The brain is a complex organ that controls all the vital functions of our body - thoughts, speech and body movement. The formation of a brain tumor and its treatment often leads to significant changes in these processes for life. Therefore, it is very important to detect the development of a neoplasm in a timely manner.
In this article, we tell you how to recognize brain cancer: what you should pay attention to, when it’s time to make an appointment with a doctor, whether brain cancer can be cured, what methods of diagnosing and treating this disease exist.
What to look out for in case of brain cancer
A cancerous brain tumor does not metastasize, that is, secondary foci. However, already in the early stages of the development of the process, the patient begins to feel its signs. The following symptoms of trouble should alert you:
- progressive impairment of speech function;
- disturbances in coordination of movements;
- constant fainting;
- chronic headaches. Remember that headaches with a brain tumor are constant. They do not subside after taking analgesics, which are usually found in our home medicine cabinet. This phenomenon should be more alarming than others;
- the occurrence of hallucinations of various types. Most often, a person feels the constant presence of a certain odor.
Causes of brain tumor development
Cerebral neoplasms and other tumors are associated with the following negative factors:
- radiation and chemical exposure;
- significant environmental pollution;
- disruption of the formation of cerebral tissues during intrauterine development;
- traumatic brain injuries and radiation therapy;
- a predisposition also exists in patients with hereditary diseases such as tuberous sclerosis and neurofibromatosis.
The nature of headache during a tumor
Headache during brain tumors is significantly different from others. Not only is it permanent and does not go away after strong enough painkillers. It is oppressive in nature. In some cases it is quite intense. The headache intensifies in the following cases:
- exercise stress;
- sharp bends of the body;
- cough;
- abdominal muscle tension.
The headache is also worse in the morning. This occurs as a result of the fact that huge amounts of fluid accumulate in the brain tissue overnight.
Such pain also has warning signs. Usually they are nausea. In addition to such characteristics as intensity and duration, the patient can also describe his sensations this way:
- the pain seems to “pulsate” in the head”;
- after waking up the sensations are the strongest;
- confusion of consciousness and speech is often noted;
- migraine symptoms are completely absent;
- Sometimes the painful sensation is complemented by dizziness, decreased sensitivity of certain parts of the body, mental disorders, and signs of depression.
What is a brain tumor?
A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that divide and grow rapidly.
They rarely spread to other parts of the body, but most can spread through brain tissue. The danger of this type of tumor lies in the disruption of basic brain functions. There are more than 130 types of brain cancer. They are classified depending on how quickly they grow and the likelihood of relapse after treatment.
There are two main types of brain tumors - benign and malignant.
Benign brain tumors, grade 1 or 2, are characterized by relatively slow growth and are less likely to return after treatment. Benign tumors in the brain, which are rarely life-threatening when they develop in other parts of the body, can press on and destroy healthy brain tissue as they grow, which can lead to serious and sometimes life-threatening damage.
Benign ones include: chordomas (most common in people aged 50 to 60 years), craniophagiomas, gangliocytomas, gangliomas, angioplastic gangliomas (occur mainly in young people), meningiomas, pineocytomas, pituitary adenomas (usually affecting people over the age of 30 up to 40 years) and schwanoma.
Malignant brain tumors, grade 3 or 4, can develop directly in the brain (primary tumors) or metastasize there from a tumor in another part of the body (secondary tumors), and also have an increased likelihood of recurrence. The most common tumors that metastasize to the brain are lung tumors, breast tumors, colorectal cancer, kidney cancer, and skin melanoma.
The most common type of malignant brain tumor in adults is gliomas, these include: astrocytomas (most often found in middle-aged adult men), ependyomas, multihormonal gliolastoma (more common in people aged 50 to 70 years and in men than in women), medulloblastomas and oligodendrogliomas.
What to do for headaches
If you notice any alarming symptoms, the first thing you should do is visit a doctor. Under no circumstances should you buy painkillers for yourself. There is no need to trust your precious health to healers.
Remember that only early diagnosis of brain tumors will significantly increase the likelihood of successful treatment.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 5/5 — 4 votes
Share article on social networks
How are cerebral tumors diagnosed?
