General information
Agenesis of the corpus callosum (ACC) is a rare disorder that is present at birth (congenital).
It is characterized by partial or complete absence (agenesis) of the corpus callosum. The corpus callosum consists of transverse fibers. The cause of agenesis of the corpus callosum is usually unknown, but it can be hereditary in either an autosomal recessive or X-linked dominant pattern. In addition, agenesis can also be caused by infection or injury during weeks 12 to 22 of pregnancy (intrauterine life), resulting in impaired fetal brain development. Prenatal alcohol exposure can also lead to AMT. In some cases, with AMT, mental retardation may occur, but intelligence is mildly impaired, and subtle psychosocial symptoms may also be present.
Partial agenesis of the corpus callosum
Fig.1
Complete agenesis of the corpus callosum
Fig.2
AMT is often diagnosed during the first 2 years of life. Seizures of epilepsy may be the first symptom indicating that a child should be tested for brain dysfunction. The disorder can also remain without visible symptoms in the mildest cases for many years.
Skeletal and other abnormalities
- These are basically anomalies that appear as hemivertebrae and missing ribs.
- In medical practice, cases of jaw and facial anomalies are known. Of which, the most noted violations were in the form of protruding incisors and a reduced angle of the nasal septum.
- There were also such anomalies as an upturned tip of the nose, etc. It should also be noted that almost a quarter of the patients had various skin lesions, and just over seven percent had various pathologies of the extremities.
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and frequent cases of cancer were also noted.
An effective therapeutic treatment for the syndrome has not yet been created, although developments are ongoing, so symptomatic treatment is mainly used, which is mainly aimed at eliminating infantile spasms.
Septo-optic dysplasia can present as an isolated brain abnormality, but is sometimes observed in association with other syndromes. These include:
- Aicardi syndrome.
- Combination of SOD with brachydactyly (short-fingered) type B and mental retardation.
- Porencephaly syndrome with absence of the septum pellucida.
- Holoprosencephaly.
To date, there are no therapeutic procedures that would help cure a child from agenesis of the corpus callosum. Only corrective techniques are used, which are selected individually depending on the degree of violations and the general condition of the patient’s body.
Treatment can only alleviate the symptoms of the pathology. But most experts say that all generally accepted methods do not give any results. The use of potent drugs is mainly practiced. They try to alleviate the patient’s condition with the help of:
- Benzidiazepines. These are psychoactive substances that have hypnotic, sedative, muscle relaxant and anticonvulsant properties.
- Phenobarbital. It is a barbiturate with antiepileptic action. It reduces the frequency of attacks if there are infantile spasms.
- Corticosteroid hormones. Such as Prednisolone, Dexamethasone. They are usually combined with antiepileptic drugs.
- Neuroleptics. With the help of which psychotic disorders are eliminated.
- Diazepam. It helps reduce behavioral disorders.
- Nootropics that have a specific effect on the mental functions of the brain. Treatment with Piracetam or Semax is usually used. They help improve the nutrition of brain tissue, which has a positive effect on its functioning.
- Neuropeptides. The most commonly used is Cerebrolysin.
In addition to medications, sometimes there is a need for surgical intervention. For example, they can stimulate the vagus nerve. But such therapy is allowed to be carried out only in situations where, as a result of agenesis, serious malfunctions in the functioning of vital organs have occurred. This procedure is performed if other types of surgical interventions fail.
Thanks to the procedure, the frequency of epileptic seizures decreases and they are more easily tolerated. But this treatment works differently for each patient.
Since agenesis of the corpus callosum of the brain can lead to musculoskeletal disorders and causes scoliosis, physiotherapeutic techniques and exercise therapy can be used. Sometimes surgery may be performed.
Morphology
Classic neuroradiological signs of agenesis of the corpus callosum:
- The anterior horns and bodies of the lateral ventricles are widely spaced and parallel (not curved). The anterior horns are narrow and acute-angled. The posterior horns are often disproportionately enlarged (colpocephaly). The concave medial borders of the lateral ventricles are caused by protrusion of the longitudinal fasciculi.
- The third ventricle is usually dilated and elevated with varying degrees of dorsal expansion and mixing between the lateral ventricles. The interventricular foramina are often elongated.
