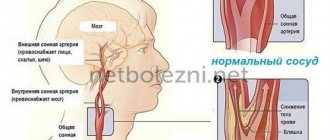
Causes of chronic cerebral ischemia
- The main causes of chronic cerebral ischemia include arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis. Chronic cerebral ischemia caused by a combination of two conditions is common. In addition, among other reasons causing this disease, there will be symptoms of cardiovascular diseases, which are expressed in heart rhythm disturbances (for example, arrhythmia), which, in turn, leads to a decrease in systemic hemodynamics.
- Doctors attach great importance to the study of vascular anomalies, both in the brain and in the vessels of the cervical spine. Such anomalies, like those associated with the aorta or vessels of the shoulder girdle, often do not manifest themselves for a long time, until the development of atherosclerotic and hypertensive processes.
- In recent years, neurologists have identified a number of other reasons that contribute to the development of chronic cerebral ischemia, including venous pathology of an intracranial and extracranial nature. It is possible that the occurrence of chronic ischemia is influenced by compression of arterial and venous vessels. Doctors take into account both the spondylogenic effect and possible compression of blood vessels by muscles, an aneurysm or a tumor. Another possible cause of this pathology is developing cerebral amyloidosis.
Typically, identified encephalopathy manifests itself symptomatically mixed. If factors have been discovered that caused the development of chronic cerebral ischemia, then all other possible causes are considered additional causes. Of course, identifying and accurately identifying additional factors that aggravate the course of the disease will be very necessary, first of all, in order to make the right decision regarding symptomatic or etiopathogenetic treatment.
In medicine in recent years, the occurrence of chronic cerebral ischemia is usually considered in two ways: according to the nature and nature of the damage and according to the usual localization. In the case of bilateral diffuse damage to the brain, more precisely, its white matter, they speak of a leukoencephalopathic type of encephalopathy. The second option is the lacunar type, which has a large number of lacunar foci. If such two options are most often found in theory, then in practice they speak of their mixed type.
Most often, the lacunar variant is caused by a process such as occlusion of small vessels. A significant role in the pathogenesis of diffuse damage is assigned to a decrease in systemic hemodynamics or, as it is also called, arterial hypotension. The reason for the decrease in blood pressure will be improperly administered antihypertensive therapy, as well as a decrease in cardiac output. A significant role is played by severe cough and orthostatic hypotension, which often happens in the case of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
As is known, the main pathogenetic link of this disease is the depletion of the compensation mechanism, as well as a decrease in the energy work of the brain, which leads to the obvious development of functional disorders and such irreversible processes of a morphological nature as a slowdown in blood flow, a decrease in blood glucose levels, a decrease in oxygen levels, and the occurrence of capillary stasis, the appearance of slow cerebral blood flow, thrombus formation, the ability to depolarize cell membranes.
Read also
Swelling of the legs
Causes of Swelling in the Legs The legs are common sites for swelling due to the effect of gravity on the fluids in the human body.
However, fluid retention is not the only cause of leg swelling. Injuries… Read more
Atherosclerosis
What is atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a narrowing of the arteries caused by the formation of plaque. As a person gets older, fat and cholesterol can accumulate in the arteries and form plaque. Accumulation…
More details
Alzheimer's disease
47,000,000 people suffer from dementia in the world. Doctors call Alzheimer's disease the most common cause of dementia. Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease accompanied by...
More details
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
What it is? Why is this happening? Is this condition dangerous? What to do if doctors make such a diagnosis? These questions are always asked by patients who come to see a neurologist. According to classification...
More details
Vegetative-vascular dystonia
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system, which manifests itself in the form of various clinical symptoms. This disease is diagnosed at different times...
More details
Symptoms of chronic cerebral ischemia
The main symptomatic manifestations of chronic cerebral ischemia include:
- movement disorders of polymorphic type;
- decreased memory and mental abilities;
- changes in the patient's emotional background.
A feature of chronic cerebral ischemia is its progressive course. In addition, the disease is characterized by the presence of stages and syndromes. Doctors note the so-called inverse relationship between present complaints (especially those related to concentration and the ability to remember) and the degree of manifestation of this disease. The more the patient's cognitive functions are weakened, the fewer complaints he will have. As practice shows, the patient’s subjective complaints do not indicate the severity or nature of the disease process.
