- Causes and symptoms
- Treatment of the sciatic nerve
- Effective treatment at the Open Clinic
- How to treat the sciatic nerve correctly?
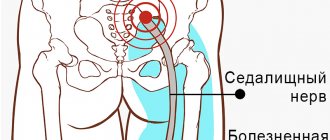
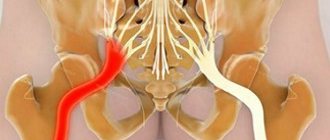
The sciatic nerve originates from five spinal roots: spinal segments LIV – SIII, and is the largest nerve in the human body.
Accordingly, sciatic nerve neuropathy can develop at different levels and give different symptoms depending on the level of damage. There are four main levels of sciatic nerve damage:
- With peroneal nerve neuropathy;
- With neuropathy of the tibial nerve;
- Pure sciatic neuropathy;
- And neuropathy of the sciatic nerve with damage to the inferior gluteal artery.
Damage to the sciatic nerve can be of an inflammatory nature - neuritis, or non-inflammatory - neuropathy, in this case the lesion is the result of compression (squeezing) of the nerve at some level. Accordingly, depending on the cause: neuropathy or inflammation of the sciatic nerve (neuritis), treatment will be different.
Causes of pathology during pregnancy and childbirth
The likelihood of a pinched sciatic nerve is not related to the age of the expectant mother. Pathology is diagnosed even in young healthy girls who have not previously had problems with the musculoskeletal system and the spine in particular.
The reasons for the occurrence of a condition where the sciatic nerve hurts during pregnancy and during childbirth may be:
- increased load on the sacral region and the spine as a whole;
- a shift in the center of gravity due to an enlarged abdomen;
- pressure of the enlarged uterus on the sciatic nerve;
- hypothermia;
- excessive physical activity;
- inflammatory processes in the joints;
- multiple pregnancy or large fetus;
- polyhydramnios;
- concomitant diseases - diabetes mellitus, genitourinary system infections, osteochondrosis, thrombosis, spinal injuries;
- intervertebral hernia;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- malignant neoplasms;
- muscle spasms when pushing;
- divergence of the pelvic bones and their return to their natural position;
- postpartum trauma;
- displacement of the vertebrae during childbirth;
- complications during childbirth that required the use of a vacuum or obstetric forceps.
Most often, after childbirth, due to a decrease in load, discomfort disappears without the need for additional treatment. It is important for a young mother to learn how to lift the baby correctly and take a comfortable position while feeding the baby. In rare cases, a woman may need the help of a specialist even after the baby is born.
Treatment of sciatic nerve pain
In most cases, successful healing of the sciatic nerve can be achieved using conservative methods. The procedures are carried out in several stages. Initially, pain and growing inflammation are eliminated. To do this, the doctor may use analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs. In addition, the patient is treated with physiotherapy and massage treatments. Particular importance should be given to special gymnastics, the complex of which is prescribed by the attending physician. It is important to note that the appearance of the symptoms described above is a sure sign that you should change your living conditions. Doctors often advise patients, after solving problems with pain, to start playing sports, eating right and putting physical stress on their body.
Danger of pathology
First of all, sciatica is dangerous due to the threat of miscarriage in the early stages and premature birth in the later stages. Often, symptoms of pinched sciatic nerve that develop before the 10th week do not allow saving the fetus.
The weakening and loss of elasticity of the pelvic floor muscles and adjacent muscle tissue, which is caused by sciatica, can negatively affect the general condition of a woman, both during pregnancy and after childbirth.
Pathology can significantly complicate the process of delivery itself. Hyperthermia and necrosis of surrounding tissue can harm the baby.
Symptoms
The disease makes you feel the whole range of possible pain sensations: from burning and aching to shooting and sore. The nature of the pain syndrome is unstable, the pain can subside and suddenly intensify, intensifying with any muscle tension. Pain appears along the sciatic nerve, moving to the buttock area. The following signs are added to it:
- swelling in the lumbar region;
- increased body temperature;
- numbness in the legs or pelvis;
- leg weakness;
- incontinence.
Depending on the cause, the pathology can develop at different rates and be characterized by different pain sensations.