- The interhemispheric groove appears to be a continuation of the anterior section of the third ventricle, since the knee is absent. In the coronal projection, the interhemispheric groove expands downwards between the lateral ventricles towards the roof of the third ventricle. In the sagittal plane, the usual cingulate gyrus is absent, and the middle sulci have a radial or spoke-shaped configuration. Interhemispheric cysts are often visible around the third ventricle. As they increase in size, these cysts can acquire an abnormal configuration and hide underlying defects.
- Absence of the corpus callosum and septum pellucidum.
- Angulation of the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles and their depression along the medial surface by Probst's bundles.
- Radial pattern of grooves and convolutions extending from the roof of the third ventricle.
How and with what we treat
Basically, the course of treatment for this pathology is to minimize the manifestations of the disease and achieve the cessation of infantile spasms.
Therapeutic methods, according to experts, that are used in treatment do not bring the desired effectiveness. In addition, the technique has not been improved and not fully developed.
Mostly strong drugs are used, in maximum doses and courses. Such shortcomings are explained by completely objective reasons. Since the method of treating agenesis is in a constant search for new and improved methods of getting rid of this disease.
The disease itself is carefully studied, but tangible desired results are almost impossible to achieve, because it is very difficult to diagnose at the stage of development of the disease. All this is due to the position of the fetus, which does not allow a clear and visual examination of the cavities and structures of the brain.
Pathologies of the corpus callosum or its insufficient development in children, as a rule, affect the state of their neurological development. However, there are cases where, in the absence of any other anomalies, a normal karyotype was noted. The observation period in this case was quite long. Children were observed until they were 11 years old.
Among the forms of manifestation of agenesis, the most common cases are Aicardi syndrome. At the same time, about five hundred manifestations of this syndrome have been noted on the planet, the largest number in the land of the “rising sun” Japan.
In those who had a similar pathology, disorders associated with abnormal eye development were noted. One of these anomalies is retinitis pigmentosa, which is expressed in decreased visual acuity, cataracts, damage to the optic nerve and other pathologies.
Signs and symptoms
Agenesis of the corpus callosum (ACC) may initially present with the onset of epileptic seizures in the first weeks of life or during the first two years. However, not all people with AMT have seizures. Other symptoms that may begin early in life are problems with feeding and holding the head up. Sitting, standing and walking may also be affected. Impaired mental and physical development and/or hydrocephalus are also early-onset symptoms of this disorder.
Non-progressive mental retardation, impaired hand-eye coordination, and visual or auditory memory can be diagnosed through neurological testing in patients with AMT. In some mild cases, symptoms may not appear for many years. In mild cases, AMT may be missed due to the absence of obvious symptoms in childhood.
Some patients may have deep-set eyes and a bulging forehead. There may be an abnormally small head (microcephaly) or an unusually large head (macrocephaly). Folds of skin in front of the ears, one or more bent fingers (camptodactyly), and slow growth may also be associated with some cases of agenesis of the corpus callosum. In other cases, wide eyes, a small nose with inverted nostrils, abnormally shaped ears, an excessively long neck, short arms, decreased muscle tone (hypotonia), laryngeal abnormalities, heart defects, and symptoms of Pierre-Robin syndrome may be present.
Aicardi syndrome , considered to be inherited in an X-linked dominant pattern, consists of agenesis of the corpus callosum, infantile spasms, and abnormal ocular structure. This syndrome is an extremely rare congenital disorder that affects the middle layer of the eyes (choroid) and retina, as well as the absence of the corpus callosum, accompanied by severe mental retardation. Only women suffer from this syndrome.
Anderman syndrome is a genetic disease characterized by a combination of agenesis of the corpus callosum, mental retardation and progressive sensorimotor disorders of the nervous system (neuropathy). All known cases of this disorder come from the Charlevoux district and the Saguenay-Lac Saint-Jean region in Quebec, Canada. The gene causing this rare form of agenesis of the corpus callosum has recently been identified and is currently being tested (SLC12A6).
XLAG (X-linked lissencephaly with true hermaphroditism) is a rare genetic disorder in which males have a small and smooth brain (lissencephaly), a small penis, severe mental retardation and intractable epilepsy. It is caused by mutations in the ARX gene. In women, these same mutations can cause agenesis of the corpus callosum on their own, while less severe mutations in men can cause mental retardation. Diagnosis of this disorder is available in clinical use.
