Based on modern ideas about the mechanisms of development of ischemic stroke, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital identify 2 main directions of pathogenetic therapy: improving the perfusion of brain tissue (the passage of blood through them) and neuroprotection (a set of measures aimed at improving the biochemical and restorative properties of the nerve cell).
Complex therapy of ischemic cerebral stroke
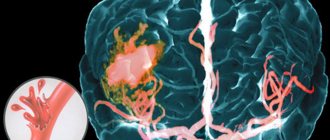
It is known that in the absence of adequate therapy, approximately 2 million neurons die within ten minutes of ischemia. Each stage of the ischemic cascade is a potential target for therapeutic intervention. The earlier neuroprotective treatment is started, the greater the chances of success, the less the degree of damage to the brain substance.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital begin complex therapy for ischemic stroke immediately after the patient is admitted to the neurology department and an accurate diagnosis is established. Neurologists draw up treatment regimens for patients with cerebral infarction individually, taking into account which vessel has impaired blood flow, the size of the ischemic focus, and how damaged the nerve cells around the area of cerebral infarction are. Due to the fact that the clinic conducts research on modern drugs for the treatment of acute cerebrovascular accidents, patients at the Yusupov Hospital have the opportunity to receive the most modern drugs.
Drug treatment of acute ischemic stroke includes basic and specific therapy. Basic therapy consists of:
- measures to support respiratory and circulatory functions;
- correction of metabolic disorders and the volume of circulating fluid;
- blood pressure control.
The main goal of intensive care is to prevent oxygen deprivation of brain tissue and the associated increase in brain damage. To ensure adequate water-electrolyte balance and blood flow, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital provide infusion therapy to patients with ischemic stroke. The purpose of infusion therapy is:
- achieving blood thinning;
- maintaining adequate cerebral perfusion pressure (a physiological indicator characterizing the level of blood supply) not lower than 70 mm Hg. Art. to eliminate ischemia and oxygen starvation of neurons;
- correction of electrolyte disturbances, primarily high or low sodium levels in the blood.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital achieve a normal level of cerebral perfusion pressure in patients with ischemic stroke by increasing systemic arterial pressure and decreasing intracranial pressure. To increase blood pressure, crystalloid solutions and sympathomimetics are administered intravenously.
In case of ischemic stroke, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital maintain the patient’s circulating blood volume at the proper level and prevent the development of hypovolemia, which increases the risk of low blood pressure and reduces central perfusion pressure. These changes in the equilibrium of the internal environment of the body lead to vasodilation and increased intracranial pressure.
To maintain the overall water-electrolyte balance and ensure sufficient blood flow in the cerebral vessels, patients with ischemic stroke in the neurology clinic are administered 30-35 ml/kg/day of fluid. Patients who, upon admission to the Yusupov Hospital, have low blood pressure, elevated hematocrit, dry mucous membranes and no decompensated heart failure, are prescribed infusion therapy in a volume of 1000-1500 ml of Ringer's solution or 0.9% sodium chloride solution. Patients with developed cerebral edema are maintained in a negative water balance.
Mechanism of action of nootropic drugs
The mechanism of action of nootropics has not been fully studied to date. However, the principle underlying the therapeutic effect, repeatedly confirmed in vivo, is still of interest to researchers in the fields of biochemistry, cytology and pharmacology. In particular, researchers know that the effectiveness of nootropics in clinical medicine is associated with several mechanisms observed at the cellular level in the central nervous system:
- enhance the synthesis of ATP and its derivatives;
- enhance the process of synaptic transmission in the central nervous system;
- enhance the plastic process in the central nervous system by increasing the synthesis of RNA and proteins;
- enhance the process of glucose utilization;
- have a membrane-stabilizing and antioxidant effect.
Thus, the mechanism of action of nootropic drugs is associated with the restoration of metabolic and bioenergetic processes in the brain, which affect a person’s mood, performance and well-being. A correctly selected nootropic will have the effects necessary for treatment, which manifest themselves over a long period of time, provided that the recommendations of the attending physician are followed (for example, regarding a rational and healthy lifestyle, attending psychotherapy sessions, taking first-line medications).
Rice. 1. Neuron
Treatment of ischemic cerebral stroke with neuroprotectors
Currently, there are many drugs that have a neuroprotective effect. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use only neuroprotectors, the effectiveness of which has been proven by scientific research, to treat ischemic stroke. One of these drugs, which has the most versatile mechanisms of action in relation to oxidative stress (damage to brain cells as a result of oxidation) and a wide evidence base for ischemic stroke, is EMHPS (ethyl-methyl-hydroxypyridine succinate).
