Indications for the study
The presence of a retrocerebellar cyst can be suspected by some characteristic symptoms:
- Severe headaches that do not go away even after taking painkillers;
- Unreasonable loss of consciousness or fainting state;
- Sensation of squeezing and pulsation in the head;
- Deterioration of hearing or vision;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Numbness of the limbs;
- Impaired coordination of movements;
- Epileptic seizures.
Magnetic resonance imaging is required if surgical intervention in the brain area is necessary.
Note that the clinical picture and severity of symptoms depend on the exact location and size of the retrocerebellar cyst.
Clinical course of the disease in a child
In a small patient, the development of this pathology is accompanied, as in an adult, by a number of similar signs:
- hearing impairment;
- paralysis and paresis of limbs;
- cramps, numbness;
- impaired coordination of motor activity.
If the cyst progresses in size, intracranial pressure may increase, which as a result affects the appearance of the following symptoms:
- vomit;
- intense headaches;
- pulsation in the head area;
- increased drowsiness and fatigue.
A more severe degree of the disease causes divergence of the bone sutures (problems with the overgrowth of the fontanel in infants), which affects the delay in the development of the baby, both mental and physical.
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging is safe for the body only if all contraindications are excluded.
Magnetic resonance imaging is not recommended in the following cases:
Very often, to obtain more informative images, doctors prescribe additional contrast. In this case, you must ensure that there are no following contraindications:
- Pregnancy of any stage.
- Breastfeeding period.
- Kidney failure.
- Chronic liver diseases.
- Allergic reaction to components included in contrast agents.
Suitability categories
Articles 23 and 25 in the Schedule of Diseases have clauses that determine the categories of suitability of a conscript for military service. Under point “a”, examinations are carried out in case of significant disturbances in the functioning of the body. In this case, the disease must be severe, treatment of the pathology does not bring a positive result, and negative changes progress. A conscript must be hospitalized for at least 60 days more than twice a year. In this case, they give the non-conscription category “D”.
When examined under point “b”, the conscript receives category “B”. The disease progresses with moderate disturbances in the functioning of the body against the background of increased intracranial pressure. Clause “c” also provides for the non-conscription category “B”. In this case, there is no syndrome of increased intracranial pressure, but there are neurological changes that interfere with military service. There are no positive changes during treatment.
Point “d” includes the consequences of the disease, which have individual signs of vegetative-vascular instability, but there are no motor or sensory disorders, coordination is normal. Such conscripts receive category “B”, which provides for service with restrictions due to the corresponding disease.
Preparation rules
During a routine examination, doctors recommend following a few simple recommendations:
- If it is necessary to administer contrast, you must come to the clinic on an empty stomach, that is, do not eat food for 7-8 hours.
- If you are afraid of research or confined spaces, be sure to consult with a specialist. Your doctor may prescribe you sedatives to make the examination process more comfortable.
- Do not bring any metal products inside the tomograph. For this reason, doctors recommend removing metal accessories in advance.
- Prepare a change of clothes that do not have metal or metal-containing accessories.
- The duration of the diagnostic test is about 40 minutes. Empty your bladder in advance to avoid discomfort during the procedure.
Treatment methods for brain cysts
Treatment of brain cysts is mainly surgical.
This neoplasm must be surgically removed, and drug therapy in this case is ineffective. At the same time, the drugs will help get rid of pain caused by an imbalance of hormones or disturbances in brain activity caused by a cyst. Our clinic employs excellent neurosurgeons with many years of experience behind them. The neurosurgical department of the Ikhilov Complex clinic is equipped with ultra-modern technology, and in 90% of cases, neurosurgeons use minimally invasive techniques for operations, which allow complex interventions to be performed without incisions.
A patient with an established brain cyst is offered to undergo treatment that will give the highest results.
- Diagnostic observation . Benign brain cysts do not always need to be removed. If they are small in size and do not put pressure on the brain tissue, then regular monitoring will be enough so that doctors can understand how the cyst behaves over time. During diagnostic observation, tomographic techniques (CT, MRI) are used. If, after a series of studies, it is established that the cyst is growing, which threatens to compress neighboring brain structures, then a decision is made to perform surgery to remove the cyst. More often, the cyst remains unchanged, without threatening the health and life of a person. However, the patient should undergo examinations in a disciplined manner within the stipulated time frame to eliminate the possibility of complications.
