Indications for therapeutic blockade
- pain in the neck, back;
- osteochondrosis;
- neuralgia, neuritis;
- pain in the spine due to intervertebral hernia;
- rheumatism;
- osteoarthritis;
- pain in the postoperative period;
- phantom pain;
- Minière's syndrome;
- neuropathy;
- spasticity;
- amputation pain;
- pain and spasticity after a stroke;
- radiculitis;
- migraine;
- sciatica;
- tunnel syndrome.
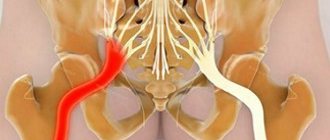
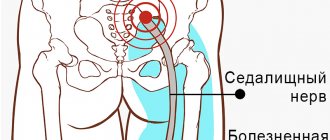
Causes of pinched sciatic nerve
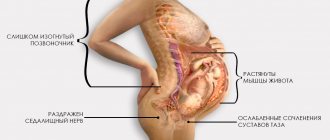
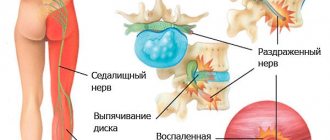
The nature of the development of pathology and clinical manifestations are very diverse. The most common cause of the disease is compression of nerve fibers in the structure of the spine. Pressure on the nerve roots sometimes leads to their inflammation, accompanied by severe pain. Symptoms manifest themselves differently, depending on the location of the pathological process.
- When one of the roots of the sacral nerve plexuses is compressed by a hernial protrusion, the symptoms manifest as sharp pain, intense when coughing and movement. On the first day, signs of impaired skin sensitivity and muscle weakness appear.
- A root pinched by a dense ligament or bone growths, displacement of discs or narrowing of the spinal canal caused by osteochondrosis causes gradually increasing pain and signs of complete or partial paresthesia. Muscle weakness appears later, and if the process is advanced, muscle atrophy cannot be ruled out.
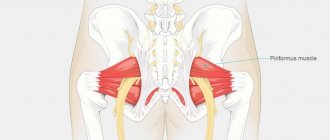
- Compression of the sciatic nerve by muscles (called tunnel syndrome) can be a consequence of articular pathologies, spinal diseases, injuries, flat feet, and unsuccessful injections in the buttock. It manifests itself as pain in the buttock, burning pain in the sole area, loss of control of the functions of the foot.
- Cut and puncture wounds, injuries and bruises of the sciatic nerve are accompanied by moderate pain. By blocking impulse transmission, they can provoke muscle atrophy, the development of paralysis, dry skin and ulcers on the legs.
Kazieva Aminat Ziyavovna
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University
Experience since 2012
A kind of trigger for the development of pain can be:
- the influence of unusual physical activity in patients with a tendency to physical inactivity;
- prolonged stay in a forced position at work;
- vibration or power loads;
- body hypothermia;
- infectious pathologies.
The greatest vulnerability to the development of sciatica is observed in middle-aged and elderly patients. Aging of the body leads to degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs. They become coarser, gradually lose moisture, elasticity and height, which leads to compression of the nerve roots and the development of acute pain.
Types of therapeutic and diagnostic blockades
Local
The injection is made into the affected area, under or around the lesion, into the area of altered tissue reactions, into inflammation, etc. They are divided into periarticular (in the tissue near the joints) and perineural (into the nerve canals).
Segmental
Injections into various segments, these include paravertebral blockades, which are given in the projection of segments of the spine. Each spinal nerve and spinal segment corresponds to a dermatome (a section of the skin, connective tissue), a sclerotome (an area of the skeletal system), and a myotome (part of the muscular system). By injecting the drug intradermally into any dermatome, it is possible to influence the corresponding part of the spine and/or internal organ. The most common indication is myotonic reactions of paravertebral muscles in osteochondrosis.
Vertebral
This therapeutic blockade combines several techniques in neurology. Used for back pain. The anesthetic can be injected intradermally, between the spinous processes of the vertebrae to a depth of 2-4 cm, into the area of the vertebral body. In the latter case, they retreat 3-4 cm to the side from the line of the spinous processes. The needle is directed at an angle of 35° and inserted 8-10 cm in depth.