The main clinical manifestation of dyscirculatory encephalopathy today is considered to be cognitive impairment, which can be detected even at the first stage. Their nature, as a rule, is progressive, which is noticeable already at the third stage of the disease. In parallel with emotional disorders (such as emotional lability, inertia and all kinds of loss of interest), a variety of motor disorders can occur, including the inability to control and perform both simple reflex and complex automated movements).
Symptoms of the 2nd degree
The chronic form is formed from the acute one and has degrees of its development. The most progressive of them is degree 2, characterized by special symptoms:
- increased headaches, feeling of heaviness in the head;
- approaching nausea;
general malaise;- slow speech;
- unsteady gait, loss of balance when walking;
- irritation and aggression, isolation and unpredictability;
- decision to change your usual lifestyle;
- loss of interest in life situations, in society;
- decreased appetite, weight loss.
In the chronic form of cerebral ischemia, transformations begin in the white matter with the subsequent formation of microfoci, increasing compression of microcapillaries, and destructive processes in the cortical and stem connections of neurons.
First stage
At the first stage, there is a combination of classical complaints with a diffuse type of neurological symptoms, which manifests itself as anisoreflexia and a mild type of reflexes. It is also possible that the gait may change (walking may become slow, the patient often moves in small steps). The first stage is characterized by decreased coordination stability and uncertainty when performing movements.
Very often, doctors note emotional disturbances in patients in the form of irritability and anxiety, and depression is often observed. At this stage, minor cognitive deviations of the neurodynamic type occur, which implies exhaustion of the nervous system, decreased attention, and inertia of the intellect. However, in general, patients perform well on memory tests and on routine tasks, but only on tasks that do not require timed performance. Life activity and working abilities at the first stage are not limited for the patient.
Treatment of the disease
To date, no specific treatment tactics for such a disease have been developed, which means that there are no special medications, IVs or physiotherapeutic procedures that can replace or restore dead brain tissue. However, there are methods to help the patient rehabilitate.
With a mild course of the disease and mild symptoms, the most effective will be:
- therapeutic massage course;
- pine and oxygen baths;
- taking statins and tranquilizers;
- gentle diet;
- exercise therapy;
- use of vitamin complexes.
Treatment of the second stage of the disease includes:
- bypass;
Brain shunt
- use of diuretics, anticonvulsants, anticoagulants and vasodilators;
- relaxing massage;
- medicinal electrophoresis;
- surgical removal of blood clots - performed according to individual indications.
The most severe form of the disease is treated with:
- intubation or mechanical ventilation;
- surgical excision of blood clots;
- relief of symptoms of hydrocephalus, which is carried out by taking diuretic drugs and shunting;
- vasodilators, anticonvulsants and anticoagulants;
- electrophoresis and massage;
- physical therapy.
Second stage
It is characterized by worsening neurological symptoms, which are characterized by the formation of an invisible syndrome, however, one that subsequently dominates. In addition, various kinds of extrapyramidal disorders can be detected, as well as ataxia, pseudobulbar syndrome, and even CN dysfunction. It is interesting that over time the complaints become less and less pronounced; they are no longer so acutely perceived by the patient himself. However, at this time the emotional background worsens and intensifies. There is an increase in cognitive function, up to the onset of neurodynamic disorders, which can later be supplemented by dysregulatory syndrome.
In addition, at the second stage, the patient’s ability to control his own actions deteriorates, and there are also difficulties in planning what the person wants to do at the next point in time. Although there is a violation in the performance of actions, the ability to compensate remains for a long time. In addition, signs of reduced social adaptation appear.
Classification of the disease
The main division of the disease suggests the existence of several variants of the course, namely:
- cerebral ischemia grade 1 - characterized by mild symptoms. However, if the disease is diagnosed at this stage and appropriate treatment is carried out, then the likelihood of complications will be minimal;
- cerebral ischemia stage 2 - clinical signs will be more striking than at the previous stage, and attacks will be longer. If the symptoms are identified in a timely manner, then the chances of a successful outcome and full recovery remain;
- cerebral ischemia of the 3rd degree - differs in that the symptoms are so severe that all therapeutic manipulations are carried out only in intensive care conditions. This is the most dangerous form of pathology, leading to irreparable consequences.
In addition to the above forms of the disease, it is also divided into:
- acute cerebral ischemia - it is advisable to refer only to newborns, since in adults it is often secondary in nature and has a sluggish course;
- chronic cerebral ischemia is the most common type of disease, because oxygen starvation and insufficient blood supply to the brain develops quite slowly.