Clinical case of aplasia of the corpus callosum in a Rottweiler, similar to Aicardi syndrome in humans
Lyudmila Konikova (), Olga Dubovitskaya, veterinary clinic "Bely Klyk" - department of neurology, Moscow Lecturers NVC
Two clinical cases of pathology of the corpus callosum in dogs of varying degrees and etiologies are described. Literary data on the disease are presented, characteristic symptoms, diagnostic methods and possible concomitant pathologies of other organs and systems are described. It has been suggested that there may be genetic malformations. An analogy has been drawn with Aicardi syndrome in humans.
Introduction
The corpus callosum (corpus calossum) is a plexus of 250 bundles of nerve fibers and is the largest structure of the brain of placental animals, connecting the right and left hemispheres. The functions of the corpus callosum include: communication between the hemispheres, participation in osmoregulation processes, coordination of information and the exchange of sensory stimuli between the hemispheres in the process of learning and memory.
The corpus callosum can be visualized on MRI from 8 weeks of age. It has a hyperintense signal on T1 sequences and a hypointense signal on T2-weighted MR images.
The most informative for studying the corpus callosum are sagittal sections [6].
Fibers in the corpus callosum run mainly in the transverse direction, connecting symmetrical areas of the opposite hemispheres. However, some fibers also connect asymmetrical places of opposite hemispheres, for example, the frontal gyri with the parietal or occipital, as well as different parts of the same hemisphere (the so-called associative pathways).
Anomalies of the corpus callosum include hypoplasia, hypoplasia with dysplasia, and agenesis (aplasia).
The most common symptom in dogs with pathologies of the corpus callosum is adipsia or hypodipsia [3]. Adipsic hypernatremia is characterized by chronic and acute episodes of increased sodium in the blood associated with loss of thirst [3]. In the pathogenesis of thirst in dogs, the greatest role is played by receptors for sodium ions, localized in the cranial part of the third ventricle, including the periventricular organ, subfornical organ, median nuclei, and vascular organ of the end plate [4].
Description of clinical cases
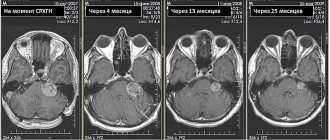
1. Clinical case of aplasia of the corpus callosum
A 6-month-old Rottweiler puppy was admitted to the Belyi Klyk clinic due to tonic generalized seizures with loss of consciousness, adipsia, episodic lethargy, hyporexia, and loss of coordination. During the examination, prognathia, microphthalmia, and underdevelopment of the lower jaw were also recorded. No neurological deficits were identified. General clinical and biochemical analysis without any features. The electrolyte profile revealed hypernatremia (Na+ 173 mmol/l (138–164), Cl– 129 mmol/l (93–119)).
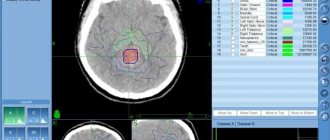
Hypernatremia (more than 170 mmol/L in dogs) [7] can cause seizures with loss of consciousness due to dehydration of nervous system cells and swelling of brain tissue, as was recorded in this case. The dog underwent a magnetic resonance imaging study of the brain.
MRI conclusion:
Suspicion of aplasia of the corpus callosum.
Treatment
Thanks to symptomatic therapy and an elementary diet with the addition of water, it was possible to stabilize the condition and prevent seizures in the dog. At the moment, the dog's condition is satisfactory, no more seizures have been noted.
2. Clinical case of hypoplasia with dysplasia of the corpus callosum in combination with hydrocephalus
A 3-month-old Yorkshire terrier dog was taken to the Belyi Klyk clinic with complaints of severe incoordination and consciousness (stupor), as well as lack of thirst (adipsia). Neurological examination revealed cranial nerve deficits.
Topical diagnosis: central vestibular syndrome (CVS). Ultrasound of the brain revealed significant ventriculomegaly (more than 60%) and an increased resistance index.
The dog was euthanized by the decision of the owners with a preliminary diagnosis: “Primary hydrocephalus. Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum."