In addition to pain, a clear sign of sciatica is paresthesia - a type of sensitivity disorder in which there is a sudden sensation of burning, pins and needles and tingling.
Clinical manifestations
Precursors of the disease - aching, nagging pain in the lower back - may appear even before conception. Often women do not pay attention to this. However, the developing fetus contributes to the worsening of the disease, so you need to take care of your health even at the stage of planning conception.
Symptoms of a pinched sciatic nerve in pregnant women:
- pain in the sacrolumbar spine, radiating to the buttocks and leg;
- pain that gets worse with movement, sneezing or coughing;
- change in gait;
- difficulty changing body position;
- difficulties with extension and abduction of limbs to the sides;
- feeling of numbness and tingling in the limbs;
- insomnia;
- increased fatigue;
- temperature increase;
- disruption of the functioning of some internal organs.
Uncontrolled urination or defecation, sharp unbearable pain in the tailbone area are a sign of a serious illness and require immediate hospitalization.
Causes and symptoms
The most common cause of damage to the sciatic nerve is compression. There can be many reasons for compression:
- Intervertebral disc herniation;
- Bone growth in osteochondrosis;
- Sciatic nerve injuries;
- Volumetric formations of the spine;
- Flat feet;
- Post-injection infiltrates;
- Herpes zoster;
- Diabetes;
- Thyroid diseases;
The sciatic nerve can be damaged for many reasons, but the leading symptom is always sharp, burning and severe pain. The pain syndrome can begin from the buttock and gradually spread along the back surface of the lower limb up to the foot.
As symptoms progress, weakness in the leg and muscle atrophy occur. The patient may also be bothered by paresthesia and numbness along the back of the thigh and lower leg, cold fingers, and blue discoloration of the foot. In 30% of cases, trophic disorders occur in the lower limb.
Diagnostics
Most known diagnostic methods are prohibited during pregnancy. This is due to the high likelihood of harm to the unborn child. To determine the presence of pathology, the doctor needs to interview and examine the woman to determine the nature of the pain, location and frequency of its occurrence.
If it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis, the expectant mother may be sent for an ultrasound. A more informative and reliable diagnostic method - magnetic resonance imaging - is allowed to be used starting from the second trimester of pregnancy.
Therapy methods
During pregnancy, the main thing is not to harm the fetus, so only a qualified specialist should treat the disease. It is necessary to carefully select medications and procedures that do not have a negative impact on the development of the unborn baby.
Drug treatment
The woman is prescribed strict bed rest, as well as injections of anti-inflammatory and painkillers based on ibuprofen or paracetamol. Drug treatment is used only for very severe unbearable pain and can last no more than 5-7 days.
In addition to injections, external agents can be used to treat inflammation of the sciatic nerve during pregnancy. They are less dangerous to the child’s health, since most of them do not enter the bloodstream and do not penetrate the placental barrier. These medications include Menovazin and Diclofenac, which have a pronounced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
The doctor may also prescribe vitamin complexes, chondroprotectors and muscle relaxants that promote complete relaxation of muscle tissue.
Self-medication is strongly not recommended. The use of all types of medications must be agreed with the attending physician.
Physiotherapy
Moderate physical activity is the best way to reduce pain and get rid of pinching. You can do physical therapy during attacks of pain and to prevent them. Systematic exercise helps prevent the progression of the disease and significantly improves a woman’s quality of life.
Exercise "Cat's spine" For pregnant women
For sciatica, you can perform the following set of exercises:
- Get on all fours. Arch your back, lower your head down. Then return to the starting position and raise your head. Perform at least 5 approaches.
- Stand against a wall, pressing your lower back tightly against it. Relax and slightly raise your pelvis. In early pregnancy, the exercise can be performed in a lying position.
- Place a chair in front of you with one leg thrown over it. You need to keep your back straight. Slowly lean forward as far as your enlarged belly allows. Continue the movement until you feel a stretch in the back of your thigh. You need to stay in this position for a few seconds, then return to the starting position and relax.
You need to perform gymnastics slowly, without much tension. It is better to stop exercising if any exercise causes pain or noticeable discomfort. The exercise therapy complex must correspond to the duration of pregnancy, so a physiotherapist or physical therapy specialist should select the appropriate exercises.