If you experience headaches that resemble the symptoms described above, you should visit a doctor as soon as possible. In a public clinic, you should first contact a general practitioner, who will perform an initial examination and refer you to a neurologist to rule out other causes of cephalgia. Often, a neurologist can determine the presence of a brain tumor after an initial examination and studying your reflexes, reactions to auditory and tactile stimuli, checking coordination and motor activity. In doubtful cases, the doctor issues a referral for research:
- echo-encephalography to assess intracranial pressure;
- electroencephalography to measure the functional activity of the brain using its bioelectric signals;
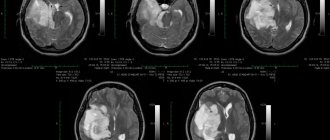
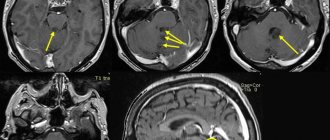
- computed tomography to visualize the tumor and identify concomitant pathological processes in brain tissue;
- magnetic resonance imaging for a more accurate assessment of the spread of the oncological process.
At the same time, ophthalmological examinations are carried out, during which your visual acuity is checked, visual fields are determined, and ophthalmoscopy is performed. In addition to standard tomography, MRI of cerebral vessels and other specialized magnetic resonance studies may be prescribed. In some cases, diagnosis requires a stereotactic biopsy and histological examination of brain tissue. After the final diagnosis is made, treatment is already completed by an oncologist.
What is pain?
Pain is a signal of trouble and the body’s response to disorder in it. Pain is a psychophysiological reaction to organic changes in any part of the human body. Pain is the body’s protective reaction to excessive irritation of nerve endings by some pathological factor. But it is the “defensive” one that confuses the most, because pain is perceived as an attack of one’s part of the body on the entire body – one’s own against one’s own.
Pain is a sensation that everyone perceives in their own way, very individually. It is almost impossible to evaluate it objectively. It would seem that the pain, which is absolutely the same due to its occurrence and localization, feels completely different in each person. You just have to trust the feelings of the one who is suffering from pain. The sensation cannot be seen, but very strong pain is visible; the painful sensation embodied in movements makes such an indelible impression that the eyewitness will forever have a fear of pain.
The whole truth about brain cancer
Despite the alarming situation associated with the development of coronavirus infection, our lives do not stop: visits to doctors, timely diagnosis and treatment must proceed according to plan. This is especially true for cancer patients, as well as those who have noticed alarming symptoms. Candidate of Medical Sciences, neurosurgeon, radiosurgeon, head of the Center for High-Precision Radiology Sergei Ilyalov talks about this.
Brain tumors have been shrouded in a veil of fatal hopelessness for many years, remaining the most frightening diagnosis of all possible in oncology. This gloomy confidence is due to the fact that half a century ago there were simply no options for treating many diseases. Thus, brain cancer became synonymous with an incurable disease.
By 2021, the picture has changed significantly, and today we can talk about the variety of methods that modern medicine offers.
What is hidden behind the concept of “brain cancer”?
Strictly speaking, there is no such diagnosis as “brain cancer”. Cancer is a tumor of epithelial cells, and there are no epithelial cells in the brain. However, the brain has a very complex cellular structure and its bulk consists of glial cells (white matter) of various types that support and nourish neurocytes (gray matter), cells of the meninges, cranial nerves and other structures, therefore there are more than a hundred varieties of malignant and benign tumors that primarily develop in the brain. In addition, secondary tumors can develop in the brain as a result of metastasis of malignant tumors of other organs.
Benign tumors are characterized by a slow growth rate, while they do not penetrate into surrounding tissues, do not metastasize and do not have a toxic effect on the body, but, increasing in size in the confined space of the cranial cavity, they can pose a threat to the patient’s life due to compression of the brain.
Why do brain tumors occur?
There are many reasons for the development of brain tumors. These include heredity, radiation, exposure to carcinogenic substances and others. According to statistics, malignant brain tumors are more common in men, but women are twice as likely to suffer from benign tumors of the meninges (meningiomas).
At various times, the ability to cause brain tumors has been attributed to microwave ovens, mobile phones and wireless Internet, but over the years of research, none of these hypotheses have been confirmed. In recent years, the ability to cause malignant tumors has been attributed to in vitro fertilization (IVF), but not a single domestic or foreign study has revealed the effect of this method on the incidence of tumors either in the brain or in other organs. Pregnancy that occurs after IVF or naturally does not cause tumors, but powerful hormonal changes can accelerate the growth of existing tumors. Fortunately, such cases are extremely rare.