Spinal blocks
Severe pain in the spine is associated with pinched spinal nerves. The blockade acts in a targeted manner and normalizes well-being. This is not a simple procedure, so it is carried out only as a last resort.
During the blockade, the nerve conduction of certain fibers is temporarily switched off. To do this, local anesthetics are used, which block cellular conduction by inhibiting voltage-dependent sodium pathways.
The procedures are indicated for disc protrusion, osteochondrosis, neuralgia, intervertebral hernia, myositis, spondyloarthrosis. Spinal blocks are cervical, thoracic, thoracolumbar, sacrolumbar, coccygeal, paravertebral. The latter are divided into intradermal and subcutaneous (numb the skin near the spine), intramuscular (relieve muscle spasm and inflammation), perineural ("turn off" the affected nerve).
The effect occurs in a few minutes. At the same time, vascular spasm is reduced, tissue restoration is accelerated, metabolism is normalized, and swelling from inflammation goes away.
Heel spur blocks
Used to relieve inflammation of the heel fascia. The injection is made into the heel spike, in the very center. Hormone-based medications are used. The effect is instant. The difficulty lies in the bone-salt structure of the spine, which complicates the process. The doctor must be highly qualified and experienced. Steroids not only relieve inflammation, but also “accelerate” metabolism. Due to the latter, the bone growth is reabsorbed. Most often, one of three glucocorticosteroids is used: Hydrocortisone, Diprospan or Kenalog. The effectiveness of the method depends 90% on the correct injection. Therefore, the procedure is carried out under ultrasound control. It is extremely painful, so local anesthesia with Ultracaine, Novocaine or other similar medicine is first provided. After the injection, do not step on your heel for 30-60 minutes. Next, to reduce pressure on the heel fascia, special insoles are used.
Joint blocks
They are used for small and large joints when pain is a consequence of a degenerative process or inflammation. The anesthetic is injected into the joint capsule. After this, the pain is completely eliminated. If the case is advanced, then it is significantly reduced. The main indications are bursitis, osteoarthritis of the joints, periarthritis, arthritis of a non-infectious nature, tenosynovitis. The procedure does not require preparation and is performed under local anesthesia. Duration – 20 minutes. The effect occurs within a few minutes. Immediately after administration of the drug, you can move. The duration of the effect depends on the degree of damage to the joint. It averages 21 days. Then repeated blockades are made. Sometimes injections are made not into a joint, but into a muscle. This is necessary to reduce the spasm that causes pain. This group also includes paravertebral blockades. The following joints are treated using this technology: ankle, hip, wrist, knee, shoulder, elbow.
Nerve blocks
An anesthetic is injected into the area along which the peripheral nerve travels. This eliminates pain, vascular spasm, muscle tension, inflammation and swelling. Indications: neuritis, neuralgia, oncology, joint pathologies, muscular-tonic and tunnel syndromes. The procedure can be performed under ultrasound guidance. Duration – up to 10 minutes. The analgesic effect occurs within a few minutes and lasts up to 21 days. Repeated procedures can be performed, except in cases where the effect does not occur after 1-2 injections.
Procedures
To prevent the blockade procedure, treatment of the disease should begin as early as possible. In addition, it is necessary to take into account that therapeutic procedures must include massage. In addition, it is necessary to unblock the sciatic nerve, which consists of performing the following procedures:
- When diagnosing an illness, it is necessary to select a sitting position that is comfortable and does not cause discomfort and pain.
- You cannot stay in one position for more than half an hour.
- It is necessary to reduce the load on the lumbar region.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects during treatment.
Age-related changes lead to loss of flexibility and shortening of the muscular system of the legs, so often after forty years of age, patients turn to specialists with pinched and inflammatory processes in the sciatic nerve. To quickly get rid of the disease, it is necessary to stretch the muscular system of the lower back, using various exercise equipment that allows you to restore blood flow and innervation of the lower extremities.
