Causes of brain stroke on the right
{banner_banstat0}
A right-sided stroke is different from a left-sided cerebral blood flow disorder because the functions of the two hemispheres are different. In the right - the centers that are responsible for sensitivity, motor skills, coordination are localized; with the help of the right hemisphere, a person understands words, uses hearing, touch, intuition, evaluates the surrounding space, perceives music, reads, writes, recognizes geometric shapes. In addition, the entire left side of the body is monitored and the information is analyzed together with data from the left hemisphere to completely solve any problem.
During a stroke, any of the listed functions are disrupted, and the trigger can be either an endogenous or an exogenous factor. The most dangerous:
- alcoholism, smoking, drugs;
- blood pressure surges, high ICP;
- binge eating;
- obesity;
- atherosclerosis;
- increased blood clotting;
- stress, psycho-emotional and physical stress;
- brain injuries;
- congenital pathologies;
- chronic somatic diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- uncontrolled use of contraceptives.
Children with heart defects, genetic blood diseases, and endocrine disorders are at particular risk for right-sided stroke.
Consequences of a right-sided stroke
When the right lobe of the brain is affected, all its functions are temporarily lost. The duration of this condition depends on the type of stroke and its severity. The first manifestations are expressed by left-sided paralysis of the limbs and facial muscles. Next, visual impairment occurs: clarity disappears, vision doubles, and certain areas disappear from the field of vision. Hearing and smell may disappear. Since speech functions are preserved in such conditions, the patient may describe the main symptoms, but at the same time be confused about the sensations.
After providing first aid and stabilizing the condition, other signs of brain damage can be detected:
- the patient does not remember his recent actions, does not recognize the faces of loved ones;
- orientation in space becomes difficult, the person is unable to dress or put on shoes correctly;
- Epileptic seizures may occur;
- Some patients take all jokes and figurative expressions literally, while others develop foolishness, previously uncharacteristic swagger, and loss of tact. Some people develop dementia after a severe right-sided stroke.
Another serious consequence is the emergence of complete apathy in the patient towards his condition and everything around him or the development of deep depression. Many people do not even notice the presence of paralysis and impaired motor functions. All this blocks psychological contact between the patient and the doctor and complicates the recovery process.
Long-term consequences of right-sided stroke include physiological disorders of the cardiovascular system. Most often they manifest themselves as peripheral edema, which is localized on the legs, characterized by symmetry and slow development. In addition, various disorders in the pelvic organs, swelling of the brain, and gradual deterioration of vision (even blindness) may appear. The risk of a recurrent stroke with possible transformation into a hemorrhagic one also increases. Nymphomania in women, read on our website.
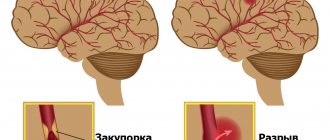
What is ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke
{banner_banstat1}
According to etiology, right-sided stroke is divided into ischemic and hemorrhagic. The first develops due to impaired cerebral blood flow on the right due to narrowing of blood vessels or their complete blockage; the speed of blood movement and its viscosity also play a role. As a result, hypoxia of brain cells is provoked with their death and necrosis of a certain area of the brain. Symptoms of ischemic stroke increase gradually, so ischemia develops over several hours or even days, which makes it possible to consult a doctor in a timely manner and avoid fatal consequences. The prognosis for this form of the disease is affected only by the extent of the lesion (necrosis).
Hemorrhagic stroke is a hemorrhage in brain tissue due to rupture of blood vessels. Often this situation leads to cerebral edema, coma and death. Vascular rupture occurs much less frequently, but has more severe consequences, since there is no time to “build up”. The spilled blood permeates the tissues, compresses vital structures, sometimes completely destroying them. Regardless of the size of the affected area of the brain, nerve cells are restored slowly; not all lost functions of the nervous system can be restored.
Types of ischemic stroke
The consequences of an ischemic stroke directly depend on the intensity of the lesion, the cause that caused it, the location of the blockage, and the speed of symptoms. Based on this, experts classify the disease by type.
| Type by rate of development and duration | Characteristic |
| A focal neurological lesion, all symptoms of which disappear within 24 hours after their onset. The condition may be accompanied by monocular blindness of the patient (vision in one eye is temporarily lost) | |
| An ischemic attack differs in duration; elimination of neurological symptoms requires from 2 to 22 days of drug therapy | |
| The condition is characterized by a rapid increase in symptoms over several hours or days. Damaged functions, as a rule, are not fully restored | |
Additionally, the severity of brain damage is distinguished:
| |
| Atherothrombotic | It occurs with atherosclerosis of the arteries and is characterized by increasing symptoms with a peak of manifestations during sleep. Damage occurs when a blood clot breaks off and clogs a blood vessel. |
| Hemodynamic | Occurs when there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure and a decrease in heart volume. The causes of this condition include pathologies of the heart vessels - stenosis, atherosclerosis and others. Damage can occur both during physical activity and at rest. |
| Lacunar | The affected area is limited to one of the small arteries located in the brain stem and hemispheres. Diagnosed most often in diabetics and hypertensive patients |
| Rheological | This type of stroke occurs in the absence of blood vessel pathologies and is characterized by very sparse symptoms. The cause of the lesion is hemorheological disorders |
Consequences of ischemia
{banner_banstat2}
With a small area of necrosis of brain tissue or a micro-stroke on the right, the prognosis for the patient’s life is favorable: neurological changes are minimal and do not criminally impair brain function. An exception is trunk ischemia, since vital centers - respiratory and cardiovascular - are concentrated here. Therefore, even a microstroke of the brain stem almost 100% ends in death in the first hours.
