Indications
Non-invasive transcranial (translated from Latin as “through the skull”) electrical stimulation is one of the few methods of physical therapy with scientifically proven effectiveness. The impact of pulsed current has analgesic, immunostimulating effects, activates regeneration processes, and regulates vascular tone. Indications for sessions are:
- pain syndrome due to neurological pathologies, cancer, extensive burn lesions, as well as phantom pain;
- depression, neurosis, anxiety;
- trophic ulcers, deep burns;
- arterial hypertension;
- chronic infectious diseases;
- low immune status;
- toxicosis during pregnancy;
- dermatological pathologies (neurodermatitis, atopic dermatitis, eczema);
- neurotic conditions against the background of menopause;
- sensorineural hearing loss;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- allergy;
- inflammatory diseases of autoimmune etiology (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis);
- alcohol or drug addiction;
- Parkinson's disease;
- insomnia.
Stimulation of the production of one's own endorphins helps relieve even severe pain; their effect is approximately 20 times stronger than the effect of morphine. For deep skin lesions, electrical stimulation activates reparative regeneration and helps slow tumor growth.
News
Transcranial electrotherapy (treatment with currents through the scalp) in various modifications has been used in clinical medicine since 1902 (122). The main direction of scientific research in Russia and abroad is the search for electrical signal parameters with maximum sedative and analgesic effects. In our country, the most well-known methods of transcranial electrotherapy in medical practice are electrosleep, electrical anesthesia and transcranial electrical stimulation. Mesodiencephalic modulation,
based on previous achievements in this area, it is based on the selection of characteristics of the electrical signal that maximally normalizes the work of the control centers of the body's adaptive system, localized in the midline structures of the brain. The primary effect is on the hypothalamic-pituitary and opioid systems, which produce a spectrum of neurohormones that regulate the activity of organs and systems at the cellular level. At the same time, analgesic and sedative effects are only a component of the multifaceted action of mesodiencephalic modulation.
ELECTROSLEEP.
Initially, electrosleep was used in psychiatry as a sedative and tranquilizing agent. Subsequently, the scope of its use expanded.
Main characteristics of the electrical signal: current strength - up to 40 mA, rectangular pulse current with a frequency from 5 to 160 Hz, pulse duration - 0.3 ms, constant component -20-30% of the threshold value of the pulse current, location of the electrodes orbital mastoid. The duration of the procedure is up to 2 hours, the course is up to 25 procedures. The devices used are “Electrosleep” and modifications. One of the latest modifications is ELEKTROSON ES-10-5.
Specifications:
Pulse repetition frequency: 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 100, 160 Hz Relative frequency setting error no more than 20% Pulse duration 0.5 ms 20% Pulse rise and fall duration no more than 50 μs, respectively. The pulse current at the output of the device is adjustable from 0 to the maximum value. The maximum amplitude of the pulse current at the output of the device is 10 mA 15% with a load of 5000 Ohms 1% The power consumed by the device from the network is no more than 25 VA. Mean time between failures is not less than 1500 hours of conditionally continuous operation. Overall dimensions 108x300x315 mm Weight of the device with a set of electrodes no more than 3.5 kg
Main applications and clinical effects:
Psychiatry
: improvement in general condition, reduction in the manifestations of asthenic and depressive syndrome, headaches and other positive effects in patients with schizophrenia, chronic alcoholism, enuresis, psychopathic syndromes, post-traumatic and vascular encephalopathies (66, 81).
Neurology:
reducing the severity of pain in radiculitis and osteochondrosis (66).
Cardiology:
acceleration of reparative processes and reduction of manifestations of astheno-depressive syndrome in acute myocardial infarction (65, 66), lowering blood pressure and improving peripheral blood flow in patients with hypertension (39).
Gastroenterology
: reduction in pain and normalization of acidity in gastritis and gastroduodenitis (82), symptomatic improvement in biliary dyskinesia (66, 92).
In addition, electrosleep is used in the complex treatment of patients with burns (93), diabetes mellitus (87), dermatitis (34) and other diseases.
There is a certain effectiveness of electrosleep in the recovery period after physical overload in athletes and sailors (25, 88).
The main disadvantages of the method: a lengthy procedure, special room design, the procedure is performed lying down, the possibility of damage to the retina due to the orbital localization of the electrodes.
ELECTRICAL PAIN RELIEF.