Is there prevention?
Due to the fact that the mechanisms of development of primary brain tumors are not fully understood, specific methods of prevention do not exist today. The vast majority of people do not have a hereditary predisposition, but a risk group, although very conditional, still exists. First of all, these are workers in the field of radiation production and enterprises where carcinogenic substances are involved - they have a higher risk than in the general population, but they also undergo medical examinations more often and more thoroughly.
Also, the risk of developing tumors depends on age. There are tumors that in most cases are characteristic exclusively of childhood, for example, medulloblastoma. In adults, benign and malignant neoplasms occur at any age, but the likelihood of their occurrence increases after 45 years. Hereditary transmission of the risk of brain tumors is characteristic of neurofibromatosis type 2 and von Hippel-Lindau disease.
A separate risk group consists of patients with malignant tumors of various locations - breast, lung, rectum, kidney and skin, which make up the top 5 tumors that most often metastasize to the brain. Therefore, cancer patients should undergo regular examinations even with long-term remission of the disease.
How to identify a tumor?
The clinical picture of the tumor depends, first of all, on its location, since each part of the brain has its own “area of responsibility.” Sometimes the tumor can be located in the “silent zone”, and then the disease is asymptomatic until the enlarging tumor affects other areas or causes an increase in intracranial pressure.
The most common symptoms include:
- intense headache, poorly relieved by analgesics. Sometimes - with nausea and vomiting
- seizures
- visual disturbances (rapid decrease in vision, limited visual fields, double vision, flashes before the eyes)
- movement disorders (impaired limb strength) in half of the body
- problems with coordination, dizziness
- sensory disturbances in half the body
- hearing impairment (ringing or tinnitus, hearing loss)
- problems with speech, memory or thinking
Many of the symptoms that occur with brain tumors can also occur as a result of other diseases, so a neurologist will help you understand the cause of your complaints. A neurological examination allows one to suspect a brain tumor and promptly refer the patient for examination.
For diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with intravenous contrast is performed - this simple and safe method allows you to clearly visualize the structures of the brain and identify any deviations from the norm.
Is there any hope for recovery?
Looking back, we can say with confidence that we are lucky to live in the age of high technology. Today, domestic medicine has all the capabilities to provide high-tech treatment. Firstly, this is an accurate diagnosis, thanks to which it is possible to differentiate active tumor tissue from healthy brain tissue, assess the actual extent of spread and monitor the dynamics of treatment. Secondly, the use of the latest drugs to control the disease. And, of course, the development of surgery and radiation therapy. Modern radiation therapy is developing towards the most precise irradiation of the tumor with minimal involvement of surrounding healthy tissue. Radiosurgery is at the forefront of high-precision radiation techniques.
The use of this technology makes it possible to cure many benign brain tumors and intracerebral metastases without trephination, pain and a long recovery period.
Despite the fact that “brain cancer” has not lost its threatening significance, you definitely shouldn’t be afraid of it - primary malignant brain tumors are statistically quite rare. The incidence rate of the most “evil” tumor, glioblastoma, is about 3 cases per 100 thousand population.
The main thing to remember is that the earlier the disease is detected, the greater the chances of a favorable outcome. This applies equally to malignant and benign tumors. “Folk methods” should be avoided, as there is no reliable evidence of their effectiveness. Self-medication can be fatal, while modern technologies improve treatment outcomes for millions of patients year after year. The best means of prevention is a healthy lifestyle and careful attention to your own health.
Original: https://med-info.ru/content/view/8689
Risk factors and prevention of head cancer
A risk factor is anything that increases a person’s likelihood of developing cancer. And although risk factors often influence the development of cancer, most do not directly cause it. Some people with multiple risk factors may never develop cancer, while others with no known risk factors will. Knowing your risk factors and discussing them with your doctor can help you make more informed lifestyle and health care choices.
There are 2 substances that significantly increase the risk of developing head and neck cancer:
- Tobacco. Tobacco use means: smoking cigarettes, cigars or pipes; chewing or snuff tobacco. This is the most significant risk factor for head and neck cancer.