- Cyst shunting . If the fluid is removed from the cyst, the walls of the neoplasm will “stick together” and the problem will disappear. For this purpose, a tube is installed into the cavity of the cyst, draining fluid into other cavities of the body. There is no need to perform a second operation to remove the tube, since it is made of self-absorbable material.
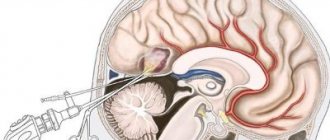
- Surgery . For a long time, removal of brain tumors was performed exclusively by craniotomy. This was the only way to penetrate brain tissue. For more than 20 years, the neurosurgical department of the clinic has been using the latest minimally invasive operating techniques, in which surgical instruments are applied to the operated area through the nose. Transanasal and transsphenoidal interventions in Israel for brain pathologies account for 85-90% of all neurosurgical interventions on the organs of the central nervous system. During the operation, the doctor inserts an endoscope equipped with an optical device and a camera into the nasal cavity. Everything that happens inside the brain is displayed on the monitor, and when the desired area is reached, a surgical instrument is brought to the cyst, which is used to excise the tumor. In approximately 5-10% of cases, the patient is not suitable for endoscopic surgery due to the complex and inaccessible location of the tumor. In such cases, the patient undergoes open surgery with craniotomy. This is a traumatic intervention with loss of a certain amount of blood, so after such an operation the patient needs rehabilitation. At Ikhilov Complex, after such operations, the patient is rehabilitated in a short time.
It is imperative that after the operation is completed, the brain cyst in Israel is examined using cytological examination. This is necessary to exclude malignancy of the formation. If histological studies reveal the presence of cancer cells, the patient is prescribed additional antitumor treatment: cytostatic drugs (chemotherapy) and radiotherapy.
Therapeutic tactics when a cyst is detected depends on the type of cavity neoplasm.
- Pineal cysts of the brain in Israel in most cases do not require special treatment, since they do not pose a threat to life and health. As a rule, the matter is limited to regular observation. In extreme cases, the patient is treated: pharmacotherapy or surgery.
- Arachnoid cyst of the brain: treatment in Israel, as in the case of a pineal cyst, is often limited to observation. If the dynamics are unfavorable and the cyst significantly increases in size, then surgery is indicated.
- Retrocerebellar cyst of the brain: treatment in Israel in this case comes down to surgical removal (usually endoscopic). Small size and the absence of pathological symptoms can serve as a basis for discontinuation of treatment and an indication for regular monitoring.
The Department of Pediatric Neurosurgery also treats brain cysts in children of all ages.
- Endoscopic operations
- Craniotomy
- Cyst drainage
How is an MRI performed?
To ensure that the procedure is as informative as possible and that the images are clear, experts recommend performing magnetic resonance imaging in closed-type tomographs. Before starting the study, the patient must change into clothes without metal structures, take off his shoes and lie down on a retractable table. If the doctor has prescribed additional contrast enhancement, a special drug is injected into a vein, which is distributed throughout the circulatory system in just a few minutes. Then the table moves inside the tomograph, where the research process takes place.
Maintaining immobility is the main requirement for the patient! Remember that even minimal movements can lead to a decrease in the information content of the procedure.
It is also worth noting that when performing magnetic resonance imaging, a specific loud noise is observed. If this scares you, you can use earplugs.
Patients generally tolerate MRI well. Inside the tomograph there is good lighting and ventilation, there is a loudspeaker, as well as a panic button for emergency stop of the study.
Principles of treatment
Treatment of a brain cyst is a rather complex procedure that requires an integrated approach. For non-progressive forms of the cyst, dynamic observation by a neurologist is prescribed and drug therapy is recommended:
- Antibacterial or antiviral therapy. In this case, the indication is the presence of an inflammatory focus of an infectious or autoimmune nature.
- Taking immunomodulators. The goal is to increase the body’s immune barrier, stopping the aggressive effects of the autoimmune environment.
Tumors, cysts and hematomas can be a consequence of severe brain contusion.
Read our article about what to do if you have a brain injury. Also learn how to provide first aid for a fracture of the base of the skull from this article.You can learn about how headaches are associated with chronic intracranial hypertension at https://gidmed.com/bolezni-nevrologii/vnutrecherepnoe-davlenie/gipertenziya.html
Drug treatment of cerebrovascular disorders consists of three areas:
- Reducing the concentration of cholesterol and blood clotting - antiplatelet agents (regular aspirin, ticlopidine, pentoxifylline).