If it is not possible to visit specialized centers, you can try water aerobics. Water helps reduce body weight, and therefore therapeutic exercises will be much easier to perform. You can also practice on the wall bars, but you will have to do the exercises despite severe algia. As the muscle system stretches, the pain will disappear.
Drugs used for therapeutic blockades
First, let's look at the most commonly used local anesthetics.
"Novocaine"
Can be injected into nerves and tissues, relieves pain and relieves spasms. In the pathological focus, strong irritation occurs and peripheral innervation is switched off. The drug improves tissue trophism, as well as:
- reduces the permeability of vascular walls;
- acts as an antiseptic and bacteriostatic;
- increases resistance to allergens;
- evens out vascular tone;
- improves nerve trophism.
It is considered the safest means of pain suppression, characterized by a minimum of side effects. Has a certain degree of toxicity.
"Lidocaine"
A local anesthetic that provides a more intense and long-lasting effect compared to Novocain. It is used in the form of hydrochloride. Blocks voltage-gated sodium channels, which stops the generation of impulses in nerve endings and blocks the conduction of impulses along nerves. Blocks not only pain impulses, but also others. Dilates blood vessels and has no local irritating effect. A few minutes after the administration of Lidocaine, the pain disappears and the muscles relax. Toxicity is lower than that of Novocain.
"Bupivacaine"
Amide drug. Its effect develops slowly, but lasts for a long time. This is a drug approximately 16 times more powerful than Novocaine. The entire group of amide anesthetics is more stable compared to ester anesthetics (for example, Novocain). Their long-lasting effect is due to the fact that they have a longer half-life. This is due to the fact that drugs are processed not by plasma, but by the liver. Bupivacaine prevents the pain impulse from spreading along the nerves by blocking sodium channels in the neuron membrane. The blockade is sequential, depending on the size of the nerve fibers (small ones are more sensitive compared to large ones), the degree of activation (a higher frequency of impulses opens more channels for blocking), and the degree of myelination (fibers with a myelin sheath are blocked better). The effect of the procedure occurs within 5-10 minutes.
Now let's move on to the most popular glucocorticosteroids. Drugs in this group are designed to enhance the effectiveness of the blockade, relieve inflammation and allergic reactions. Can also be used independently.
"Hydrocortisone"
Belongs to a group of drugs with a short duration of action. Contains artificial hormones that are similar to those produced by the adrenal glands. It is used to treat heel spurs with a course of 3-5 injections. The active substance of the drug accumulates in tissues, relieving inflammation. The main advantage is low price. However, it loses to Diprospan in terms of effectiveness.
When injected into joints together with Lidocaine, the effect develops within 24 hours and lasts up to several weeks. Able to increase blood pressure while simultaneously reducing the concentration of lymphocytes. Thanks to the first, the volume of blood circulation increases, and the second, the intensity of the immune response decreases. The drug is suitable for neurological blockades. For peri- or intra-articular blockades, it is necessary to mix the microcrystalline suspension with a local anesthetic to prevent necrosis.
"Dexamethasone"
Long-acting glucocorticosteroid. One of the most powerful drugs. It has a pronounced anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, immunosuppressive and desensitizing effect. It works especially well when used together with an anesthetic for degenerative pathologies. Reduces inadequate response to anesthetic drugs. Acts quickly, suitable for blockades of soft tissues and joints. Compared to Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone is 25-30 times more active. There are no known cases of necrosis with its use; it has little effect on electrolyte metabolism.
"Depo-Medrol"
Methylprednisolone acetate is a long-acting form of methylprednisolone. This is due to poorer solubility and lower metabolization activity. Used for blockades of soft tissues and joints. For epidural blocks - with caution, because it can provoke inflammation of the arachnoid membrane.
Used to treat all joints, with the exception of those that are difficult to reach and do not have a synovial cavity. When injecting into the hip joint, it is necessary to avoid entering large vessels. Injections into the tissue surrounding the joint may have little or no effect. If there is no positive effect from the first injection, the procedure is not repeated.