Main characteristics of the electrical signal: current strength - up to 10 mA, rectangular pulse current with a frequency from 200 to 2000 Hz, pulse duration - 0.1-0.3 ms, constant component - 10-20% of the pulse current strength, electrode location frontal -mastoid. The duration of the procedure is from 40 minutes. up to 1.5 hours, course - up to 20 procedures. The method is implemented by LENAR, BILENAR, etc. devices.
The most extensive study of electrical anesthesia was carried out by E.M. Kastrubin et al. in obstetrics for pain relief during labor and prevention of complications. No negative effects on the condition of the fetus have been identified (36, 73). The threat of miscarriage in the early and late stages of pregnancy was significantly reduced, acid-base balance and blood gas levels in pregnant women with heart defects were improved, labor analgesia was observed, and peripheral circulation improved (46, 50-52).
Positive results have been established with the use of electrical anesthesia in patients with coronary heart disease (53, 80) and hypertension (27, 37). General effects are pain relief, normalization of hemodynamics, and prevention of complications.
Acceleration of healing processes, analgesic effect and normalization of homeostasis indicators in patients with gastric and duodenal ulcers (77), during surgical interventions (38), including oncological diseases (35) and in children (62) were noted. The method is used for pain relief in dentistry (90).
The clinical course improves in patients with atopic dermatitis (63), neuroses (58), fatigue accumulates less in pilots during intense flights (42).
The main disadvantage of the method is the lengthy procedure and insufficient clinical effectiveness in patients with severe multiple organ pathology.
TRANSCRANIAL ELECTROSTIMULATION.
Transcranial electrical stimulation (TES) is based on the structure of the electrical signal proposed by the French researcher Limoges in 1975 (67, p. 11). Limoges currents consist of bipolar rectangular pulses with a fundamental frequency of 77 Hz (periodic switching to 83 and 100 Hz) and a filling frequency of 180 kHz, duration 3-4 ms, current strength up to 300 mA. In 1984 V.P. Lebedev proposed a TES with a frequency of 77 Hz (with and without 10 kHz filling), a duration of rectangular unidirectional pulses of 3.75 ms, and the addition of a galvanic component with a fixed ratio with a pulse current amplitude of 2:1.
In experiments on various types of laboratory animals, based on the use of quantitative assessment methods, it was found that using the electrical mode of TES it is possible to selectively activate the opioid structures of the brain (3, 4, 54, 59, 60, 67, 94).
The first effect of TES that was studied in detail was analgesia. Evidence of the opioid nature of such analgesia is as follows:
1. Elimination of the effect with naloxone.
2. An increase in the concentration of b-endorphin and met-enkephalin in some brain structures, cerebrospinal fluid and blood plasma.
3. Increased analgesia after administration of enkephalinase inhibitors.
4. Lack of analgesia in animals with developed tolerance to morphine.
Using radioimmunochemical determinations of b-endorphin in plasma, it was confirmed that it was the chosen regimen that caused the maximum increase in the concentration of this opioid.
In autoradiographic experiments with 3H-deoxyglucose, it was shown that a significant accumulation of this substance, indicating the activation of neurons under the influence of TES, occurs in structures rich in opiates and related to the antinociceptive system, located in the periaqueductal gray matter and raphe nuclei.
It is known from the literature that direct stimulation of the antinociceptive system and opioid peptides themselves introduced into the bloodstream can stimulate reparative processes. Experiments have confirmed the acceleration of skin wound healing (78, 94). Two important facts were noted in these experiments:
a) maximum stimulation of healing occurs under the action of the same current parameters that are optimal for stimulation of opioid structures.
b) acceleration of healing is eliminated by naloxone.
Currently, TES is widely used in clinical medicine. Devices such as “Transair” and “Etrans” are used. Data have been obtained on effective pain relief for various pathologies, primarily in patients with neurological pain syndromes (67, pp. 34-38), arthritis (67, p. 40), eye pain (67, p. 41), gastric ulcer and duodenum (5), etc. In addition, it has been established that TES activates healing processes in a number of diseases (5, 67, pp. 51-53), improves the condition of patients with alcohol withdrawal syndrome (67, p. 47), stabilizes hemodynamic parameters and reduces the number of complications during surgical interventions on the heart, lungs under artificial circulation, as well as in the abdominal cavity (67, p. 20).