- Alcohol. Alcohol abuse increases the risk of developing malignant neoplasms. .
Using alcohol and tobacco together increases this risk even further.
Factors that may increase your risk of developing head and neck cancer also include:
- Prolonged exposure to the sun. This is especially true for cancers in the lip area, as well as cancers of the scalp and neck.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV). Having sex with a person with HPV is the most common way to become infected with HPV. There are different types of HPV, called strains.
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Exposure to EBV (the virus that causes mononucleosis or “mono”) plays a significant role in the development of nasopharyngeal cancer.
- Floor. Men are 2–3 times more likely to develop head and neck cancer. However, rates of head and neck cancer in women have been increasing for decades.
- Age . People over the age of 45 are more at risk of cancer.
- Poor oral and dental hygiene.
- Environmental or occupational inhalants . Inhalation of various chemical compounds (paint materials, asbestos) can increase the risk of developing a dangerous disease.
- Marijuana use.
- Poor nutrition. A diet low in vitamins A and B increases the risks.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and laryngopharyngeal reflux disease (LPRD) . Reflux is associated with tumor growth in the area.
- Weakened immune system.
- Exposure to radioactive radiation. Directly related to the development of the oncological process.
- History of head and neck cancer. People who have had head and neck cancer once have a higher chance of developing another cancer in the future.
Prevention
Quitting tobacco is the most important component of prevention.
- Avoiding alcohol and marijuana use.
- Regular use of sunscreen, including lip balm with an adequate sun protection factor (SPF)
- Reducing the risk of getting HPV by getting the HPV vaccine or by limiting the number of sexual partners. Using a condom during sexual intercourse cannot completely protect against HPV.
- Maintain proper denture care. Poorly fitted dentures can trap carcinogens from tobacco and alcohol. Dentures should be removed every night and cleaned and washed thoroughly every day.
Surgical strike
There are several types of radiation surgery. The most modern method is the so-called gamma knife, which is more than 200 highly targeted gamma rays, which, focusing at one point, lead to radiation necrosis (destruction) of pathologically altered cells. This is a very gentle and absolutely painless method. The procedure itself is performed on an outpatient basis. A kind of helmet is put on the patient’s head, and the rays of the device are directed to certain points on it.
The advantage of gamma rays is that they not only do not cause pain to a person, but also do not damage healthy brain tissue. Alas, there are objective limits to this method - only small tumors can be removed using a gamma knife (maximum 3.5 cm in diameter). In addition, relapse (recurrence) of the tumor is common after this procedure. Even if a few tumor cells remain in the brain tissue, they will then begin to divide again and the tumor will grow again. In addition, not all tumors can be removed using a gamma knife - there are also those that do not respond to radiation. For example, for dense tumors this technique is ineffective.
But neurosurgeons have another method in their arsenal - chemotherapy. It is used in the most advanced stages of the tumor, when other treatment methods are no longer effective. The effectiveness of this remedy, unfortunately, is low, but nevertheless, this method helps to slightly prolong the patient’s life. Chemotherapy is also always carried out after surgical removal of malignant tumors - as an additional, auxiliary treatment method that can help prevent further tumor growth. The combination of surgery, radiation and chemotherapy is a mandatory algorithm for the treatment of malignant diseases of the brain today.
Surgery: is there an alternative?
Today there are three methods of treating brain tumors. Among them, alas, there is no conservative method, since medications are powerless in the fight against this disease.
The most radical method is surgical. The surgeon performs a craniotomy and removes the tumor. This is the most effective and large-scale method for this disease. The prognosis for surgical treatment of conditionally benign tumors is favorable - the 5-year survival rate of patients reaches 80 percent or more (which in medicine is equivalent to recovery). Unfortunately, with grade 4 tumor malignancy, no more than 5% of patients manage to overcome the five-year mark after surgery. However, for such people, surgery is the only chance to live at least another 3-4 years, since without treatment the tragic ending comes in a few months. Brain surgery is usually very lengthy and complex, and there are contraindications for it. Among them are severe somatic diseases (for example, acute myocardial infarction or diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation).
Tumor localization is another important point. Sometimes tumors develop in a very important area of the brain, access to which is so difficult that it threatens the patient with significant brain damage or even death. In this case, you have to resort to another treatment method - radiation.