Causes of pain
Painful sensations in the ear area and the right side of the head can occur due to inflammatory processes, as well as when the blood circulation in this area is impaired. The process can spread from the organ of hearing to part of the head and vice versa. When the first complaints appear, it is necessary to undergo an examination and determine their cause.
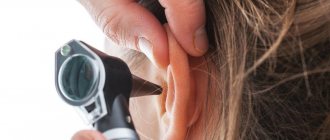
Otitis
Ear inflammation (otitis) can occur in adults and children. It occurs as a complication of viral diseases (ARVI, influenza), injuries, hypothermia or inflammation of the sinuses. At the first stage, the patient is bothered by constant pain in the ear, which spreads to the entire surface of the head. However, otitis media can progress and develop in several stages:
- aseptic inflammation, which causes aching pain;
- addition of a bacterial infection;
- development of purulent inflammation - accompanied by acute pain and hearing impairment;
- probable complications in the form of purulent melting of the eardrum, as well as the spread of infection to the inner ear and lining of the brain.
Otitis media is often chronic and appears annually. After an examination, an otolaryngologist will help you choose the most effective treatment regimen. It is important to pay attention to the first symptoms in time, since the chronic course of the inflammatory process can provoke partial or complete hearing loss.
Diseases of the external ear
The outer ear is the peripheral part of the hearing organ, which is separated from the middle part by the eardrum. Pathological processes in this area often manifest as acute pain in the right ear and head. With timely treatment, they resolve without complications, but in the absence of intervention they can spread to the middle and inner ear.
- Furunculosis, eczema, fungal skin infections - these processes are accompanied by inflammation and pain. The skin of the auricle turns red and peels, and ulcers (boils) may form on it. Treatment consists of external use of anti-inflammatory and antifungal drugs.
- Diseases that lead to the formation of cerumen plug - it forms deep in the ear canal, so it is impossible to remove it yourself. The cause may be anatomical features of the structure of the hearing organ or excessive formation of sulfur.
- Injuries, falls and bruises are another cause of inflammation of the outer ear. In young children, the process can be triggered by foreign objects entering the ear canal.
When diagnosing, it is important to assess the condition of the eardrum. Inflammatory processes can spread to it and even cause its perforation. Injuries that cause damage are also dangerous.
Inner ear diseases
Inflammation of the inner ear is the cause of acute pain in the right side of the head and in the ear. The organ has a complex structure and is responsible not only for hearing, but also for balance. It is presented in the form of channels and labyrinths filled with liquids. This is where bacteria multiply, causing inflammation.
Diseases of the inner ear require immediate treatment; in most cases, antibiotic therapy is used for this. The tympanic cavity is a comfortable environment for the growth of bacteria, and they can cause purulent inflammation. This leads to hearing loss, constant headaches, and the development of complications, including acute meningitis - inflammation of the membranes of the brain.
Change in blood pressure
An increase or decrease in blood pressure is a common reason why the right ear and the right side of the head hurt. Hypertension (high blood pressure) occurs due to insufficient elasticity of blood vessels, nervous tension and other factors. It manifests itself with characteristic symptoms:
- pressing headache that spreads to the back of the head, temple, and may affect the ear;
- deterioration of hearing and vision, the appearance of tinnitus;
- redness of the skin and mucous membranes, the appearance of small capillary hemorrhages.
With a decrease in pressure (hypotension), an increase in heart rate, weakness, and impaired coordination of movements are observed. The skin and mucous membranes may become pale. Insufficient oxygen supply to the brain is dangerous, as it can provoke a stroke or transistor ischemic attacks.
Stroke
Acute cerebrovascular accident is a stroke. It occurs when there is a sudden stop in the flow of oxygen-rich blood to certain areas of the brain. There are ischemic (manifested by blockage, compression of a vessel, low blood pressure) and hemorrhagic (the result of damage to an artery and hemorrhage in the brain) stroke. The first type is more common and is manifested by the following symptoms:
- sudden headache, often one-sided, which may affect the ear;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- weakening of the facial muscles on the injured side;
- discomfort and pain behind the sternum;
- impaired diction, the appearance of memory lapses;
- loss of consciousness.
The main reason why strokes occur is the lack of early diagnosis. Doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute recommend undergoing regular scheduled examinations to identify cardiovascular diseases in the early stages. Monitoring blood pressure, proper nutrition and dosed exercise, as well as systematically taking medications as needed are the basis for preventing stroke at any age.