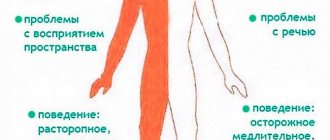
The remaining patients will experience disability because, although they are not completely bedridden, they lose even a small ability to adequately, fully perceive the surrounding reality, understand what is happening to them, and the ability to think logically. For left-handed people it’s the other way around. For them, the consequences of a right-sided stroke are similar to ischemia of the left hemisphere in right-handed people.
The main consequences are presented in the table. We must understand that the consequences of ischemic stroke decrease over time with proper treatment. About a quarter of patients under 55 years of age recover fully from a microstroke without visible signs of any neurological impairment.
At the same time, no matter how many functions are rehabilitated in the first two years after a micro-stroke, so many will remain until the end of days. Nerve cells are practically not restored.
| Outcome of stroke on the right | Consequences of micro and macro ischemic stroke |
| Complete paralysis of the left side of the body | The movements of the left limbs are minimized, the position is half-bent, the patient is able to sit, but without assistance he is not able to walk or grasp objects with his hand (hemiplegia) |
| Imbalance of sensitivity on the left | Pain and temperature threshold increases (hypoesthesia) |
| Loss of sense of spatial arrangement of arms and legs | |
| Mental disorders | Criticism decreases, foolish behavior arises, speech becomes inadequate, the person becomes aggressive |
| Memory loss | Patients remember the past, but forget what they did an hour ago; temporary complete amnesia and disorientation in space and time are possible |
| Left vision disorders | Decreased vision up to blindness, double vision, turning the head and left eye to the left |
If the area of brain necrosis is large (massive stroke), the prognosis is disappointing: up to 70% of patients die in the first few days, others become deeply disabled. The consequences are:
- persistent paralysis: patients cannot even sit;
- cerebral coma;
- complete lack of criticism and thinking;
- swallowing disorders.
The main differences between right-sided stroke
As you know, the functions of both hemispheres of the brain are different. For the left it is memory, logic, speech, the ability to read and write, but the right hemisphere is responsible for emotions and feelings. It is on the right side that information is processed in images and the development of a person’s creative abilities is ensured.
The main functions of the right lobe of the brain:
- motor activity of the left side of the body and facial expressions of the left side of the face;
- smell, hearing, vision, tactile sensations;
- spatial orientation;
- intuitive feelings;
- processing of nonverbal information;
- recognizing the emotions of others;
- perception of music and color;
- perception of complex objects as a whole, and not as a set of individual elements;
- face recognition;
- ability to spot differences.
With a stroke of the right hemisphere, complete or partial paralysis of the left side of the body, paralysis of the facial muscles, and short-term memory impairment may occur. Left-handers may additionally experience speech impairment, since their speech center is located in the right lobe of the brain. Most patients with this diagnosis either do not feel their limbs at all, or experience the feeling that they have more arms and legs than they have.
If the patient is provided with emergency qualified care within the first three hours after a stroke, the death of most of the cells can be avoided. Unfortunately, the absence of the most characteristic manifestations in the form of speech disorders makes it very difficult to determine the diagnosis, and most often it is not possible to completely restore brain function. The rehabilitation period for such patients takes longer.
What happens after a hemorrhage?
{banner_banstat3}
It makes sense to talk about the consequences of a hemorrhagic stroke only if we are talking about small hemorrhages on the right. Stroke-hematoma or large hemorrhage of the right hemisphere is almost 100% fatal.
No more than 10% of such patients can be saved by emergency removal of blood clots with drainage of the cranial cavity, but those who survive will remain deeply disabled for the rest of their days. Life expectancy is very short - from several days to several months.
With a small hemorrhage on the right, the prognosis is ambiguous: 75% survive, but become disabled, and the degree of disability is higher than with ischemia. Patients in 10% can fully recover, in 70% they are able to walk with difficulty, care for themselves, and are immobilized - up to 20%.
Differences in the consequences of hemorrhagic stroke of the right hemisphere:
- intolerance to loud sounds and bright light;
- increased irritability;
- cephalgia;
- lack of coordination;
- insomnia;
- swallowing disorder;
- hematoma in the ventricles of the brain.