"Diprospan"
A drug based on betamethasone. Used to treat heel spurs. Provides rapid analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. Relieves allergic reactions. Usually it allows you to cure a spur in 1-2 sessions. A significant drawback is the destructive effect on the adrenal glands and pituitary gland. However, the likelihood of complications in this drug is sharply reduced compared to analogues. It differs from other similar drugs in its microcrystalline structure. Can be used for epidural blockades, as well as blockades of spinal nerves, muscles, etc. It is effective for destructive-dystrophic diseases of the spine, in particular the lumbar region.
Medicines
Naproxen
Before prescribing a nerve block to a patient, the specialist prescribes non-steroidal drugs to relieve the inflammatory process. After such therapy, significant relief occurs, but the treatment does not stop there. These drugs are presented:
- Aspirin.
- Dexibuprofen.
- Ibuprofen.
- Flurbiprofen.
- Naproxen.
- Tolmetin.
The above medications should not be taken for more than a week, as long-term use can cause heart problems and stomach bleeding. To relieve pain, the doctor may prescribe medications such as:
- Opioids.
- Numorphan.
- Oxycontin.
- Percocet.
- Percodan.
- Vicodin.
Despite the fact that these drugs are good at eliminating painful sensations, they are highly addictive to the body, and if they are discontinued, the pain intensifies, causing a condition similar to drug withdrawal withdrawal. For this reason, they should be taken only to relieve severe algia.
Non-addictive drugs include Tramadol in combination with Paracetamol. They not only help relieve pain, but also relieve inflammation. A pepper patch applied to the lower lumbar region and physiotherapeutic procedures are also good for this purpose.
If these procedures do not have an effect, a specialist will prescribe a blockade for pinching the sciatic nerve using novocaine and lidocaine.
Possible complications and measures to prevent them
Therapeutic blockades have an extremely low rate of complications - 0.5%. These may be reactions to drugs, symptoms of intoxication (vomiting, dizziness, palpitations), damage to blood vessels at the injection sites. To prevent complications, additional medications are administered, and after the procedure the patient is recommended to lie down for 1-2 hours. It is not recommended to immediately put a lot of physical strain on yourself, which often happens because people get rid of pain. If you are not careful with your physical activity, the symptoms will return and be more severe.
With spinal blockades, bleeding, infection of the puncture, damage to the internal membranes and soft tissues are possible. The latter is usually due to the doctor's inexperience. Anaphylactic shock may also develop. Therefore, the procedure is carried out only in a medical facility. To prevent complications, a test injection is given.
When blocking a heel spur, 15-20% of people experience complications. Most often they occur due to improper administration of glucocorticosteroids and individual reactions to them. This may be the death of soft tissues, suppuration, or rupture of the heel fascia. You need to independently examine your heel every day after the procedure in order to notice a negative reaction in time. Its first signs are pain, blackening and/or redness of the skin, and numbness. Complications may be delayed and occur even several weeks after the procedure. This is explained by the prolonged action of glucocorticosteroids.
How to speed up the treatment process?
Advertising:
It is strictly forbidden to prescribe injections to yourself without consulting a treating specialist for neuritis. Only he will be able to select the correct and safe dose that will not cause side effects or serious complications. During injections, you can follow these recommendations to speed up the recovery process:
- Do regular or cupping massage regularly. It is best to use anti-inflammatory warming ointments for this.
- Apply with heated wax. This is very simple to do: treat the skin of your back with any fat, and then apply heated beeswax to it. Apply in several layers, then cover your back with cellophane and wrap yourself in a warm blanket. When the wax has cooled completely, you can remove it.
- Rub your back with tincture of pine buds or dandelion flowers. You can prepare it yourself or find it in any pharmacy.
- Don't forget to exercise regularly. When the pain subsides, sit on your buttocks and move around the room, do a bicycle, rotate your hips, stretch. This way you can get your muscles back into shape.
A qualified physician can determine effective medications and treatment for sciatic nerve pain, the symptoms of which are pain. We strongly do not recommend giving yourself injections at home.