Causes of brain germinoma
There is no clear opinion about the cause of the formation of brain germinoma. Scientists and oncologists are more inclined to the version of the disorder in the process of embryogenesis. There is a so-called dysontogenetic theory of the occurrence of this type of tumor. According to this theory, brain germinoma occurs as a result of disorders of tissue differentiation and tissue migration at the very first stages of embryogenesis in the first trimester of pregnancy. The basis of this hypothesis is largely based on the fact that neoplasms are more often detected in people at a young age.
Germinoma is usually classified as a type of embryonic tumor, and these neoplasms arise and develop even before the full formation of the fetus from the rudiments of embryonic tissues. The reason is a violation of embryogenesis, which occurs as a result of changes in the structure of chromosomes and mutation of genes that control the normal development of embryogenesis.
Factors that induce changes and disturbances in embryogenesis may have an indirect or direct effect on the body of the expectant mother. Such provocateurs include contact with toxic substances during pregnancy, the influence of radioactive substances, various types of infections (measles, herpes, severe stages of influenza). The risk factor will also be the influence of carcinogens.
Causes
Medical research and observations of the general picture of the development of the disease indicate that the main cause of germinoma is disturbances during embryonic development.
Active formation of the embryo's brain occurs already at 4-5 weeks of pregnancy. Adverse effects on the fetus during this period can have a particularly detrimental effect on these processes and lead to serious violations. First of all, this concerns the effects of medications, chemicals, intoxications (alcohol, smoking, drugs), hypoxia, and severe infectious diseases of the mother.
Symptoms of brain germinoma
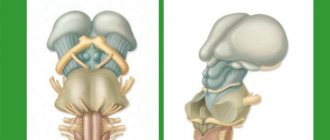
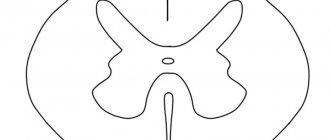
The clinical picture of brain germinoma largely depends on its location. Localization of brain germinoma - deep structures of the brain - area of the pineal gland, third ventricle.
One of the first signs of this neoplasm will be impaired blood flow and hydrocephalus as a consequence. Patients often complain of a bursting headache that is not relieved by analgesics or other painkillers. There is also a feeling of pressure in the eyes, constant nausea, independent of meals, and at times even vomiting. Visual impairment is often observed. This is explained by the fact that germinoma is localized near the chiasm of the optic nerves and, growing, infringes on them. Patients focus on double vision, visual field defects, farsightedness or myopia.
The clinical picture of brain germinoma is also characterized by deterioration or partial loss of memory, mental disorders, and emotional instability. In some cases, various kinds of neuroendocrine syndromes such as diabetes insipidus, as well as menstrual irregularities, anovulation, amenorrhea in women and disorders in the hypothalamic-pituitary system may be observed. Developmental disorders of puberty are also diagnosed. All these symptoms are explained by the location of the tumor near the hypothalamus.
Introduction
Precocious sexual development (PPD) is the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics in girls under 8 years of age and in boys under 9 years of age.
Gonadotropin-dependent PPR is distinguished, caused by premature activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal system; gonadotropin-independent PPR, caused by activation of the steroid-secreting elements of the gonads without the participation of gonadotropins, and false PPR, caused by the autonomous secretion of sex steroids by the adrenal glands or tumor [1]. Gonadotropin-dependent (central) forms of PPR are quite rare, and are much more common in girls than in boys. According to world literature, the prevalence of central forms of PPD in girls, depending on age, ranges from 0.05 to 2.8 cases per 100 thousand children, and among boys, PPD is an order of magnitude less common, regardless of age, and amounts to up to 0.05 per 100 thousand [1].
In this regard, in the Russian Federation, central forms of PPD are classified as orphan diseases.
Gonadotropin-independent PPR is even less common in the practice of pediatric endocrinologists, so the epidemiology of these forms remains unknown, and case reports are rare and always arouse clinical interest. Among the causes of these forms of PPR, hCG-secreting tumors, which can have intra- and extracranial localization, are casuistically rare. In the literature available to us (Medline, eLibrary), the most common descriptions of cases with intracranial localization of tumors: 15 cases [2–12], and the source of increased hCG secretion in all cases were germ cell tumors of the pineal region of various histogenesis (germinoma, choriocarcinoma, teratoma). Only 10 cases of tumors with extracranial localization have been described: thymic teratoma [13], testicular teratoma [14], hepatoblastoma [15–20], and lymphoma [21–22].