At the autopsy, pronounced underdevelopment of the bone structures of the skull and multiple pathologies of the brain were recorded: atrophy of all brain structures, including the sagittal venous sinus, severe ventriculomegaly, hypoplasia with dysplasia of the corpus callosum, and cerebellar hypoplasia.
Discussion
An association has been reported between early onset lysosomal storage disease (gangliosidosis) and hypoplasia of the corpus callosum. An association between pathology of the corpus callosum and inborn errors of metabolism has been established in humans.
This suggests that, at the molecular level, the development of the corpus callosum involves the synchronization of many cellular processes.
Disruption of these mechanisms underlies the complete or partial loss of the corpus callosum. Unfortunately, there are no genetic tests for lysosomal storage diseases in dogs.
The combination of aplasia of the corpus callosum, facial dysmorphism, abnormal development of the eyes, as well as a violation of the development of bone structures (clinical case No. 1) is similar to Aicardi syndrome in humans - a genetic disease characterized by partial or complete absence of one of the main structures of the brain - the corpus callosum and defects development of other organs [5].
Conclusion
There are varying degrees of malformation of the corpus callosum; in cases of hypoplasia in dogs, the corpus callosum is most damaged rostrally [3]. Dogs with malformations in the corpus callosum exhibit adipsia or hypodipsia and associated hypernatremia. Pathologies of the corpus callosum are usually combined with other malformations and structural anomalies. In the first clinical case, a combination of facial dysmorphism and aplasia of the corpus callosum, which is quite rare for dogs, was noted.
Due to the fact that congenital aplasia of the corpus callosum is a rather rare phenomenon in dogs, further scientific and comparative studies on this topic with a larger sample of patients are needed to obtain more accurate statistical data.
Literature
1. Raybaud, C. & Di Rocco. The corpus callosum, the other great forebrain commissures, and the septum pellucidum: anatomy, development, and malformation. Neuroradiology, Vol. 52, No. 6, (June 2010), pp. 447–77, ISSN 0028-3940 РС. (2007).
2. Gross B. Garcia-Tapia D, Riedisel E. Et normal canine brain maturation at MRI. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 2010;51:361–373.
3. R. Goncalves, H Volk, PM Smith, J. Penderis - Corpus colossal Abnormalities in Dogs - J vet Intern Med 2014;28:1275–1279
4. Antunes-Rodrigues J. de Castro M. Elias LL.et al. Neuroendocrine control of body fluid metabolism. Physiol Rev 2004;84:169–208
5. Uggetti, C et al. "Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome: neuroradiologic findings and follow-ups." AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009; thirty.
6. Harding BN, Copp AJ. Malformations. In: Graham DI, Lantons PL (eds): Greenfield's neuropathology. London: Arnold, 2002; 357–470.
7. Luisa De Risio, Simon Platt. Canine and Feline Epilepsy Diagnosis and Management. 2014; 64–65.
SVM No. 3/2015
Rate material
Like Like Congratulations Sympathy Outrageous Funny Thoughtful No words
Related disorders
Agenesis of the corpus callosum can be combined with spina bifida. Some of the contents of the spine may protrude through the abnormal opening, leading to the formation of a meningocele or meningomyelocele.
- hydrocephalus 30%
- arachnoid cysts
- intracranial lipoma 10%
- Dandy-Walker malformation 11%
- Interhemispheric cyst
- Arnold-Chiari malformation 7%
- Median encephalocele
- Porencephaly
- Holoprosencephaly
- Polymicrogyria
- Heterotopia
Causes
In some cases, weakness in the development of connections between the hemispheres of the brain in a child may be associated with the mother’s stressful state during pregnancy or illness.
In addition, development can be negatively affected by a peculiarity of the brain structure or anomalies of the corpus callosum, neurological disorders.
Most often, weak interaction of the cerebral hemispheres is observed in the absence of developmental activities and games in the child’s life - the comprehensive development of the child should begin from a very early age.
Other reasons may be:
- injuries during childbirth;
- serious illnesses in the first year of life;
- passive lifestyle;
- consequences of general anesthesia;
- prolonged stress.
Treatment
Treatment is symptomatic and supportive depending on the severity of symptoms. If hydrocephalus is present, it is treated with surgical shunting to reduce the elevated ICP. Genetic counseling may also benefit families with this disorder.