Pain in the ear and right side of the head due to neuralgia
If your head hurts and radiates to your right ear, this may be a sign of neuralgia. This is not a separate disease, but a type of pain that occurs when a nerve is inflamed or damaged. The trigeminal nerve is most often affected, which gives off branches to the muscles of the face, the organ of hearing, the upper and lower jaws.
Neuritis is an inflammatory process that develops in nerve fibers. It is accompanied by acute throbbing pain, which can be one-sided, affecting part of the head, ear and half of the face. It intensifies with sharp sounds, bright lighting and other irritants, as well as with chewing and turning the head. Treatment consists of taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. If they are ineffective, a nerve block is indicated - injections along its course with anesthetics and hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs.
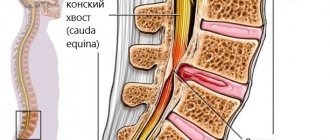
Diseases of the cervical spine
The cervical spine contains arteries that carry blood from the heart to the brain, analyzer organs, muscles and facial skin. Their mechanical pinching leads to impaired sensitivity in certain areas and chronic headaches. Normally, the vessels are located in the canals formed by the processes of the vertebrae, and blood moves freely through them. However, there are a number of diseases that lead to poor circulation, pain in the head and ear:
- osteochondrosis is a pathology of intervertebral discs, in which they become fragile and cannot absorb movement, and the distance between adjacent vertebrae decreases;
- spondylosis - fusion of two or more adjacent vertebrae as a result of injury, inflammatory or dystrophic changes, destruction of cartilage;
- curvature of the spine, most often cervical scoliosis;
- chondrocalcinosis - deposition of salts in the periarticular tissues, which leads to decreased joint mobility;
- intervertebral protrusions and hernias - protrusion of intervertebral discs, their gradual erasure until the outer fibrous membrane ruptures;
- vertebral displacement.
Spinal diseases often manifest as headaches. It can be one-sided, since the load on the spinal column becomes uneven, and mechanical compression of the vessels and nerves occurs.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes
Lymphadenitis is inflammation of the lymph nodes. Pain in the right ear and right side of the head can be caused by damage to the parotid lymph nodes. It is acute, pulsating, and may be accompanied by fever. The disease occurs as a complication of a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract; a bacterial or fungal pathogen can also be diagnosed.
With lymphadenitis, redness of the skin behind the ears and the appearance of a hard lump may be observed. The local temperature is increased and pulsation is felt. Treatment consists of taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and painkillers.
Why do my ears hurt?
Ear pain occurs for various external and internal reasons:
- ear injury. An accidental blow can damage the cartilage and external auditory canal. Sometimes pain occurs when there is strong pressure on the ear: for example, when wearing a tight hat or headphones;
- entry of a foreign object into the external auditory canal. Most often, this problem occurs in young children;
- damage to the lining of the external auditory canal. A careless attempt to remove accumulated wax from the ears can damage the thin skin of the external auditory canal. The scratch becomes inflamed and swollen, an unpleasant aching pain appears;
- ingress of water while swimming. One of the most common causes faced by both children and adults. To avoid getting water when immersed in water, it is recommended to use earplugs;
- exposure to loud noise. WHO estimates that about 1.1 billion people are at risk of hearing damage in entertainment settings due to music or noise that is too loud. This exposure is usually accompanied by minor ear pain. No less dangerous is constant exposure to noise pollution (for example, in some industries), which leads to the development of hearing loss, but is not accompanied by pain;
- accumulation of large amounts of earwax. A cerumen plug forms, which presses on the walls of the ear canal, causing pain.
Symptoms of ear diseases:
- painful sensations in the ear;
- deterioration or loss of hearing;
- feeling of ear fullness;
- pathological discharge from the ear;
- dizziness, balance disorder;
- noise in ears.
Diagnostic methods
At the Clinical Brain Institute, a complete diagnosis is carried out, which examines all possible causes of pain in the right ear and right side of the head. The initial appointment is carried out by a therapist. Based on anamnesis (medical history), examination and questioning, the patient receives a referral to a specialist. To exclude diseases of the hearing organ or paranasal sinuses, consultation with an otolaryngologist is necessary, or if a neurological picture is present, a neurologist. If you have high blood pressure, it is recommended that you undergo regular scheduled examinations with a physician.
