Ivan Drozdov 08/01/2019 0 Comments
An arachnoid cyst is considered one of the most common benign formations that form in brain tissue. It received its name because of its location - a capsule filled with cerebrospinal fluid is located in the arachnoid membrane of the brain. In ICD 10, an arachnoid cyst is classified as code G93.0 “Cerebral cysts.” If there is no tendency to grow, the tumor may be asymptomatic, otherwise signs of compression of brain tissue will significantly worsen well-being and quality of life.
Classification
According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), pathology is assigned code Q04.6.
The classification of the disease is related to the location of the pathology, and the following types are distinguished:
- Arachnoid - located between the three membranes of the brain; in children, this neoplasm can provoke hydrocephalus and an increase in the volume of the skull. When diagnosing a cyst in adults, treatment is most often not required, of course, if there is no growth of pathology.
- Retrocerebellar - localized inside the organ, this neoplasm can lead to the death of brain cellular structures.
- Subarachnoid is a congenital neoplasm that can cause unsteadiness in gait, convulsions and pulsating sensations inside the skull.
- Arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst - occurs in people of an older age group or those with atherosclerotic changes.
In accordance with the causes of the pathology, arachnoid cystic pathologies are divided into:
- congenital - their development occurs during the period of fetal growth in the mother’s womb, as well as during asphyxia of the child.
- acquired - develop after certain diseases, as well as under adverse environmental influences.
There is a classification of cysts according to symptoms: progressive - clinical signs increase, which is mainly due to an increase in the volume of the cystic cavity; frozen - are in a latent state and do not increase in size.
Important! To choose the correct and most effective therapy, it is very important to correctly classify the cyst.
Dimensions and norm
Patients are often interested in the question of the normal size of the cyst and the volume at which surgical intervention is necessary.
It must be said that we can speak of normality only in the absence of a cystic neoplasm; if there is a cyst, then this is already an anomaly, and its size essentially does not matter much.
This type can have different sizes, but the cyst still cannot grow very much. Brain fluid resists its growth. If the size of the cyst is 1-2 mm, it is considered small; if the neoplasm grows to 1 cm, it is considered medium; cysts larger than 1 cm are considered large.
When diagnosing small cysts, doctors, as a rule, do not prescribe treatment, but choose a wait-and-see approach and simply monitor changes in the volume of the tumor. Large cysts are treated surgically; surgery is also indicated for medium-sized tumors when symptoms appear.
Causes
Primary (congenital) cysts are formed due to abnormalities in the developing fetus, most often this occurs under the influence of the following factors:
- intoxication of the fetus with narcotic substances, alcohol, nicotine, medications that have a teratogenic effect;
- intrauterine infection of the fetus with viruses;
- irradiation;
- severe overheating of the body during pregnancy.
In addition, the formation can occur with Marfan syndrome - this is an anomaly of connective tissue, as well as with pathologies of the corpus callosum.
Secondary pathologies can develop when:
- brain injuries;
- pathological processes in the brain, for example, degenerative;
- in the presence of infections;
- deterioration of cerebral circulation.
In addition, pathology can be observed after surgery.
The mechanism of development of this neoplasm is quite complex and is associated with impaired circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid. As a result, a cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid is formed.
Causes
Congenital arachnoid cysts are formed as a result of disturbances in the process of intrauterine development of the brain. The factors that determine their formation include various harmful effects on the fetus that occur during pregnancy. These can be intrauterine infections (toxoplasmosis, rubella, herpes, cytomegaly, etc.), intoxication (occupational hazards, alcoholism, smoking, drug addiction, taking pharmaceuticals with a teratogenic effect), radiation exposure, overheating (a pregnant woman visiting a sauna or bathhouse, excessive insolation, habit of taking hot baths). Cysts localized in the arachnoid membrane are often observed in patients with Marfan syndrome and hypogenesis of the corpus callosum. Acquired arachnoid cysts occur after traumatic brain injury (concussion, brain contusion), and can also be a consequence of brain surgery. The formation of a secondary cyst is possible after meningitis, arachnoiditis or meningoencephalitis. Arachnoid cyst formation may occur after resolution of subarachnoid hemorrhage or subdural hematoma. Factors that can provoke the formation of an arachnoid cyst can also cause a progressive increase in the volume of a small subclinical cystic formation previously existing in the arachnoid membrane due to overproduction and accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in it.
Symptomatic manifestations
This cystic neoplasm is characterized by an asymptomatic course .
Most often, such neoplasms are detected during a patient examination for neurological pathologies with similar symptoms.