Yoga
Yoga classes will help prevent the onset of the disease and significantly reduce the number of attacks if pinching has already occurred. Practice helps strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, normalize blood circulation, and restore proper breathing.
It is necessary to start classes under the supervision of a qualified instructor who has experience working with pregnant women.
It is preferable to sign up for special yoga for expectant mothers, because many classical yoga poses are prohibited during pregnancy, for example, training the abdominal muscles, deep stretching or squats.
Swimming
Water procedures can relieve stress from the spine, reduce pressure on muscle groups and ligaments, thereby reducing pain and the frequency of its occurrence. It is preferable to use indoor pools and attend classes for expectant mothers under the supervision of an instructor.
Swimming helps strengthen muscles and increase their elasticity, greatly facilitates the course of pregnancy and helps the expectant mother prepare for the upcoming birth.
Massage
Massage can only be trusted by an experienced specialist.
Light massage movements of the lumbar region help relax the muscles, thereby reducing the frequency of pain attacks. A massage course consisting of 8-10 sessions will help significantly alleviate the condition.
It is better not to perform massage manipulations yourself at home, but to entrust this activity to an experienced specialist who has skills in working with pregnant women.
Manual therapy and osteopathy
Treatment can be carried out in combination with acupuncture and other similar procedures aimed at reducing the intensity of pain. An experienced chiropractor or osteopath will use gentle massage movements to help relieve pinching and improve the patient’s general condition.
Before using this treatment method, you should consult a gynecologist. Some complications during pregnancy do not allow the use of manual therapy.
Warming up
During the next attack, a warm scarf or blanket that needs to be wrapped around the lower back will help relieve the pain. The use of additional warming ointments and gels is permitted only as prescribed by a doctor. Most medications that relieve inflammation are contraindicated during pregnancy.
You can put warm compresses on your lower back and take salt baths. To do this, you need to dissolve a couple of kilograms of salt in warm water. This procedure is allowed only in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Alcohol lotions and rubbing, for example, tinctures of lilac flowers, horseradish, hot pepper or garlic, can help with back pain caused by a pinched nerve. Such remedies help increase blood circulation and relieve spasms.
Prenatal bandage
Doctors recommend that women wear special devices starting from the 20th week of pregnancy. The prenatal bandage reduces the load on the spine, distributing it evenly across all joints. This reduces pressure on the sciatic nerve and prevents pain attacks.
The device must be selected in size, not restrict movement and not squeeze the stomach. It is better to purchase a bandage in specialized stores and clinics.
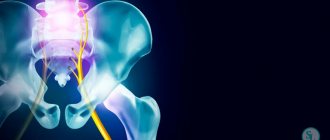
Sciatic nerve neuropathy (piriformis syndrome)
The sciatic nerve is the longest nerve in the human body. There are a total of 2 sciatic nerves in the human body, each of which is formed by combining fibers of the last two lumbar (L4 and L5) and the first three sacral (S1, S2 and S3) nerve roots of the spinal cord. Simply put, the sciatic nerve originates at five different levels of the spinal cord in the lumbosacral spine, which bears the main axial load during human life.
Radiculopathy is a lesion of the roots of the lumbosacral spine, which is manifested by pain and impaired sensitivity, as well as a decrease in muscle strength.
Radiculitis and sciatica are outdated terms that were previously used in relation to the concept of radiculopathy. Sciatica also has another name, completely similar in meaning - sciatic nerve neuropathy .
Causes of sciatic nerve neuropathy
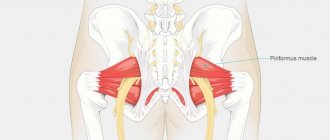
The cause of damage to the sciatic nerve may be entrapment (compression, irritation) by an intervertebral hernia, spasm of the piriformis muscle, or gluteus maximus muscle.
The main causes of inflammation of the sciatic nerve can be hypothermia, spinal diseases, spinal injuries, joint inflammation, diabetes, heavy physical activity, and various infections.