Clinical case
Boy 6 years 9 months. A child from the 1st pregnancy, which occurred against the background of a complicated obstetric history, anemia, oligohydramnios, from dichorionic diamniotic twins, 1st term birth in the breech presentation. Body weight at birth – 3470 g, length – 54 cm. Physical and neuropsychic development corresponded to age.
At the age of 6 years 6 months, the mother noticed the appearance and rapid progression within a month of pubic hair growth, an increase in the size of the penis, and acne. We consulted an endocrinologist at our place of residence, and a diagnosis of PPR was made. An examination was ordered, during which complaints of severe headaches accompanied by vomiting, drowsiness, and the appearance of strabismus appeared.
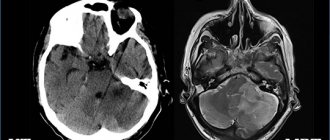
A child aged 6 years 8 months was urgently hospitalized at the Federal Neurosurgical Center of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation in Tyumen, where a magnetic resonance imaging scan of the brain revealed a space-occupying lesion measuring 2.5×2.9×2.5 cm in pineal region with extension to the posterior parts of the 3rd ventricle, as well as occlusive triventricular hydrocephalus with periventricular edema. Endoscopic ventriculocisternostomy of the floor of the 3rd ventricle and endoscopic biopsy of the space-occupying lesion were performed. The histological conclusion turned out to be uninformative. During the examination, high values of β-hCG were obtained - 429.5 mIU/ml (reference interval - RI: <0.5 mIU/ml), α-fetoprotein (AFP) - 424.5 IU/ml (RI: <6.67 IU/ml), testosterone – 55.55 nmol/l (RI: <0.5 nmol/l) and estradiol – 440.52 pmol/l (RI: <69 pmol/l) against the background of suppressed LH levels – 0. 04 IU/ml (RI: 1.6–5.7 IU/ml) and FSH – 0.04 IU/l (RI: 0.4–1.6 IU/l).
The child was consulted in absentia at the Federal State Budgetary Institution "Russian Scientific Center for Radiology" of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation: based on the characteristic localization of the tumor in the pineal region, the manifestation of the disease with symptoms of PPR, and an increased level of tumor markers in the blood by 100 times, a diagnosis of a germ cell tumor, a secreting variant, was made. It is recommended to carry out chemoradiotherapy according to the SIOP-GCT-2011 protocol in the oncohematology department of Yekaterinburg.
Upon admission: complaints of pubic hair, enlargement of the penis, acne, headaches. Objective status: moderate condition due to neurological symptoms. The physique is masculine. The skin is dry, multiple acne with a predominant distribution on the face and anterior chest wall. For systems without features. Neurological status: friendly convergent strobism, diplopia, upward gaze paresis. Physical development: height – 134 cm, SDS (standard deviation score) height +2.6 (tall), body weight – 36.7 kg, body mass index (BMI) – 20.4 kg/m2, SDS BMI +2, 0. The genitals are formed correctly, according to the male type (see picture). Sexual development according to Tanner – III: Ax 2, P 3, testicular volume – 2 ml, penile length – 7 cm, erections on examination.
From the examination: β-hCG – 1849.94 mIU/l, AFP – 635.34 IU/l, LH – 0.03 IU/ml, FSH – 0.0 IU/l, prolactin – 638.62 IU/l, estradiol – 709 pmol/l, testosterone – 51.85 nmol/l, cortisol – 373.59 nmol/l. Bone age – 9 years. Cytology of the cerebrospinal fluid: no tumor cells were detected, β-hCG in the cerebrospinal fluid was not tested.
High levels of testosterone and β-hCG against the background of suppressed values of LH and FSH made it possible to establish the gonadotropin-independent genesis of PPR against the background of a germ cell tumor of the pineal region.
Taking into account the high sensitivity of germ cell tumors to chemotherapy, conservative treatment tactics were chosen.
Discussion
Germ cell tumors are relatively rare malignancies that account for approximately 3% of all malignancies diagnosed in children and adolescents under 15 years of age, but only a small number of these tumors (about 30%) may be accompanied by hypersecretion of β-hCG [12], and their manifestation from clinical manifestations of PPR is extremely rare, as evidenced by literature data [2–22].
The mechanism of excessive production of androgens in hCG-secreting tumors is due to the similarity in structure of the β-subunit of hCG with LH, resulting in stimulation of the LH receptor in the gonads and an increase in the secretion of testosterone by Leydig cells in boys and theca cells of the follicles in girls. And if in boys this naturally leads to the development of PPD of the isosexual type, then in girls either clinical manifestations of hyperandrogenism or PPD of the heterosexual type should be observed. However, in the available literature there is a description of only three cases of PPR in girls, all of them of the isosexual type [4, 9, 23], which requires hyperproduction of estrogen.
For the secretion of estrogens in the female body, in addition to LH, FSH is necessary, which stimulates the maturation of granulosa cells in the ovarian follicles and increases the activity of the aromatase enzyme, which converts androgens secreted by theca cells into estrogens. In cases of hCG-secreting tumors, the secretion of FSH is suppressed by an increased level of testosterone through a negative feedback mechanism, and therefore the formation of estrogens and the development of clinical manifestations of isosexual PPR in girls should not occur. Probably, in this regard, in both domestic [1] and foreign classifications of PPR [24], hCG-secreting tumors are considered as the cause of gonadotropin-independent PPR exclusively in boys.
An explanation of the phenomenon of the development of PPR in girls is given in the publication of O'Marcaigh et al., who, using an immunohistochemical study, revealed the expression of aromatase in a germ cell tumor of the central nervous system in an 8-year-old girl [23].
Thus, the spectrum of clinical manifestations from the endocrine system in hCG-secreting tumors depends on gender, age of tumor manifestation and the presence of aromatase expression in tumor tissue in girls, and is also probably associated with the level of increase in β-hCG: in boys up to 9- summer age - the appearance of a clinical picture of PPR of the isosexual type, and after this age - the rapid development of secondary sexual characteristics against the background of pre-pubertal testicular volume (up to 4 ml). In girls under 8 years of age, PPD is of the isosexual type, and after 8 years of age, there are clinical manifestations of hyperandrogenism (acne, hirustism, menstrual irregularities of the oligo-, amenorrhea type). Awareness of doctors of various specialties about the first clinical symptoms, which may appear several months before diagnosis, will facilitate timely diagnosis and improve the prognosis of hCG-secreting tumors in children.
Conclusion
We hope that the description of this rare clinical case of hCG-secreting pineal germinoma, manifested by gonadotropin-independent PPR, the presented literature review, developmental mechanisms and possible manifest clinical manifestations of endocrine disorders in children will arouse practical interest among doctors of various specialties and will find application in their clinical practice . For the authors personally, the work on preparing the article served as an incentive to study the prospects of using drugs from the group of aromatase inhibitors to prevent bone maturation and improve growth prognosis in children with PPD.
Additional Information
Patient consent. The legal representative (mother) of the patient voluntarily signed an informed consent for the publication of personal medical information and photographs in an anonymized form in the Pharmateka magazine.
Diagnosis of brain germinoma
The first diagnostic conclusions are made during the first examination by a neurologist. A neurological examination and questioning of the patient, his complaints and accents in the characteristics of general well-being makes it possible to establish or suspect the presence of hydrocephalus.
Methods for diagnosing brain germinoma:
- Echo-encephalogram. Firstly, it allows you to diagnose intracranial pressure, and secondly, in the case of a large tumor, this diagnostic method can reveal displacement of the deep structures of the brain.
- Tomographic methods - CT and MRI of the brain. They make it possible to identify the nature of the tumor, location and size. Almost half of patients diagnosed with brain germinoma have a clinical picture of tumor infiltration of the visual tuberosities and petrification in the middle (the so-called butterfly symptom). This diagnosis can be confirmed by the presence of tumor bodies in the lateral ventricles and metastases in the infundibular region of the third ventricle.
- Biochemical blood test - establishing markers of hCG, ACE, PAL.
- Steretactic brain biopsy. This method will be the most accurate in making a diagnosis, since a laboratory examination of the tumor body is performed. In some cases, such a study may not give accurate results if the tumor is heterogeneous.
- Morphological examination of tumor areas after its removal. The difficulty of this method is in localizing the tumor in the deep structures of the brain, so doctors often prefer stereotactic biopsy.
Brain germinoma has a similar clinical picture to a number of neoplasms in the central nervous system, and therefore requires careful diagnosis and differentiation from diseases with similar symptoms. Among these diseases:
- astrocytoma;
- glioma;
- ganglioneuroma;
- hematoblastoma;
- medulloblastoma;
- brain abscess;
- intracerebral hematoma;
- cystosis in the third ventricle.
Treatment
The method of treating germinoma depends on the volume of the tumor, location, and the presence of complications. In uncomplicated cases, the possibility of choosing a radical method of surgical treatment or less traumatic radiosurgical treatment using CyberKnife (stereotactic radiosurgery) .
Treatment of germinoma using the CyberKnife system
Radiosurgical system CyberKnife
With the advent of CyberKnife in the clinical practice of the world's leading oncology centers, treatment of germinomas ceased to be carried out exclusively by surgical methods, which, due to the development of germinomas in the deep structures of the brain, led to serious, often irreparable neurological damage associated with access to the tumor itself. Today, the choice of tactics for treating germinoma is limited only by the qualifications of the attending physician, who in modern conditions should know about the advantages of radiosurgery, and the patient’s ability to access treatment with CyberKnife.
The greatest effectiveness is shown by combined treatment of germinomas, consisting of high-dose radiosurgery and subsequent chemotherapy of the tumor. In this case, the entire volume of germinoma, determined by a combination of CT and MRI data, receives an equal dose, leading to the biological death of tumor cells, and healthy tissues surrounding the tumor receive minimal doses of ionizing radiation.
Chemotherapy after germine treatment on CyberKnife is designed to combat possible tumor micrometastases and single tumor cells that may not have received a sufficient dose of radiation due to the complex shape of the tumor or its growth into those brain structures to which applying a single therapeutic dose of radiation for the entire volume can be dangerous .
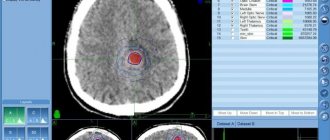
Germinoma - radiosurgical treatment of a brain tumor on CyberKnife without surgery, treatment plan. The red outline indicates the area that will be exposed to a high dose of ionizing radiation
Treatment of germinoma using the CyberKnife radiosurgical system is carried out on an outpatient basis. Many patients do not leave their usual work schedule, without advertising the fact of the disease and treatment to their friends.
If the tumor is difficult to reach, but its size exceeds those recommended for the effective use of CyberKnife (radiosurgery), a stereotactic biopsy is performed and high-precision IMRT radiation therapy is started on the tumor area. Combined radiation treatment is combined with rational chemotherapy.
IMRT radiation therapy in the treatment of germinoma
Elekta linear accelerator
Germinoma is a brain tumor that occurs during embryonic development. But in the early stages, when a non-surgical technique - radiosurgery on CyberKnife - can be used to combat the tumor, it is extremely difficult to detect and identify germinoma. For this reason, the most effective treatment involves removing part of the tumor located outside the critical structures of the brain and highly precise irradiation of those areas that cannot be removed.
One of the most accurate methods of delivering ionizing radiation, which allows delivering an exact dose that is already destructive for germinoma tumor tissues, but still tolerant for healthy brain cells, concentrated precisely in a given volume, is high-precision radiation therapy IMRT.
Targeted delivery of a given dose of ionizing radiation (leading to the stop of biological processes in the tissues of the tumor) into a given volume with controlled delivery of radiation.
The accuracy of treatment is determined by the creation of a model of the location of the remaining part of the tumor in the brain, which is built on the basis of CT and MRI images in a special program. Using this model, the radiologist determines and plots the contours of the germinoma and healthy tissues, for each of which the radiation therapist sets the permissible minimum and maximum doses.
Germinoma - radiation treatment plan - high-precision IMRT radiation therapy, which allows you to deliver a high dose to large tumors with fields of complex shape, minimizing the doses received by healthy tissues.
The medical physicist then develops a plan for the passage of the radiation fields, each of which will have a different shape and will be delivered from different positions of the linear accelerator. Thus, the required radiation dose will be limited to the areas of mutual intersection of the fields, and healthy tissues along the path of the fields will receive a small dose that will not lead to irreversible damage.
The duration of treatment of germinoma using a high-precision linear accelerator is 20-30 daily sessions, during which the patient is conscious and lies in a comfortable position, his head is fixed with an elastic individual mask to avoid displacement. Due to the non-invasive nature of the treatment method, the patient returns to his normal daily routine after a session (fraction) of treatment.
The prognosis depends on the histological structure and operability of the tumor. As a rule, germinoma is sensitive to both chemotherapy and radiation therapy. The five-year survival rate exceeds 85%.
Treatment of brain germinoma
The most common treatment strategy for brain germinoma is radiation therapy. If the patient’s age is too young, their general condition does not allow radiation therapy, or there are contraindications, then polychemotherapy is prescribed. Sometimes surgery will be a mandatory and forced method of treatment and may be accompanied by radiation or chemotherapy. But such a complex method of treating this disease is extremely undesirable for young or child patients, as it entails severe intoxication of the entire body.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of brain germinoma can be carried out in various ways and is performed when an accurate diagnosis is made and the location, nature and size of the tumor is established. Often, surgical treatment is the only possible method, since other methods will be ineffective. In some cases, surgical intervention requires additional procedures - ventriculocisternostomy or ventriculoperitoneostomy.
Contraindications for surgical treatment of brain germinoma may include inoperable location of the tumor or disseminated tumor growth, as well as multiple foci. If the size of the tumor is small, then it is advisable to use radiosurgery methods. The essence is a single exposure to the location of the tumor with a high dose of radiation.
Treatment of the disease is within the competence of specialized departments of neurosurgery, which are equipped with equipment and a computer imaging neuronavigation system.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture of this disease is characterized by diversity. And first of all, it is determined by where the tumor is located. Most common localizations:
In much more rare cases, such tumors are diagnosed in the mediastinum, retroperitoneum, stomach, neck (that is, in the nasopharynx), bladder, liver, and vagina.
Figure 1. Variants of location of germ cell formations in children.
Prognosis and prevention of brain germinoma
The main methods of preventing brain germinoma can be considered the exclusion of any negative impact on the body of the expectant mother. A pregnant woman should lead a healthy lifestyle and avoid contact with radioactive and toxic substances.
This disease, if detected in the early stages, responds well to chemotherapy and radiation therapy. In the future, to monitor your condition and the course of the disease after treatment, you must consult a neurologist at least once a year. Even with surgery, the prognosis can be quite encouraging - the survival rate after such operations is approximately 85 percent.
Rekomed - Choosing a clinic for the treatment of germinoma
The Rekomed company will help you choose a clinic and a doctor, organize a trip for consultation, diagnosis, treatment or surgery. We will provide all coordination services for you and will help in solving organizational issues throughout the treatment. It is important to note that payment for treatment is always made directly to the clinic’s cash desk at the clinic’s prices.
Contact us by phone or use the “doctor” form to send your request.
doctor
| Rating | 1341 views | Recommend to friends | Roman KM |
Where to treat Germinoma?
Samsung Medical Center
Irwon-Dong, Gangnam-Gu, Seoul Korea View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
Founded in 1994, already in 1996 the medical facility was recognized as a “Hospital of Presidential Standards.” In addition, the international department of the center is recognized as the best Korean clinic for receiving foreigners. So, not only patients living in Korea, but also patients specially coming for treatment turn to Samsung. Read more >>>
Cheongsim International Medical Center
267-177, Misari-ro, Seorak-myeon, Gapyeong-gun, Gyeonggi-do, Korea View on map
1 positive review 0 negative review
International medical practice combines Western and Eastern methods and approaches to the treatment of vomiting. Thus, modern technologies are favorably combined with oriental subtleties, and acupuncture, all kinds of moxibustion and preparations based on plant extracts significantly speed up recovery. Read more >>>
National Cancer Center of Korea
323 Ilsan-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang-si Gyeonggi-do, Korea View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The National Cancer Center specializes in cancer. It operates six centers dedicated to the most common cancer diseases in the world. 180 highly qualified oncologists, whose research is published in reputable scientific publications, 430 nurses, as well as the latest technical equipment, make it possible to effectively combat the scourge of our century. Read more >>>
University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf
Martinistr. 52, Hamburg, Germany View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf (German: Universitätsklinikum Hamburg-Eppendorf) is a medical center in the North of Germany, located in the Eppendorf district of Hamburg. Read more >>>
Concern Clinics of St. Antonius
Birkenallee 18, Wegberg, Germany View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The St. Antonius Clinics concern is an association of eleven specialized clinics covering all areas of modern medicine; 30 medical departments; 1,600 hospital beds; 50,000 inpatients per year; about 3,500 first-class specialists. Read more >>>
Charite Clinic
Charitestraße 1, 10117 Berlin, Germany View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
One of the oldest medical institutions in Germany, the Charite Clinic was founded in 1710. The level of this university hospital, which in addition to providing medical care also offers fundamental training for doctors and scientists, is extremely high. Read more >>>
University Hospital Dusseldorf
Moorenstr. 5, Düsseldorf, Germany View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The participation of the University Hospital of Düsseldorf in various international medical projects allows the application of progressive techniques in practice, which makes treatment even more effective. Read more >>>
University Hospital Münster
Domagkstraße 5, Münster, Germany View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The University Hospital of Münster is one of the oldest and largest medical centers not only in Germany, but also in Europe. The history of the clinic is inextricably linked with the medical faculty of the University of Münster, which allowed and allows the use of Read more>>>
Clinic "Assuta"
Tel-Aviv, Israel View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The Assuta Private Clinic, one of the most popular medical institutions in Israel, was founded in Tel Aviv in 1934 by Dr. Ben-Zion Harel, his son and repatriated doctors from Germany. Now this is a whole network of private clinics: 4 hospitals, medical complexes More >>>