The clinical signs of the cyst are nonspecific; their severity depends on the size of the tumor and its location. Patients may complain of general cerebral symptoms, which are associated with compression of brain areas. A focal clinical picture is observed in rare cases, and is most often caused by the presence of hygroma or rupture of the cystic cavity.
The main features are:
- dizziness , which are not associated with pregnancy, taking certain medications, severe fatigue, iron deficiency, and so on;
- vomiting , which is also not associated with gastrointestinal poisoning, taking medications, and so on;
- mental disorders, hallucinations ;
- convulsive syndrome;
- loss of consciousness;
- hemiparesis , decreased sensitivity in the limbs;
- failure to coordinate the activity of the body muscles;
- headaches that are not relieved by painkillers;
- a feeling of fullness , pressure, compression and increased pulsation in the affected area;
- visual and hearing problems;
- extraneous sounds in the ears;
- heaviness in the skull;
- painful or uncomfortable sensations when turning the head.
Reference! Secondary arachnoid cystic neoplasms may be accompanied by symptoms of injury or primary disease, which served as an impetus for the development of the disease.
Symptoms of an arachnoid cyst
Depending on the location and size of the cyst, one or more symptoms may appear:
- Headache;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Lethargy, including excessive fatigue or lack of energy;
- Seizures;
- Developmental delays;
- Hydrocephalus caused by disruption of the natural circulation of cerebrospinal fluid;
- Problems with the endocrine system, for example, early onset of puberty;
- Involuntary shaking of the head;
- Vision problems.
The larger the cyst, the more symptoms will appear, their frequency and severity will increase. With prolonged and strong compression, it can lead to irreversible changes in brain tissue. If excessive compression and rupture of the cyst membranes occurs, the patient may die.
Characteristics by location
The cyst in question may be located:
- in the temporal lobes;
- in the parietal part;
- in the frontal region;
- in the region of the cerebellum;
- in the spinal canal;
- in the spinal column;
- in the lumbar region.
In the posterior cranial fossa
This cyst in the posterior cranial fossa (posterior cranial fossa) is accompanied by symptoms:
- persistent headaches;
- vomit;
- failure to coordinate movements;
- intermittent paralysis of body parts;
- convulsive syndrome;
- mental disorders;
- hallucinations.
According to statistics, tumors of this type are more often observed in men, in addition, the increase in the volume of the cystic cavity in men occurs more actively than in women. With a very large cyst, speech defects, hearing loss, and temporary memory problems may occur.
In the sacral canal
An arachnoid type cyst in the sacral region is a cavity. In it, the spinal membrane forms web-like walls. If the cyst size is more than 1.5 cm, the patient may complain of:
- lower back pain with increased loads;
- numbness, paresis, impaired functionality of the limbs;
- headaches, blood pressure surges, dizziness;
- if the cyst is located at the S2 level, sexual function is impaired, and intestinal problems also arise.
In the temporal lobe
A cyst in the temporal lobe is most often observed on the left side. This is due to the more delicate structure of the left-sided meninges and their increased sensitivity to infections. A person with a cyst in this area experiences:
- unsteady gait;
- lack of motor coordination;
- deterioration of sensitivity of the limbs;
- convulsions;
- blackouts;
- mental disorders.
These symptoms are caused by hydrocephalus - the accumulation of fluid in the skull. A cyst of the right frontal lobe is accompanied by a similar clinical picture.
Retrocerebellar type formation
This is a fairly rare pathology, which is diagnosed in 5% of the population.
This neoplasm combines several types of neoplasms that differ in location:
- arachnoid,
- intracerebral - can form in any part,
- inferior retrocerebellar.
This cyst is spoken of when the tumor is localized only in the cerebellum. In this case we observe:
- migraine;
- vomit;
- paralysis and paresis;
- problems with balance;
- the image before your eyes becomes unclear;
- decreased concentration;
- deterioration of character;
- loss of consciousness;
- twitching of the eyeballs;
- deterioration of thinking;
- violation of orientation in space and time;
- decreased muscle tone.
In children
In children, this neoplasm is diagnosed based on symptomatic manifestations and the child’s medical history.
The specialist will find out whether the child has had injuries or operations in the brain, whether he or she also suffered from meningitis, or whether there have been hemorrhages.
After this, a neurological examination is performed, and a CT or MRI is also prescribed.
It must be said that this pathology is dangerous for the child. It consists in provoking persistent neurological disorders and epileptic seizures.
Under no circumstances should parents independently treat their child, much less let the disease take its course. The baby urgently needs to be shown to a doctor who will prescribe the correct treatment regimen. If the clinical picture is pronounced, surgical intervention may be required.
