndrome;
- chronic diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia, arthrosis, osteoporosis, spondylitis, scoliosis, protrusion);
- benign or malignant neoplasms in the spinal column;
- infections affecting nerve trunks;
- inflammation of the back muscles;
- inflammatory processes in the blood vessels of the sacrum;
- pathologies of the hip joint;
- diseases of the abdominal organs;
- prolonged sitting;
- unsuccessful injections into the epidural cavity;
- postoperative complications.
They increase the risk of developing the disease and provoke relapses in the chronic form:
- hypothermia of the body;
- prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position;
- long work at the computer;
- improper performance of exercises during sports;
- increased physical activity;
- constant work in the garden (sometimes lumboischialgia is called summer residents’ disease);
- poor posture;
- age-related degenerative processes in the spine;
- excess weight;
- frequent stressful situations;
- depression;
- pregnancy;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking.
What does a cold sciatic nerve mean?
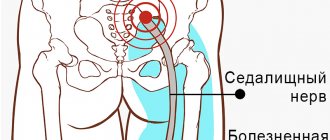
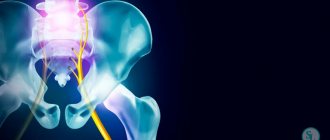
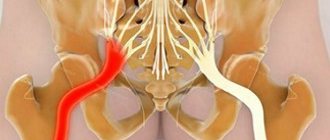
We have already discussed above that the sciatic nerve consists of many branches of the lumbar roots. It forms in the nerve plexus. Then it passes through the piriformis muscle and along the back of the thigh (between the muscles) down into the popliteal fossa. Bifurcation occurs in it - division into the tibial and peroneal branches. The nerve then runs along the side of the leg to the ankle joint. Partially innervates the tissues of the foot.
Throughout the entire path of the sciatic nerve, it can be negatively affected. And it is precisely these pathologies that are evidenced by inflammation of the sciatic nerve, which the patient subjectively regards as a cold spot.
What actually happens when exposed to cold as a strong stress factor:
- in the lumbar region, in the thickness of the skin, a reflex reaction begins - narrowing of blood vessels, thus carrying out primary thermoregulation;
- when the intensity of blood microcirculation decreases, a dehydration reaction of the intervertebral discs begins;
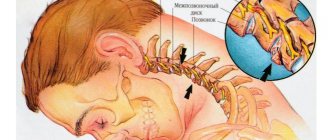
- they temporarily lose elasticity and do not protect the radicular nerves and their branches from compression by neighboring vertebral bodies (this occurs only in those patients who have had osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine for a long time; in healthy people this reaction is not observed);
- when compressed, the radicular nerves become inflamed, which creates unfavorable conditions for the sciatic nerve - this reaction also affects it;
- then, as it progresses, infiltrative swelling begins to develop, which can cause sciatica and piriformis syndrome;
- the patient experiences a burning pain, which is intensified by lumbago when moving;
- Neurological signs gradually appear.
With plexitis, similar pathological changes occur. But there is also an ascending type of damage to the sciatic nerve. Pinching is observed in the popliteal fossa. If a person often likes to sit with one leg crossed over the other, then gradual degeneration of the nerve fiber occurs. The surrounding tissues become thinner, most often due to insufficient innervation. Therefore, when the knee area is overcooled, an aggravation occurs and it seems that the sciatic nerve has caught a cold. In fact, everything is a little different.
When the area behind the knee is exposed to cold, an emergency constriction of the blood vessels begins. The blood flow practically stops, as evidenced by the pallor and even cyanosis of the outer skin. Against the background of a decrease in the intensity of capillary blood flow, ischemic reactions begin to occur in the structure of the nerve fiber. This is what causes quite a lot of pain.
It can spread upward and downward. With ascending irradiation, pain can spread along the back of the thigh to the buttock and lumbar spine. In this case, diagnostic functional tests help make the diagnosis.
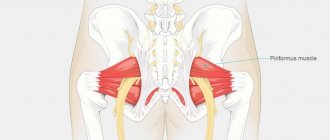
Another common disease in which similar unpleasant symptoms can occur under the influence of negative temperatures is piriformis syndrome. As mentioned above, there is a tunnel inside it. It ensures the passage of the sciatic nerve from the lumbar iliac region to the trochanter of the hip joint. When exposed to cold, a sharp spasm of the piriformis muscle is possible.
At the same time, the compression pressure on the sciatic nerve and accompanying blood vessels increases sharply. An ischemic and inflammatory reaction begins. This is accompanied by acute pain, lumbago, limited mobility, a feeling of stiffness and other symptoms.
As you can see, the situation is not always as clear as the patient imagines. In principle, there is no such thing in medical terminology as a cold sciatic nerve. There are diseases in which this structure becomes inflamed, subject to ischemia or compression. As a result, sciatica develops - inflammation of the sciatic nerve. And already this standing is assessed by the patient subjectively as a cold nerve. But, as you understand, in such a situation a thorough differential diagnosis is necessary. The success of the treatment depends on how accurately the diagnosis is made. Do you agree that it is difficult to expect a positive result from the treatment of piriformis syndrome if the real cause of the pain is located in the popliteal fossa?