In the USA, the Alpha-Stim 100 TES device is widely used with an alternating current frequency of 0.5, 1.5 and 100 Hz, a current intensity of 10 to 600 μA, and a procedure duration of 10, 20 and 60 minutes. The greatest effectiveness was achieved in patients with pain of various localizations (mainly headaches), chronic stress, neuroses and drug addiction (101-104, 116, 119, 126, 134, 135, 143, 145). At the same time, it is possible to reduce the amount of consumed painkillers and sedatives.
In all of the listed methods of transcranial electrotherapy, the cathode (galvanic component) is located on the forehead, the anode - on the mastoid processes. There is a hypothesis that the current, predominantly passing through the subcutaneous fat layer, partially enters the brain through the orbital and small openings in the skull bones and ensures the polarization of neuronal membranes (cathodization of the frontal lobes). This, in turn, causes reflex effects from the cerebral cortex on subcortical structures, in particular, the opioid system, with its subsequent activation.
MESODIENCEPHAL MODULATION.
Mesodiencephalic modulation first appeared as a new direction in 1987. This direction was started by the collaboration of the developer of TES, Professor V.P. Lebedev and academician A.P. Golikov (Head of the Center for Emergency Cardiology of the N.V. Sklifosovsky Research Institute of Emergency Medicine). It was decided to try to use TES to relieve anginal status in the most acute stage of myocardial infarction. The results left much to be desired and it was planned to close the research topic. However, V.A. Karev determined the dynamics of protein-bound hydroxyproline in the blood, on the basis of which it was possible to assume the acceleration of the formation of a post-infarction scar. Further study of transcranial electrotherapy in patients with myocardial infarction was carried out from the standpoint of assessing reparative processes. During the research, the parameters of the electrical signal and the method of applying electrodes changed significantly; the term “mesodiencephalic modulation” was proposed, which more accurately reflects the areas and mechanisms of action of this technique. As data on the dynamics of hormones, indicators of lipid peroxidation, and the immune system were obtained, a concept was developed about the influence on the state of the body's adaptive system through neuroendocrine control centers.
The first serial devices for mesodiencephalic modulation MDM-1 began to be produced in 1990. Subsequently, devices MDM-101, MDM 2000 (in the Czech Republic), MDMK-4 (Medapton) were produced. Currently, the devices MDMK-5k, MDMK-6 and MDMK-7 are prepared for serial production or are at the R&D stage.
Carrying out the procedure
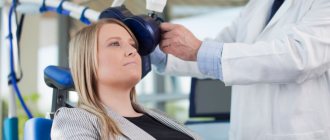
A transcranial electrical stimulation session lasts about 30 minutes. The patient is placed in a sitting or lying position. Electrodes are attached to the scalp, to which a low-power pulsed current is supplied from the device. A specific arrangement of electrodes is used, taking into account the direction of current application (from the forehead to the mastoid processes) and the resonant parameters of the current. The procedure is completely painless; the patient may feel slight vibration, warmth, and tingling in the area of treatment.
During the session, the doctor controls the person’s sensations in order to regulate the strength of the current supplied. As a rule, during the first procedure the current strength is not changed. In subsequent sessions, the specialist may slightly increase the impact to achieve a more pronounced effect. The required number of procedures is about 10, determined individually for each patient.
The skin under the electrodes does not suffer and looks exactly the same as before the session. No complications or negative consequences of the procedure were identified.
Transcranial therapy: what is the principle of the technique based on
During the procedure, brain structures are activated that regulate the production of endogenous opioid peptides - a group of neurotransmitters that determine a person’s emotional state, the functioning of the immune, cardiovascular, nervous and, in part, endocrine systems. The impact is carried out with strictly defined, dosed impulses, which eliminates complications and ensures a positive result of TES of the brain after the first procedure.
Transcranial neurostimulation: main advantages
- Safety. The treatment does not cause any side effects; specialists at the Ugodie clinic select its duration individually, taking into account the severity of the addiction and the psychological state of the patient (propensity to relapse, general attitude towards the treatment process, etc.).
- Efficiency. One course of TES therapy includes up to 10 physical procedures, and the result of transcranial exposure lasts up to 12 weeks. To consolidate the achieved effect, it can be repeated at intervals of 2–3 months.