Author: radiologist, Ph.D. Vlasov Evgeniy Alexandrovich
Full or partial reprint of this article is permitted by installing an active hyperlink to the source
If you still have doubts about the conclusions of your MRI, you can order a review of your study with a detailed transcript here:
Signs of insufficient development of interhemispheric connections in children
These connections are formed in a child up to 12–15 years of age, and in stages. Experts consider the period from 3 to 8 years to be very important for generation. At this time, the child develops kinetic, sound and visual meaning discrimination, etc.
If a child has the following symptoms, you should think about a possible disruption of interhemispheric interaction:
- aggression;
- poor memorization;
- incomprehensible and confused speech;
- mirror writing of letters and numbers;
- difficulty in describing the action shown in the figure;
- difficulties in communicating with peers;
- problems in writing dictations or rewriting texts.
Reference! In infants, a violation of interhemispheric interaction can be suspected by “inhibition” before any action, as well as by the absence of the crawling stage.
What is the corpus callosum: general information
The corpus callosum of the brain (MC), or the greater commissure, as experts call this element, is a collection of nerve fibers.
It connects the two parts that form the brain - the right and left hemispheres. Also, the corpus callosum coordinates their stable operation, ensures the coherence of the transmission and reception of signals from each of the hemispheres. In addition, the corpus callosum unites the gray matter of each of the cerebral hemispheres.
The formation is a dense white structure. The anatomy of the corpus callosum is quite complex - in general, it is an elongated structure from front to back, the length of which, depending on age and gender, ranges from 7 to 9 cm.
The location of the large commissure is the longitudinal fissure of the human brain.
The discovery of this part of the brain occurred more than 50 years ago during the search for ways to treat a complex disease - epilepsy and related problems. Further research has shown that the corpus callosum is responsible for a range of behaviors, causes sexual dimorphism (differences between people) and is responsible for some of the abilities and capabilities that a person has.
The big commission is under attack...
Disorders of the corpus callosum are a rare phenomenon, occurring in 2% of all cases of diseases of the brain and central nervous system. In case of diseases of the corpus callosum, the following are observed:
- disorders of various nature and intensity, manifested in the emotional, personal and cognitive spheres;
- physiological problems in the functioning of the limbs;
- problems with the eyeballs and vision in general.
Corresponding diseases develop - agenesis, hypoplasia and dysplasia (dysgenesis) of the corpus callosum of the brain.
Anatomy and functions
The corpus callosum is covered on top by a small layer of cerebral gray matter, which explains, accordingly, the gray covering on it. Upon visual examination, 3 main sections can be distinguished:
- trunk (or midbrain);
- knee (part of the brain located in the front);
- beak or splenium of the corpus callosum (posterior section).
The brightness of the large commissure (when viewed on photographs or in section) is provided by fibers that are located radially and are located in each of the hemispheres.
The middle section, when viewed, looks like a bulge, which is also the longest part of the entire brain. The posterior section is visually visible as a thickening relative to other sections and zones, which is freely located above neighboring areas of the brain. The gray matter is represented by stripes and is located on top.
Functions provided by the corpus callosum:
- transfer of information (impulses) important for the functioning of the body from one hemisphere to the other;
- formation of the main characteristics that define personality and its characteristics;
- basic (basic, defining) skills and the possibility of their application throughout a person’s life;
- work on the formation of the emotional and personal sphere.
In dry but important remainder
Thus, the corpus callosum of the brain, despite its tiny size, has a great influence on a person’s life.
It allows the formation of personality, is responsible for the emergence of habits, conscious actions, the ability to communicate and distinguish between objects. That is why it is extremely important to take care of your health during pregnancy, since the main metabolic disorders are formed during this period.
We should not forget that the corpus callosum forms the intellect and makes a person a personality. Despite all attempts to study this structure, scientists have not yet been able to uncover all its secrets, and therefore very few methods for treating disorders, if any, have been developed.
The main ones are drug therapy and a special set of exercises - exercise therapy, which allows you to maintain optimal indicators of physical development. Measures to eliminate the symptoms of disorders should be taken immediately, otherwise the desired improvements may not occur.