Accordingly, the first thing to do if it seems that the sciatic nerve has caught a cold is to contact an experienced neurologist. You can also visit a vertebrologist or orthopedist. We do not recommend visiting your local physician for such problems. This doctor does not have sufficient professional competence to make an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective course of treatment.
In most cases, with such requests, the local physician establishes a diagnosis of lumbosacral osteochondrosis, standard for such a situation. Prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and chondroprotectors. After 10–14 days, the patient is discharged to work. And the disease he has is only suppressed temporarily and continues to develop.
Therefore, the first thing to do if the sciatic nerve has caught a cold is to look for an experienced neurologist or vertebrologist. This specialist will provide real professional assistance, and will not provide symptomatic treatment with the goal of discharging you to work as quickly as possible.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of lumboischialgia is acute lumbago (sharp pain of a shooting nature) in the buttocks and back of the legs, radiating to the lower extremities. The pain is provoked by sudden movements, lifting heavy objects, sneezing, coughing. Attacks can last several minutes or several days.
The patient may experience other symptoms:
- decreased or loss of sensitivity in the skin of the buttocks and affected leg;
- stiffness in the lower back;
- muscle tension;
- pain when standing on your leg;
- cramps in the calf muscle;
- numbness of the toes;
- pallor of the skin in the sacral area;
- increased body temperature;
- chills and fever;
- weakness in the legs;
- indigestion;
- difficulty and pain in urination and defecation;
- itching, burning or subcutaneous throbbing.
If left untreated, blood circulation is impaired. Over time, lumbago with sciatica can cause urinary and fecal incontinence, sexual dysfunction, cause a decrease in muscle mass in one limb, and lead to disability.
First aid for an attack at home
As first aid for sciatica attacks, it is important for patients to:
- eliminate any movement;
- lie down on a hard surface;
- completely immobilize the affected limb;
- take a pain reliever (Spazmalgon, No-shpa, Analgin);
- Observe bed rest until the pain subsides.
IMPORTANT! The following symptoms cannot be tolerated: swelling of the skin, burning and sharp pain with a feeling of numbness, stiffness of movements in the legs (hips, pelvic area), burning sensation when urinating, fever above 38 degrees.
Diagnostics
The doctor will be able to draw preliminary conclusions by studying the medical history and examining the affected area.
To confirm the diagnosis, determine the cause of the disease and determine the condition of the tissues, he refers the patient for diagnostics:
- radiography;
- ultrasonography;
- densitometry;
- computed or magnetic resonance imaging;
- blood test for infections and autoimmune diseases;
- analysis for tumor markers (if a tumor is suspected).
Treatment with folk remedies
If a pinched nerve is present, applying dry heat as a distraction will help. Heat helps relieve pain and relieve muscle spasms. Additionally, it is advisable to combine it with reflexology and relaxing massage.
To help with treatment at home - compresses, Chinese remedies, medicinal plants:
- pepper patch for sticking to the affected areas, leaving overnight;
- apple cider vinegar for rubbing;
- wax moth tincture;
- saline dressings;
- infusion of burdock root, calendula flowers, horse sorrel, elecampane.
Traditional medicines can be quite effective in relieving pain.
Treatment methods
Treatment of lumboischialgia consists of two stages: medication and complex.
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating muscle spasms and relieving pain. The patient must be prescribed bed rest (for a couple of weeks). In this case, the bed should be flat and firm. For particularly severe pain, it is recommended to use a corset.
Drug treatment includes taking:
- anti-inflammatory medications – relieve inflammation, relieve pain;
- analgesics – relieve pain;
- muscle relaxants - eliminate muscle spasms;
- vasodilators - activate blood circulation and accelerate metabolism;
- diuretics – have a diuretic effect, eliminate swelling, remove toxins from the body;
- antidepressants – relieve depression, nervousness, fears;
- vitamin complexes - provide the body with useful substances, accelerate regeneration, help restore nerve structures and improve conductivity.
Local agents (ointments, creams and gels) that improve blood circulation and have an analgesic effect will help increase the effectiveness of treatment. For severe, unremitting pain, blockades with novocaine or glucocorticosteroids are made.
Under no circumstances should you massage or knead the sore area, as this can lead to a significant deterioration in your well-being.
After the pain disappears, they move on to the second stage, aimed at eliminating the cause of the pathology.
For complex therapy the following is used:
- physiotherapeutic procedures (shock wave therapy, ultra-high frequency therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis, ionization, Bernard currents, laser therapy, magnetotherapy, electrotherapy, diathermy, reflexology, ozone therapy, muscle relaxation, paraffin baths) - effectively relieve inflammation and pain, restore the functionality of the lower back;
- physical therapy – special exercises are selected to relieve pinched nerves.
Additionally, you can use traditional medicine recipes.