- Normalization of blood pressure indicators - Enalapril, Capoten.
- Resorption of adhesions - anticoagulants.
- Improving the flow of oxygen and glucose into brain cells - a group of nootropic drugs (Cerebramin, Cerebrolysin, Nootropil, Vinpotropil, Vinpocetine)
- Increasing the resistance of the cellular composition of the brain to increases in intracranial pressure - antioxidants.
If the severity of the disease is high, the surgeon will decide how to treat the retrocerebellar cyst of the brain.
Maybe:
- endoscopic intervention;
- cystocystrenostomy;
- cavitary cyst shunting;
- excision of the tumor.
Video of an operation to remove a retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst of the brain:
MRI with contrast
In most cases, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is performed with contrast, especially if any neoplasm is suspected. This makes it possible to examine the tumor in detail and distinguish a benign tumor from a malignant one.
The contrast agent clearly highlights the vessels, which allows you to see any tissue pathologies. Don't worry, contrast agents are safe for the human body. Most patients tolerate this procedure well. You must first consult a doctor and exclude all possible contraindications.
Examination rules
Examination of conscripts takes place according to the Schedule of Diseases. This is a special list of pathologies with which young people are not accepted for service in the country’s armed forces. The list is regularly reviewed and updated.
A brain cyst is regulated under Article 23 of this list. It can assign different categories of suitability for service:
Author:
Kirill Savchenko
Didn't understand the article and need help?
auto RU
- “A” – suitable without restrictions;
- “B” – fit with some restrictions on diseases;
- “B” – not fit for conscription in peacetime, subject to release from service;
- “G” – temporarily unfit for health reasons, receives a 6 or 12 month deferment for treatment, then undergoes a military medical commission again;
- “D” – exempted from military service due to a serious illness.
Decoding the results
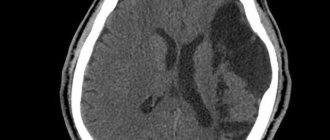
A retrocerebellar cyst is located in the brain behind the cerebellum, in the posterior cranial fossa. During magnetic resonance imaging, it is possible to clarify the exact location and size of the formation.
The report will contain all the information, but the MRI specialist cannot make a diagnosis - this must be done by your attending physician. If the diagnosis of retrocerebellar cyst is confirmed, the doctor will determine treatment tactics. For benign tumors, it is often possible to do without surgical interventions - they are required only in cases of large tumors or rapid growth. To avoid serious consequences, consult a doctor at the first alarming symptoms. Be healthy!
Rehabilitation in the postoperative period
Rehabilitation after removal of a brain cyst includes a number of points that deserve special attention. For example, drinking alcohol is prohibited for a certain period of time. Air travel is not advisable for approximately 3 months. Active sports that may involve mechanical impact on the head are also prohibited. Visiting a bathhouse, sauna, or ultraviolet radiation can have negative consequences.
As a rule, rehabilitation after brain surgery is carried out according to a specially developed program, which is formed depending on the type of cyst, type of neurosurgical intervention, the presence of complications, and the postoperative condition of the patient. It is advisable to contact your doctor at the first suspicion that something is going wrong.
Symptoms of a spinal cyst
Depending on the location, spinal cysts can be divided into:
- Cysts in the cervical spine;
- Cysts in the thoracic spine;
- Cysts in the lumbar spine;
- Cysts in the lumbosacral spine;
- Cysts in the sacral spine.
According to the nature of education, experts distinguish the following types:
- Perineural cyst of the spine (usually an incidental finding and does not require treatment)
- Paraarticular cyst (paraarticular synovial cyst of the intervertebral facet joint, requires spinal surgery)
- Arachnoid cyst (extremely rare)
As experts note, there are dozens of types of spinal cysts, most of which are considered normal
.
Surgical treatment is indicated for paraarticular synovial cyst of the intervertebral facet joint if radicular compression symptoms are observed.
In practice, this means that the patient suffers from regular pain in the area where the cyst is located in the spine and in the limbs. Often the discomfort is accompanied by numbness in the arm or leg. If the pain becomes unbearable, emergency surgery is recommended.