How does neuritis of the facial nerve appear?
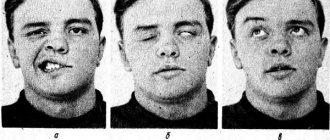
Neuritis of the facial nerve can begin with mild pain in the ear area. Simultaneously with the onset of pain or after a couple of days, the facial muscles partially or completely lose mobility. The patient's face becomes distorted, the affected part freezes in the mask.
With timely treatment, the patient has a great chance of recovery - in 75% of cases the disease goes away completely. If facial paralysis does not resolve within three months, the patient's chances of making a full recovery are greatly reduced.
In order for facial neuritis to pass without consequences, you need to consult a doctor in the first hours after the onset of symptoms.
Restoring facial nerve function
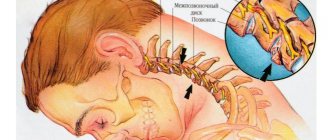
Damage to the facial nerve, as well as its diseases, occupy first place among lesions of the cranial nerves. The number of patients aged 10 to 30 years is 60-70%.
A motor deficit that occurs when a nerve is damaged leads not only to a cosmetic defect, but also disrupts the full acts of chewing and swallowing, and the voice changes. Neuroparalytic keratitis, the cause of which in patients with damage to the facial nerve is lagophthalmos and impaired tear secretion, ultimately leads to damage to the cornea, including loss of vision.
All these factors bring severe mental trauma to the patient with damage to the facial nerve and reduce the quality of life.
Causes of damage to the facial nerve:
1) Iatrogenic damage (removal of tumors of the cerebellopontine angle, surgery on the hearing organs, interventions on the parotid region and on the face)
2) Injuries (injuries of the skull and brain, accompanied by fractures of the bones of the base of the skull, wounds of the neck and face)
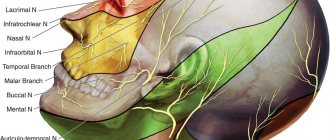
3) Inflammatory lesions (neuritis and otogenic lesions) The clinical picture of damage to the facial nerve is well known and depends on the level of damage and the degree of conduction disturbance.
The leading symptom of damage to the facial nerve is weakness of the facial muscles of the corresponding half of the face. Surgeries to restore facial nerve function are indicated for the following conditions:
1. Complete damage to the anatomical integrity of the facial nerve when removing tumors of the skull base (neurinoma of the VIII nerve, meningiomas, etc.)
2. Partial damage to the anatomical integrity of the facial nerve during removal of the same tumors where signs of restoration of the function of the damaged nerve did not appear within 5-6 months after surgery.
3. Paralysis of the facial muscles that developed after the same operations, while maintaining the anatomical integrity of the facial nerve in cases where no signs of restoration of function were detected within 10-12 months.
4. Paralysis of the facial muscles that developed after these operations when the surgeon did not see the facial nerve, due to the fact that the facial nerve was included in the tumor.
5. Paralysis of the facial muscles that developed as a result of traumatic fractures of the temporal bone, in the absence of signs of restoration of nerve function 3-4 months after the injury.
6. Paralysis of the facial muscles that developed after radical operations on the inner and middle ear.
Surgeries to restore nerve function performed in our center are aimed at forming an anastomosis between the damaged facial nerve and the donor nerve, thereby achieving innervation of the facial muscles.
In each specific case, the surgeon chooses the most optimal technique for the patient. To eliminate defects associated with damage to the facial nerve, facial plastic surgery is also used, which can be divided into two groups: static and dynamic. Static surgeries are aimed at reducing facial asymmetry. Dynamic operations aim to replace the function of paralyzed muscles. Currently, combinations of surgical interventions are increasingly used in the treatment of patients with damage to the facial nerve: stage 1 - surgery on the facial nerve, stage 2 - plastic surgery to eliminate residual effects that impair the function.
Symptoms
The following symptoms of inflammation of the facial nerve are distinguished:
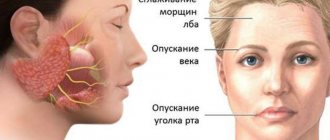
- partial or complete impairment of facial muscle movements;
- the corner of the mouth lowers, the nasolabial fold on one side is smoothed out;
- the face becomes asymmetrical;
- the eyelid does not close completely;
- the eyeball protrudes and turns upward;
- pain in the ear, taste disorder;
- watery or dry eyes;
- hearing loss or sensitivity to loud sounds;
- the patient cannot whistle or stretch out his lips with a straw.
Causes
The causes of facial paresis in a child and an adult may be different. Most often, the problem is provoked by severe hypothermia of the parotid area or head. The disease is also caused by:
- respiratory diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- nerve damage during otitis media or surgery;
- head injuries;
- herpes virus;
- tuberculosis;
- mumps;
- syphilis;
- polio.
All of these diseases contribute to the occurrence of a strong inflammatory process.
Another factor that triggers the pathological process is a violation of the blood supply to the face, which is noted in hypertensive crisis, ischemic stroke, multiple sclerosis, and diabetes mellitus. Sometimes the sensitive and motor functions of the facial nerve are disrupted during dental procedures.