In difficult cases (for example, if lumboischialgia is combined with an intervertebral hernia), surgical intervention is resorted to.
Shock wave therapy treatment
Among physiotherapeutic procedures, shock wave therapy is the most effective.
During the procedure, the affected tissues are exposed to acoustic shock waves of a given frequency, which are generated by a special sensor. The therapy has a complex effect on all components of the pathological process: destroys salt deposits, increases blood flow in capillaries tens (and sometimes hundreds) times, normalizes metabolism, improves cell nutrition, eliminates muscle spasms and inflammation, relieves pain, and restores spinal mobility . In addition, it activates the body’s own forces, contributing to its restoration and return to a full life.
Quite often, when drug treatment fails, shock wave therapy leads to complete recovery, making it a worthy alternative to injections and avoiding surgical treatment.
To increase the effectiveness of the procedure, individual parameters are selected on the device for each patient, taking into account the general condition of the body and associated pathologies.
The full course of treatment includes 8-10 weekly procedures.
How to treat if the sciatic nerve is cold
If the sciatic nerve is cold, treatment should begin with differential diagnosis. There is no such disease as a cold nerve. There is a pathology in which a number of corresponding clinical symptoms arise. This disease needs to be treated. Otherwise, no positive change will be achieved.
So, after the disease is identified, the doctor develops an individual course of therapy. For example, if a patient has a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs and, as a result, compression pressure is exerted on the roots responsible for the formation of the sciatic nerve, then he is offered spinal traction. Manual traction of the spinal column allows you to quickly relieve pressure from the radicular nerves and their branches. The patient experiences relief from his condition. And then it is already possible to carry out complex treatment aimed at restoring damaged intervertebral discs.
Before treating a cold sciatic nerve due to piriformis muscle syndrome, it is necessary to relieve its spasm. For this purpose, it is advisable to use osteopathy and kinesiotherapy. Using acupressure, the doctor achieves relaxation of the muscle fiber. Osteopathy allows you to start disrupted processes of microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid. This creates conditions for rapid tissue regeneration inside the piriformis muscle. Reflexology, physiotherapy, exercise therapy and massage are then used.
If you need effective and safe treatment of the sciatic nerve, then we invite you to a free consultation with a neurologist at our manual therapy clinic in Moscow.
Disease prevention
To prevent the development of lumboischialgia, it is recommended:
- eat rationally;
- move more often;
- exercise;
- perform exercises that strengthen the back muscles and stretch the muscles;
- when doing physical work, use the principles of biomechanics;
- balance the load with the body’s capabilities;
- fight excess weight;
- promptly treat diseases of the spine, blood vessels and digestive system;
- don't get too cold.
Principles of treatment
If symptoms appear that the sciatic nerve is cold, treatment is carried out using not one remedy, but a combination of them. For effectiveness, a combination of drug therapy, physiotherapy, massage, and physical therapy is practiced. If there is no result from these measures, as well as in severe cases of damage and the impossibility of stopping the tissue abscess, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Drug therapy
Medicines for the treatment of sciatica are designed to:
- eliminate pain;
- stop the inflammatory process;
- make up for the lack of substances that improve health and accelerate recovery.
Options for sciatica prevention
In order to minimize the risk of developing such a serious problem as pinched sciatic nerve, doctors recommend strengthening the back muscles.
It is necessary to constantly monitor your posture. When working in an office (sedentary mode), you need to find time for periodic pauses (getting up from your seat). It is advisable to avoid hypothermia and significant physical exertion.
Women should avoid wearing high heels for a while. You can avoid the disease by maintaining an active lifestyle.
Therapeutic and preventive gymnastics will have an excellent effect in the treatment of sciatica. Thanks to a set of simple exercises, you can normalize nerve inflammation and return to normal life. Before selecting exercises, you should consult your doctor.
Ways to relieve sciatic nerve pain
It is important to pay attention to emerging symptoms in a timely manner and not to start the problem. Coping with the task at the initial stage will be much easier and much cheaper.
We offer simple options for eliminating sciatic nerve pain:
1. Cat pose. You need to squat down, place your palms under your shoulders, knees under your hips. As you inhale, raise your head, look at the ceiling, lowering your stomach down. As you exhale, arch your back and look at your hips with your head. The exercise should be repeated 10 to 20 times.
2. Hamstring stretch. You need to sit on the floor, stretch your legs forward. We bend the right leg at the knee, the foot is located on the inside of the opposite thigh.
You need to reach as low as possible towards your left foot with your hands, without bending your knee. After 30 seconds, return to the original position. The exercise is performed 2-3 times for each leg.
Stretching activates the thigh muscles, relieves tension, and reduces pain.
3. Dog pose. You need to get on all fours, place your palms under your shoulders, place your knees under your hips. With your back and pelvis motionless, stretch your right arm forward and your left leg back. After a second, return to the original position. When this exercise is performed systematically, your posture straightens, pressure on the lower back disappears, and the muscles of the buttocks become stronger.