Clinical picture in a newborn baby:
- strong pulsation in the fontanel region;
- limbs are flaccid;
- unoriented look.
One of the clearest signs of a cyst in a newborn is severe regurgitation during or after feeding.
Useful video on the topic:
Arachnoid cyst of the brain in a child
In children, the formation of an arachnoid cyst manifests itself with more pronounced symptoms, and quite often it is confused with signs of other neurological diseases.
Symptoms that may indicate tumor growth in newborns include:
- copious and frequent regurgitation after feeding;
- decreased muscle tone of the limbs;
- wandering gaze;
- intense pulsation of the fontanel.
As the child grows, the growth of the arachnoid cyst is accompanied by signs of increased intracranial pressure. Compression of brain tissue usually leads to delayed psychomotor, physical and mental development.
Diagnosis and treatment
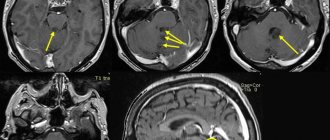
Diagnosis consists of CT or MRI.
Based on the results of these studies, it is possible to accurately determine the presence of a cyst, its size and location.
Since the cyst is considered a consequence of other pathologies, the following is prescribed:
- blood test to detect viruses, infections and autoimmune pathologies;
- prothrombin index;
- blood test for cholesterol levels;
- Doppler of cerebral vessels;
- ECG;
- monitoring blood pressure.
Small and medium cysts are treated conservatively and are prescribed:
- drugs that resolve adhesions - Longidaza, Karipatin;
- means that improve metabolic processes - Gliatilin, Actovegin;
- immunomodulators – Thymogen, Viferon;
- antiviral agents – Amiksin, Pyrogenal.
Complicated cysts, as well as large cysts that provoke an acute clinical picture, are removed surgically. This is, as a rule, an endoscopic intervention - piercing the wall of a cystic neoplasm and pumping out liquid contents from it. If such an operation is impossible, bypass surgery or microneurosurgery is performed.
Treatment with folk remedies
The use of traditional medicine for brain cysts only has a supporting effect, so I use them only when the pathology is asymptomatic. Most often used:
- hemlock;
- Caucasian Dioscorea;
- yeast elixir.
You must understand that it is impossible to cure pathology using traditional methods; they are aimed at cleansing and dilating the blood vessels of the brain, stopping inflammation and having a positive effect on brain function.
Diagnostics
In most cases, an arachnoid cyst is detected by chance, as it rarely manifests itself with pathological signs. In cases where there is a risk of its formation and any neurological symptoms are disturbing, the patient is prescribed an instrumental study aimed not only at visualizing the tumor, but also determining the cause of its occurrence. A comprehensive examination includes:
- MRI – allows you to clearly determine the location, size and etiology of the cyst;
- CT scan – is prescribed to establish the mechanism and causes of tumor formation;
- electroencephalogram - indicated to assess the severity of the consequences of the development of an arachnoid cyst, in particular, with the manifestation of epileptic seizures and other signs of nervous excitability;
- Ultrasound of vessels with Doppler - allows you to assess the patency of blood vessels and the speed of blood flow, on which the sufficiency of blood supply to the brain depends.
- Blood and cerebrospinal fluid tests are prescribed to determine the causes of infectious and inflammatory cysts.
- Assessment of intracranial pressure using lumbar puncture.
Only after a detailed examination and exclusion of other pathologies does the doctor make a definitive diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Development options
Most often, the cyst does not interfere with brain activity. In case of an increase in the volume of the tumor and the appearance of neurological abnormalities, the options for the development of the cyst will depend on the timeliness of diagnosis and correct treatment.
When pressure increases in the head, serious problems with speech, hearing, vision and memory can occur. Persistent neurological disorders may occur. A sharp increase in the size of the tumor can provoke its rupture and death of the patient. If diagnosis and therapy are carried out on time, the prognosis is quite optimistic and after treatment the patient recovers 100%.
Symptoms
The symptoms are varied, as they directly depend on the disease itself that caused the cyst:
- Feeling of pressure or pounding in the head.
- Headache.
- Pulsation in the head.
- There is noise in the ear, but the hearing remains normal.
- Double vision, spots before the eyes.
- Episodic loss of consciousness.
- Hearing impairment.
- Paresis of a leg or arm.
- Poor coordination.
- Symptomatic epilepsy.
- Numbness of various parts of the body.
There may be no symptoms at all if the cyst appeared as a result of a long-term illness, or was congenital.