In seriously ill patients after a stroke on the right side, regardless of the form, delayed complications occur: congestive pneumonia, bedsores, exhaustion due to great difficulties in caring for such patients. It is complications of this nature that cause the death of patients in the first two years of post-stroke life. About 15% live 10 years or more.
Features of therapy
{banner_banstat4}
Complex therapy for right-sided stroke is divided into correction of the acute period and rehabilitation. During the acute period, if there is a risk of severe consequences, surgical intervention may be required. The patient remains in the intensive care unit throughout the acute period. Treatment of right-sided stroke of any origin is carried out in several areas:
- basic: for ischemia - thrombolytics, disaggregants, anticoagulants (thrombolysis with a recombined type plasminogen activator is most effective), for hemorrhage - emergency hemostatic and vasoconstrictor agents;
- hypotensive: drugs that lower blood pressure relieve compression of nerves, remove tissue pastiness (Betalok, Stugeron, Triampur);
- normalizing cerebral blood flow: drugs with vasoactive and antiplatelet properties (Trental, Cavinton, Eufillin);
- neuroprotective: restore connections between neurons (Cellex);
- antioxidant: detoxify tissues, remove free radicals, renew cells (Vitamin E, C, Lycopene).
In the acute phase, it is important to control breathing, heart rate, and body temperature. Treatment is most effective during the first three, maximum five hours after the attack. Within a day, irreversible processes occur in neurons.
Rehabilitation
{banner_banstat5}
The recovery period begins approximately a week after intensive therapy, it is developed by doctors of various specialties: rehabilitation specialists, neurologists, psychologists, physiotherapists, speech therapists, reflexologists, occupational therapists (specialists in the restoration of social, everyday, functional, motor skills), neurodefectologists.
There is a whole playlist on Youtube on this topic https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLb9qc1uRvT8oorWN7lanTWl2BVkTJGm3v
The first stage is inpatient, the second is sanatorium, but the full course is carried out at home, which can last for several years. The set of measures includes: medications, exercise therapy, acupuncture, reflexology, physiotherapy, kinesiotherapy (exercise therapy based on oriental practices), massage, diet. The treatment regimen is strictly individual.
At home you need:
- eliminate all physical and psycho-emotional stress;
- balance the drinking and food diet with limiting lipoproteins;
- master a course of exercise therapy, including breathing;
- Constantly massage, especially in areas that have lost sensitivity;
- sanitize chronic foci of infection, somatic pathologies;
- eliminate all bad habits.
Particular attention to the prevention of bedsores, purulent corneal ulcers, hypostatic pneumonia, and contractures. To do this, special exercises are performed, the upper respiratory tract is cleaned, and if necessary, parenteral nutrition and bladder catheterization are provided.
The duration of rehabilitation can be only a month (for a mild form) or up to two or more years (for a severe form). Average rehabilitation is six months.
Forecast
{banner_banstat6}
Life expectancy after a stroke in the right hemisphere depends on many factors, which are listed in the table:
| What affects the consequences of a stroke and life expectancy | How exactly |
| Ischemia or hemorrhage at the heart of stroke | After an ischemic stroke, the chances of recovery are higher |
| Lesion size | The larger the area of brain tissue damage, the worse the prognosis |
| Involvement of vital brain centers in pathological changes | Brainstem stroke – fatal |
| Age, physical condition of the patient | In elderly and frail patients, the prognosis is a priori worse |
| Timeliness of medical care | If assistance is provided later than three to five hours after the impact, the consequences are irreversible |
Specifics of right-sided strokes
When the pathological focus is localized in the right hemisphere, the opposite (left) side of the body is affected. Muscle tone changes in a spastic manner, all types of sensitivity suffer, and muscle contractures appear. When a stroke develops, the patient in most cases loses consciousness for a relatively short time. With a significant size of the lesion, a “cerebral coma” cannot be ruled out.
Characteristic cerebral manifestations are also:
- severe dizziness;
- intense headache;
- unsteadiness of gait or falls caused by impaired coordination of movement.
The hemorrhagic form is characterized by central pain syndrome, persistent sleep disturbances and decreased visual acuity in the left eye (in severe cases, blindness is possible). In addition, the patient has difficulty swallowing. The most important problem is paralysis and the resulting muscle contractures and arthropathy (joint pathologies). Prolonged immobility during paralysis causes bedsores. Recovery after a stroke on the right side in such cases should begin as early as possible. The ischemic form is characterized by a rather slow development. The rehabilitation process is often slowed down, since many patients develop disturbances in the emotional-volitional area, and they do not notice that the left side is paralyzed.
Possible complications of the ischemic form (cerebral infarction) include:
- hydrocephalus due to cerebral edema;
- recurrent stroke;
- transformation of the ischemic form into the hemorrhagic one;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs.