The ENT organs, being an outpost of the immune system on the path of infection into the body, are the first to encounter the effects of various pathogens. That is why inflammatory processes often begin in them. Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses is called sinusitis . In total, a person has 4 pairs of paranasal sinuses, these are cavities filled with air. As a result of inflammatory processes, pus is formed in the sinuses, and the person begins to feel weak and unwell.
1
Nasal endoscopy in MedicCity
2 Nasal endoscopy in MedicCity
3 Rhinoscopy in MedicCity
Symptoms of sinusitis
There are acute and chronic forms of sinusitis, which differ in their symptoms.
Acute sinusitis. Symptoms:
- Runny nose lasting more than 7-10 days, without signs of improvement;
- nasal congestion, mucous or purulent discharge from the nose;
- mucus running down the back of the throat, copious discharge of purulent sputum in the morning;
- headache, heaviness and pain in the inflamed sinus area. Sometimes pain in the teeth, eyes, cheekbones, cheeks;
- increased sensitivity of the facial skin in the projection of the affected sinus;
- increase in body temperature (up to 38°C and above). As a rule, this symptom is observed in an acute case. In a chronic process, body temperature rarely rises or remains at subfebrile levels (37-37.50°C);
- weakness, fatigue, irritability. Photophobia, lacrimation, loss of appetite, sleep disturbance;
- weakened or absent sense of smell;
- swelling of the cheeks and eyelids.
Chronic sinusitis. Symptoms:
Symptoms of chronic sinusitis depend on the form of the disease. Outside of an exacerbation, symptoms may be very mild or absent. The most common symptoms of concern are:
- nasal congestion, difficulty in nasal breathing;
- scant mucous or purulent discharge from the nose, may be in the form of drying crusts;
- constant leakage from the nose, causing cracks and abrasions at the entrance to the nose;
- mucus running down the back of the throat;
- dry throat;
- headache;
- bad breath.
As the disease worsens, symptoms characteristic of acute sinusitis may appear.
What is the difference between headaches due to colds and flu?
A headache with a cold is less intense and can occur without fever1. With the flu, pain is usually localized in the eye sockets, temples and forehead2. If the pain intensifies with coughing, sneezing, bending, turning and physical activity, you should urgently see a specialist.
Another dangerous symptom is a body temperature of 38 °C or higher, which does not decrease for 4-5 days3. This condition may indicate that the flu is complicated by a bacterial infection or that the disease has a different, non-infectious nature of origin.
Up to contents
Sinusitis in children
Sometimes sinusitis in children is more difficult to see than sinusitis in adults. The disease usually develops after an infection: influenza or sore throat, and is often accompanied by otitis media. The symptoms are somewhat blurred and appear weaker than in adults. Here are the main ones:
- purulent or mucous discharge from the nose;
- general weakness, malaise;
- pungent odor from the mouth.
With sinusitis in children, one side of the face is often inflamed. While sinusitis in adults is often accompanied by headaches, headaches in children are extremely rare.
Prevention methods
At home, it is easy to prevent most diseases that manifest themselves as headaches and nasal congestion. To do this, you need to follow the recommendations of doctors and follow simple rules:
- choose a complete diet with a sufficient amount of vitamins, especially in the cold season;
- dress according to weather conditions;
- in case of colds, undergo the full course of treatment to avoid complications;
- If you have an allergy, apply for an allergy test and determine the cause of this reaction;
- avoid stress, increased mental and physical tension.
At the Clinical Brain Institute you can get informative advice on headaches and nasal congestion. Diagnosis is carried out by experienced specialists of a narrow and broad profile, so in a short time it will be possible to establish the cause of deterioration in well-being. Also, only modern equipment is used here, which allows you to get accurate results in a short time.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 5/5 — 1 votes
Share article on social networks
Types of sinusitis
There are several types of sinusitis:
- sinusitis;
- frontal sinusitis;
- ethmoiditis;
- sphenoiditis, but the latter type of sinusitis is extremely rare and almost always together with ethmoiditis.
1 Examination of the nasal cavity in MedicCity
2 Examination of the nasal cavity in MedicCity
3 ENT unit Atmos S 31
How to treat sinus inflammation in adults and children?
Sinusitis, sinusitis and other inflammatory processes have similar symptoms. Treatment in adults will be effective if a specialist makes an accurate diagnosis and selects the optimal complex therapy, which will include:
- special medicines;
- healing procedures;
- prevention.
It is important not only to relieve the symptoms of the disease, but also to eliminate the causes of the disease. And they can be different. Some people have a weakened immune system, while others should have their body examined or give up bad habits and an unhealthy lifestyle.
In children, treatment of sinusitis, sinusitis and other inflammatory processes of the nasal sinuses also includes a whole range of measures:
- it is important to see a doctor quickly to make a diagnosis and avoid complications;
- you need to strictly adhere to the recommendations of specialists and monitor the child’s condition;
- It will be necessary to prevent inflammation in order to maintain the health of the child’s sinuses.
In the fight against serious inflammatory processes, one must not hesitate. For example, sinusitis can lead to inflammation in the skull or meninges. Acute catarrhal sinusitis develops in 70% of children who regularly suffer from ARVI. Odontogenic sinusitis develops in those who have dental problems.
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is one of the most common types of sinusitis. This disease is accompanied by inflammation in the maxillary and maxillary cavities. During inflammation, swelling of the mucous membrane occurs, which blocks the opening from the sinus to the nasal cavity. Mucus begins to accumulate in the sinus space, pathogenic bacteria multiply, and pus appears. Inside the cavity, pressure occurs on the vessels, and the person begins to feel pressing pain at the site of accumulation of pus.
Chronic sinusitis is the result of a long inflammatory process, when a person has had sinusitis for more than 2 months. The patient develops general weakness, nasal discharge has an unpleasant odor, the sense of smell is impaired, and a night cough appears. Chronic sinusitis is characterized by inflammation of only one sinus, right or left. Pressure in the sinus can cause a deviated nasal septum.
Symptoms of sinusitis
The following symptoms are characteristic of sinusitis:
- increased body temperature;
- copious discharge, nasal congestion;
- disturbances of smell;
- weakness;
- headache radiating to the forehead, bridge of the nose, teeth;
- pain that intensifies when tilting the head and pressing on the sinus;
- constant, intense pain;
- a feeling of fullness in the forehead and cheeks, aggravated by tilting the head, coughing and sneezing;
- photophobia and lacrimation.
Signs of sinusitis
If after a flu or cold the temperature rises again, your health worsens, severe pain appears when tilting your head and when pressing on the sinuses, then you need to urgently consult an otolaryngologist. These could be manifestations of sinusitis! Sinusitis in adults is often advanced, since adults are usually in no hurry to see a doctor.
Treatment of sinusitis
Antibiotics for sinusitis are used only after a complete examination of the patient, based on the characteristics of his body and possible allergic reactions.
Antibiotics are not advisable in case of sinusitis of allergic or fungal origin. For mild sinusitis, inhalations, rinses and immunotherapy are also sufficient.
1 Rhinoscopy in MedicCity
2 Video endoscopy of the nasopharynx in MedicCity
3 ENT office in MedicCity
Causes of pain development
Viruses, bacteria and microbes cause intoxication. For this reason, along with protective mechanisms (increased body temperature, runny nose), a headache begins. The immune system devotes all its strength to fighting the infection. In this case, general weakness, a feeling of “foggy” consciousness and discomfort in the frontal part of the head are a signal for a person about the need for treatment.
Another reason is increased cranial pressure. The tissues of the upper respiratory tract swell due to prolonged runny nose. The movement of blood flow is disrupted, causing the vessels to dilate. A symptom of high blood pressure is a bursting, periodically acute headache.
If complications are added to the disease - sinusitis, otitis - the patient feels “lumbago”. They arise due to swelling of the nasal mucosa and disruption of the outflow of fluid from the middle ear and paranasal sinuses.
Often the cause of a headache and subsequent acute respiratory disease (acute respiratory disease) is simple hypothermia, which leads to vasoconstriction. In this case, it has a “squeezing” character, appears before the development of rhinitis (runny nose) and persists in the early stages of the development of a cold.
Frontit
Frontal sinusitis (frontal sinusitis) is an inflammatory disease of the frontal paranasal sinus. This type of sinusitis is the most severe. There are forms of acute and chronic frontal sinusitis.
Symptoms of sinusitis
Acute frontal sinusitis, symptoms:
- pain and swelling around the nose and eyes;
- increased pain when tapping in the projection area of the inflamed sinuses;
- heavy breathing due to inflammation of the nasal passages;
- runny nose with thick yellow or green mucus;
- increase in body temperature to 38-39 degrees;
- severe headache (minor relief occurs when lying down);
- pain radiating to the ears and teeth;
- fear of light;
- severe weakness;
- sometimes sore throat, difficulty identifying odors, decreased pungency of taste.
Chronic frontal sinusitis, symptoms:
- aching headache;
- purulent, unpleasant-smelling nasal discharge in the morning;
- slight increase in temperature;
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- sputum discharge in the morning.
Causes of frontal sinusitis
The following reasons for the development of frontal sinusitis are distinguished:
- viral, bacterial or fungal infection;
- complication after influenza, ARVI, etc.;
- getting foreign objects into the nose;
- long-term infectious or allergic rhinitis (rhinitis);
- deviated nasal septum;
- adenoids;
- allergy;
- nasal polyps.
Treatment of frontal sinusitis
How to treat frontal sinusitis? Definitely under the supervision of an otolaryngologist! The disease is not only difficult for many patients to tolerate, but also has dangerous complications, including orbital abscess, meningitis, sepsis, etc.
Treatment of sinusitis is aimed at eliminating infection in the sinuses and stopping inflammation. Medicines will help relieve swelling, improve ventilation of the sinuses and lead to the discharge of contents from them. If the disease is viral in nature, then antibiotics for frontal sinusitis are mandatory!
The following antibiotics are used to treat sinusitis:
- penicillin antibiotics (semi-synthetic or synthetic amoxicillin preparations);
- cephalosporin antibiotics;
- macrolide antibiotics (they do not affect the intestinal microflora);
- local antibiotics in the form of nasal drops, nasal spray, aerosol;
- homeopathic medicines;
- symptomatic remedies for frontal sinusitis in the form of vasoconstrictor nasal drops, antipyretics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
In case of severe frontal sinusitis and insufficient effectiveness of conservative treatment, sinus lavage using the method of displacement and puncture is prescribed.
1 Rhinoscopy in MedicCity
2 Consultation with an ENT specialist in MedicCity
3 ENT consultation in MedicCity
Prevention of frontal sinusitis
To prevent frontal sinusitis, you need to monitor the state of your immune system, promptly eliminate foci of inflammation in the ENT organs, harden your body, and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Drug treatment includes:
- antibiotics (“Augmentin”, “Ampicillin”, “Cefixime”, etc. - the medicine is prescribed exclusively by an otolaryngologist);
- local antibacterial drugs (Isofra, Polidexa);
- vasoconstrictor nasal drops - used to relieve swelling of the nasal passages and anastomoses (Otrivin, Rinofluimucil, etc.);
- antihistamines (Zirtek, Suprastin, etc.);
- solutions for rinsing the nasal passages (“Aquamaris”, “Dolphin”, etc.);
- antipyretic drugs for high temperatures in the patient (Nurofen, Paracetamol).
An important stage of treatment is to thoroughly rinse the sinuses from pus. The rinsing is performed by an ENT doctor in the clinic. There are two methods: the method of moving fluid (Proetz lavage, or “cuckoo”) and rinsing with a YAMIK catheter. Sinuses cleared of pus can be subjected to physiotherapy. The following procedures have proven themselves to be effective:
- infrared laser therapy;
- vibroacoustic therapy;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- photodynamic therapy;
- magnetotherapy.
In especially severe cases, when the patient does not get better because the purulent masses are not washed out, the ENT doctor performs a puncture of the maxillary sinus (“puncture”). Using a Kulikovsky needle, the wall of the sinus is pierced and the pus is drawn out using a syringe with an antiseptic solution. After the first procedure, the patient feels much better.
Ethmoiditis
Ethmoiditis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth (anatomical labyrinth in the bridge of the nose). Ethmoiditis is bacterial or viral in nature.
There are acute and chronic ethmoiditis. Acute ethmoiditis accompanies influenza, rhinitis and is complemented by inflammation of the paranasal sinuses.
Ethmoiditis in adults affects both the frontal and maxillary cavities. With weak immunity, the acute form of ethmoiditis turns into long-term chronic ethmoiditis with periods of exacerbation and remission.
Polypous ethmoiditis is characterized by the appearance of polyps in the mucous membrane of the ethmoid labyrinth of the forehead. Polypous ethmoiditis may appear after chronic, allergic rhinitis.
Catarrhal ethmoiditis occurs due to the activity of viruses. It is characterized by increased lacrimation, weakness, nausea, dizziness, swelling in the bridge of the nose, and fever.
Ethmoiditis in children is a very serious disease. The infection spreads very quickly due to the anatomical structure of the ethmoid labyrinth. The development of ethmoiditis in children requires urgent hospitalization.
Symptoms of ethmoiditis
Acute catarrhal ethmoiditis. Symptoms
- pain in the bridge of the nose and at the wings of the nose;
- heavy breathing through the nose;
- loss of smell;
- headache, weakness;
- profuse nasal discharge, which gradually becomes purulent;
- temperature rises to 38 degrees;
- In children, the inner corner of the eye socket also swells and turns red.
In the acute form, primary and secondary ethmoiditis are distinguished.
With primary ethmoiditis, anxiety, vomiting, dyspepsia and toxicosis appear, the temperature is 39-40 degrees.
Secondary ethmoiditis is more severe and develops faster. The patient is in extremely serious condition with pronounced septic symptoms. The eyelids become swollen and cyanotic, swelling of the conjunctiva and noticeable protrusion of the eyeball are observed, and nasal breathing becomes difficult.
Chronic ethmoiditis. Symptoms
- headaches that are difficult to register by localization;
- weakness, rapid fatigue of the patient;
- soreness in the bridge of the nose when pressed and painful points at the wings of the nose;
- purulent discharge with a nauseating odor;
- extensive mucus in the nasopharynx, which is difficult to spit out;
- emerging polyps.
Complications after ethmoiditis:
- meningitis;
- encephalitis,
- intraocular and intracranial pressure;
- destruction of the ethmoid bone.
Treatment of ethmoiditis
Treatment of ethmoiditis in acute form is predominantly conservative. It is necessary to ensure the outflow of mucus with the help of vasoconstrictors and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Treatment of ethmoiditis in chronic form is predominantly surgical.
1 MRI in MedicCity
2 Laboratory diagnostics in MedicCity
3 Ultrasound examination of the paranasal sinuses in MedicCity
Why does inflammation of the sinuses develop?
Pain in the sinuses most often acts as one of the main symptoms of sinusitis or its varieties, for example, sinusitis, sinusitis and ethmoiditis. With sinusitis, the inflammatory process is localized in the paranasal sinuses of the upper respiratory tract, and with sinusitis, the maxillary sinuses become inflamed.
Why do the sinuses hurt with these diseases? These air cavities connect to the nasal cavity, which in turn is connected to the throat and ear canals. If a healthy person constantly produces mucus in the sinuses, which flows into the nose at a speed of 1 cm/min, then during the inflammatory process the following processes are observed:
- mucus production increases significantly and pus quickly forms in the sinuses;
- narrow passages for the outflow of mucus are completely blocked, it becomes difficult to breathe;
- fluid accumulates in the sinuses and presses on the walls - this is how a person begins to experience pain.
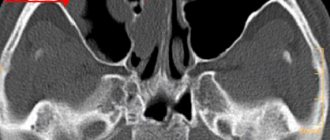
Diagnosis of sinusitis using modern techniques
To confirm the diagnosis of sinusitis, the following types of examination are used:
- Video endoscopy of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx to identify features of the anatomical structure and determine predisposing factors for the development of sinusitis;
- radiography of the paranasal sinuses;
- Ultrasound examination of the paranasal sinuses is a safe method with no contraindications, used to diagnose sinusitis and monitor the treatment process;
- CT, MRI - according to indications;
- laboratory diagnostics according to indications in full.
How to cure sinusitis, sinusitis and other inflammations?
What you definitely shouldn’t do is diagnose yourself and buy medications without a prescription or doctor’s recommendations. If sinusitis is mild, then the body will quickly cope with the source of the problem and defeat the infection or virus. But if sinusitis has become chronic, special therapy is needed:
- medicines that clear the air passages;
- antibacterial drugs to eliminate infection;
- rinsing the sinuses with antibiotics;
- surgical intervention in selected cases;
- regular preventive measures.
Of course, it is better to prevent sinusitis from becoming severe. Indeed, in this case, surgical intervention cannot be avoided. Why is this scary?? Just look at the image below, the hand-drawn picture of surgical techniques will give you a chill between your shoulder blades!
Treatment of sinusitis at MedicCity
Conservative methods of treating sinusitis
If you are concerned about how to treat sinusitis in Moscow, be sure to contact the MedicCity specialists! Our clinic provides treatment for sinusitis without puncture and without pain. However, non-surgical treatment of sinusitis is possible only at the initial stage. Don't waste time!
In the vast majority of cases, treatment of sinusitis in our clinic is carried out without a puncture.
- Using YAMIK (sinus catheter). The YAMIK method is the use of a device called the “YAMIK sinus catheter.” Using the YAMIK sinus catheter, controlled pressure is created in the nasal cavity and the purulent contents of the sinus are pumped out through the natural anastomosis (openings), and then a medicinal substance (antibiotics, mucolytics) is administered.
- Rinsing the nose and paranasal sinuses using the moving method (“cuckoo”). It is carried out using a special suction - an aspirator; in the process, pathological contents are removed from the nasal cavity and sinuses and the drug is injected into the sinuses.
- Inhalation therapy using a special inhaler PARI SINUS. This method is based on the introduction of microparticles of the drug into the affected paranasal sinuses through a pulsating supply of an aerosol. In this case, the aerosol of the medicinal substance is deposited in the sinuses and has an effect directly at the site of inflammation.
All proposed methods for treating sinusitis are painless and effective.
When using combined treatment, complete recovery in case of acute sinusitis is achieved within 7-10 days.
If puncture treatment is necessary, it is possible to install special catheters in the sinus, which eliminate the need for repeated punctures.
Complications
The most common complication of the disease is chronicity of the inflammatory process. If the disease is “neglected”, treatment is started incorrectly or treatment is abandoned halfway, the acute inflammatory process quickly becomes chronic. An illness that could have been cured in a couple of weeks takes a long, annoying course.
Other complications are directly related to the presence of pus in the sinuses. If purulent masses cannot exit into the nasal cavity due to blocked anastomosis, they find another way out. Accumulated pus can break through the walls of its “dwelling” and enter the orbit or membranes of the brain, leading to dangerous consequences for the body:
- phlegmon of the orbit;
- periostitis of the orbit of the eye;
- osteomyelitis;
- meningitis;
- encephalitis;
- sepsis;
- brain abscess.
Some of these conditions can lead to blindness and death. Death due to a runny nose is a very real situation, so for purulent sinusitis, treatment must be timely and correct! No self-medication! Elimination of inflammation of the maxillary sinuses and its symptoms - the profile of an otolaryngologist.