Third stage
It is distinguished by a clear manifestation of neurological syndromes. In this case, there is a disturbance in walking and the ability to maintain balance (the patient may often fall). Urinary incontinence is observed, and parkinsonian syndrome is also characteristic. Due to the absence or decrease in a sober understanding of what is happening to the patient, the volume of his complaints decreases.
Personality disorders can manifest themselves as inhibited reactions, explosive states, apathetic-abulic symptoms and psychological abnormalities. In addition to neurodynamic (or dysregulatory) disruptions in the cognitive sphere, the manifestation of such operational disorders as speech and memory impairment, decreased thinking ability, etc. is possible. All these symptoms can later develop into dementia. The latter leads to an inability to quickly adapt to a new situation and to a drop in performance in personal, social and professional areas of life. Very often, doctors indicate a person’s inability to work. At a certain point, the patient stops caring for himself.
Instrumental studies
In order to determine the degree of damage to the blood vessels of the brain, as well as its substance, and to detect any other underlying diseases, doctors recommend undergoing such instrumental studies as:
- ECG;
- echocardiography;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- Doppler ultrasound (primarily, this study is performed for the main arteries of the head);
- cervical spondylography;
- triplex (or duplex) scanning of vessels of intracranial and extracranial types;
- vascular angiography (to detect vascular anomalies).
All patient complaints usually characteristic of the chronic type of cerebral ischemia can also be detected in various somatic pathologies and in some cases in oncology. The symptoms inherent in chronic cerebral ischemia can also be signs of various mental disorders and endogenous disorders. Therefore, differential diagnosis is necessary. But it will be problematic because chronic cerebral ischemia is often confused with neurodegenerative diseases, which share the same cognitive impairments and neurological manifestations.
Diseases with which chronic cerebral ischemia should be differentiated are:
- progressive supranuclear palsy;
- Parkinson's disease;
- corticobasal degeneration;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- multiple system atrophy.
Very often it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of this disease with malignant and benign brain tumors, idiopathic dysplasia, normal pressure hydrocephalus and ataxia.
Treatment
Mostly conservative. Operations according to indications. The point is to restore normal cerebral blood flow.
To do this, it is necessary to eliminate the root cause of hemodynamic disturbances. There are a lot of options here.
If hypertension is to blame, systematic use of medications to lower blood pressure is prescribed.
- ACE inhibitors.
- Mild diuretics.
- Calcium antagonists.
- Beta blockers and other drugs of this kind, including central effect (Moxonidine, as an option).
Endocrine pathologies are controlled by hormonal replacement. Depends on the specific form of the disease.
A decrease in myocardial contractility, heart failure requires the use of glycosides (Digoxin) in combination with drugs to activate metabolic processes in the heart muscle (Riboxin or Mildronate).
Dosages are determined by a specialist; both categories of medications are potentially dangerous when used independently.
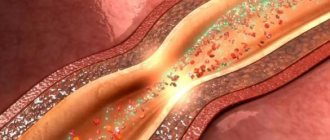
Atherosclerosis is considered the number one cause. This is a narrowing or, more often, blockage of blood vessels with cholesterol plaques. Statins are used. Special preparations for the destruction of fatty deposits and the removal of excess lipids. This is the basis of therapy.
As for symptomatic effects. The following groups of medications are prescribed:
- Cerebrovascular. Normalize brain nutrition and accelerate blood flow. Vestibo, Actovegin, Piracetam and others. There are many names.
- Antispasmodics. Eliminate pathological tension in the walls of blood vessels.
- Analgesics. To relieve headaches when they occur.
- Angioprotectors. To protect arteries from negative influences.
- Antiplatelet agents. Restore blood fluidity. Prevents the formation of blood clots.
All names are selected only by a doctor. Self-medication is fraught with complications and death.
With the development of infectious diseases, the use of antibiotics and detoxification is indicated. It is important to use diuretics to prevent brain swelling and early death.
Surgical treatment is prescribed in extreme cases. The reasons for treatment with surgical methods are arteriovenous anomalies, aneurysms and malformations, obstruction of neck vessels (basilar, etc.), advanced atherosclerosis with plaque hardening, brain tumors.
Therapy can last a long time, from six months to 12 months. Depends on the severity of the condition. In some cases, the use of drugs is a lifelong measure. This is the key to permanent compensation for deviations.