Complex impact. Transcranial electrical stimulation has a positive effect on both the psycho-emotional and physical condition of the patient. This allows you to reduce the dosage or completely abandon medications used for the conservative treatment of alcohol or drug addiction. In this way, you can avoid unnecessary stress on the liver, digestive tract, and kidneys affected by toxins.
At the Ugodie drug treatment clinic, we provide the opportunity to conduct transcranial procedures both in the hospital and on an outpatient basis. We provide all our clients with maximum comfort, strict adherence to confidentiality, and reasonable prices. We offer TES therapy as one of the stages of complex treatment of alcoholism or drug addiction, along with detoxification, coding, work with a psychologist, and rehabilitation.
Equipment used
To conduct sessions, special equipment is used that generates pulsed currents. The devices are designed taking into account safety and ergonomic standards.
Currently, the most widely used devices for transcranial electrical stimulation are:
- Etrans-1, Etrans-2, Etrans-3;
- Transair (modifications 02, 01В, 01С, 01П);
- MDM-1, MDM-101.
Various devices have been developed, both stationary and portable. Some models are intended for professional use in medical institutions. There are also devices for carrying out procedures at home.
Effects
Transcranial brain stimulation has a wide range of therapeutic effects. This:
restoration of a full psycho-emotional status: improvement of mood, normalization of sleep, fight against depression and depression (data have now been obtained on the positive effect of TES therapy for clinical depression);- relief of pathological craving for alcohol and drugs;
- improvement of microcirculation, blood flow in the vessels of the brain, supply of tissues with oxygen and nutrients;
- normalization of blood pressure;
- stimulation of the immune system;
- improvement of tissue regeneration;
- restoration of liver detoxification function, regulation of metabolism;
- inhibition of inflammatory processes.
Effect of transcranial electrical stimulation
During clinical studies, the following effects of this method of physical influence were confirmed:
- pronounced analgesic effect even in those patients whose pain syndrome is not relieved by medication;
- antidepressant effect, normalization of psychophysiological processes, improvement of performance, elimination of chronic fatigue syndrome;
- improved sleep;
- activation of regeneration of all types of tissues;
- stimulation of the immune system, increasing the body's resistance;
- normalization of vascular tone and, as a result, blood pressure;
- improvement of well-being, reduction of pain intensity and inhibition of the development of tumor processes in cancer;
- relieving symptoms of acute withdrawal in patients with alcohol and drug addiction, reducing cravings for alcohol and drugs, eliminating disorders that arise during the period after abstinence;
- reduction in the intensity and frequency of allergic reactions; after sessions, you can reduce the dosage of antiallergic drugs;
- relief of inflammation in infectious and autoimmune diseases.
Transcranial electrical stimulation can effectively treat many pathologies and improve results from the use of medications while reducing the dosage.
You can undergo treatment with transcranial electrical stimulation in Moscow in most clinics. You can sign up for the procedure at the selected institution by phone. The price of one session ranges from 500 to 2500 rubles, depending on the level of the institution and the type of equipment used.
Main indications and contraindications of the technique
There are quite a few areas of application for transcranial electrical stimulation. The most popular technique turned out to be for a variety of neurological and psychiatric pathological conditions, for example, for:
- depression, stress, sleep disturbances;
- hyperactivity, increased body fatigue, impaired attention;
- increased anxiety, chronic fatigue syndrome;
- menopausal neurosis, headaches of various origins;
- disorders of autonomic regulation, meteorological reactions;
- orofacial, phantom pain and pain in oncology;
- diseases of the sciatic nerves, as well as inflammatory processes of the trigeminal nerves;
- pain syndromes accompanying osteochondrosis, neuralgia, radiculitis;
- dyscirculatory encephalopathy, Parkinson's disease;
- motor disorders after a stroke.
Other pathological features that transcranial electrical stimulation can help combat include:
- coronary heart disease;
- painful sensations in the eyes, decreased vision, sensorineural hearing loss;
- various types of skin injuries and ulcers, including those that form in the postoperative period, as well as neurodermatitis, eczema, seborrhea (except for places where electrodes are applied);
- decreased immunity;
- the occurrence of neoplasms (except for the brain);
- toxicosis, allergies, inflammatory processes, disturbances in human hormonal levels;
- endometriosis, osteoarthritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, duodenitis and gastritis;
- alcoholism and drug addiction.