Causes of inflammation
Primary neuritis of the facial nerve occurs due to:
- hypothermia of the face, cold, wind, drafts;
- insufficient blood supply (ischemia) to the nerve.
Secondary neuritis of the facial nerve is caused by the following reasons:
- inflammatory diseases of the ear: otitis media, eustachitis, mastoiditis;
- infections: mumps virus, measles, herpes;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- vascular disorders - for example, atherosclerosis of the vertebral arteries;
- brain tumors;
- anesthesia of the inferior alveolar nerve by the dentist.
Other factors that provoke inflammation include:
- traveling on a bus or minibus next to an open window;
- long work under air conditioning;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- endocrine diseases - for example, diabetes;
- hypertension, intoxication of the body;
- nervous stress, emotional instability.
No complications
We often hear that nerves do not recover, so when faced with neuritis, many patients believe that their disease cannot be treated. Fortunately, this is not true. The functionality of the nerve after neuritis is restored, but this happens quite slowly. The recovery period can take about a year - and during this time it is important to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and not neglect the prescribed treatment. Otherwise, complications may occur.
Article on the topic
A blow to the nerves. Why do neuropathic pain occur?
The most common of these is contraction of the facial muscles, which can distort the face. Muscle atrophy on the side of inflammation may also occur. In this case, the muscles weaken and seem to sag, causing facial paralysis. In addition, the result of untreated neuritis can be twitching of the facial muscles, excessive lacrimation, inability to close the eye, prolonged conjunctivitis or keratitis (inflammation of the cornea of the eye).
To avoid complications, it is necessary to undergo medication and physical therapy. Depending on the causes of inflammation and symptoms, the complex of medications will include anti-inflammatory drugs, antiviral, neurotropic and anticholinesterase agents, B vitamins, diuretics and antispasmodics.
After 7–10 days from the onset of inflammation, physiotherapy is prescribed, which is also selected individually. Phototherapy and laser therapy, electrophoresis, ultraphonophoresis, pulse and decimeter therapy, paraffin and ozokerite applications are successfully used.
An average course of physiotherapy consists of 20 procedures. Sometimes several courses are needed.
Often, for neuritis of the facial nerve, massage is prescribed, but such treatment can be started no earlier than 7 days after the onset of inflammation. It is advisable to massage not only the affected part of the face, but also the neck-collar area. Usually 10–20 massage sessions are needed.
Article on the topic
The root of the problems. How to treat a damaged nerve
If conservative treatment fails within 8–10 months, surgery may be necessary. At the same time, it is impossible to delay surgical intervention - the operation is effective only in the first year of treatment, since later irreversible changes in the muscle tissue on the side of the affected nerve may occur.
Complications of the disease
Neuritis of the facial nerve can lead to contracture of the facial muscles. It appears 4-6 weeks after the onset of the disease due to incomplete restoration of the motor functions of the facial muscles. Contracture is a contraction of the muscles of the affected half of the face. At the same time, it seems that it is not the diseased part of the face that is paralyzed, but the healthy one.
To avoid complications of inflammation of the facial nerve, you need to consult a doctor in time. For prevention, we recommend doing facial exercises. You will find examples of exercises at the end of the article.
Making a diagnosis
Sometimes patients confuse inflammation of the facial nerve with toothache or migraine. However, there is a simple test. If it is not possible to wrinkle your forehead, frown your eyebrows, wrinkle your nose, alternately puff out your cheeks and fully close your eyes, then there is nothing to guess about. This is neuritis of the facial nerve.
Article on the topic
Pus in the head. Minor ailments that can kill you
Of course, without being a specialist, it is difficult to distinguish inflammation of the facial nerve from trigeminal neuralgia or the consequences of a stroke. However, you are not faced with the task of accurately diagnosing yourself. There are relevant specialists and research for this. The most important thing if you suspect inflammation of the facial nerve is not to delay going to the doctor. It is necessary to contact a neurologist or a dental neurologist, or, as a last resort, any specialist in the field of dentistry. For a high-quality diagnosis, it is advisable to undergo an MRI or CT scan of the brain to rule out inflammatory and other pathological processes in the brain.
Other important studies include electromyography and electroneurography. These methods will determine the presence of damage along the entire length of the facial nerve. During these examinations, the doctor attaches electrodes to the skin, which irritate the nerve with light shocks of electricity. Special sensors record nerve impulses and transmit them to a computer, with which the doctor interprets the study.
Treatment of facial nerve paresis
Whether it will be possible to completely get rid of facial nerve paresis depends on whether the patient sought medical help in time. If the process becomes chronic, it is impossible to restore the innervation of the nerve 100%. This means that the patient will forever be left with an asymmetrical face, which looks unnatural.
Treatment for facial paresis usually takes about six months. All this time it is necessary to take various medications, do massage, special gymnastics, and undergo physical therapy sessions.
Treatment of facial nerve paresis with medications
Before starting treatment for acute facial paresis, the cause of the disease is identified. Afterwards, measures are taken to relieve swelling, eliminate the inflammatory process and activate the process of nerve cell regeneration.