Treatment of chronic cerebral ischemia
The main goal in the treatment of chronic cerebral ischemia is to stabilize the destructive process of cerebral ischemia in order to restore blood circulation in the vessels. Proper treatment will help slow down the rate of disease progression by activating the sanogenetic mechanism of function compensation. Therapy also involves the prevention of this disease and its attendants.
Pathology is not an indication for urgent hospitalization of the patient. Treatment in a hospital is necessary when the course of the disease is complicated by the development of a stroke condition or severe pathology. If a cognitive type of disorder is detected, if the patient is deprived of his usual environment, the condition may worsen.
Treatment of chronic ischemia is usually carried out by a neurologist on an outpatient basis. If the disease develops to stage 3, doctors prescribe patronage.
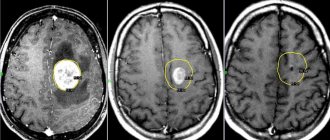
What to do if MRI shows chronic ischemia?
If, when decoding the results of a head scan, the presence of ischemic brain disease is detected, it is recommended to consult a neurologist. You may need to consult a therapist or cardiologist. To slow the progression of ischemic damage, it is necessary to achieve target levels of blood pressure, blood glucose and cholesterol levels. Doctors will evaluate metabolic changes and select treatment to compensate for chronic diseases.
The diagnostic department performs MRI of the brain from 2,690 rubles. Contrasting is carried out from the age of 12. You can ask the administrator any questions you may have by calling +7 (812) 407-32-31.
Antihypertensive therapy
Antihypertensive therapy is aimed at maintaining normal blood pressure and stabilizing the state of chronic ischemia. If doctors prescribe antihypertensive drugs, the patient should be careful and monitor for fluctuations in their blood pressure. As is known, in the case of developing chronic ischemia, the mechanism of autoregulation of cerebral blood flow begins to work intermittently.
If we talk directly about antihypertensive drugs prescribed by doctors, then first of all we are talking about medications of two groups:
- angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors;
- angiotensin II receptor antagonists.
Drugs of both the first and second groups are capable of simultaneously exerting two effects: in addition to angiohypertensive, they are also angioprotective, which means protecting the affected organs, which usually include the kidneys, heart and brain. The effect of antihypertensive drugs usually increases significantly when they are combined with antihypertensive drugs such as hydrochlorothiazide and indapamide.
Combination drugs
In addition to the main therapy described above, depending on the mechanism that caused the disease, individual treatment is prescribed, which is designed to normalize the rheological properties of the blood and improve venous blood flow, bringing microcirculation back to normal. Typically, such drugs have neurotrophic and angioprotective properties. For example, a doctor may prescribe one of the following combinations:
- cinnarizine (no more than 75 mg) together with piracetam (1-1.2 g per day);
- piracetam (no more than 1.2 g) with vinpocetine (15 mg per day);
- nicergoline (no more than 30 mg per day) and pentoxifylline (approximately 300 mg per day).
Typically, such combinations of drugs are prescribed no more than twice a year, each course lasting approximately 2 months.
Prognosis and prevention
With timely diagnosis and correctly prescribed treatment, it is most often possible to stop the progressive course of chronic cerebral ischemia. If the disease is quite severe, being aggravated by parallel pathologies (for example, diabetes mellitus or hypertension), there may be a noticeable decrease in the usual ability to work, and sometimes even to the point of complete disability of the patient.
Among the preventive measures that can prevent this disease are the following:
- prevention of obesity in general, and in particular, obesity of cerebral vessels;
- active lifestyle;
- giving up alcohol and smoking;
- avoidance of stressful situations.
An important preventive measure will be the prevention of hypertension and diabetes. Not everyone knows that atherosclerosis can also contribute to the development of chronic cerebral ischemia, so it must be dealt with in the early stages.
As soon as a person discovers the first symptoms of chronic cerebral ischemia, one should immediately reduce the amount of alcohol consumed (or better yet, give it up altogether), reduce physical activity and avoid direct sunlight.
Prognosis, disease prevention
If the dynamics of chronic cerebral ischemia are suspected, timely diagnosis and the prescription of adequate drug therapy are important. The course of the disease is significantly worsened by the presence of concomitant pathological conditions - hypertension, diabetes mellitus. In severe clinical cases, the patient may become disabled.
Prevention consists of preventing the development of ischemic factors. Risk factors include: obesity, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, frequent stressful situations.