To obtain a complete picture of the disease, an individual diagnostic regimen is prescribed. It may include the following steps:
- general and biochemical blood tests - will show the concentration of leukocytes (an indicator of the inflammatory process), deficiency of important microelements, as well as glucose levels;
- additional tests - studies to determine the gas composition of arterial blood (to detect hypoxia) and hormones;
- MRI and CT are the most accurate and informative ways to assess the condition of the brain; they are prescribed for suspected neoplasms, various defects of nervous tissue, and pathological changes in blood vessels;
- electroencephalography - a method for assessing the bioelectrical activity of brain tissue;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head (Dopplerography) - indicates areas of narrowing of the arteries, impaired blood flow and other pathologies;
- examination by an otolaryngologist to identify diseases of the hearing organ.
Based on the diagnostic results, an individual treatment regimen can be prescribed. It is important to go through all the stages and carry out the necessary tests. At the Clinical Brain Institute, examinations are carried out using modern equipment, which allows you to obtain the most accurate results.
What is otitis media and how does it manifest?
Ear pain is often caused by otitis media, an infectious inflammation of the hearing aid. Otolaryngologists distinguish three forms of the disease:
- otitis externa A disease of the outer ear in which a purulent boil forms in the ear canal. If the inflammation is not treated, it spreads to the eardrum, which causes not only pain, but also hearing impairment;
- Otitis media Develops when an infection enters the middle ear. Causes shooting pain and a feeling of pressure. The patient's temperature rises, pus or ichor may be discharged from the ear;
- internal otitis or labyrinthitis. Otitis media can spread to the inner ear and cause labyrinthitis. Symptoms of otitis media include severe headaches, loss of balance, and dizziness.
Otitis can be acute and chronic. In the acute stage, the disease is manifested by high fever (38.5℃), weakness, lethargy and apathy. Chronic otitis media leads to a gradual decrease in hearing; the pain may not be severe, but constant.
What to do if your ear and right side of your head hurt
Treatment is selected individually, depending on the nature and intensity of the pain syndrome, the exact diagnosis, the patient’s age and other factors. The scheme may include several stages that are combined with each other.
- Drug treatment: in the first stages, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Meloxicam and others) are prescribed. They affect inflammatory processes of any origin, not complicated by bacterial infection. To relieve episodic pain, analgesics are used - painkillers (Analgin).
- Antibacterial therapy: antibiotics are indicated for purulent inflammation, as well as to prevent its development. These drugs are often prescribed for otitis media.
- Muscle relaxants are used in addition to the main treatment regimen (Mydocalm). These drugs help relax muscles and relieve vascular spasms.
- Nootropics are a group of drugs to improve blood supply to the brain (Glycine, Phenibut). The decision about their effectiveness for various disorders is made by the attending physician.
- Surgical treatment - surgery is prescribed only if conservative methods do not bring results. It may be necessary for purulent otitis, some pathologies of the cervical spine, and the consequences of injuries.
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of headaches. The center is equipped with the necessary technical facilities for a full examination of patients. Treatment is carried out both on an outpatient basis and in a hospital, with constant supervision by competent specialists. Doctors recommend not to endure pain in the ear and head, especially if it is intense or occurs frequently - timely diagnosis and initiation of treatment will prevent dangerous consequences.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 4/5 — 10 votes
Share article on social networks
Why does it shoot in my ear?
Acute shooting pain in the ear can be a symptom of infection; severe and severe pain is caused by diseases such as:
- mastoiditis – inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone, accompanied by the accumulation of pus;
- Otitis externa is an inflammation of the outer part of the ear, which includes the pinna, external auditory canal and eardrum;
- Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle section. Usually develops as a complication of other ENT infections: for example, tonsillitis or laryngitis;
- Labyrinthitis is an irritation of the inner ear caused by viruses or bacteria. In addition to severe pain, the patient may complain of dizziness and loss of balance.
Any pain in the ear indicates pathological processes occurring in it. Chronic infections and untreated injuries cause hearing loss. To get rid of pain and prevent the development of hearing loss, it is recommended to make an appointment with an otolaryngologist.