In this case, based on clinical experience in the use of EMGPS, the following scheme for its administration is used:
- at the prehospital stage, 400 mg is administered intravenously as a bolus once;
- in the acute period of ischemic stroke (up to 14 days), 5 mg/kg/day is administered intravenously, but more than 800 mg/day;
- during the recovery period (within 14 days), 400–800 mg of the drug 2-3 times a day is administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
One of the mechanisms of the damaging effect of ischemia is cholinergic insufficiency. With pathology of cerebral vessels, the number and size of cholinergic neurons in brain structures decreases. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital use the following regimen for the use of choline alfoscerate for acute ischemic stroke: for the first 3-7 days, 1000 mg is administered intravenously 2 times a day, and from the second week they switch to taking 400 mg of the drug per day 2 times a day (course of treatment - 2 month).
The combination of ethyl-methyl-hydroxypyridine succinate and choline alfoscerate in the context of ischemic stroke allows doctors at the Yusupov Hospital to fully influence the fundamental mechanisms of the development of clinical symptoms associated with ischemia and cholinergic insufficiency.
Drugs with proven effectiveness in ischemic stroke include the cerebroprotector Citicoline. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use it for both primary and secondary neuroprotection. Primary protection of brain cells begins from the first minutes of ischemia and continues during the first three days of stroke, especially active during the first twelve hours. Secondary neuroprotection reduces the severity of long-term consequences of ischemia. Neurologists begin it 3-6 hours after the onset of a stroke and carry it out for at least seven days.
Acetylsalicylic acid as a way to prevent stroke
Do not forget about preventive measures for this disease. The use of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is today considered one of the most important methods of preventing stroke. The fact is that the occurrence of blood clots is the cause of the development of the disease. Acetylsalicylic acid inhibits platelet enzymes that affect vasoconstriction and blood clotting. This mechanism of acid’s effect on platelets reduces blood clotting, which, in turn, has a preventive effect on the human body. The acid can have an irreversible effect on platelets, so a person only needs to take this medicine once a day.
It is important to note the fact that small doses of this substance are just as effective in preventing disease as high dosages. Moreover, since the side effects of acetylsalicylic acid may depend on the dose of the drug, the desire to minimize the dose is a necessity.
The recommended dose for stroke prevention, according to the European Stroke Initiative's Stroke Treatment Guidelines, is 50 mg.
Drugs after ischemic cerebral stroke
In order to prevent recurrent acute cerebrovascular accident. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe antihypertensive drugs to patients who have suffered an ischemic stroke. During your stay at the neurology clinic, cardiologists individually select the most effective drug and its dose. In some cases, it is recommended to take combination antihypertensive drugs.
If there is a depressive state, antidepressants are prescribed. They not only eliminate the patient’s feeling of fear, but also eliminate the negative symptoms that develop as a result of cerebrovascular accidents. If the patient has no contraindications, he is prescribed antiplatelet agents. These include:
- acetylsalicylic acid and its derivatives (Trombo-AS, Aspirin Cardio, Acecardol, Cardiomagnyl, Aspicor, CardiASK);
- ADP receptor blockers (Clopidogrel, Ticlopidine);
- phosphodiesterase inhibitors (Triflusal, Dipyridamole);
- glycoprotein receptor blockers (Lamifiban, Eptifibatide, Tirofiban, Abciximab);
- inhibitors of arachidonic acid metabolism (Indobufen, Picotamide);
- medicines based on the Ginkgo Biloba plant (Bilobil, Ginos, Ginkyo).
Some plants also have an antiplatelet effect: horse chestnut, blueberries, green tea, ginger, garlic. Vitamin E also falls into this category.
In order to receive treatment and rehabilitation after an ischemic stroke with modern drugs, call us by phone. You will make an appointment with a neurologist, who, after the examination, will select an individual treatment regimen. The collective decision on the choice of treatment method for the most severe patients with ischemic stroke is made by doctors of the highest category, candidates and doctors of medical sciences on an expert council.
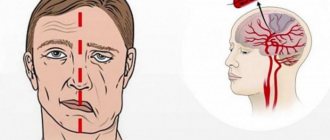
What is a stroke?
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of the human brain is interrupted. Due to the occurrence and development of the disease, patients usually experience paralysis of half the body and deterioration of the patient's speech. Even for a minor recovery of the body after a stroke, a person may need several months, and in some cases, years of rehabilitation. Very often, people suffering from this disease become disabled.
It is for this reason that scientists around the world are developing new and effective methods for treating stroke, and also focusing on the importance of preventing the disease.
The effectiveness of drugs used in chemotherapy
In order to judge the effectiveness of chemotherapy, at least 2-3 cycles of treatment are usually necessary. Then they perform tests that help visualize and measure the tumor, and conduct tests for tumor markers. One of four results is possible:
- Full answer. The tumor has disappeared, the tumor marker level has decreased and is within normal limits.
- Partial answer. The tumor has shrunk, and the tumor marker level may also decrease.
- Stable condition: the size and number of tumors, tumor marker levels have not changed.
- Progression during treatment: the tumor continues to grow, new lesions appear, and the tumor marker level increases.
If the treatment is effective, it is continued according to the previous regimen. Otherwise, combinations of chemotherapy drugs need to be changed.