Piriformis syndrome
In some cases, the underlying cause of sciatic nerve neuropathy may be piriformis syndrome . This muscle is located under the gluteus maximus muscle, and the sciatic nerve passes under or through it. This syndrome is characterized by stretching or irritation of the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle. The pain is most often associated with a reflex spasm of the piriformis muscle, which can result in stretching or irritation of the sciatic nerve. There are many causes of spasm of the piriformis muscle, one of which may be lumbar osteochondrosis (lumbosacral osteochondrosis).
Symptoms of radiculopathy:
- Lesion of L4 – pain in the anterior thigh, along the inner surface of the knee joint and lower leg, hyperesthesia along the anterior surface of the thigh and lower leg, weakness of the lower leg flexors and hip adduction, the knee reflex is reduced, the Achilles is preserved.
- Lesion of L5 – pain along the sciatic nerve with irradiation to the first toe, hypoesthesia on the back of the big toe, along the anterior outer surface of the leg, weakness of the dorsiflexion of the main phalanx of the 1st toe – it is impossible to stand on the heel.
- S1 – pain along the sciatic nerve, radiating to the heel and 3 – 5 fingers, hypoesthesia along the posterior outer surface of the leg, weakness of the fingers and the entire foot, the Achilles reflex fades.
Diagnosis of sciatic nerve neuropathy
The diagnosis is made based on the characteristic signs of the disease, radiological studies - radiography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging.
Treatment of sciatic nerve neuropathy
, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed - injection (intravenously, intramuscularly), blockades, analgesic mixtures drips, gabapentins, antioxidants, vascular therapy, B vitamins, muscle relaxants, anticholinesterase drugs, ointments, gels, dry heat, corsetry are used externally. Physiotherapeutic procedures are also used - diadynamic currents, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, darsonval, myoton, amplipulse, reflexology, laser therapy, hydrotherapy, gymnastics, massage, manual therapy. If conservative treatment is ineffective and there is a disc herniation with root compression, neurosurgical treatment . The scope of surgical treatment is individual. Physical therapy, massage, aqua aerobics, underwater traction, and swimming are very important. These measures are important in order to prevent complications (especially with long-term illness) in the form of muscle and tendon contractures, as well as the development of stiffness in the joints.
Prevention
Prevention of radiculopathy involves strengthening the back muscles. To prevent sciatica, you need to:
- keep your back straight: walk with a straight back, do not sit leaning forward too much;
- when working sedentarily, often get up and walk around the room;
- Do regular exercise to strengthen your back muscles;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- do not overcool;
- Women, especially those who already have periodic back pain, should not wear high-heeled shoes.
Possible complications and consequences
Women most often encounter pinched sciatic nerves in the second half of pregnancy. The consequences of this condition can be:
- numbness of the limbs;
- neuralgia;
- rachiocampsis.
Only timely, competent therapy will avoid the development of dangerous complications and successfully get rid of the disease.
Favorable terms of cooperation
Symptoms and treatment of the sciatic nerve are always the responsibility of specialists. So, as soon as you feel the corresponding symptoms, you should definitely consult a doctor. Our clinic will help you relieve pain and inflammation and restore the joy of active life.
Our specialists have at their disposal all the advanced methods of treating the sciatic nerve - from physiotherapy to massage. Doctors will also prescribe the right combination of medications for you and make sure that the pain does not develop into chronic pain.
Our patients can count on truly attractive prices and comfortable treatment conditions. Give yourself the gift of health and relief from pain and discomfort.
Preventive measures
To significantly reduce the risk of pathology, you must adhere to the following recommendations from doctors:
- in late pregnancy, wear a bandage;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- walk in the fresh air more often;
- wear comfortable clothes and flat shoes;
- perform special gymnastics, swim and do yoga;
- purchase an orthopedic mattress and pillow for pregnant women;
Maternity pillow - watch your posture;
- eat properly and nutritiously;
- control your weight;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- reduce the intensity of physical activity;
- avoid hypothermia;
- take complex vitamins and calcium supplements.
Don’t be shy about asking your loved ones for help and delegating some of your responsibilities to them. A pregnant woman needs to rest more often during the day, fully relax all muscle groups, and relieve stress from the spine and lower extremities.