Outer and inner ear: causes of inflammation
Otitis externa can develop due to improper ear hygiene. If you don't take care of your ears, dirt will accumulate in them, and this is a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria. Excessive hygiene is also harmful: earwax is a natural barrier against the penetration of bacteria into the ear. If you diligently clean the ear canals every day, a person loses this barrier and opens the way for pathogens. Another mistake that leads to acute ear inflammation is cleaning the ears with sharp objects that are not intended for this (toothpicks, matches, hairpins). Such actions can lead to damage to the auricle, which in turn leads to infection entering the wounds. Another factor is dirty water that gets into the ear, which contains pathogens. “Swimmer’s ear” is another name for this type of disease.
As we have already said, inflammation of the internal region occurs due to undertreated otitis media, if due attention has not been paid to the treatment of otitis media. Bacteria can also get here from the meninges, for example, with meningitis. This type of inflammation can be caused by injuries and fractures of the skull or temporal bone.
In order to recognize the disease in time and choose the right treatment, you need to be able to identify its signs.
Ear pain at night - what to do?
Due to the structural features of the hearing aid, ear pain intensifies when a person assumes a horizontal body position. Therefore, the pain often worsens at night during sleep. To reduce pain, you can:
- move your jaws (make chewing movements) - this allows you to equalize the pressure in the middle and inner ear and helps reduce pain;
- apply a cold compress - soak a towel in cool water and place it on the sore ear;
- Take your usual pain reliever.
Be sure to make an appointment with an ENT doctor. You cannot treat ear pain on your own, as this can aggravate the disease and lead to the development of hearing loss.
Ear otitis - how to treat?
Treatment of otitis depends on the form and stage of the disease. To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to contact an ENT specialist. The doctor will develop a treatment regimen taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Typically treatment for otitis media is as follows:
- taking antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs. Medicines fight the pathogen, relieve swelling and inflammation;
- Antipyretics are prescribed for high temperatures. Also, if necessary, the otolaryngologist can prescribe a course of antibiotics;
- removal of pus from the outer ear. To do this, cotton swabs (turundas) moistened with alcohol or other disinfectant are immersed in the ear canal. They collect pus and disinfect surrounding tissues.
After recovery, the ENT specialist may prescribe physiotherapy to restore local immunity (for example, UHF, drug electrophoresis). Untreated otitis media can lead to a ruptured eardrum. Therefore, if ear pain occurs, it is important not to self-medicate, but to seek medical help.
Price
| Service | price, rub. |
| Removal of a foreign body from the external auditory canal | 1430,00 |
| Primary surgical treatment of wounds of the auricle up to 1.5 cm | 2750,00 |
| Primary surgical treatment of wounds of the auricle over 1.5 cm | 3960,00 |
| Removal of postoperative sutures | 385,00 |
| Removing wax plug from one side | 1450,00 |
| Pneumatic massage of the eardrum on one side | 1100,00 |
| Catheterization of the auditory tube on one side | 1450,00 |
| Procedure using enzymes (Lidase/Chymotrypsin) | 170,00 |
| Toilet of the middle ear with mesotympanitis, acute purulent otitis (on one side) | 900,00 |
| Outer ear toilet (one side) | 600,00 |
| Placement of medicinal turunda in the ear (microcompress according to Tsitovich, on one side) | 600,00 |
| Medicinal (ointment) treatment of the external auditory canal (on one side) | 600,00 |
| Blowing of the auditory tubes according to Politzer | 600,00 |
| Medical cauterization of the mucous membranes of the ENT organs | 1000,00 |
| Block behind the ear according to Soldatov with drugs (one side) | 1450,00 |
| Opening of suppurating atheroma of the earlobe (on one side) | 4180,00 |
| Removal of postoperative sutures | 715,00 |
| Placement of medicinal turunda in the ear | 450,00 |
How to distinguish otitis media from cerumen plug?
Ear pain does not always indicate the development of an infection. Perhaps the painful sensations are caused by sulfur plugs. In the outer ear there are special glands that produce earwax, a secretion that protects the organ from pathogenic bacteria. When the glands malfunction, the wax becomes too dense and begins to accumulate in the ear, which leads to the formation of a plug.
For a long time, the accumulation of sulfur does not cause any discomfort, but over time the plug becomes larger and larger and can completely block the lumen of the ear canal. As a result, a person experiences a feeling of fullness in the ears.
If the plug puts pressure on the eardrum, headaches and nausea may occur. But at the same time, the plug does not lead to an increase in body temperature and purulent discharge from the ear canal (as happens with purulent otitis media). The pain with a plug is moderate, not shooting, which also makes it possible to distinguish it from an infection.