Drug treatment of facial nerve paresis includes the use of:
- Analgesics in the form of tablets or injections. “Baralgin”, “Ketorol”, “Spazgan” are suitable.
- Decongestant drugs - Furosemide, Triampur.
- Corticosteroids. If moderate or severe paresis is diagnosed, Prednisolone is used. It allows you to relieve inflammation and swelling in a minimally short period of time.
- Vasodilator drugs - nicotinic acid, Complamin.
- Sedatives (if there is a high level of patient anxiety) - “Sibazon”, “Relanium”. They help the patient calm down and relax, thereby reducing muscle tone.
- Vitamin-mineral complexes (B vitamins are especially necessary).
- Artificial tears – if the eyes are affected. Their use makes it possible to exclude the addition of a secondary infection and drying out of the mucous membranes.
- Other medications aimed at eliminating pronounced symptoms.
Surgical treatment of facial nerve paresis
Surgical treatment of paresis is carried out if a complete nerve rupture is diagnosed. This happens with congenital anomalies or injuries. The operation can achieve positive results only if it is performed within a year from the onset of the disease. If you wait longer, the facial muscles will atrophy and the restored nerve will no longer be able to control them.
In case of rupture, the nerve is sutured. If we are talking about a congenital anomaly, autotransplantation is performed - the graft is taken from the patient’s leg and placed in the desired place on the face. Then the branches of the nerve from the healthy side are sewn to it. As a result, the facial expressions of the operated person are controlled by one nerve. The scar remains only behind the ear. There are no other changes to the skin associated with the operation.
Physiotherapeutic treatment of facial nerve paresis
During the first week, the disease can be treated with Sollux. This is a special lamp designed for light therapy. Later, the patient is prescribed UHF sessions, paraffin therapy and phonophoresis.
Acupuncture and homeopathy in the treatment of facial paresis
You cannot hope for the success of homeopathy in all cases. If improvements are not observed within a month, it is wiser to turn to traditional methods of treating paresis. Otherwise, the disease can severely disfigure the face, and it will no longer be possible to change anything. It is important not to exceed the dosage of homeopathic medicines, because they may contain extracts of poisonous plants.
The homeopathic drug Gelsemium is most often used to treat paresis. However, you should not prescribe it yourself. Consult a specialist at your nearest homeopathy center
.
Acupuncture can also achieve good results.
Psychotherapy for paresis
A distorted face negatively affects the emotional state of many patients. They develop depression, their mood worsens, and their self-esteem decreases.
If sedative medications prescribed by a doctor do not help improve the current situation, consultation with a qualified psychotherapist is recommended. It is also important that the patient remains at home during the acute period of illness.
Traditional methods of treating facial nerve paresis
Treatment of facial nerve paresis at home can be carried out using folk recipes. But they should complement drug therapy and not be used in isolation.
- The affected side of the face should be rubbed with fir oil every evening.
- Heat sand or salt. Place in fabric bags and apply to the inflamed part of the face.
- Mix tinctures of hawthorn, calendula, motherwort and peony in equal proportions. Add 25 ml of Corvalol and 3 tbsp to 50 ml of the resulting mixture. natural honey. Take a teaspoon shortly before bed for 3 months. Afterwards, take a month's break and repeat the course.
Gymnastics for facial nerve paresis
A very important stage in the process of restoring the functioning of a damaged nerve is gymnastics. The patient needs to do the following exercises every day:
- Frown your eyebrows, count to 5, relax your face. Repeat at any time as often as possible.
- Puff out your cheeks and hold your breath. To increase the effectiveness of the exercise, you can press on your puffed out cheeks with your palms, thus creating resistance.
- Curl your lips into a tube and pull them forward.
- Open your eyes wide and close your eyes tightly.
A set of exercise therapy exercises for facial nerve paresis is usually selected by the attending physician on an individual basis. This takes into account the form of pathology and the severity of symptoms.
Massage for paresis
Massage helps improve muscle function with facial nerve paresis. a medical massage center near you
. You can start sessions 5-7 days after the first symptoms of the disease. Since massage has its own characteristics, it is better if it is done by an experienced massage therapist.
- First you need to stretch your neck muscles. To do this, tilt the head in different directions and rotate. They need to be done very slowly and carefully (10 times for each movement).
- Start the massage from the neck and back of the head. This allows you to prepare the lymphatic vessels to supply an additional portion of lymph from the facial part of the head.
- You need to massage both the healthy and diseased sides of the face.
- Perform all movements along the lymph outflow lines.
- Combine stroking with light vibration.
- Pay maximum attention to the mastoid process, neck, collar area, and face.
- For muscle soreness, the massage should be light and superficial.
- Useful movements are from the middle of the chin, forehead and nose to the parotid glands.
- There is no need to massage the areas around the lymph nodes (they may become inflamed).
- Place your thumb behind your cheek and gently stretch the muscles.
- At the end of the session, re-massage the muscles of the neck and back of the head. This allows you to accelerate the outflow of lymph to the main vessels.
- You should always finish with neck exercises.
The massage should be repeated until all symptoms of facial nerve paresis disappear.