TES therapy is also widely used in sports, since its effects significantly increase the effectiveness of training. This technique helps athletes withstand peak loads, restore their own strength, and improve performance.
Among the main contraindications for use in the treatment of transcranial electrical stimulation, experts identify the presence of epileptic seizures or convulsions, arterial hypertension, hypertensive crisis, hyperthyroidism, angina attacks, head injuries, brain injuries and the occurrence of tumors in the brain. In addition, such therapy cannot be carried out for thalamic pain, infections of the central nervous system, acute mental illness, hydrocephalus, atrial fibrillation, under the age of 5 years and with an implanted pacemaker.
How does a TES therapy session work?
Treatment is carried out in a comfortable office. The patient is asked to either lie down on a couch or sit in a chair, then special electrodes connected to a transcranial electrical stimulation machine are attached to his head. The duration of the first session is about 20–25 minutes, subsequently the procedure can take up to 40–45 minutes. In this case, the doctor is next to the patient, closely monitors his condition and adjusts the intensity of the effect.
The frequency of sessions is determined on an individual basis. In severe cases (for example, with severe withdrawal), TES therapy can be carried out twice a day (but with an interval of at least 10 hours), subsequently switching to a daily regimen or inviting the patient for treatment once every two days.
Exposure is not accompanied by any unpleasant symptoms. On the contrary, soon after the start of TES therapy, you feel an emotional uplift, a surge of vitality and energy, and your well-being improves.
Narcologists at the Ugodie clinic offer the latest and safest methods for overcoming drug and alcohol addiction. Contact us! Take the first step towards a sober life!
Need some advice?
OR CALL A DOCTOR
CALL!
+7
Physiological rationale for the method of interstitial electrical stimulation
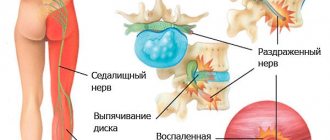
The main source of pain is the bone and periosteum, while nerves and muscles are indirectly involved in the pathological process. Interstitial electrical stimulation acts with current on bone receptors directly in the area of the painful focus. The current passes through the nerves, normalizing their conductivity. This has a beneficial effect on the vital functions of tissues and organs and improves bone circulation.
The nutrition of cartilage tissue is normalized, its breakdown in joints and intervertebral discs is prevented. Dystrophic processes first slow down and then stop. The formation of growths on the bones stops, swelling in the tissues that put pressure on the roots of the spinal cord decreases. This eliminates the source of pain in the bone tissue and eliminates trigger zones.
Transcranial brain stimulation: contraindications
Before starting a course of TES therapy, the narcologist at the Ugodie clinic carefully collects anamnesis and, if necessary, prescribes additional laboratory tests to exclude possible contraindications. These include:
oncological neoplasms;- epilepsy, complications of neuroinfections and other diseases accompanied by convulsive syndrome;
- severe form of hypertension;
- rehabilitation period after ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- consequences of traumatic brain injury;
- violations of the secretory function of the thyroid gland.
A relative contraindication is damage to the skin in the area where the electrodes are attached. The physiotherapy procedure should be postponed until the wounds have completely healed.
Method of interstitial electrical stimulation according to Gerasimov
The method of interstitial electrical stimulation according to Gerasimov was approved by the Russian Ministry of Health and is listed in the state register under No. 2001/115. Disposable needles are used for the procedure. Unlike acupuncture, special points are not calculated for inserting needles, but a scheme of segmental tissue innervation is used. Needles are inserted under the skin in the area requiring treatment. A therapeutic current passes through this conductor to the area affected by the pathological process. Its impulses are as close as possible to the biocurrents of the body itself. After the current begins to flow through the needle, the patient feels only a slight vibration.
As a result of exposure to current, the following changes occur in the bones:
- bone circulation improves;
- cartilage tissue in the intervertebral discs is regenerated;
- the bone structure is normalized;
- muscle spasm is relieved;
- the pain goes away;
- become flexible and regain their original range of motion in the joints.
The procedure is absolutely painless for the patient. There are only positive reviews about interstitial electrical stimulation according to Gerasimov.
In order to undergo a course of interstitial electrical stimulation using the Gerasimov method, you should call the Yusupov Hospital. The contact center is open 24 hours a day. The procedure is carried out by specialists who have undergone special training in the use of electrical stimulation methods for diseases of the musculoskeletal system.